Pre-Annotation Overview
Generative AI Lab offers out-of-the-box support for
These features are highly effective for bootstrapping new annotation projects, allowing teams to begin with model-generated labels instead of starting from scratch. By leveraging pre-trained or domain-specific models, users can transfer expert knowledge directly into the annotation process—significantly reducing manual effort and improving consistency.
To run pre-annotation on one or several tasks, a
A dialog will appear displaying information about the currently deployed model servers, including the list of models available and the labels each model predicts.
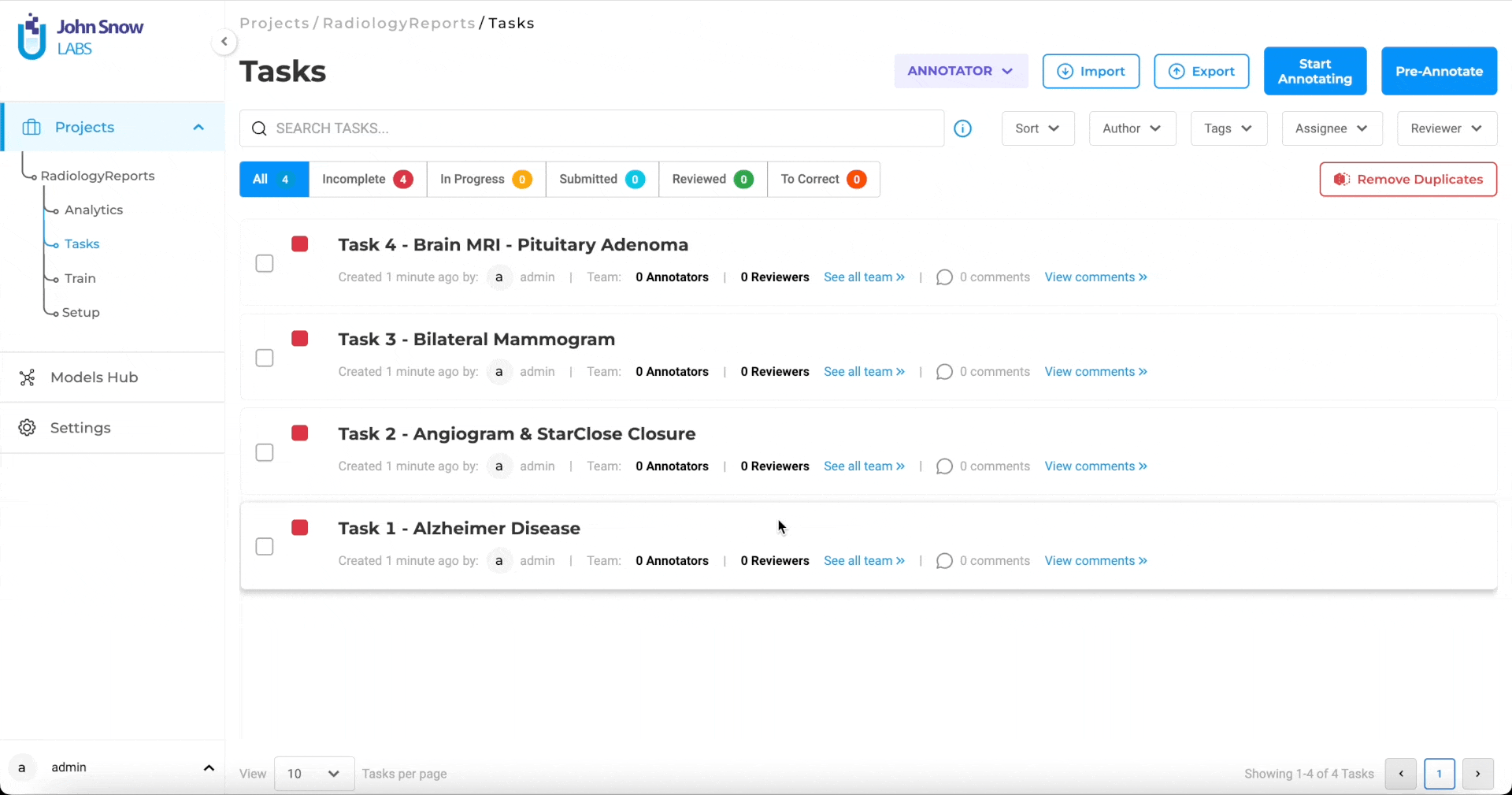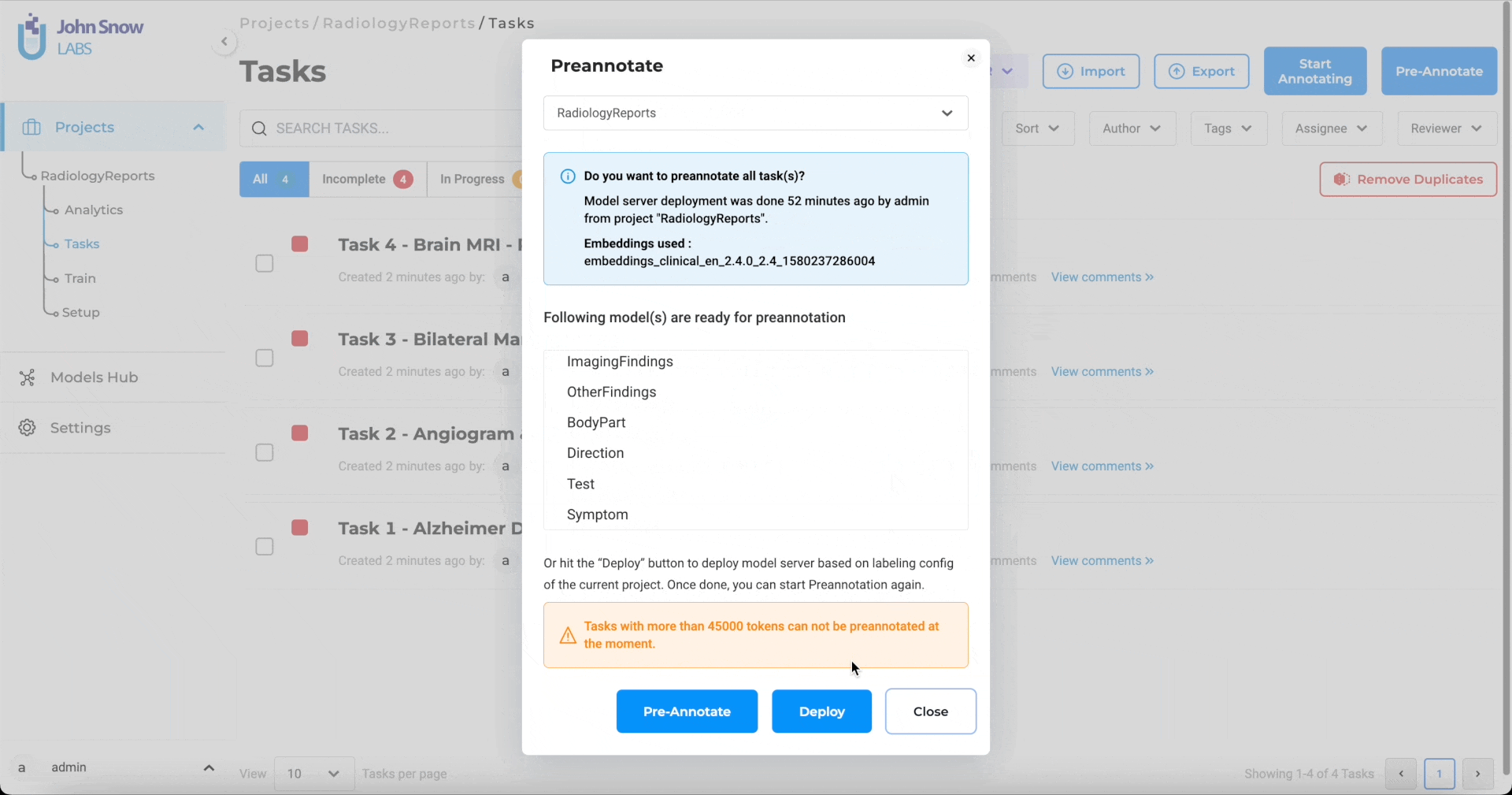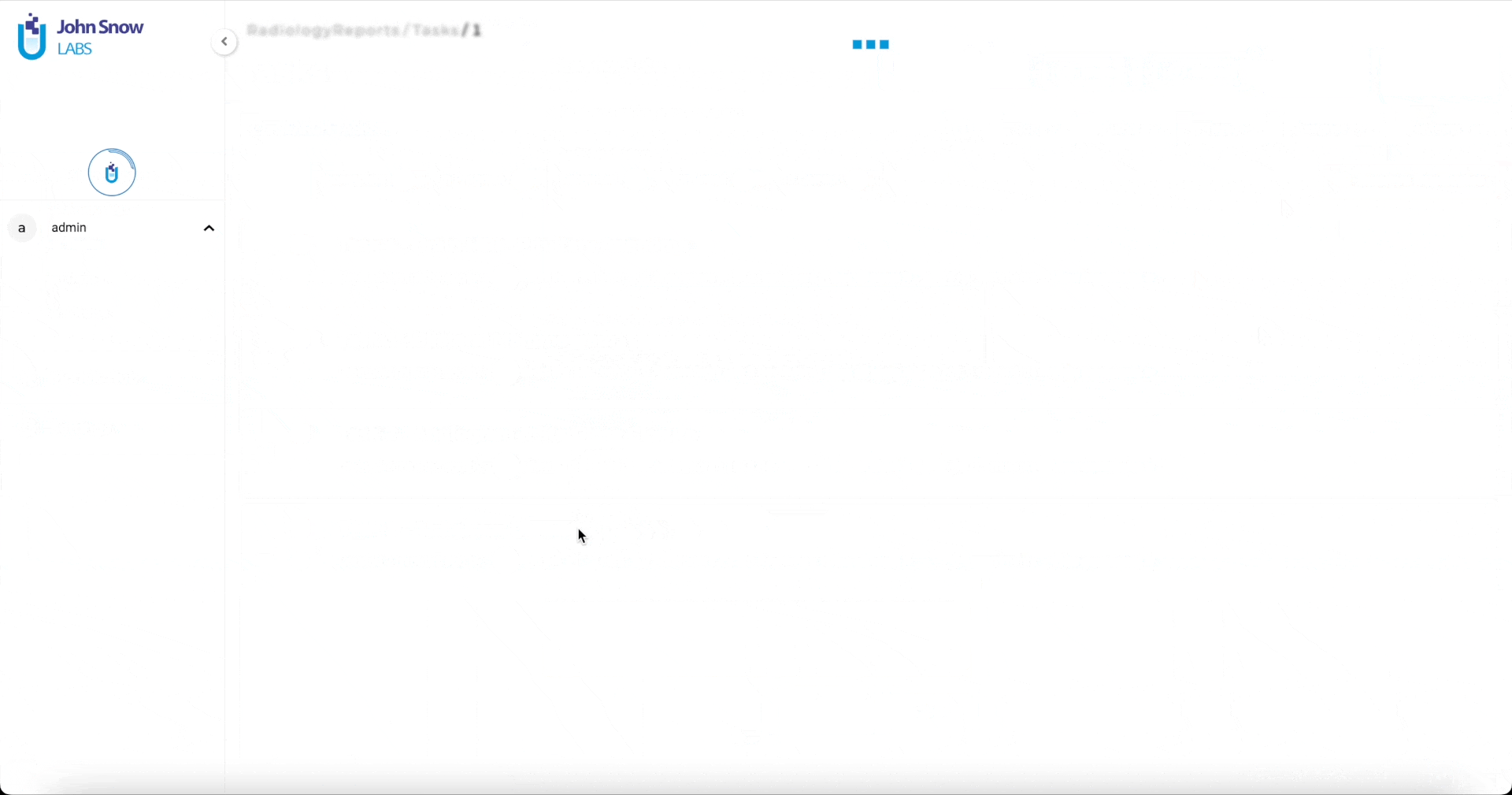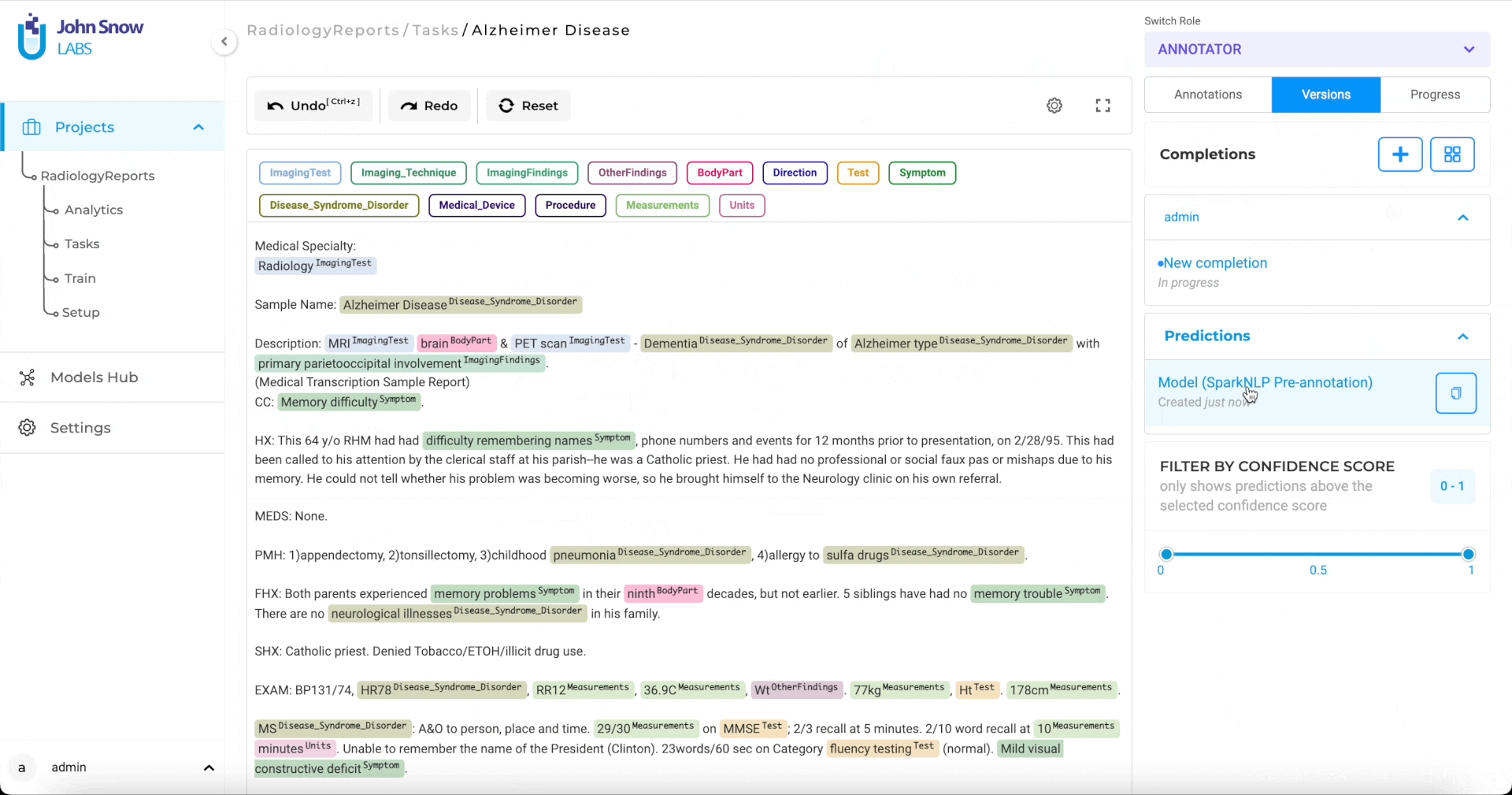
This information is important, especially when multiple users are training and deploying models simultaneously. Always review the list of deployed models and their corresponding labels before starting pre-annotation to ensure alignment with your project configuration.
