6.4.0
Release date: 07-25-2024
Introducing Support for De-Identification in Generative AI Lab 6.4
We are happy to announce the release of Generative AI Lab 6.4, bringing exciting new features and enhancements. Leading this release is the support for de-identification projects, which enables users to anonymize documents containing sensitive data, such as PII (Personally Identifiable Information) and PHI (Protected Health Information). This ensures robust data privacy and compliance with privacy regulations while maintaining the utility of the data for further analysis and processing.
Additionally, version 6.4 enhances collaboration and quality control in the annotation process by allowing annotators to view completions submitted by reviewers. Annotators can now view and clone reviewed submissions, make corrections, or add comments directly on the annotated chunks, providing clear communication and improving overall annotation quality. The new release also simplifies the identification of differences between two completions by automatically highlighting discrepancies, streamlining the validation process.
Alongside these major updates, this release includes numerous improvements and bug fixes, making Generative AI Lab more efficient and user-friendly than ever.
Support for De-identification
Version 6.4 of the Generative AI Lab introduces a new de-identification feature, enabling users to anonymize documents containing sensitive information such as PII (Personally Identifiable Information) and PHI (Protected Health Information). This functionality is intended to protect data privacy and ensure compliance with privacy regulations while preserving the data’s usefulness for subsequent analysis and processing.
De-identification Projects: When creating a new project in the Generative AI Lab, users can mark it as De-Identification specific. These projects allow the use of manually trained or pre-trained text-based NER models, together with prompts, rules, and custom labels created by the user for identifying sensitive data inside of tasks. Once the sensitive data is identified (either automatically or manually) and validated by human users, it can be exported for further processing. When creating De-identification projects make sure you only target sensitive entities as part of your project configuration and avoid annotating relevant data you need for downstream processing as all those entities will be removed when exporting the project tasks as de-identified documents. The best practice, in this case, is to re-use de-identification specific models combined with custom prompts/rules.
Exporting De-identified Documents: The tasks of your project with PII/PHI labeled entities can be exported as de-identified documents. During the export process, labeled entities will be replaced by the label names, or special characters (such as “*”), or obfuscated and replaced with fake data. This ensures that sensitive information is removed and not available for downstream analysis.
Re-importing and Further Processing: The de-identified documents can be re-imported into any text-based project. This allows for further labeling and data preparation for model training/tuning by annotators, ensuring that the de-identified data can be utilized effectively.
Types of De-identification
Generative AI Lab supports four kinds of de-identification:
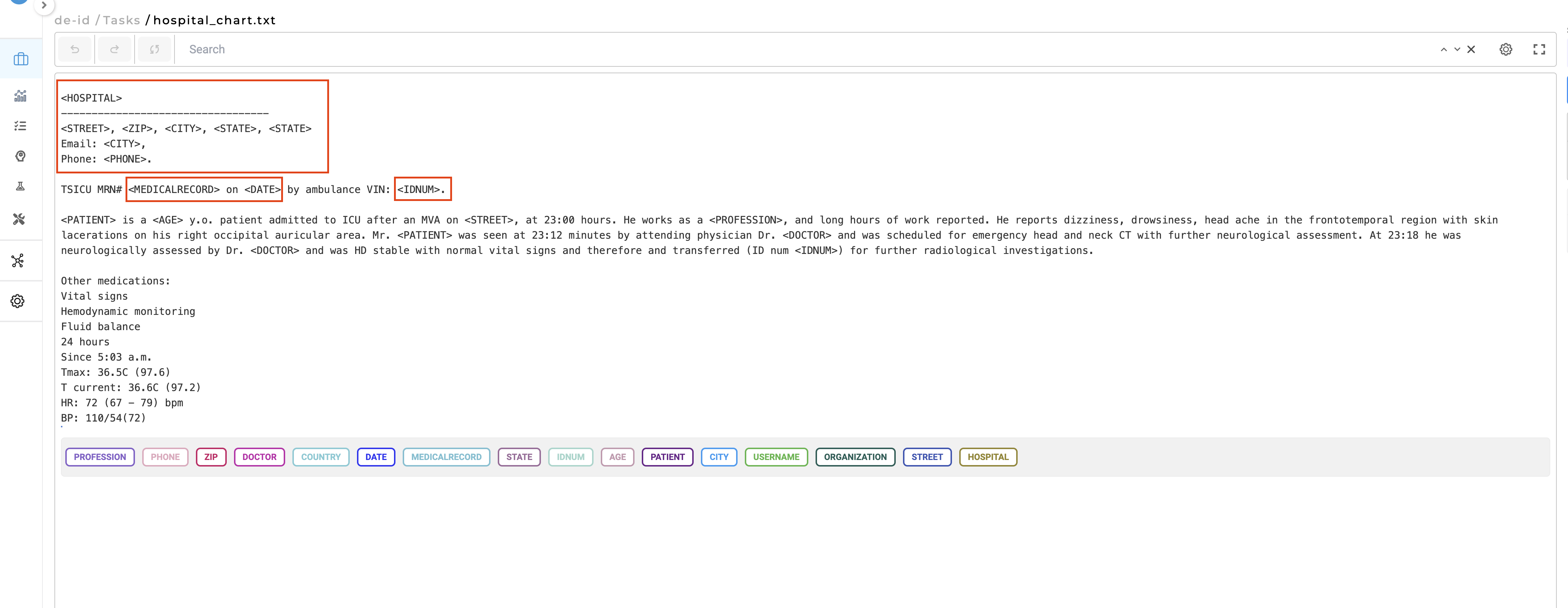
- Mask with Entity Labels: Identified tokens are replaced with their respective label names. For instance, in the text “ John Davies is a 62 y.o. patient admitted to ICU after an MVA.” where John Davies is labeled as Patient and 62 as Age, the de-identified exported text would be: “<Patient> is a <Age> y.o. patient admitted to ICU after an MVA. “
- Mask with Characters: All characters of the identified tokens are replaced by *. For the above example, if John Davies was labeled as Patient and 62 was labeled as Age, then on task export, the resulting text will look like “
**********is a**y.o. patient admitted to ICU after an MVA.” This option ensures the number of characters is kept the same between the original document and the anonymized one. - Mask with Fixed Length Characters: The identified tokens are replaced by
****(4 star characters). For the same example, the output will be “********is a****y.o. patient admitted to ICU after an MVA.” - Obfuscation: The identified tokens are replaced by new (fake) tokens. For the above example, the obfuscated result will be “Mark Doe is a 48 y.o. patient admitted to ICU after an MVA. “
Working with de-identification projects
Step 1. When creating a new project, after defining the project name and general settings, check the de-identification option at the bottom of the Project setup page, and select the type of anonymization you prefer.
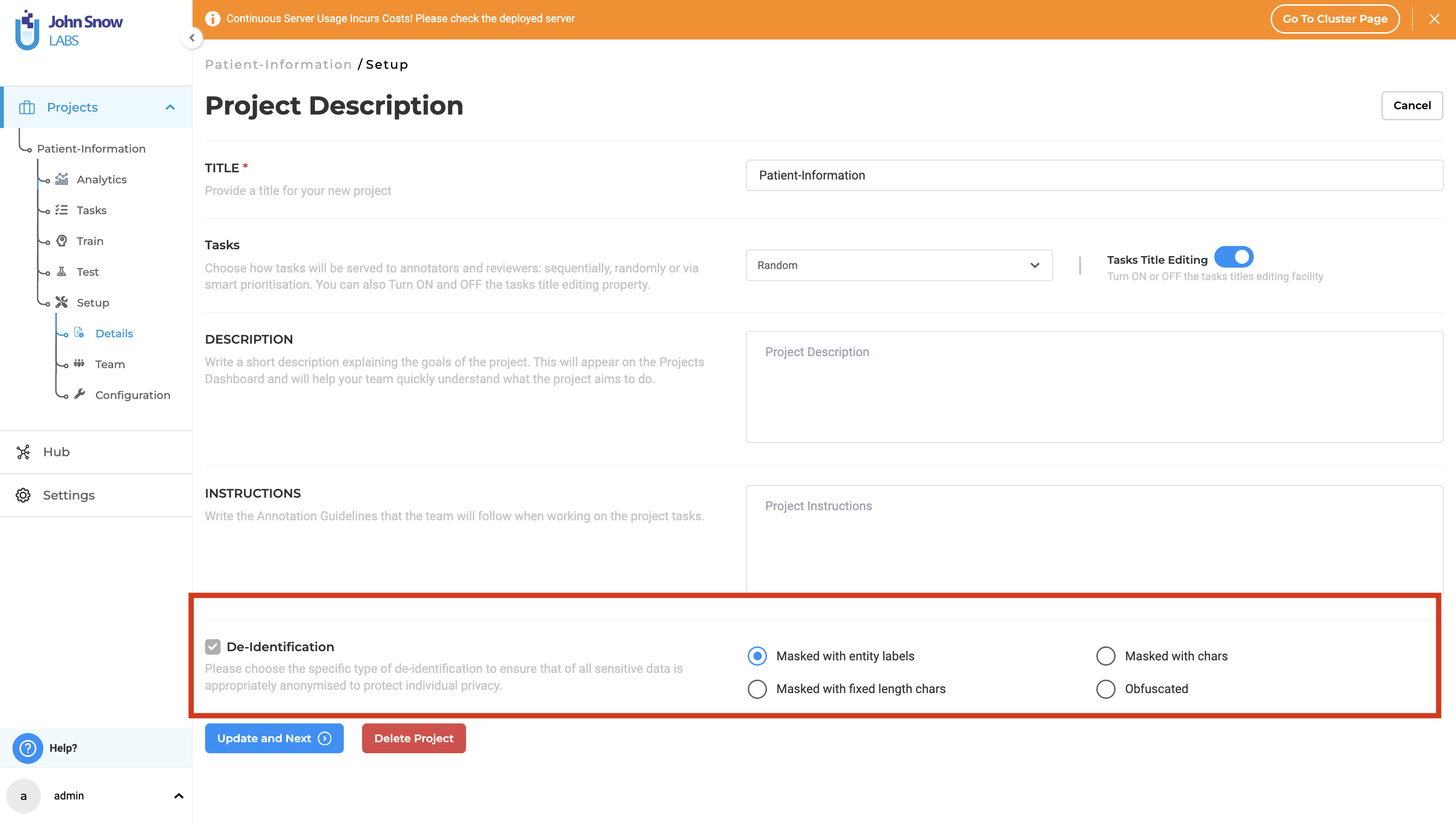
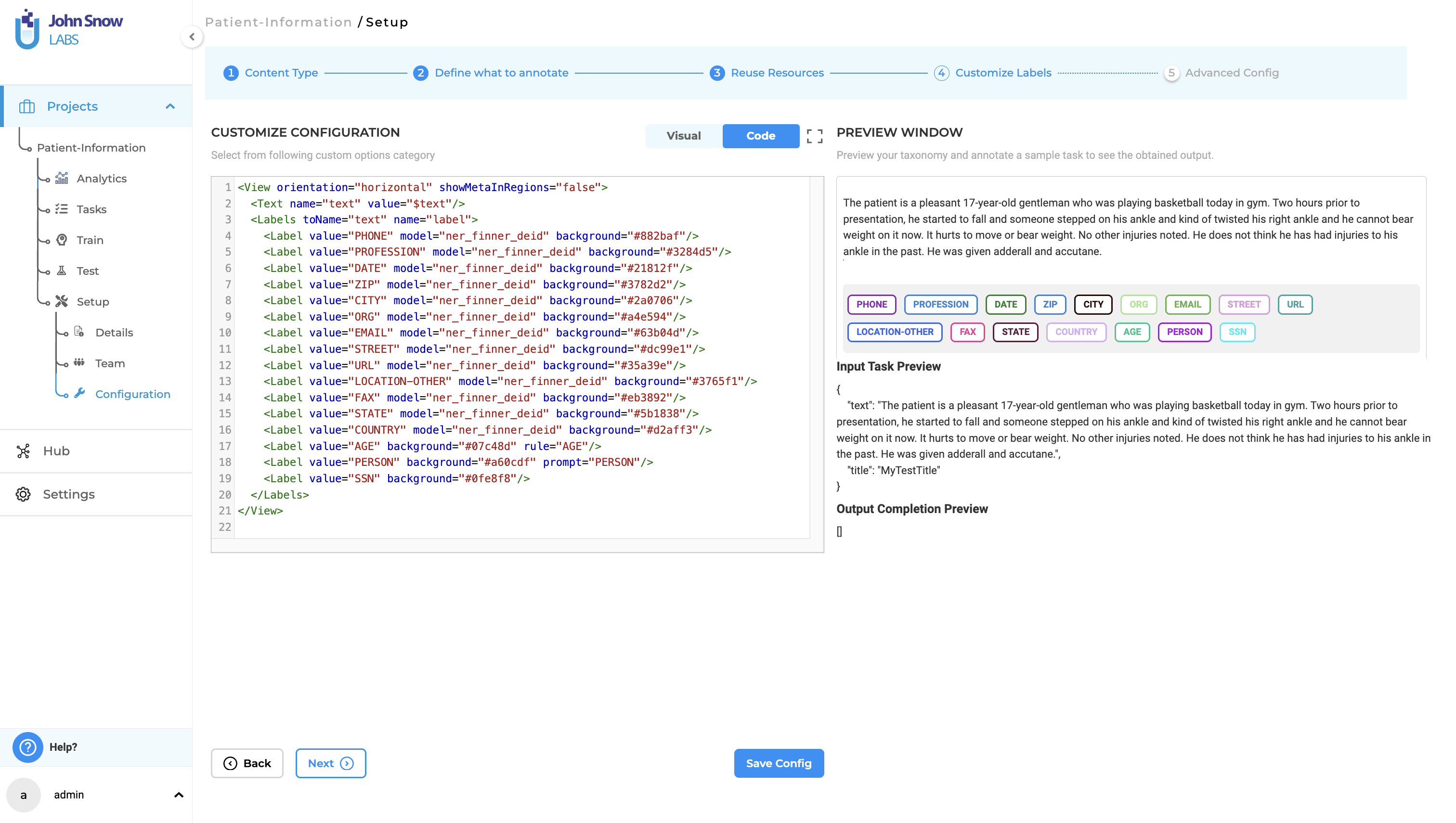
Step 2. Configure your project to reuse sensitive labels from existing NER Models, Rules, Prompts. It is also possible to create custom labels that can be used to manually annotate the entities you want to anonymize in your documents.
When selecting pre-annotation resources for your project, ensure that no critical downstream data is inadvertently identified and removed. For instance, if you pre-annotate documents with models, rules, or prompts that identify diseases, those labels will be anonymized upon export, rendering them unavailable to document consumers.
To mitigate this, employ pre-trained or custom de-identification models and augment them with rules and prompts tailored to your specific use cases (e.g., unique identifiers present in your documents). You can also selectively include specific labels from each model in your project configuration. For example, if age information is essential for your consumers, you can exclude this label from the project configuration to retain the data in your document.
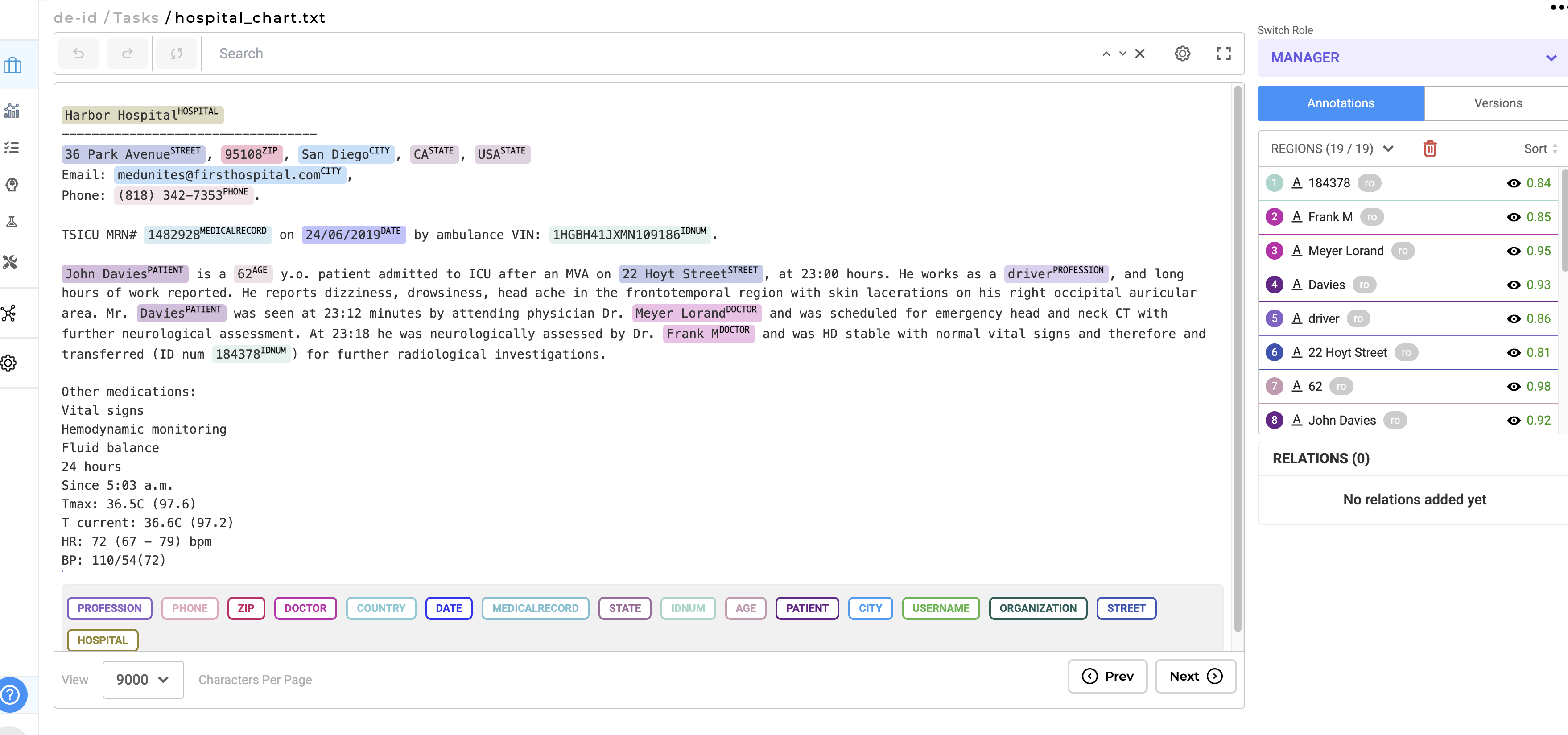
Step 3. Pre-annotate your documents, then have your team review them for any overlooked sensitive data. Once your project is set up and tasks are imported, use the pre-annotation feature to automatically identify sensitive information. Incorporate a review process where your team checks the pre-annotations using the standard annotation workflow, making manual corrections or annotations to any sensitive segments as necessary. Ensure that all sensitive information is accurately labeled for effective de-identification.