If needed, users can deploy models defined in the current project (based on its Labeling Config) by clicking Deploy. Once deployment completes, pre-annotation can be triggered immediately.
Selecting Pre-Annotation Servers
Generative AI Lab supports multiple pre-annotation servers, enabling parallel annotation across different projects or configurations.
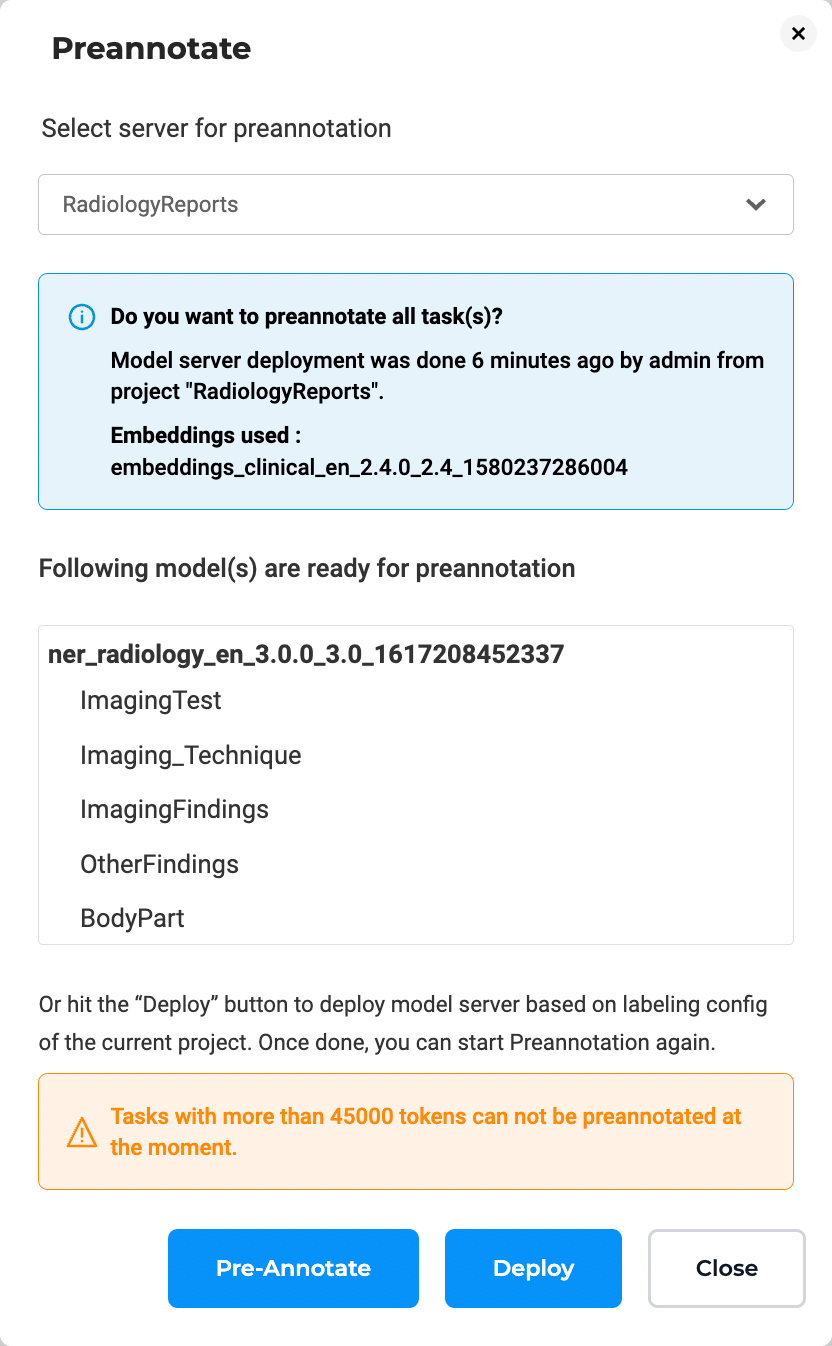
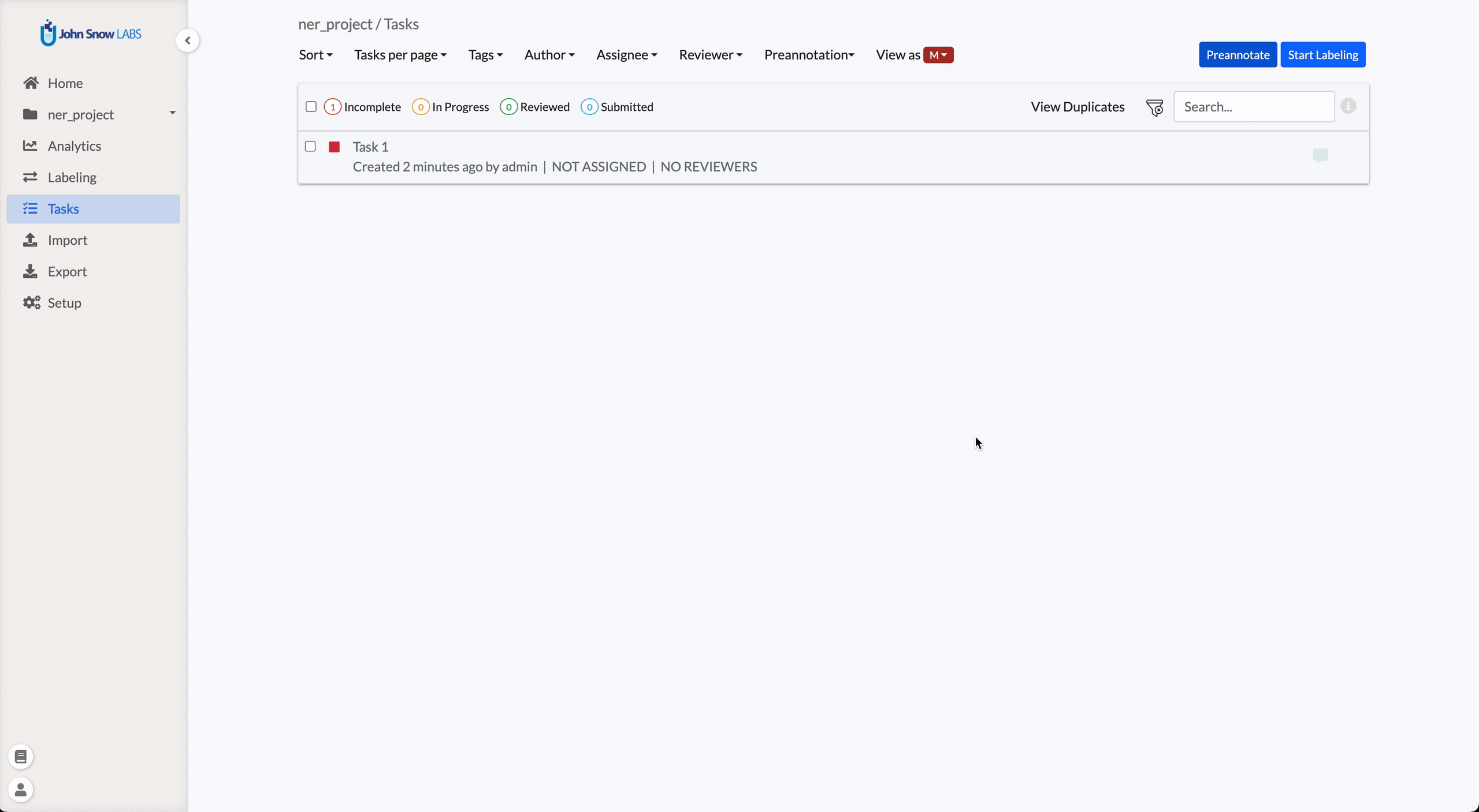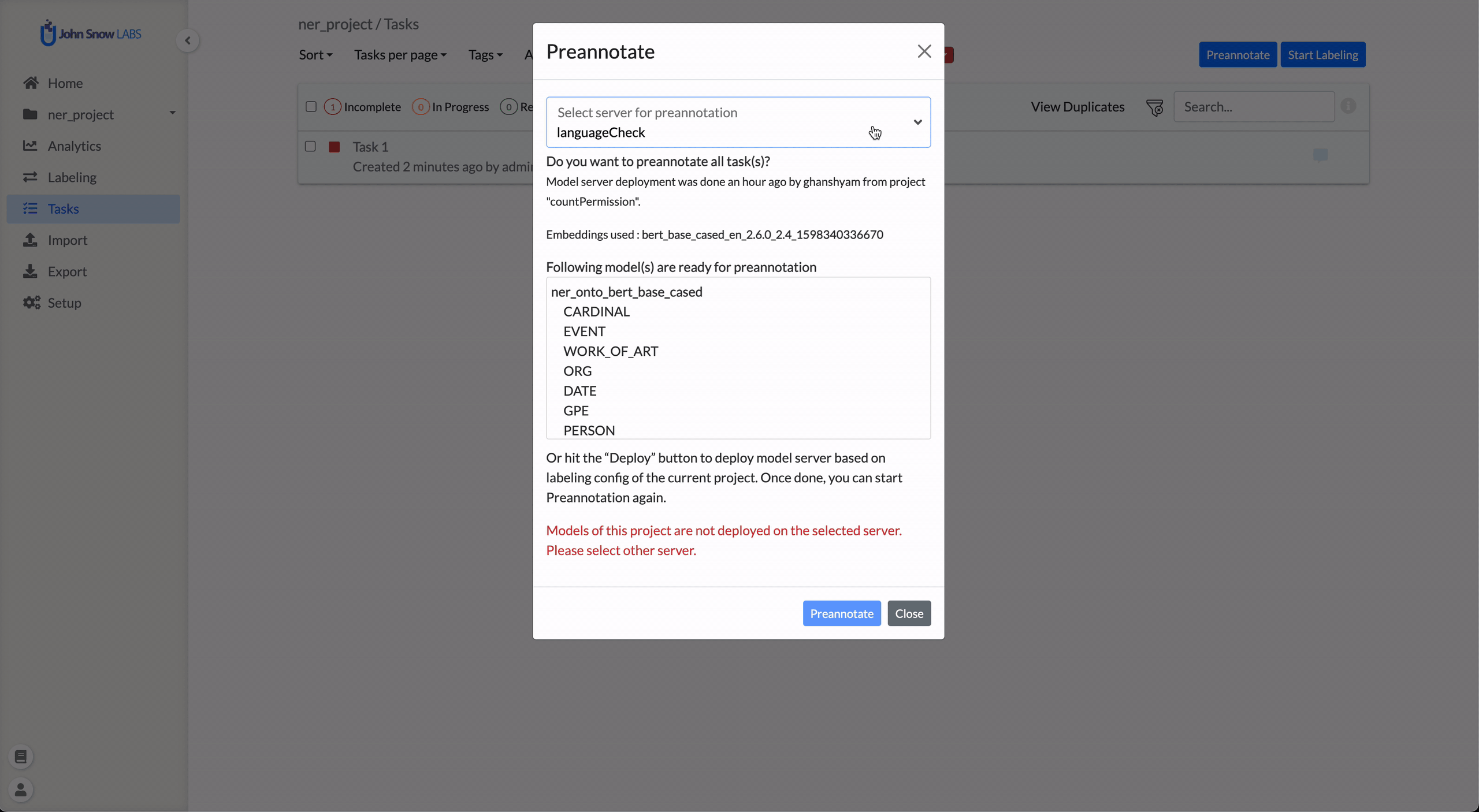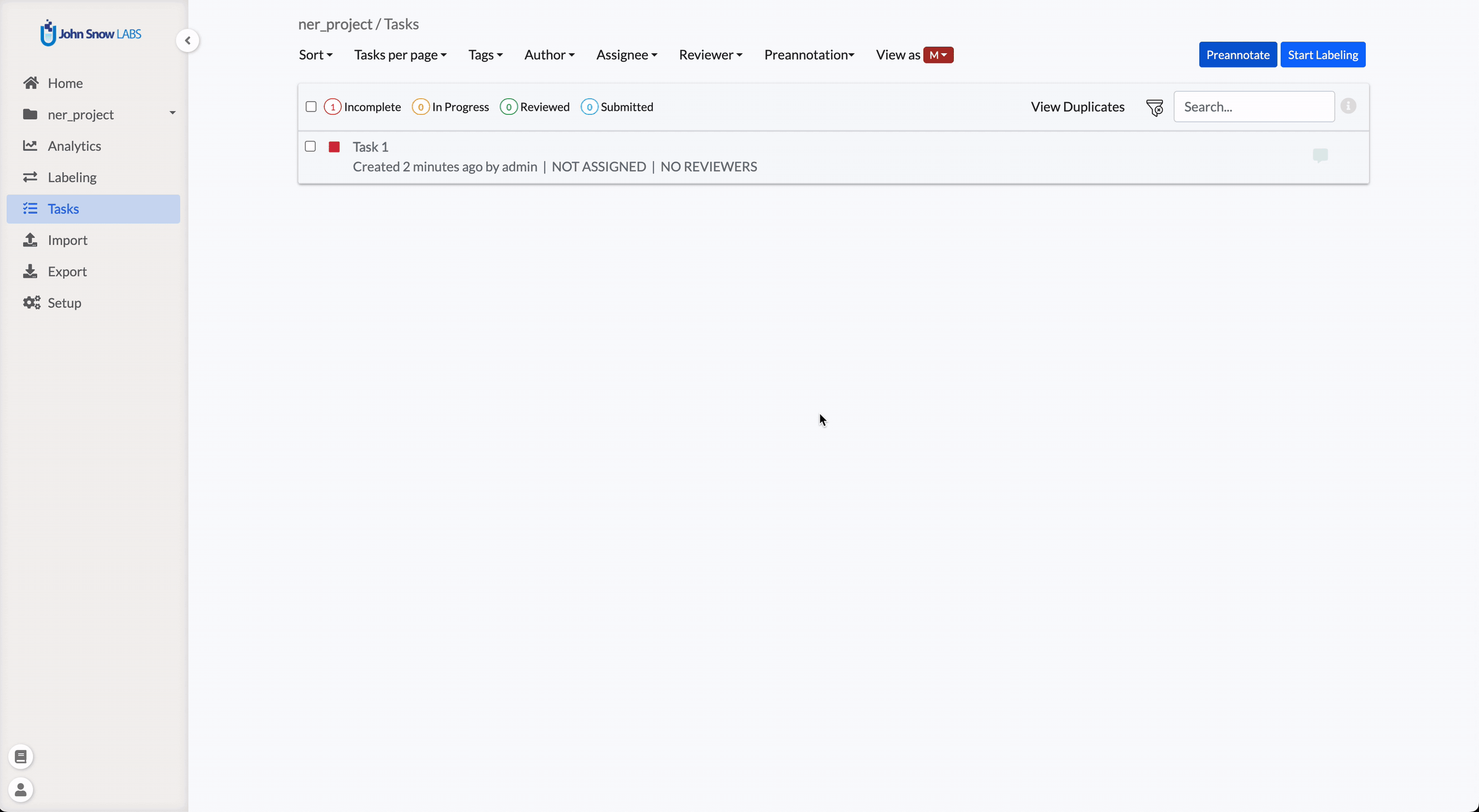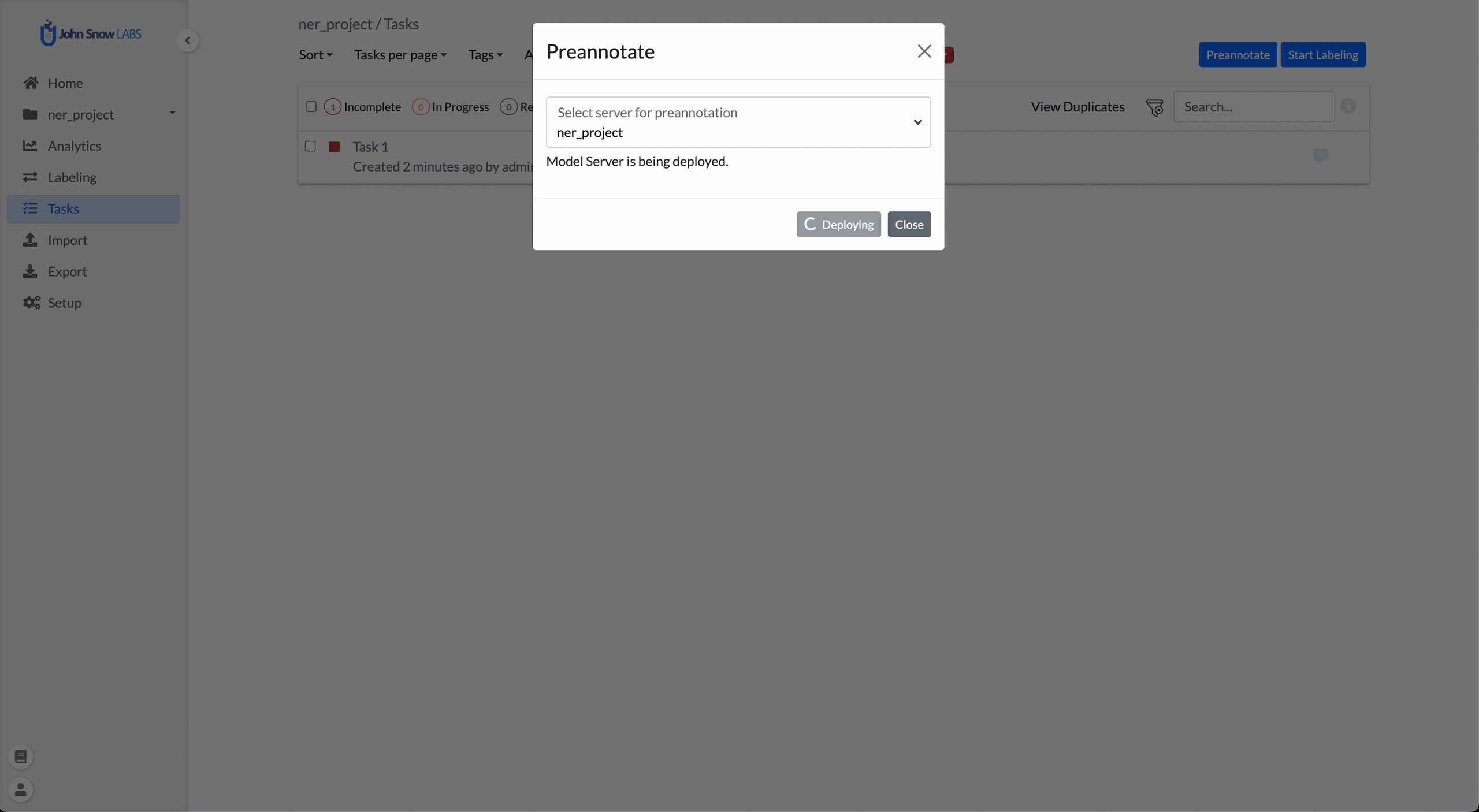
When clicking Pre-Annotate, the dialog lists all available servers.
If no pre-annotation server currently exists for the project, the dialog provides an option to deploy a new server using the active labeling configuration.
If sufficient resources and licensing are available, the deployment begins automatically and pre-annotation starts once the server is ready.
If resources are unavailable, users can delete older or idle servers from the Clusters page under Settings to free capacity.
Concurrent Processing
Generative AI Lab fully supports concurrent pre-annotation and training operations.
Multiple pre-annotation servers can run simultaneously, and training can occur on one project while pre-annotation runs on another.
This enables continuous productivity and optimal use of resources across multiple active projects.
Pre-annotation Approaches
Pretrained Models
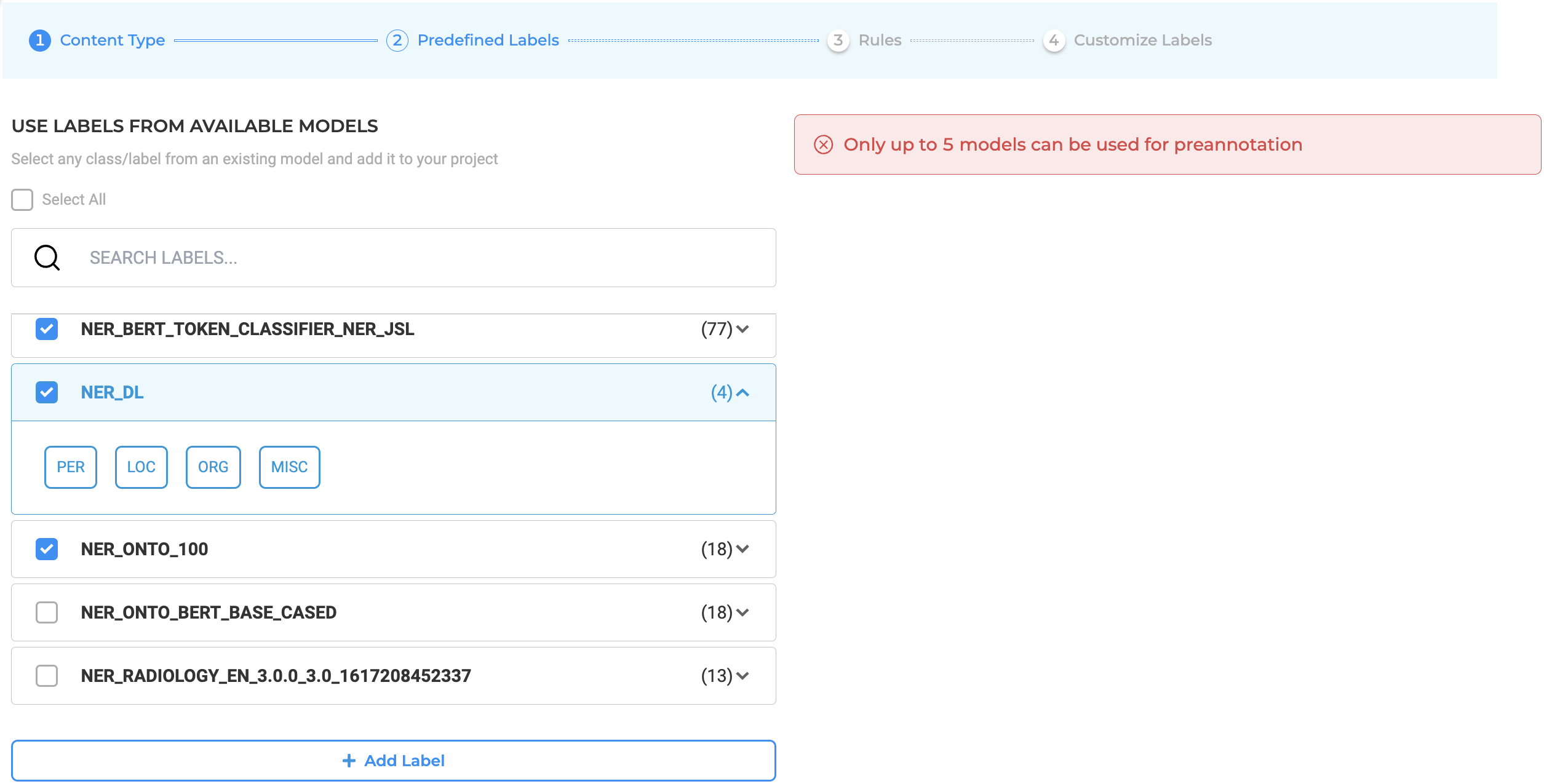
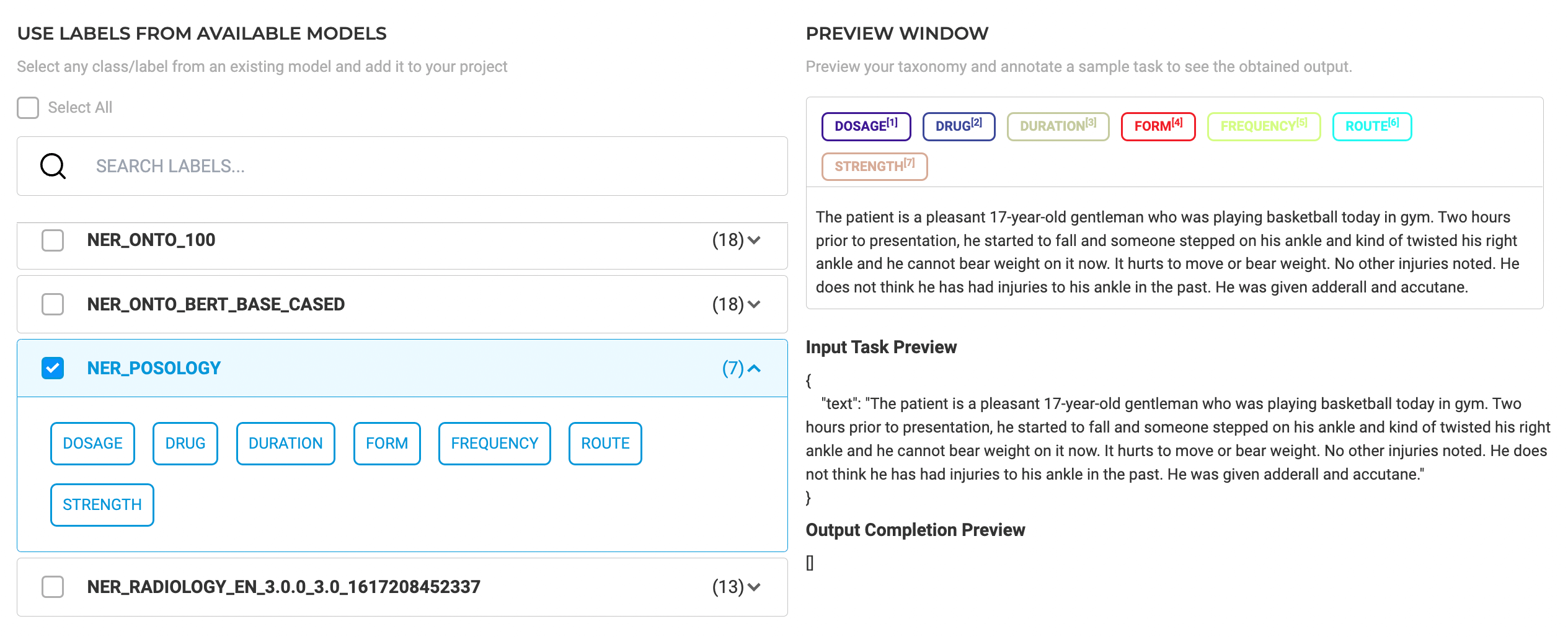
On the Add Label button you can add the predefined labels to your project configuration and take advantage of the Spark NLP auto labeling capabilities.
In the example below, we are reusing the ner_posology model that comes with 7 labels related to drugs.
In the same way,
This allows teams to automate label generation for a wide variety of task types, not just NER, ensuring a consistent and efficient workflow across multiple annotation domains.
Finance, Legal, and Visual models downloaded from the Models Hub can be used directly for pre-annotation of NER, classification, or assertion projects.
Visual NER models, in particular, support pre-annotating text extracted from image-based or scanned documents, enabling end-to-end annotation of complex data types.
Once a model is downloaded from the Models Hub page, its associated labels become available under the Predefined Labels tab in the project configuration.
From there, you can review and customize the labels or link them with additional rules and prompts before triggering pre-annotation.