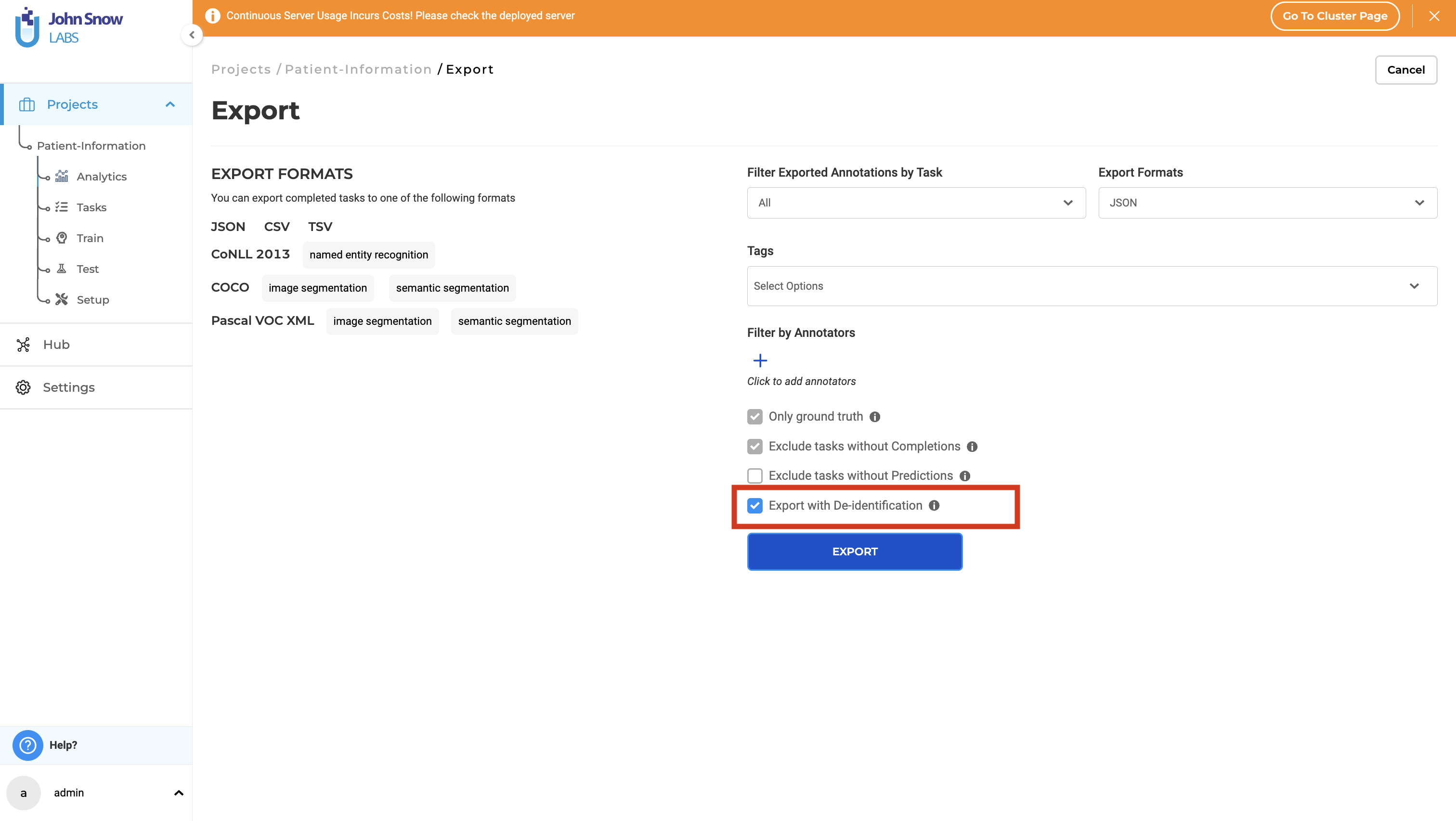
Step 4. Export De-identified Documents. After completing the labeling process, proceed to export the de-identified documents. Ensure the “Export with De-identification” option is selected on the export page to generate de-identified documents.
During the export process, de-identification is executed based on the type of anonymization selected during project setup. This de-identification option can be updated at any time if necessary.
Step 5. Import the de-identified tasks in a new project for further processing. These tasks, once exported, can be re-imported into any text-based project in case you need to extract additional data or in case you want to use them for model training/tuning.
HOW TO: De-identification projects can be easily identified without opening them. A small de-identification icon is displayed in the bottom left corner of the project card, clearly indicating the project’s status.
LIMITATION: Projects must be designated as de-identification projects during their initial creation. It is not possible to convert existing projects or newly created non-de-identification projects into de-identification projects.
Export of De-identified tasks
Completion Submission: Pre-annotations alone are not sufficient for exporting de-identified data. Only starred completions are considered during the export of de-identified tasks. This means that each task intended for de-identified export must be validated by a human user, with at least one completion marked with a star by an annotator, reviewer, or manager.
Multiple Submissions: In instances where multiple submissions exist from various annotators, the de-identification process will prioritize the starred completion from the highest priority user as specified on the Teams page. This ensures that de-identification is based on the most relevant and prioritized annotations.
This new de-identification feature significantly enhances data privacy by anonymizing sensitive document information. We are confident that this feature will empower users to handle sensitive data responsibly while maintaining the integrity and usability of their datasets.
Annotators Can View Completions Submitted by Reviewers
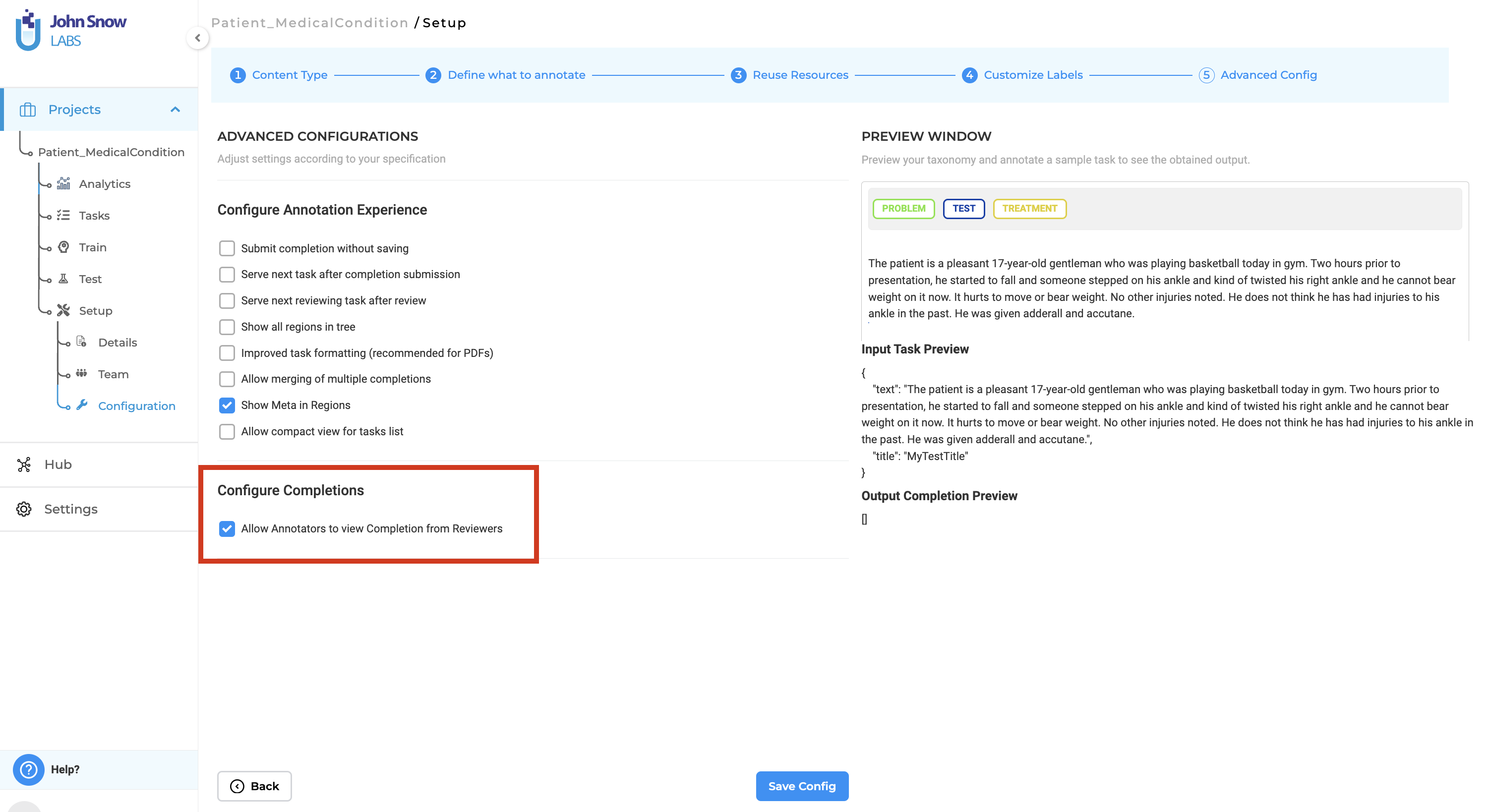
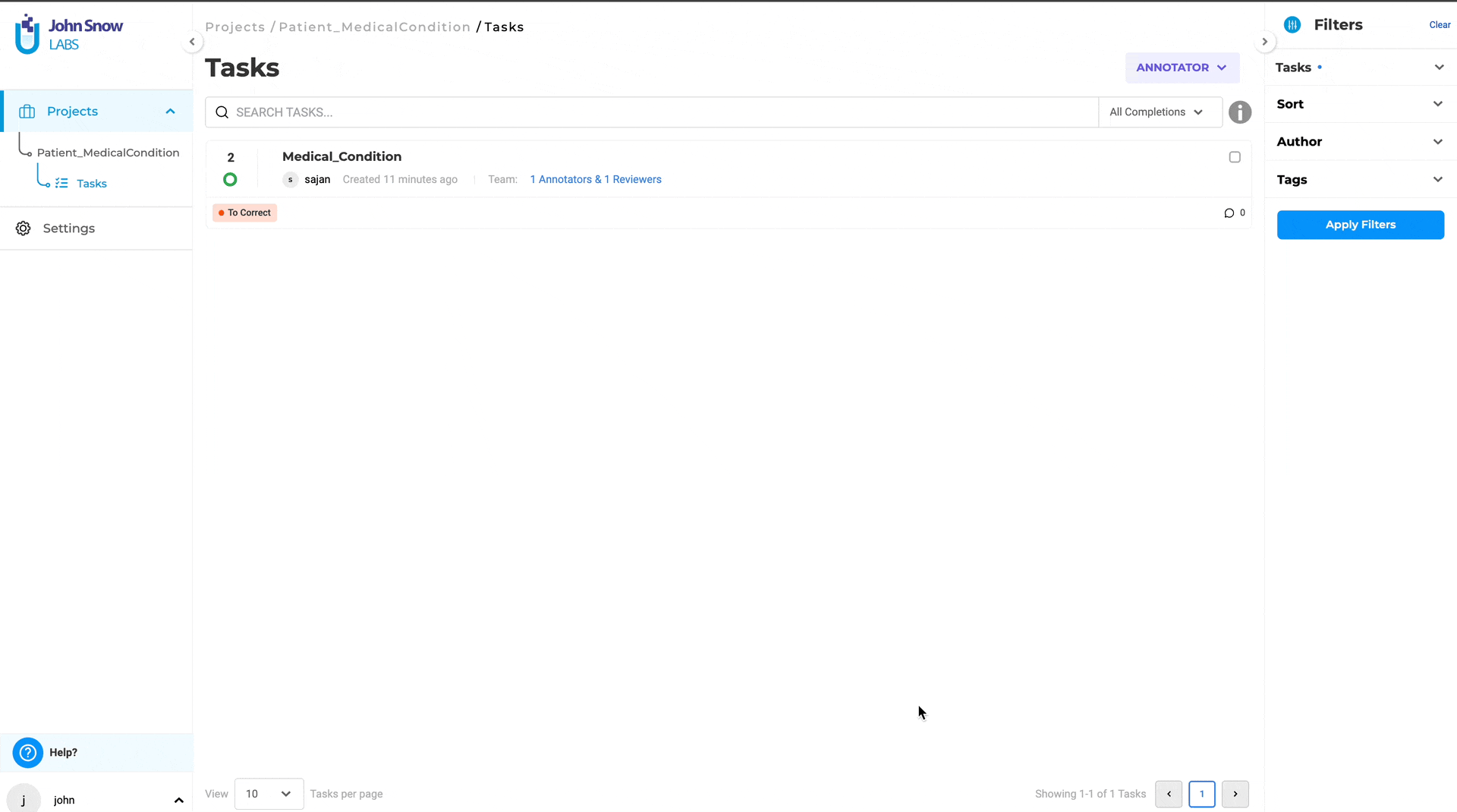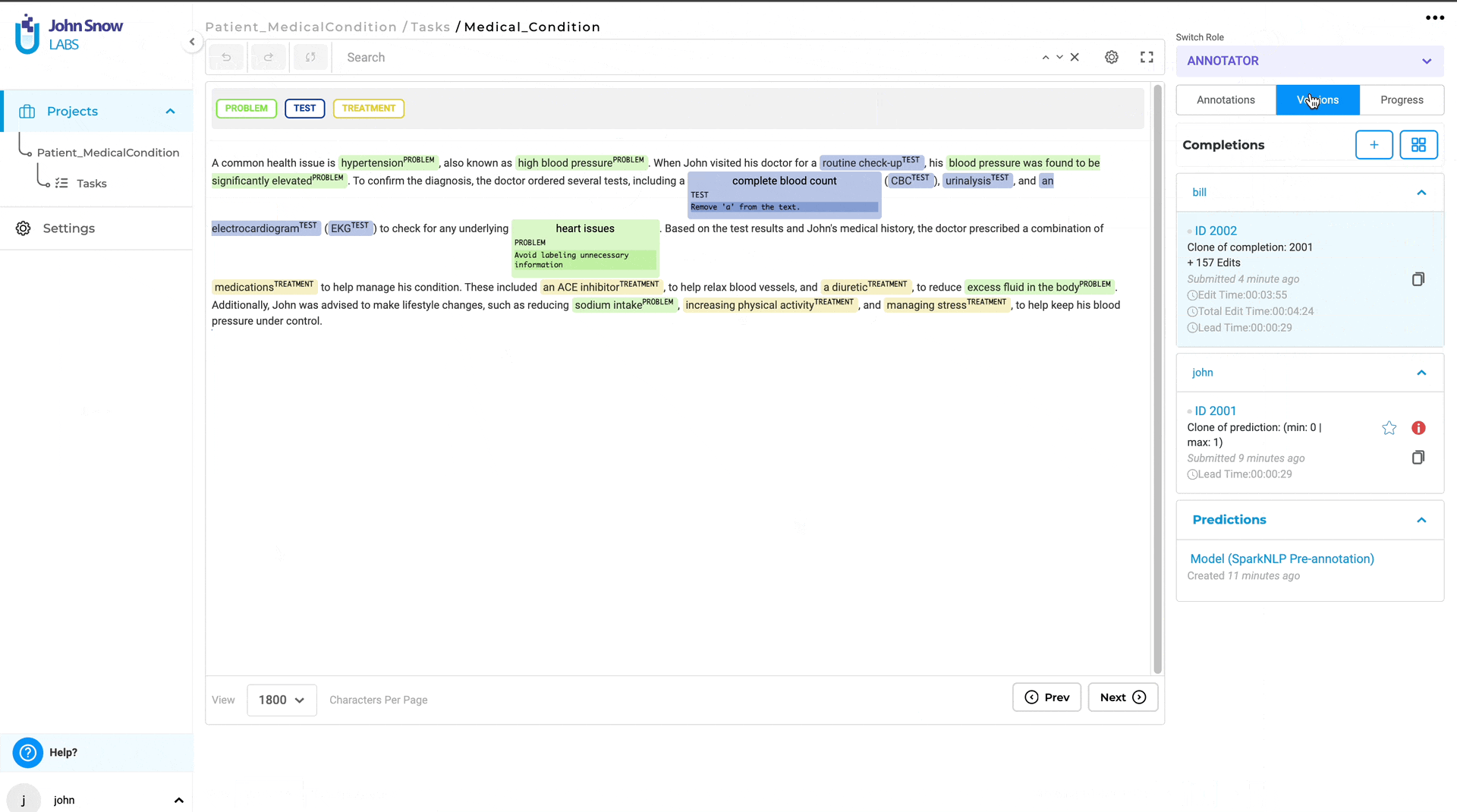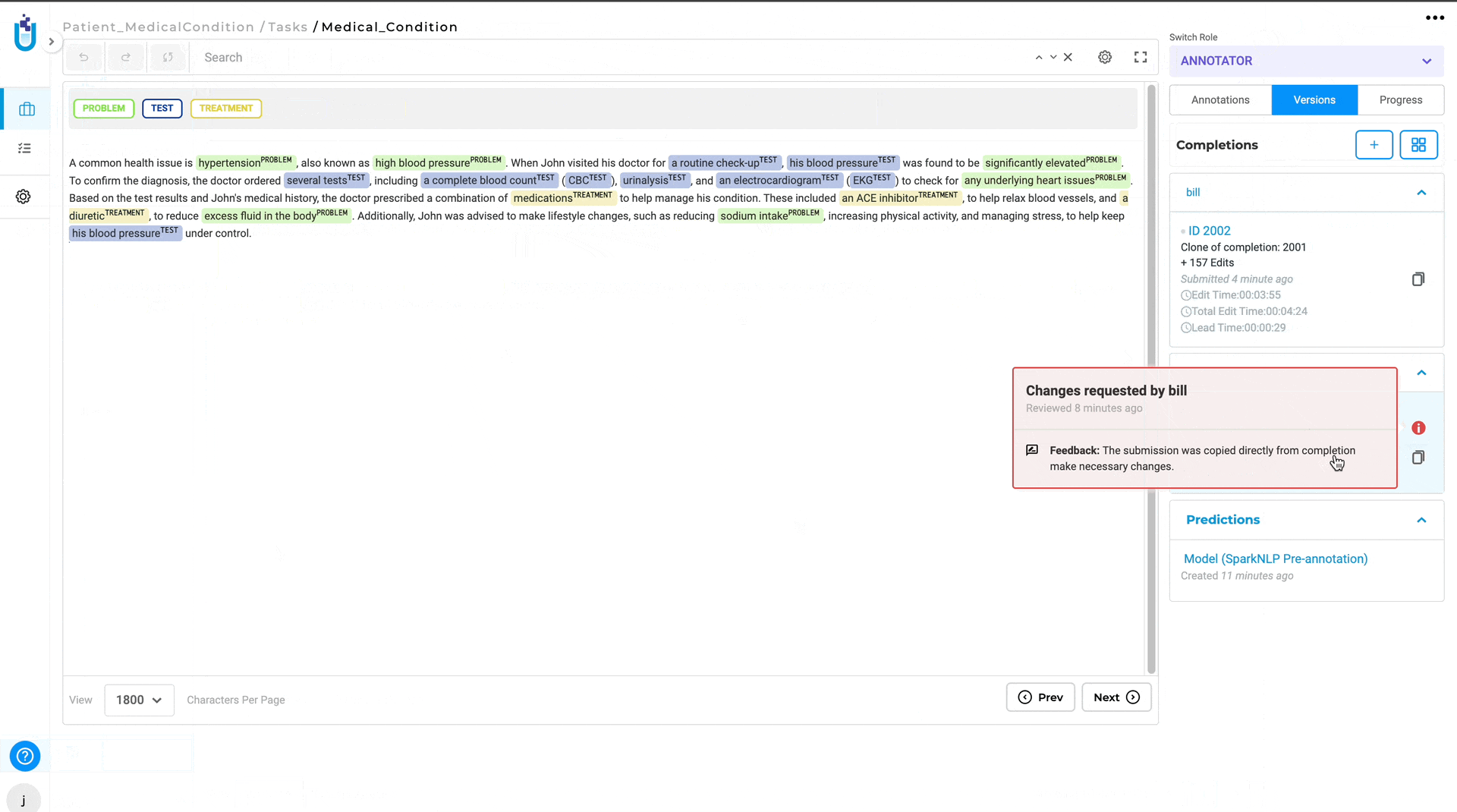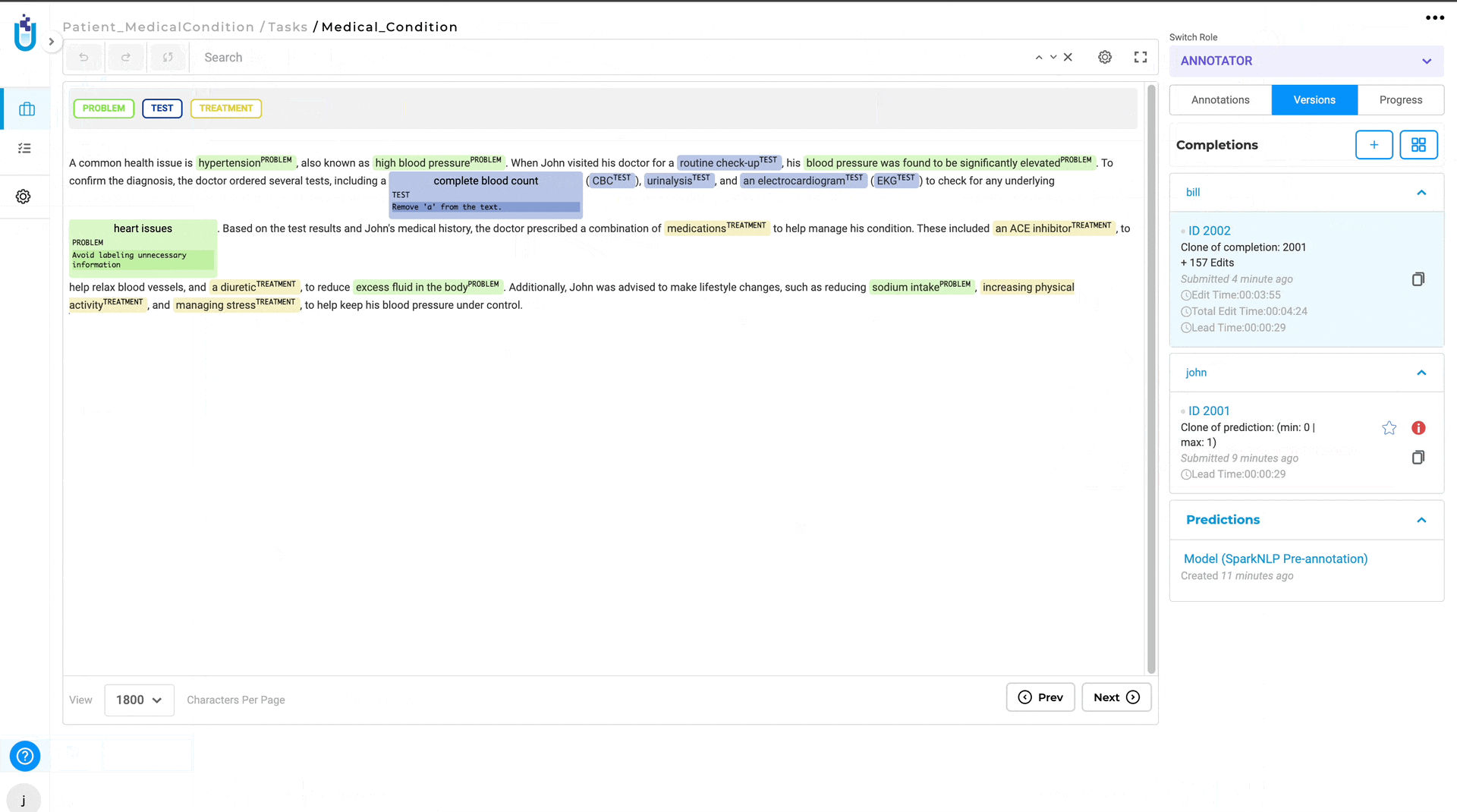
In version 6.4, of the Generative AI Lab, a new feature has been added that allows annotators to view the completion submitted by the reviewer. This enhancement fosters better collaboration and quality control in the annotation process. Previously, reviewers could only provide feedback on annotations, but now they can clone annotator submissions, make corrections, and add comments directly within the text using meta information. The updated submissions are then visible to the original annotator, providing clear insights into the reviewer’s expectations and suggestions.
How to Enable:
- The project manager must enable the option “Allow annotators to view completions from reviewers” in the project settings.
 >
>
Workflow:
- Reviewer Clones Submission: Reviewers can clone the annotator’s submission and make necessary corrections or add comments directly in the text using the meta option for the annotated chunks.
- Submit Reviewed Completion: The reviewer submits the cloned completion with corrections and comments.
- Annotator Reviews Feedback: The annotator whose submission was reviewed can view the reviewer’s cloned completion and see the comments and corrections made.
- Implement Changes: The annotator can then make the required changes based on the detailed feedback provided by the reviewer.
Benefits:
- Enhanced Feedback: Reviewers can now make precise corrections and add detailed comments on individual labels, helping annotators understand exactly what changes are needed.
- Improved Collaboration: Annotators can better align their work with the reviewer’s expectations by viewing the reviewer’s cloned submission.
- Quality Control: This feature helps in maintaining a higher standard of annotations by ensuring that feedback is clear and actionable.
This feature significantly enhances the annotation process, making it more transparent and collaborative, and ensuring that annotators have a clear understanding of the reviewer’s feedback.
Enhanced Comparison View for Completion Differences
In version 6.4, a new feature has been introduced in Generative AI Lab that allows annotators and project managers to easily compare the differences between two completions. This enhancement significantly simplifies the process of identifying discrepancies between annotations. Previously, differences between completions had to be manually validated, which could be a time-consuming and tedious process. With the new comparison feature, differences are automatically highlighted, making it easy for users to spot discrepancies in annotations.
How to Use:
- Step 1: Click on the Comparison View button.
- Step 2: Select the two completions you want to compare.
- Step 3: Click on Show Diff.
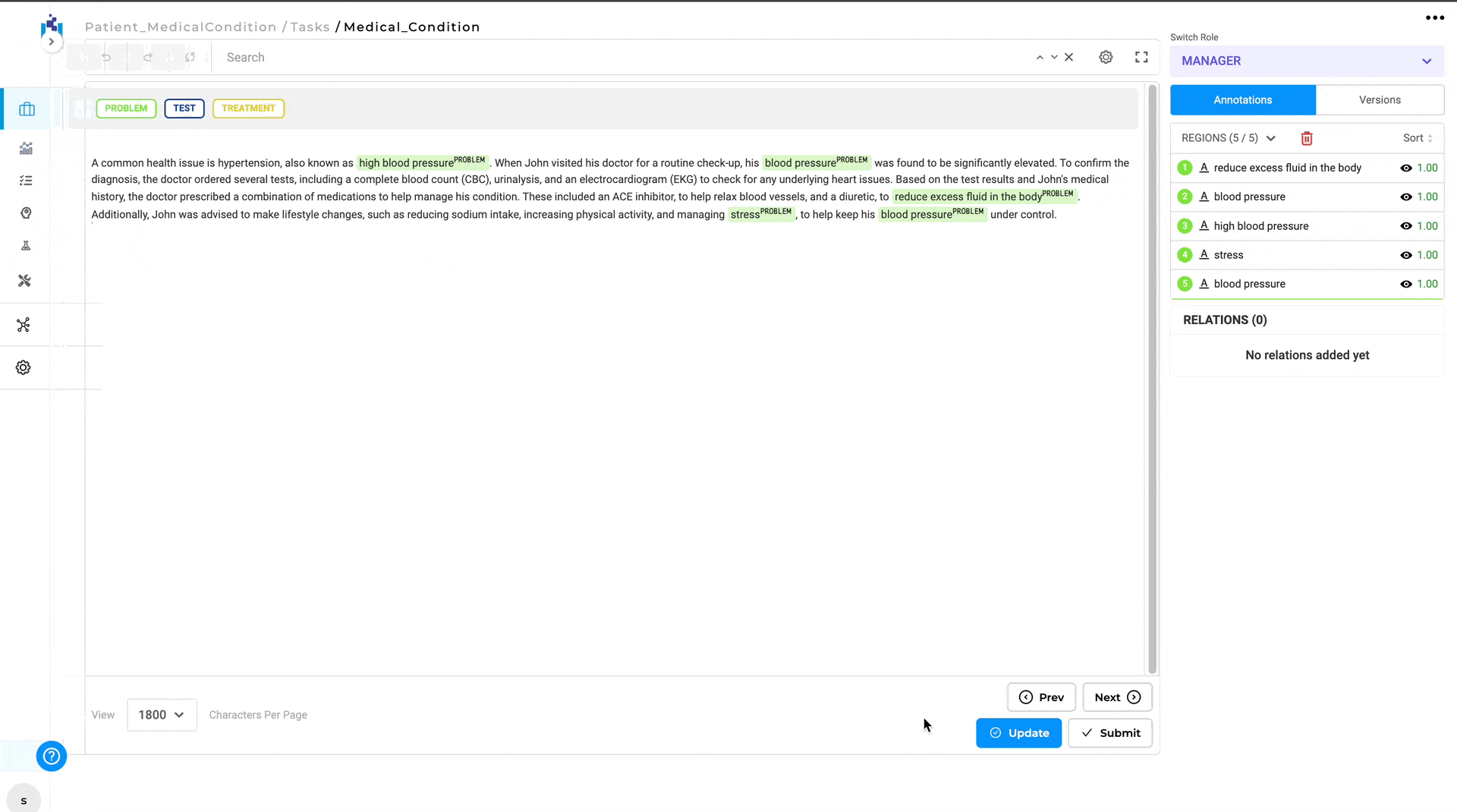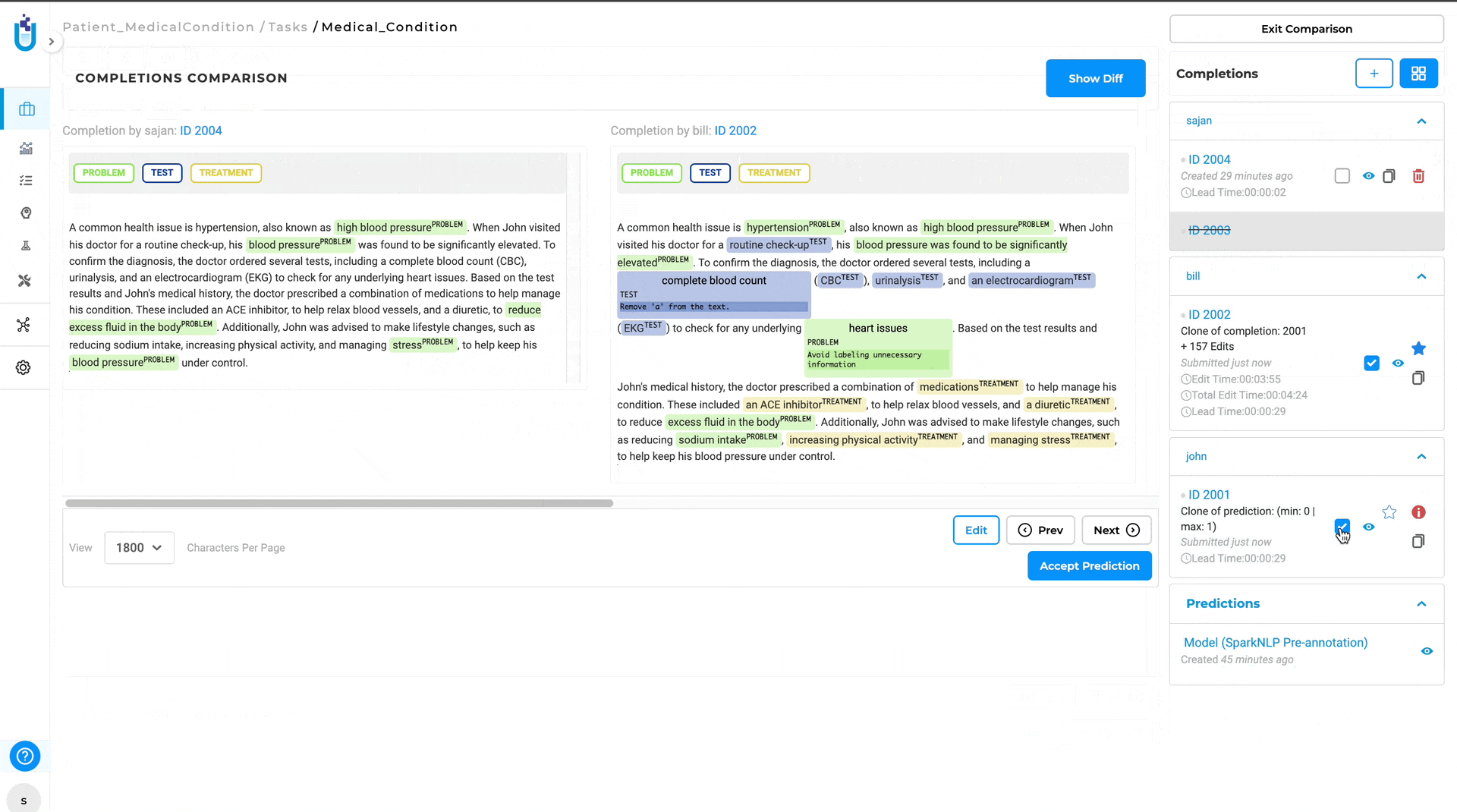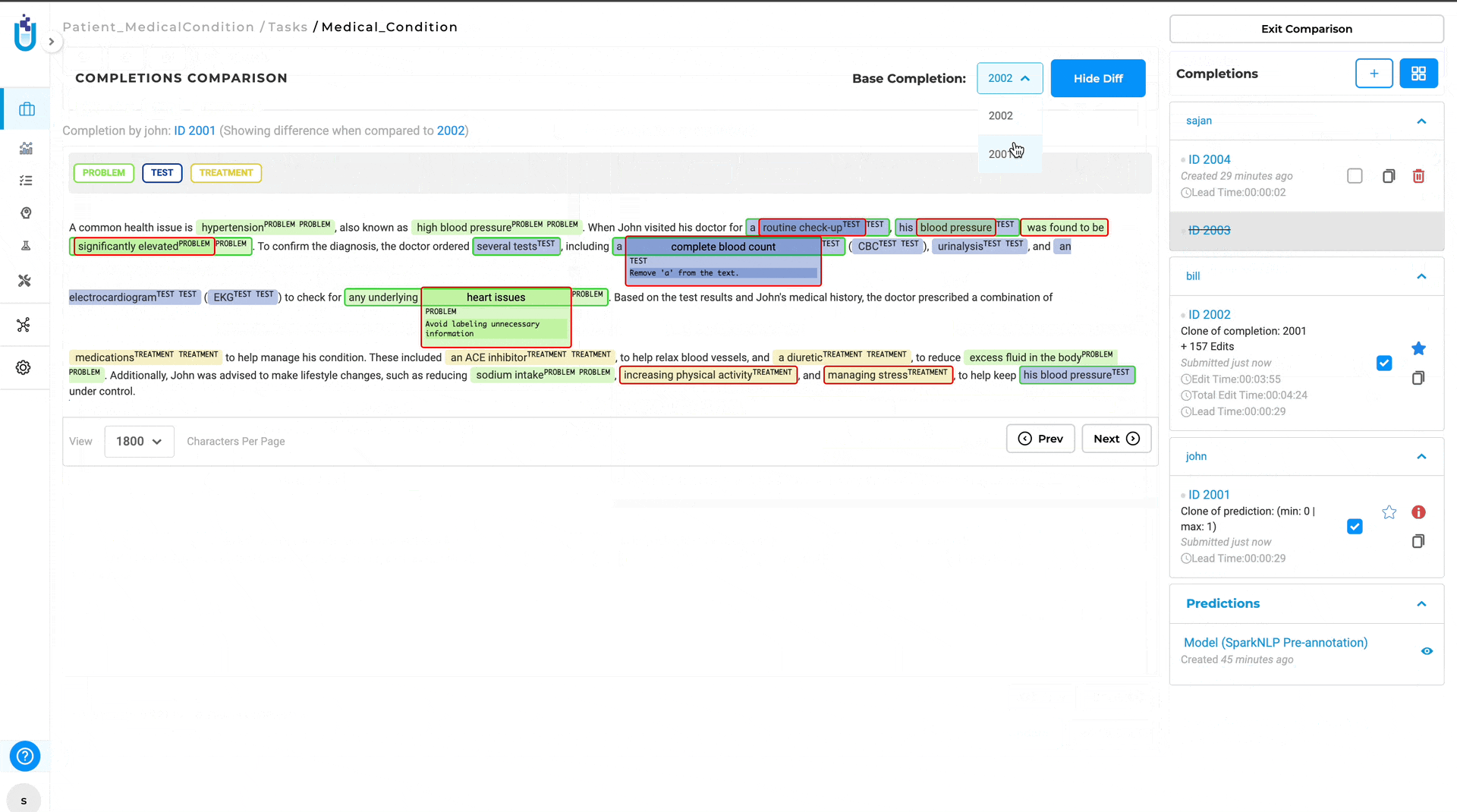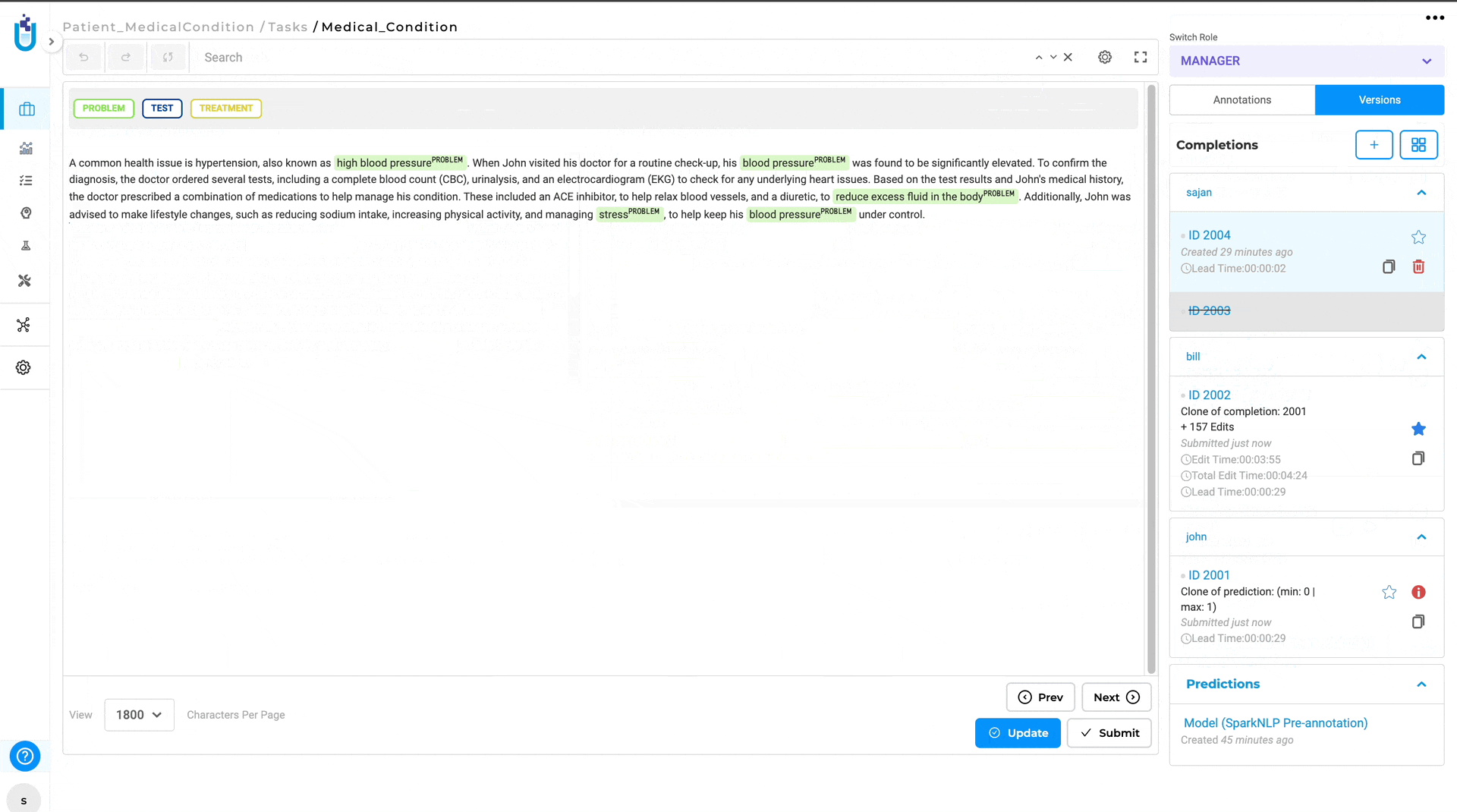
The Diff View will then open, displaying the differences between the two completions. Annotations that differ are highlighted, with green indicating the annotation in base completion and red indicating the annotations in compared completion.
Benefits:
- Efficiency and Clarity: Automatically highlighting differences saves time and reduces the potential for human error in identifying discrepancies. Also, the visual differentiation between annotations makes it easy to understand what changes have been made.
- Collaboration: Facilitates better communication between annotators and project managers by clearly showing where differences occur.
This feature enhances the accuracy and efficiency of the annotation process, ensuring that all team members can easily identify and address any inconsistencies between completions.
Improvements
Support for CPU cluster nodes in Azure
Previously, when creating a cluster in Azure, only instances with GPU resources were supported. This restriction limited the available options for users who did not require GPU capabilities. With the latest update, users can now select instances that do not have GPU resources. This enhancement provides greater flexibility in cluster configuration, allowing for a wider range of use cases and cost-effective options. The following instance types have been added to the list of allowed instance types:
- “Standard_D8_v3”
- “Standard_D8s_v3”
- “Standard_D8d_v4”
- “Standard_D8ds_v4”
- “Standard_DC8_v2”
Updated validation for Imports
Version 6.4 of Generative AI Lab introduces an enhancement for improving the application’s security and robustness by restricting the types of files that can be uploaded or imported from URL, S3, and Azure as well. Previously this was implemented for the local upload and import only. This change ensures that only supported and safe file types are processed, providing a more secure and efficient user experience, and maintaining the platform’s integrity and reliability while enhancing its security.
Users can confidently upload and import files, knowing that the system will enforce these important security measures.
Key features and benefits:
- File Type Validation: The application now checks the type of files being uploaded or imported from URL, S3, and Azure. Only supported file types are allowed, and any unsupported file types are automatically restricted.
- Enhanced Security Measures: Increased application security by preventing the upload or import of potentially harmful files reducing the risk of introducing malicious files into the system. Attempts to bypass these restrictions by changing file extensions are now detected and logged.
- File Name Length: The application checks the length of the file name to ensure it meets specified requirements before import or upload.
- Improved User Experience: Immediate feedback is provided when attempting to upload an unsupported file type, preventing potential errors and confusion during the project configuration workflow.
- Robust Monitoring: Attempts to circumvent file type restrictions by changing file extensions are detected and logged, providing an additional layer of security and oversight.
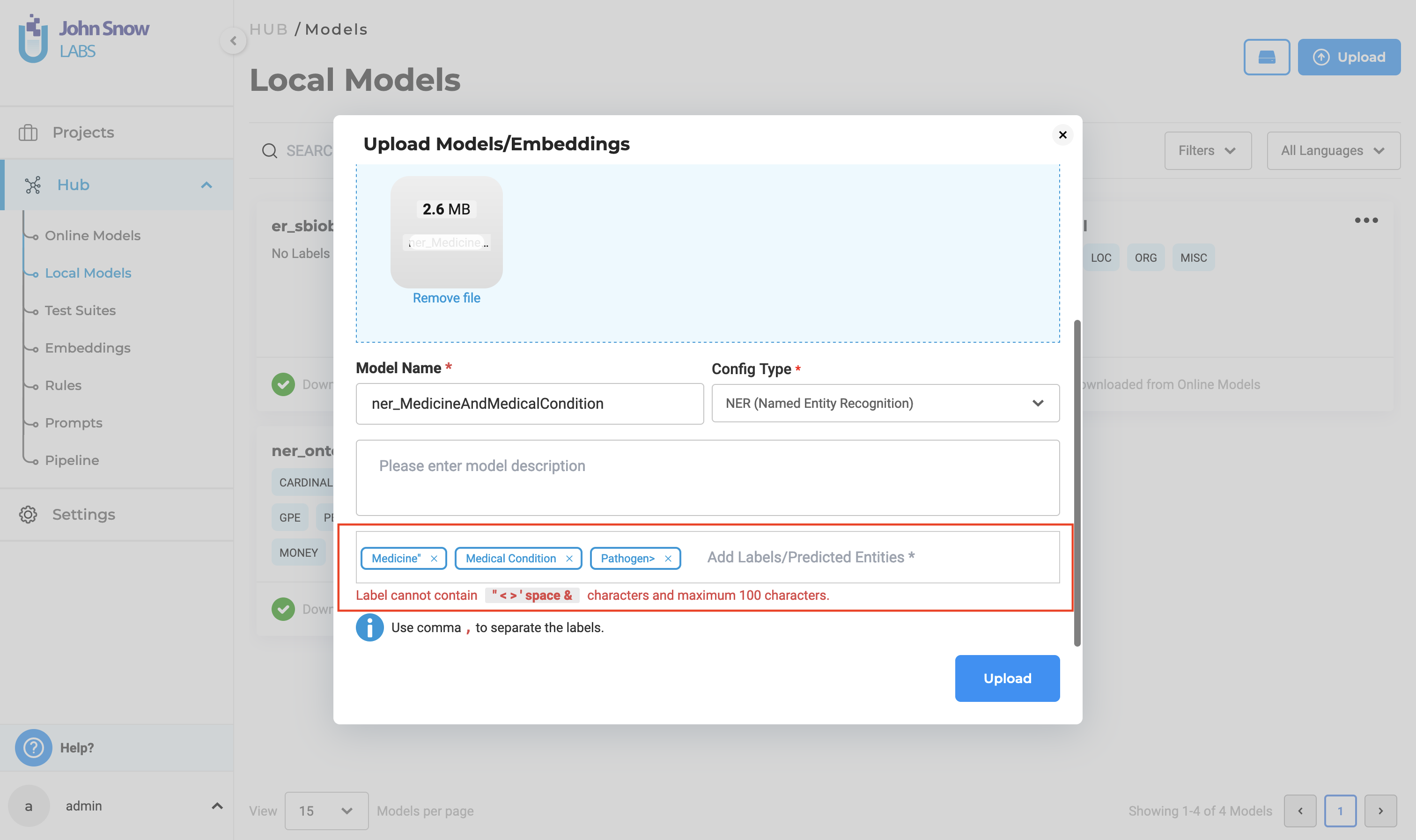
Upload model form will support special characters
When uploading a model, users are permitted to use special characters in labels and choices, except the following six characters:
- double quote (“)
- single quote (‘)
- less than (<)
- greater than (>)
- ampersand (&)
- space ( )
The inclusion of any of the above characters in labels or choices will result in an error during the model upload process. This restriction is implemented to ensure proper parsing and handling of the data. Users should take care to avoid these characters to prevent upload failures and ensure a smooth model deployment experience.
List deployed resolver in the pre-annotation popup
In previous versions, users were unable to view the resolvers in the pre-annotation pop-up. With this update, the deployed resolver list is now displayed in the pre-annotation pop-up. This enhancement ensures that users can easily access and utilize the resolvers, streamlining the pre-annotation process and improving overall efficiency.
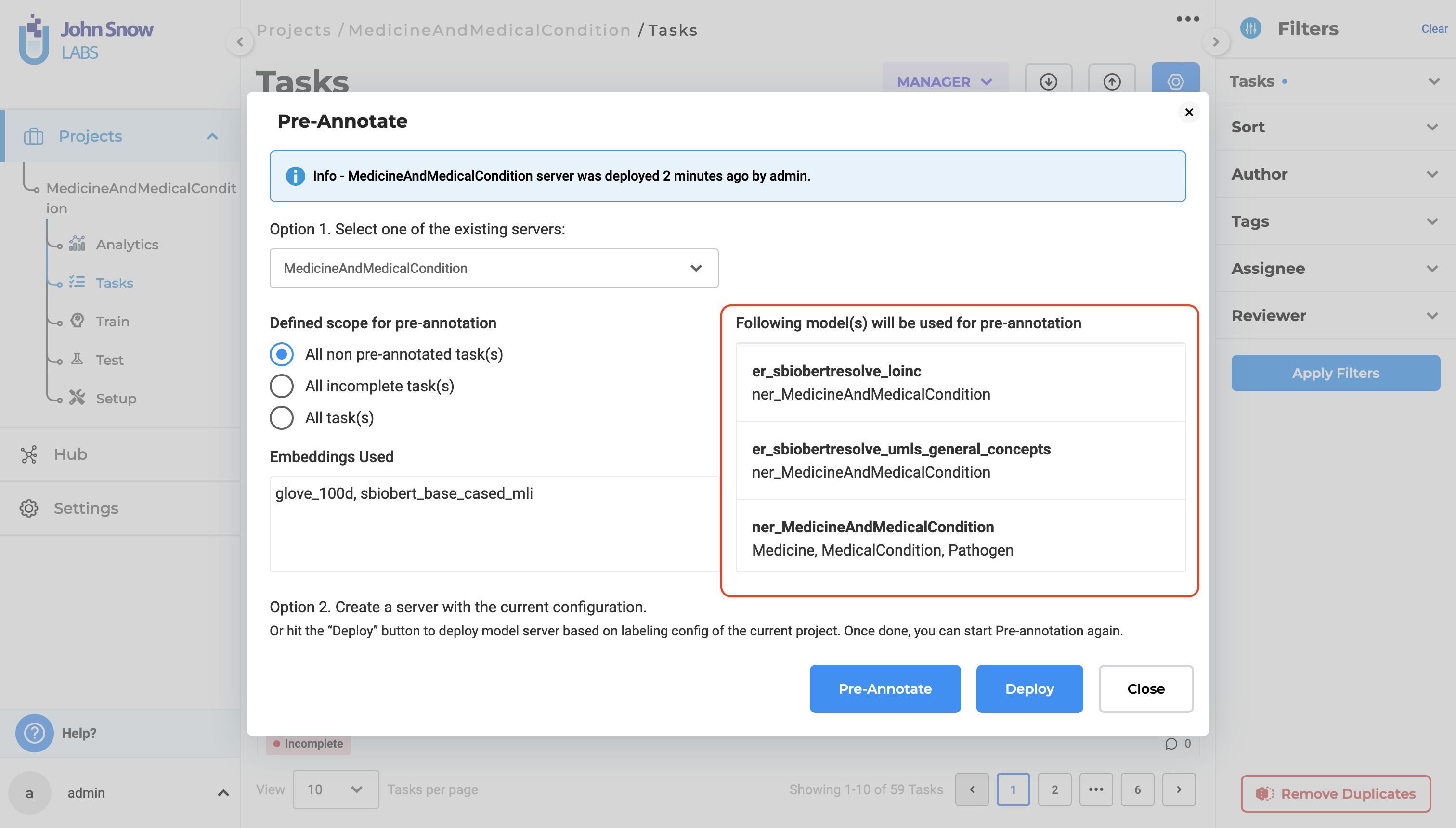
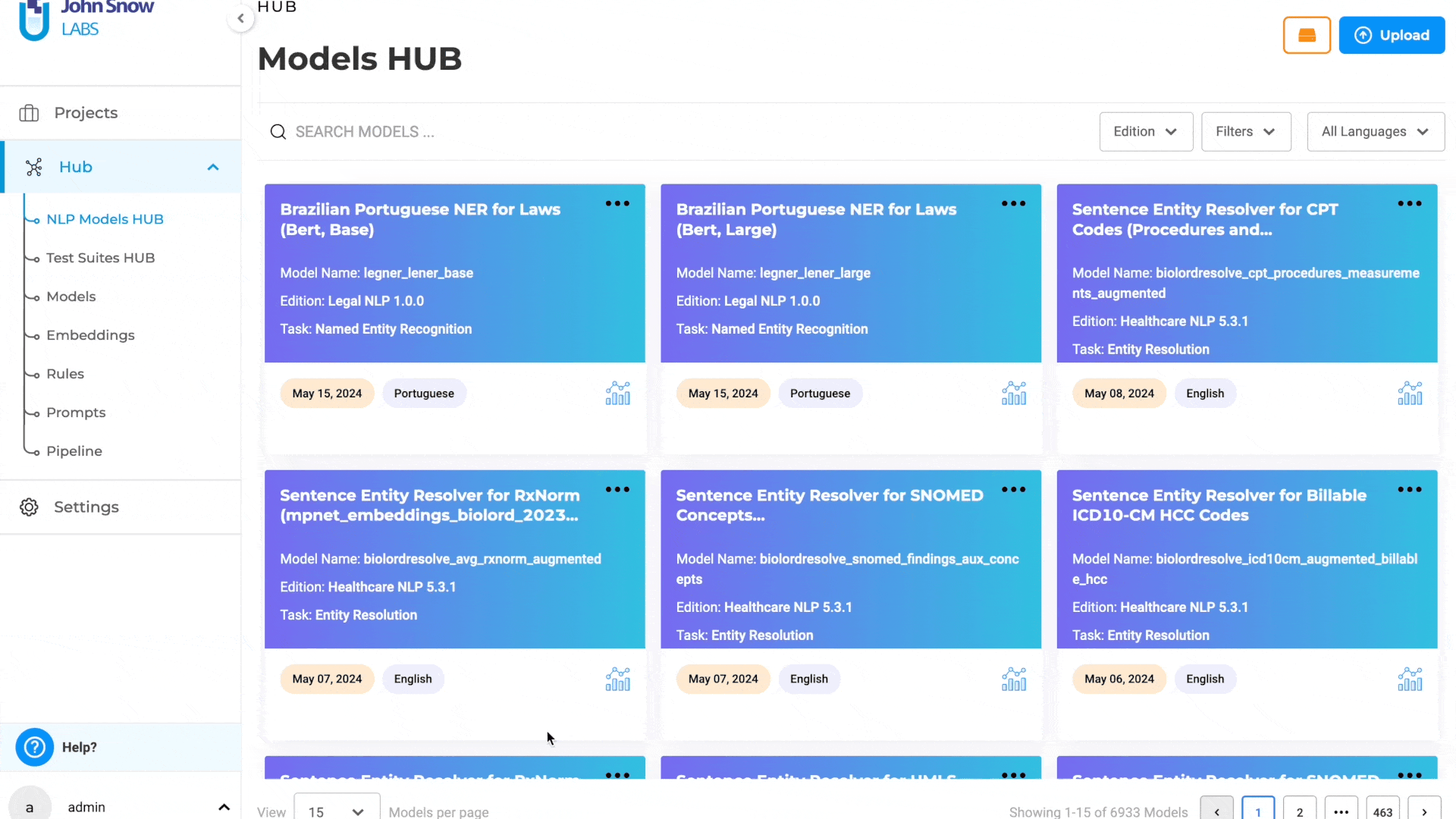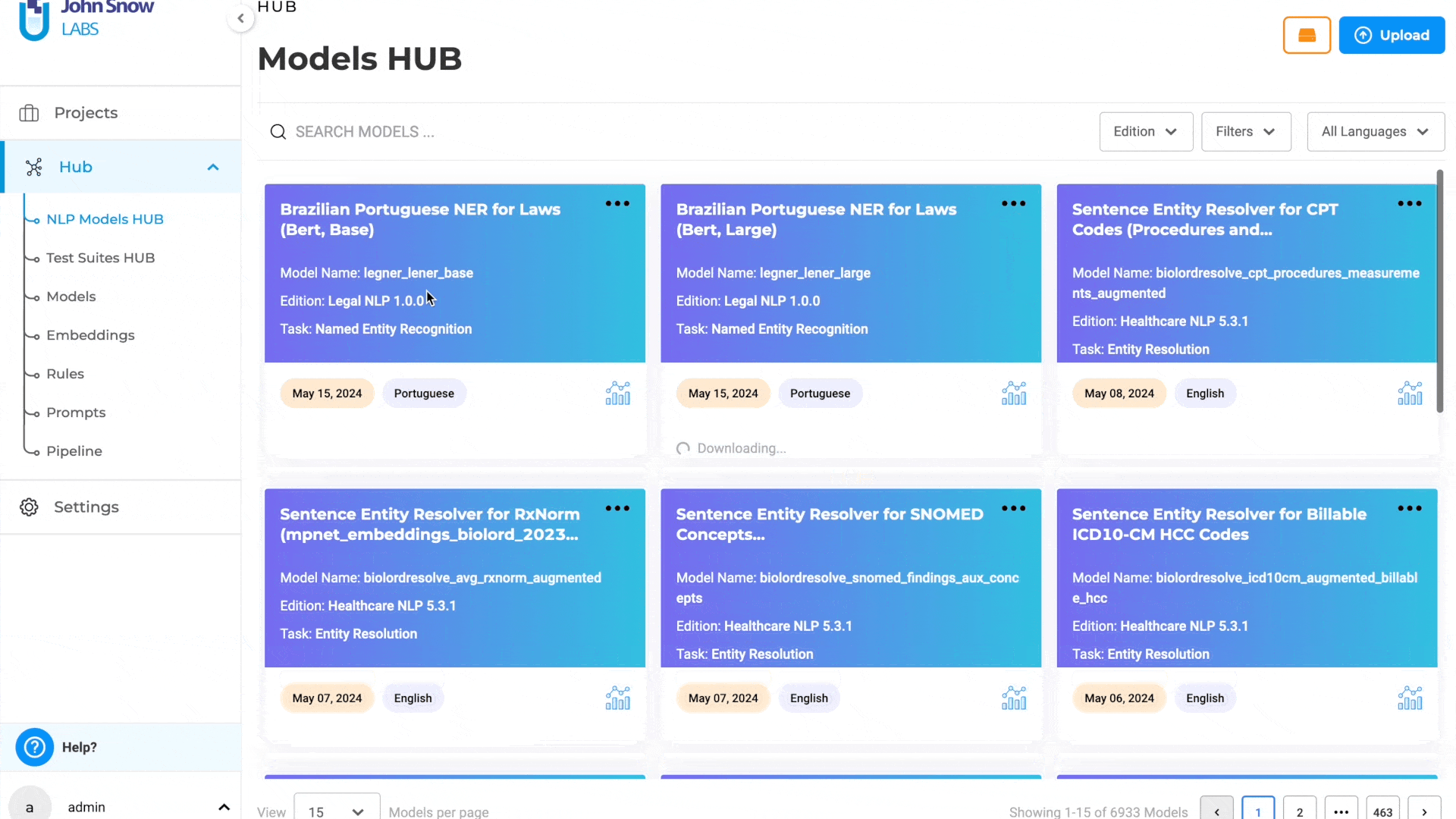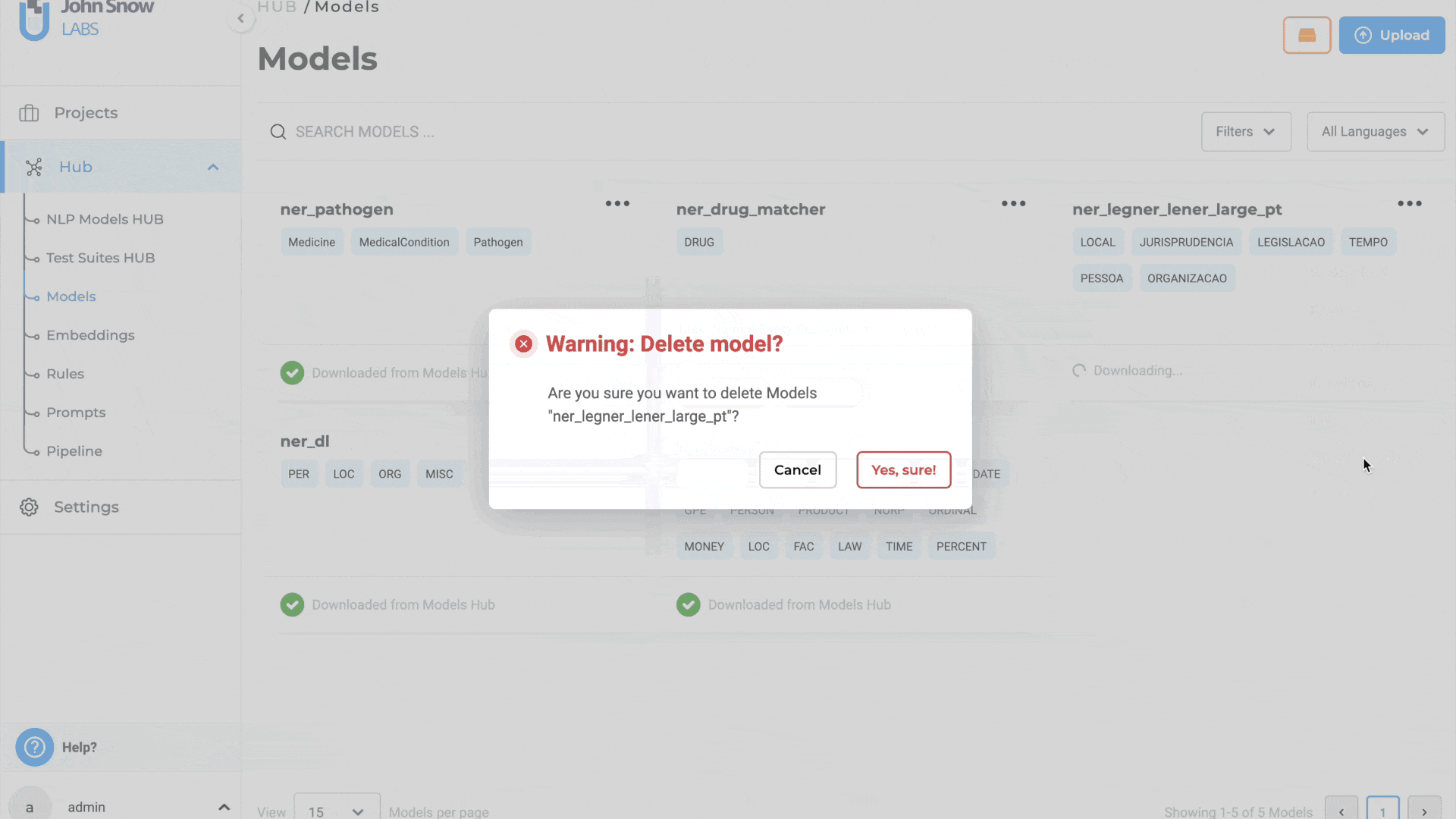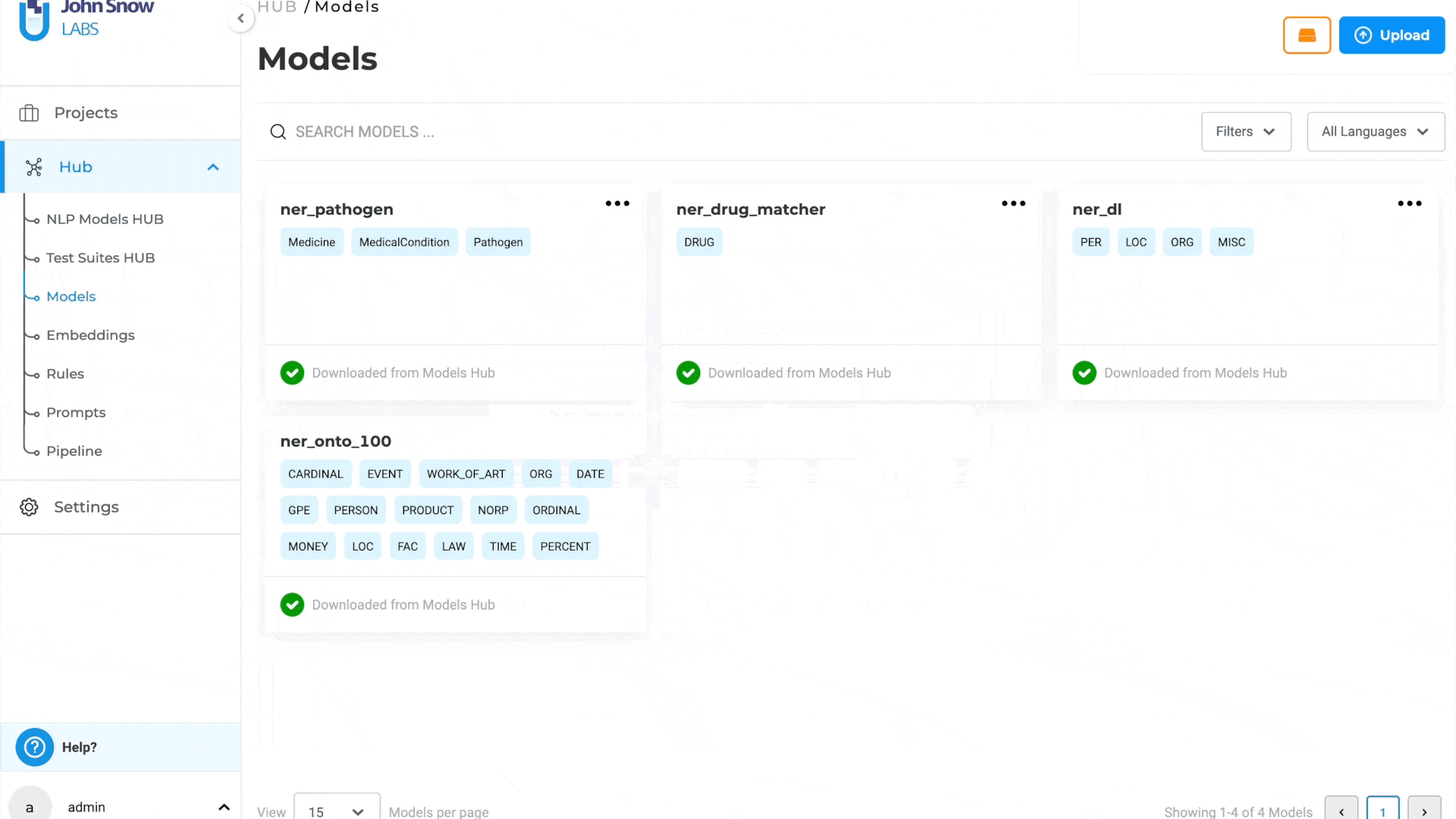
Delete the downloading models from the Models page
In previous versions, there was no option to cancel a model download once it had started. This limitation posed significant challenges for users, particularly in scenarios where the model download became stuck or took an unusually long time to complete. With this update, users can cancel an ongoing model download directly from the Local Models page. This enhancement provides greater control and flexibility, allowing users to efficiently manage their model downloads and avoid unnecessary delays.
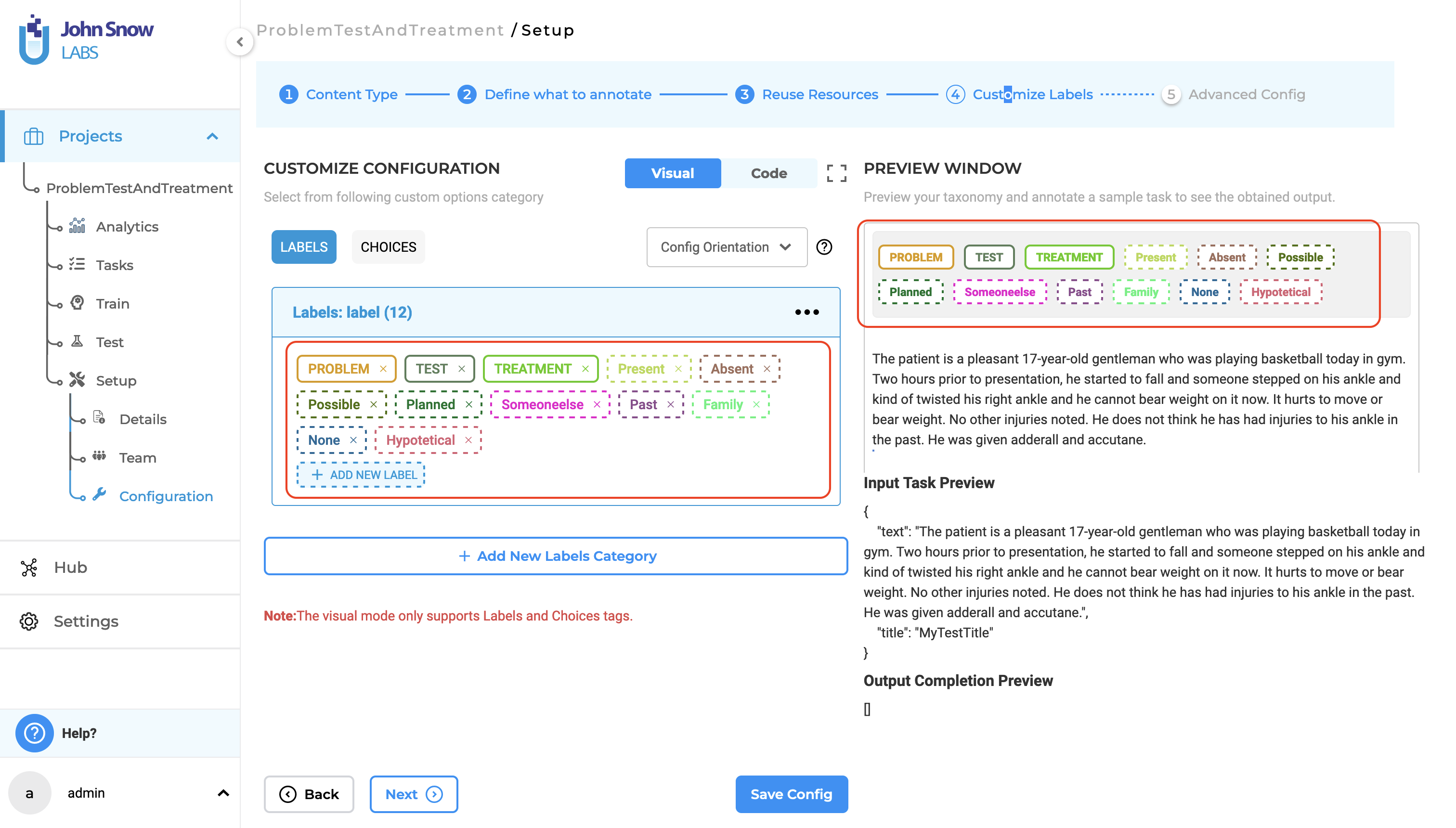
Assertion Labels are differentiated with a dashed border
In previous versions, assertion labels were displayed with solid border lines. This made it difficult for annotators to quickly distinguish assertion labels from other types of labels. In this update, assertion labels feature dashed border lines in both the preview section and the labels section. This visual enhancement helps annotators to easily identify and differentiate assertion labels, thereby improving the annotation process and reducing potential errors.
Disable the “Generate License” button when the license is available in AMI
In previous versions, the “Generate License” button was always available, even if a license was already present in the AMI. Clicking this button when a license was already available had no effect, leading to potential confusion and unnecessary actions. With this update, the “Generate License” button is now disabled by default if a license is already present in the AMI. The button will only be enabled if the license is missing. This improvement ensures a more intuitive user experience, preventing redundant actions and making it clear when a new license generation is necessary.
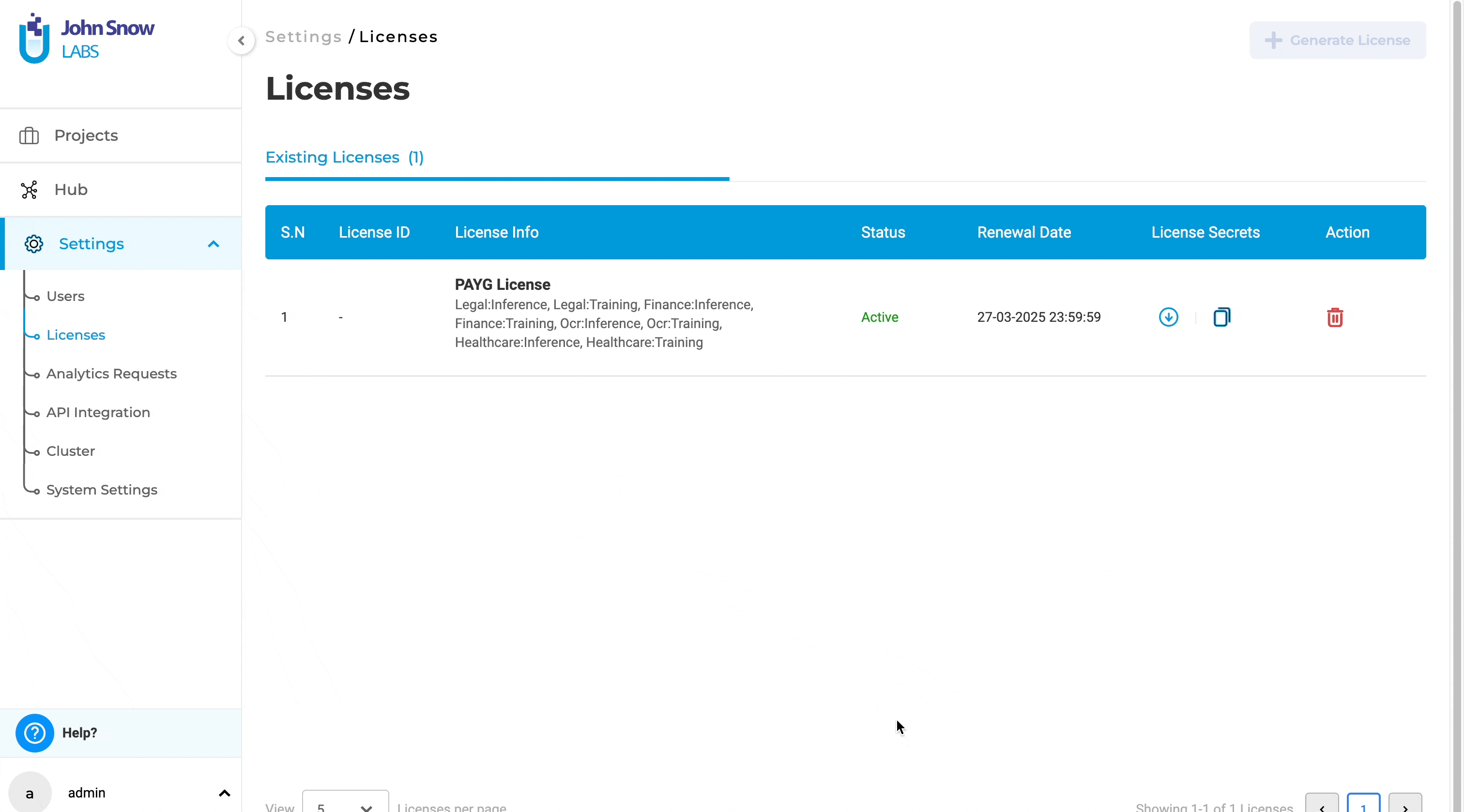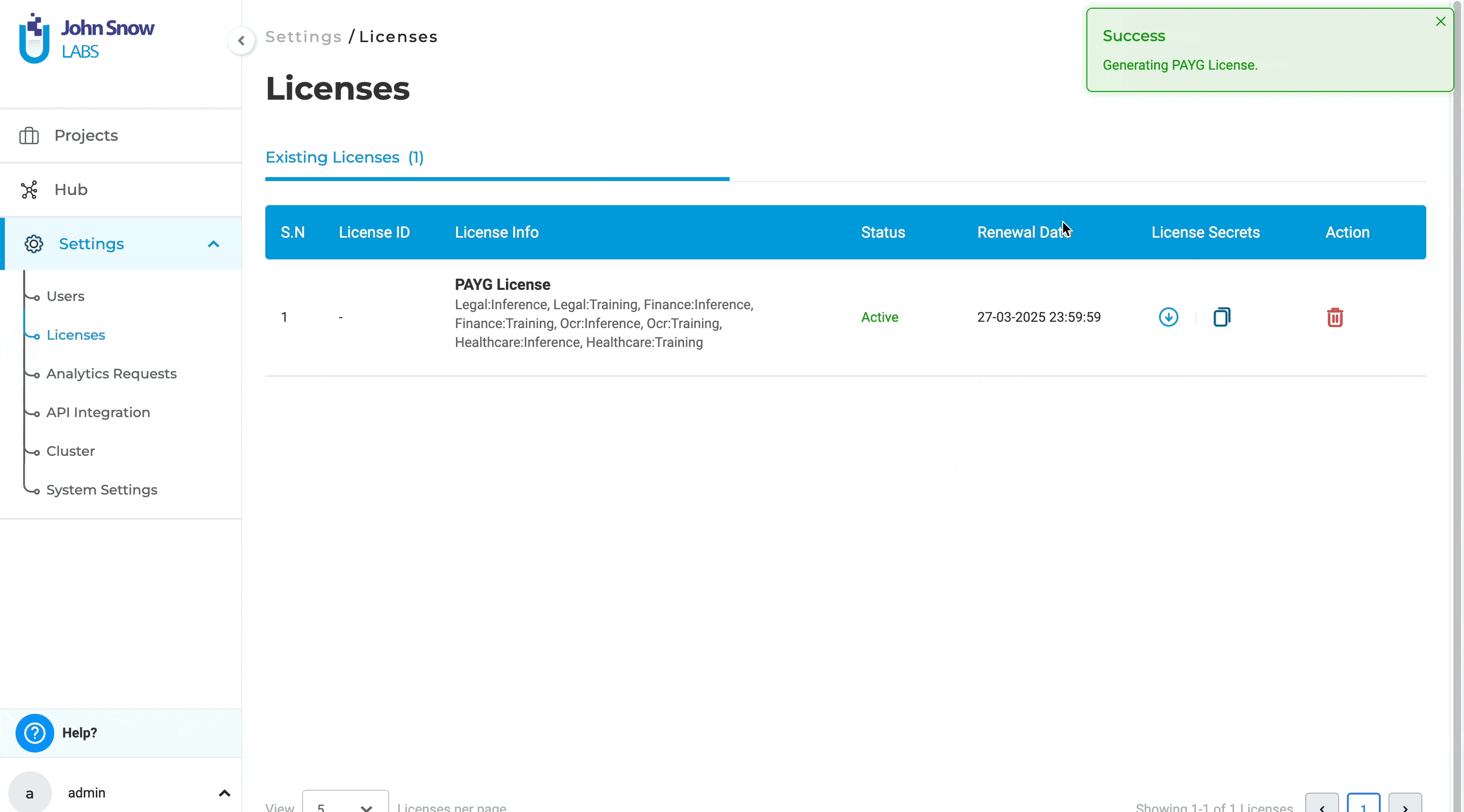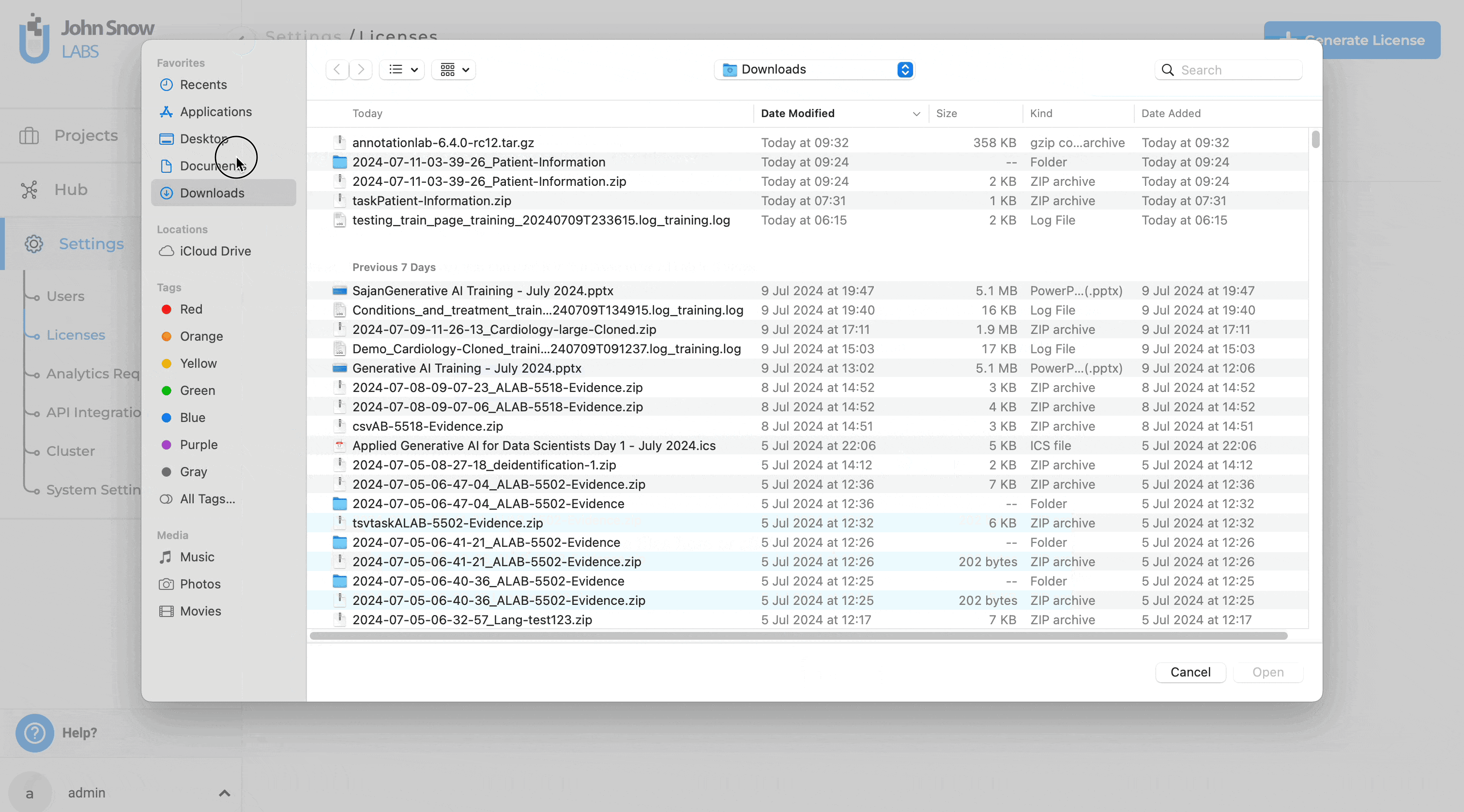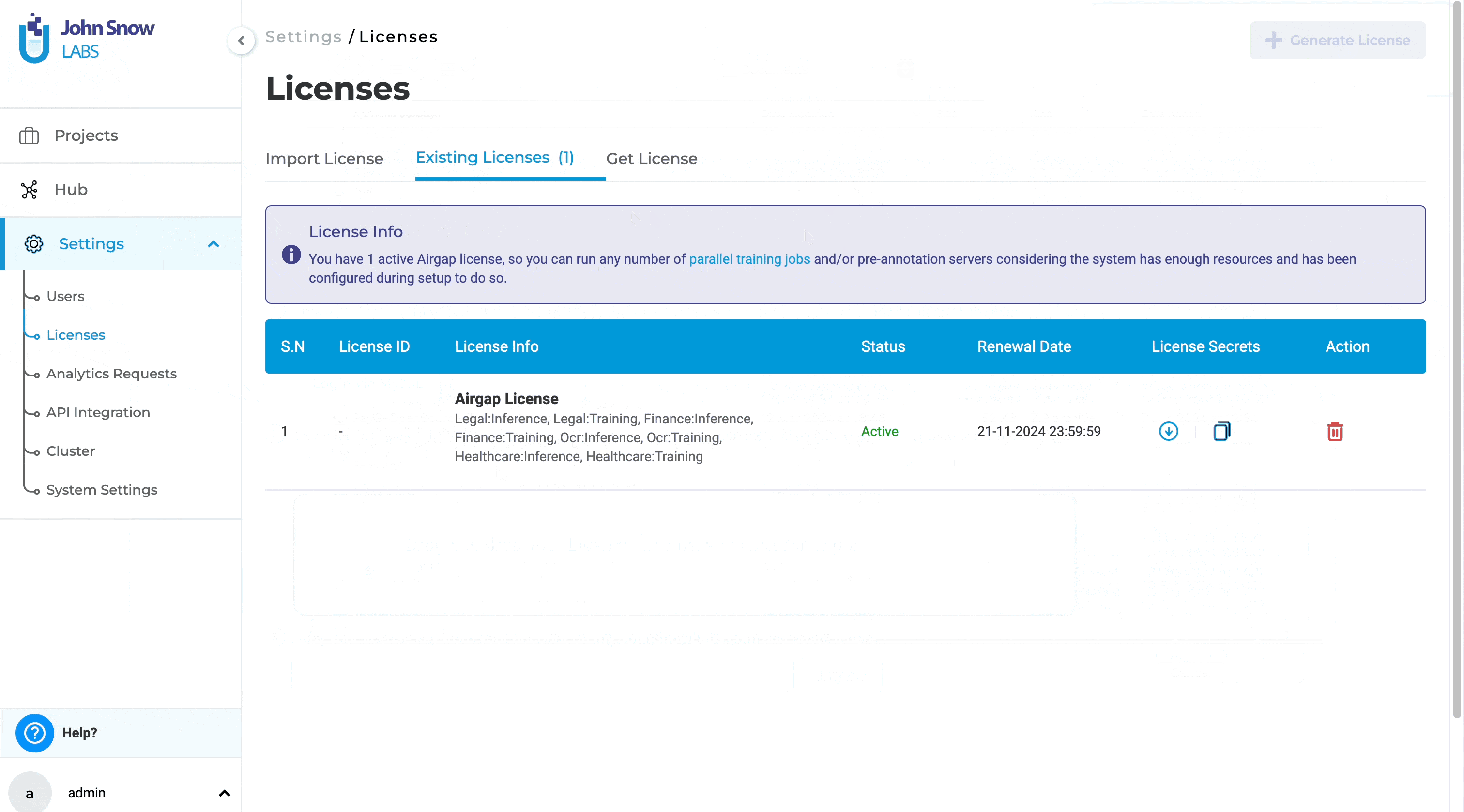
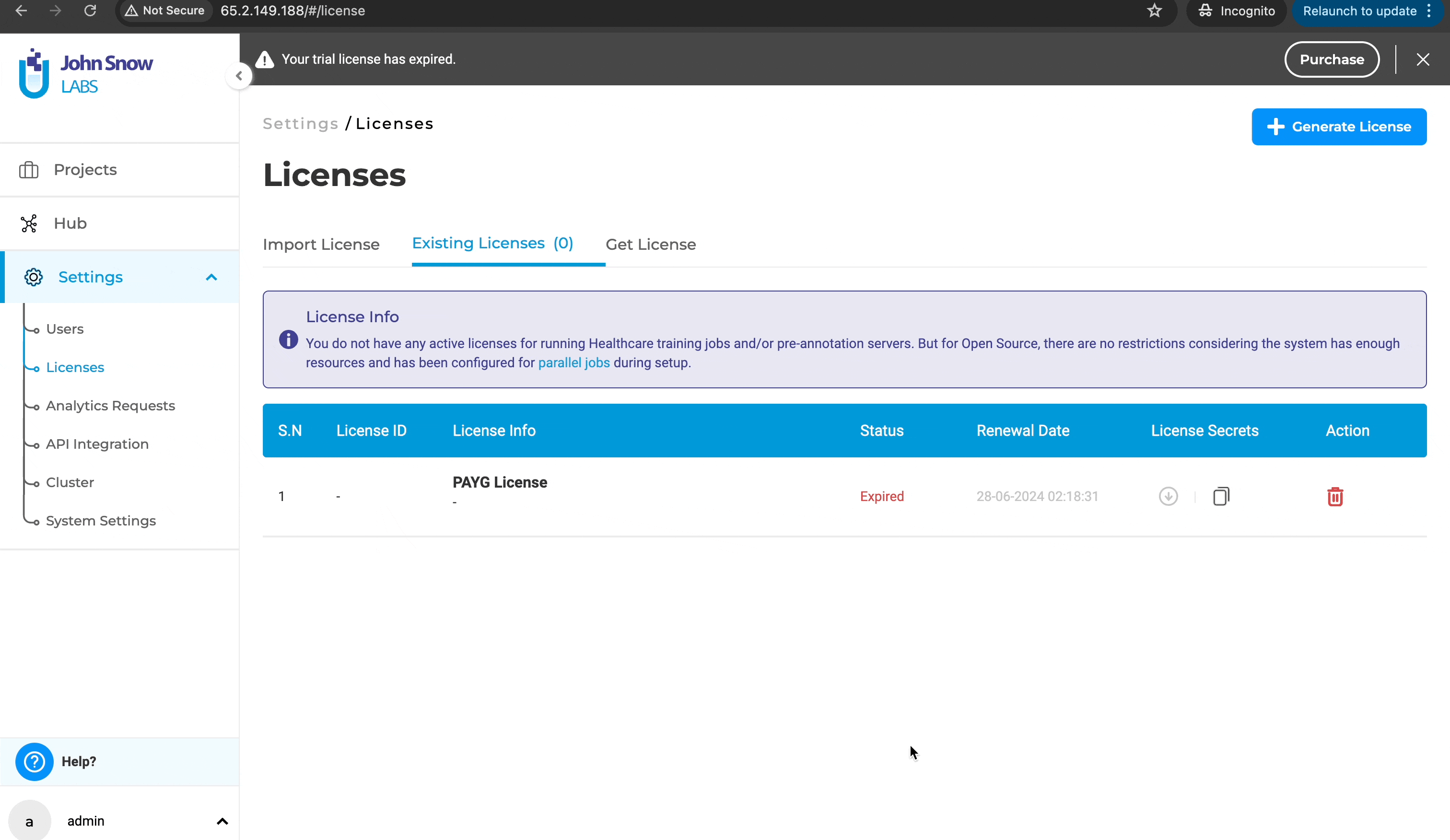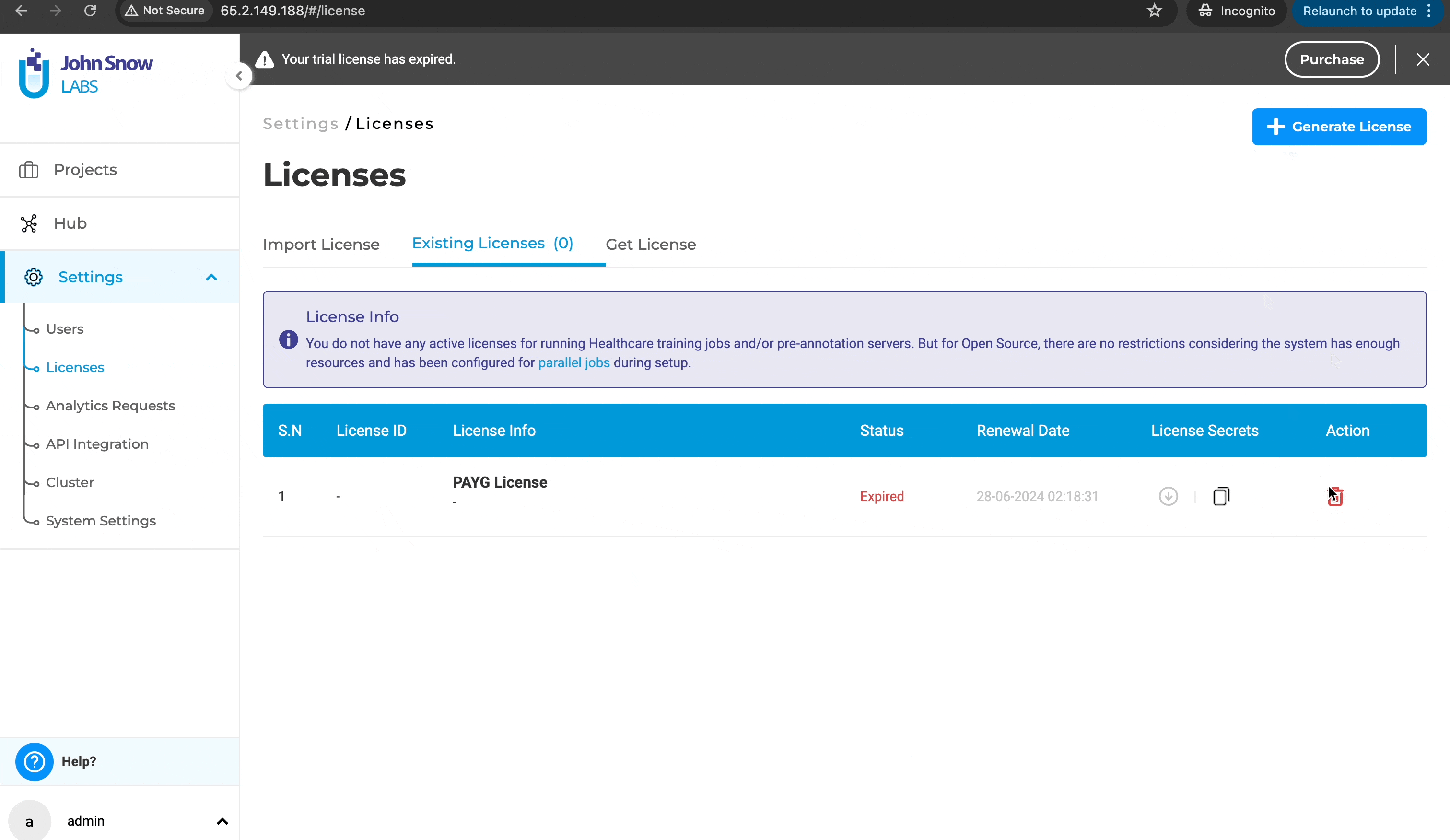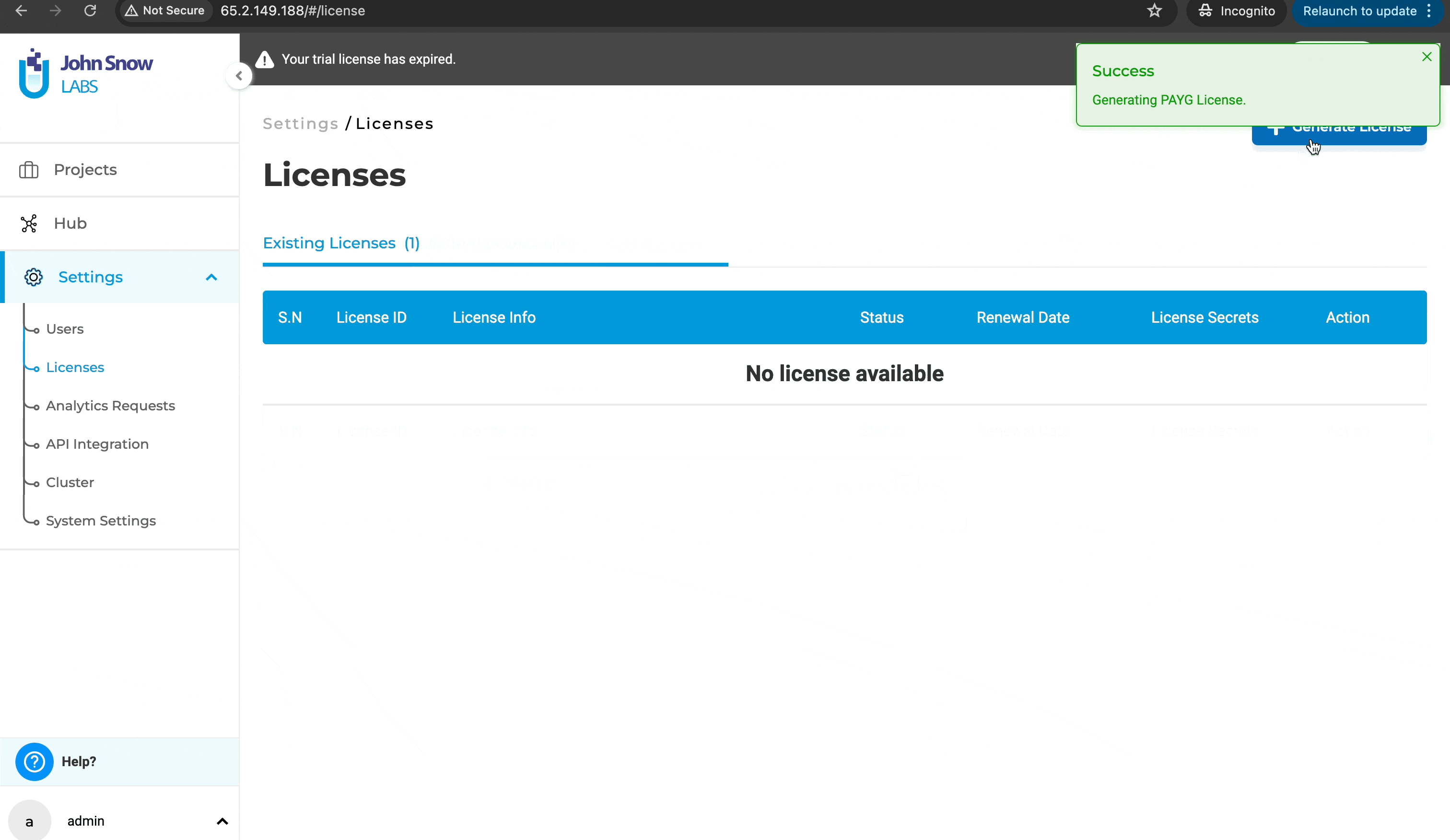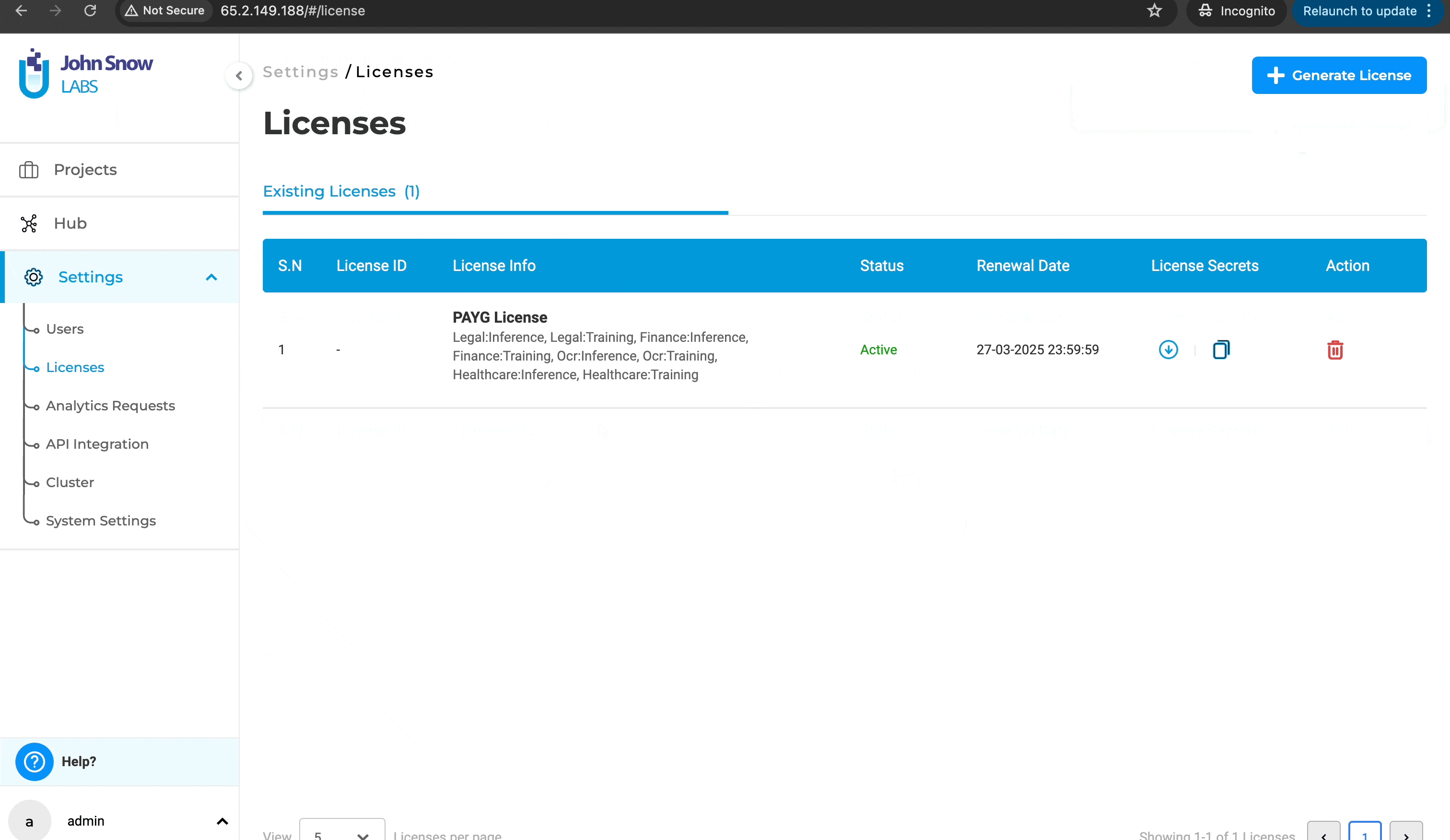
License page crash on empty license file loading
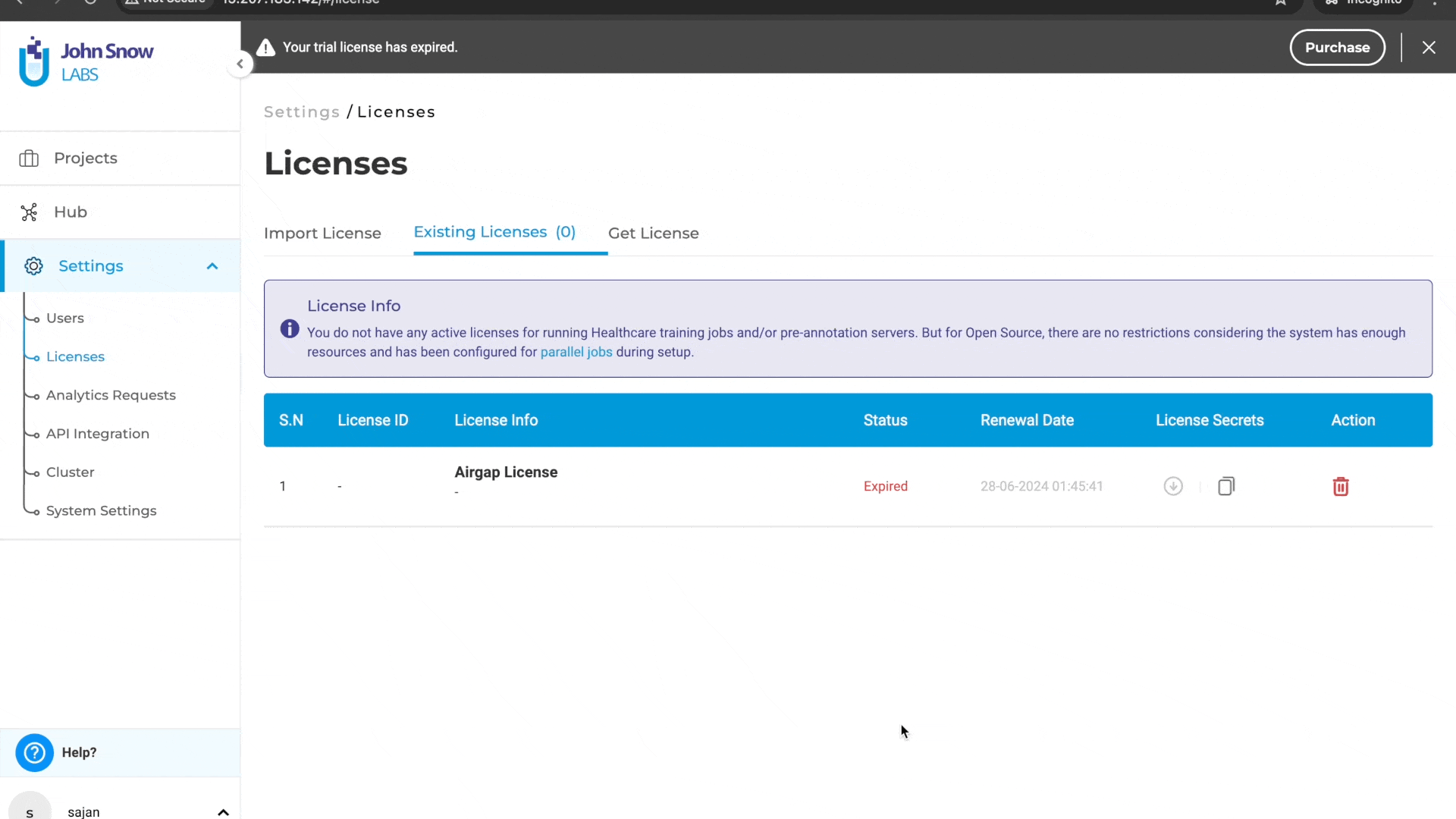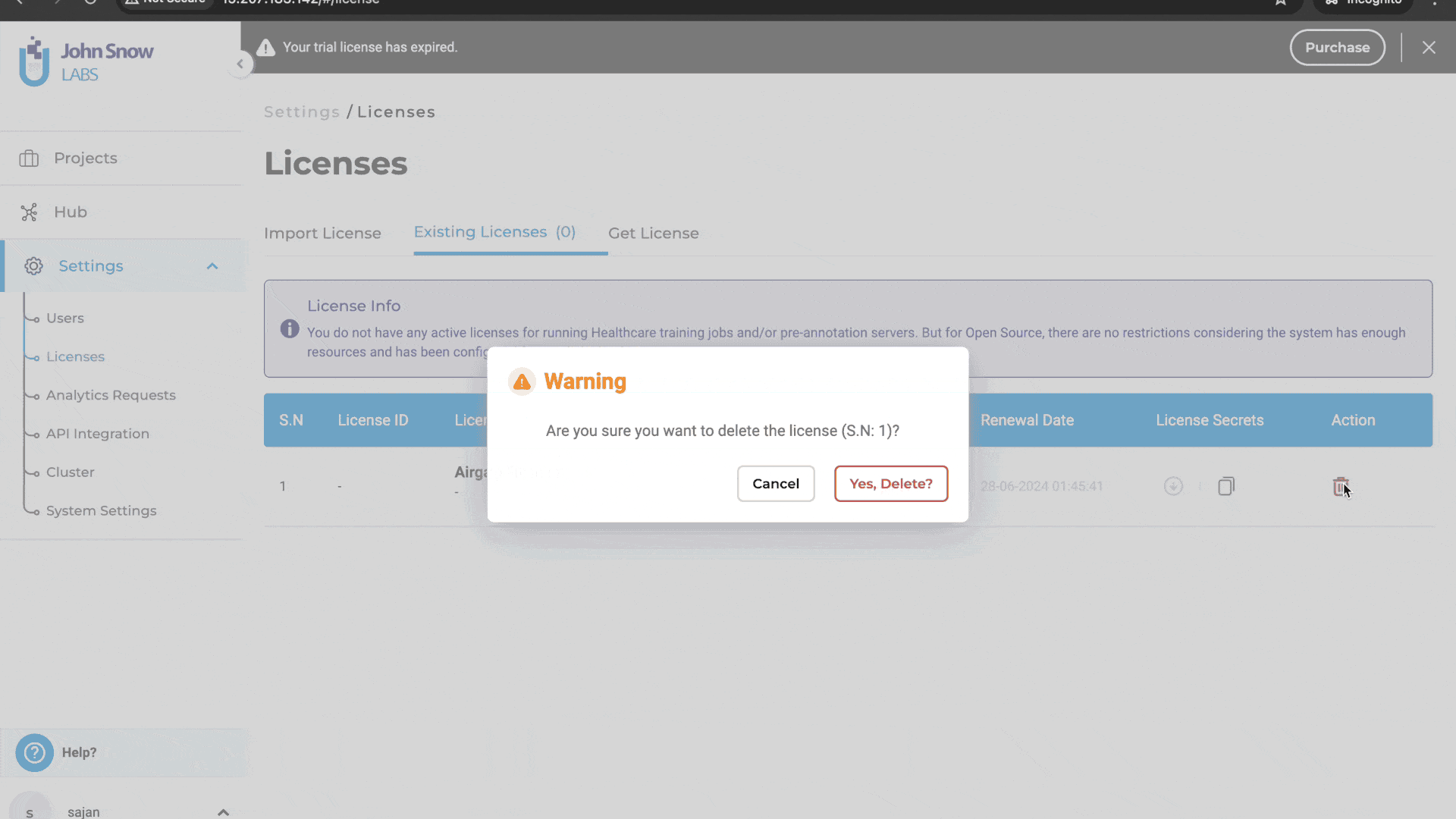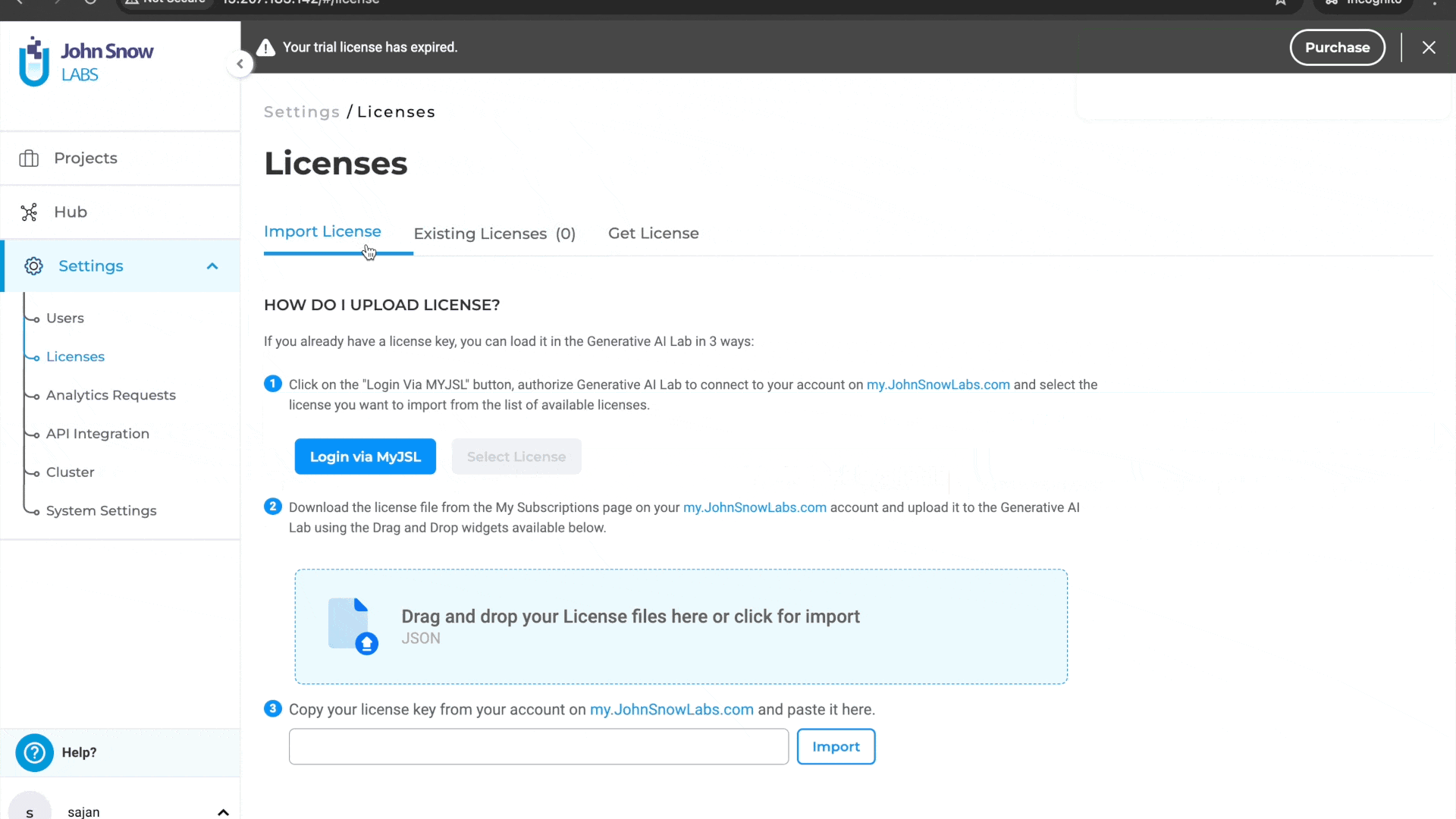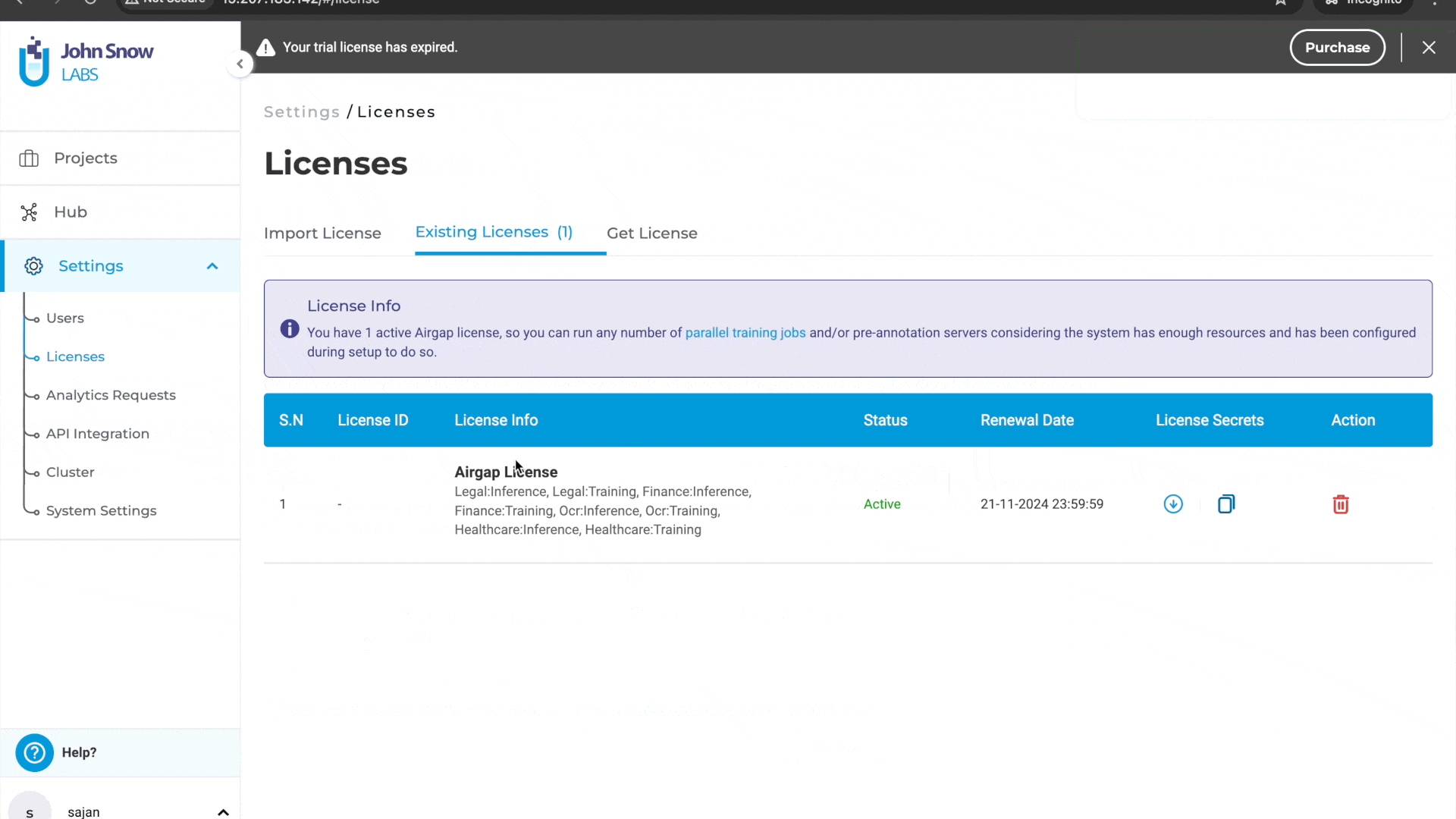
Previously, users were unable to access the license page to delete an existing license or add a new one if the license key was empty. This limitation hindered users from managing licenses effectively when dealing with empty license keys. With this improvement, users can now delete licenses with empty license keys and add or generate new licenses as needed. This enhancement provides greater flexibility and control over license management, ensuring a smoother and more efficient workflow.
Delete and add new licenses:
Delete and generate a new license:
Bug Fixes
-
Entries of failed training are skipped in History View
Previously, the Training and Active Learning History Tab only displayed successful training sessions. If the latest training failed, it was shown on the Train page, but there was no way to know the exact number of failed training sessions. This issue has now been fixed, and users can see the history of both failed and successful training logs.
-
User needs to click the “Apply Filter” twice to apply the selected filter
Previously, users had to click “Apply Filter” twice to apply the selected filter, and the options would collapse after each click. Now, the filter is applied with a single click, and the filter options remain expanded.
-
Edit count in Visual NER project is inconsistent(temporarily) and Pagination is not working for multipage tasks while comparing completions
Previously, the edit count number was random when the compare completion button was pressed. Additionally, navigating to different pages during comparison displayed a single completion instead of the comparison between completions. Now, the pagination works as expected for multi-page tasks while comparing completions.
-
Labels are still shown after deleting tasks(sample task) with meta and adding another sample task
Previously, labels were still shown after deleting tasks (sample tasks) with metadata and adding another sample task. This issue has now been resolved, and the labels no longer appear in newly added tasks.
-
Zoomed images cannot be moved around in Visual NER project
Previously, zoomed images could not be moved around in Visual NER projects as the move function was not working as expected. This issue has now been resolved, and the move function can be used in Visual NER tasks without any problems.
-
Consecutive texts that should be predicted as different tokens are merged as one in Visual NER project
Consecutive texts that should be predicted as different tokens were previously merged into one in Visual NER projects. This issue has now been resolved, and consecutive tokens with the same labels are no longer merged.
-
Cronjob for backup created without validation and backup page doesn’t auto refresh
Previously, the cron job for backups was created without validation, and the backup page did not auto-refresh. This issue has been resolved. Users can now independently trigger an ad-hoc backup without needing to save the backup information.
-
When non-GPU instance type is used for GPU-enabled AMI, “GPU Resource Available” is seen on the Infrastructure page
Previously, if the instance type was changed from GPU to non-GPU, the “GPU Resource Available” message still appeared on the Infrastructure page, which could be confusing for users. Additionally, the GPU option was visible in the Visual NER project mode. This issue has been addressed. The system now actively monitors such changes and removes GPU features from the application as needed.
-
Internal server error when trying to export/import the project for RatePDF project type
Previously, there was an internal server error when trying to export or import projects for the RatePDF project type. This issue has now been resolved, allowing users to export and import tasks without any problems. Additionally, tasks are now accessible for both CustomXML and regular RatePDF project types.
-
External Service Provider cannot be integrated when character count exceeds 128
External Service Provider integration was previously not possible when the URL character count exceeded 128. Now, integration with external service providers is possible even when the URL character count exceeds 128.
-
Editing Non-Editable Generated Test Cases Causes Repeated Error Popup Until UI Refresh
Previously, when users edited generated test cases, such as accuracy tests that didn’t require text modifications, a constant popup would appear. Now, editing non-editable generated test cases no longer triggers repeated error popups.
Versions
- 7.7
- 7.6.0
- 7.5.1
- 7.5.0
- 7.4.0
- 7.3.1
- 7.3.0
- 7.2.2
- 7.2.2
- 7.2.0
- 7.1.0
- 7.0.1
- 7.0.0
- 6.11.3
- 6.11.2
- 6.11.1
- 6.11.0
- 6.10.1
- 6.10.0
- 6.9.1
- 6.9.0
- 6.8.1
- 6.8.0
- 6.7.2
- 6.7.0
- 6.6.0
- 6.5.1
- 6.5.0
- 6.4.1
- 6.4.0
- 6.3.2
- 6.3.0
- 6.2.1
- 6.2.0
- 6.1.2
- 6.1.1
- 6.1.0
- 6.0.2
- 6.0.0
- 5.9.3
- 5.9.2
- 5.9.1
- 5.9.0
- 5.8.1
- 5.8.0
- 5.7.1
- 5.7.0
- 5.6.2
- 5.6.1
- 5.6.0
- 5.5.3
- 5.5.2
- 5.5.1
- 5.5.0
- 5.4.1
- 5.3.2
- 5.2.3
- 5.2.2
- 5.1.1
- 5.1.0