Text Pre-annotation
Pre-annotation is available for projects with text contents as the tasks. When you setup a project to use existing Spark NLP models for pre-annotation, you can run the designated models on all of your tasks by pressing the Pre-Annotate button on the top-right corner of the
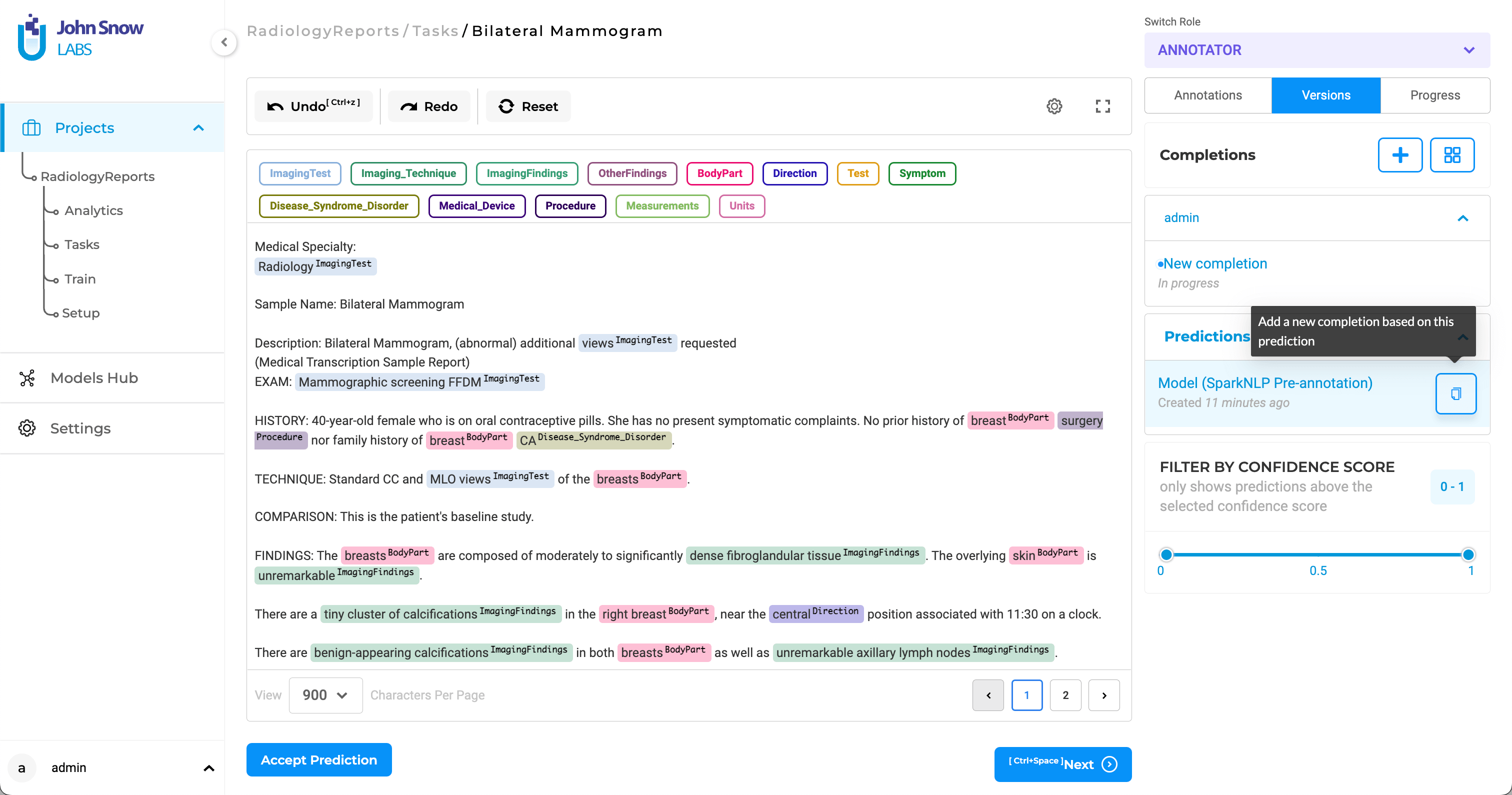

As a result, all predicted labels for a given task will be available in the
Re-purpose Text-Based NER Models for PDF and Image Projects
Generative AI Lab allows you to leverage the extensive library of pre-trained text-based NER models — including more than 6,600 models available on the Models Hub — for pre-annotation of PDF and image-based tasks.
This capability bridges the gap between text and visual document processing, enabling you to apply domain-specific NER models directly to scanned or image-based content that includes extracted OCR text.
With this functionality, you can:
- Jumpstart Visual Data Preparation: Quickly begin preparing training data for Visual NER projects without starting from scratch, reducing manual labeling time and effort.
- Leverage Domain Expertise: Use existing, domain-specialized NER models (such as Healthcare, Finance, or Legal) to accurately identify entities in PDFs and images — even when those models were originally built for plain text.
- Streamline Workflows: Skip the need to train new Visual NER models for common entity types when suitable pre-trained text models are already available. Simply select and attach the relevant model(s) from the Models Hub, and they will integrate seamlessly into your Visual NER project configuration.
This reusability makes the pre-annotation process more efficient and ensures consistency between text-based and image-based workflows across projects.
Effortlessly Pre-annotate PDF or Image Documents with NER Models
Configuring your Visual NER project to use text-specific NER models for pre-annotation is a breeze:
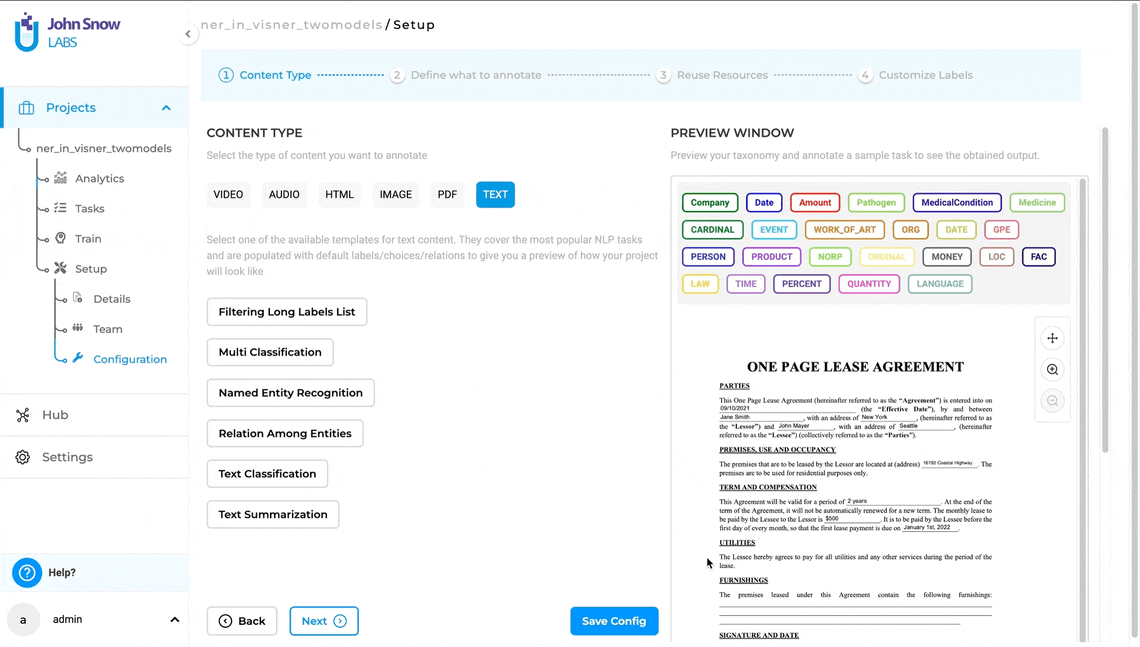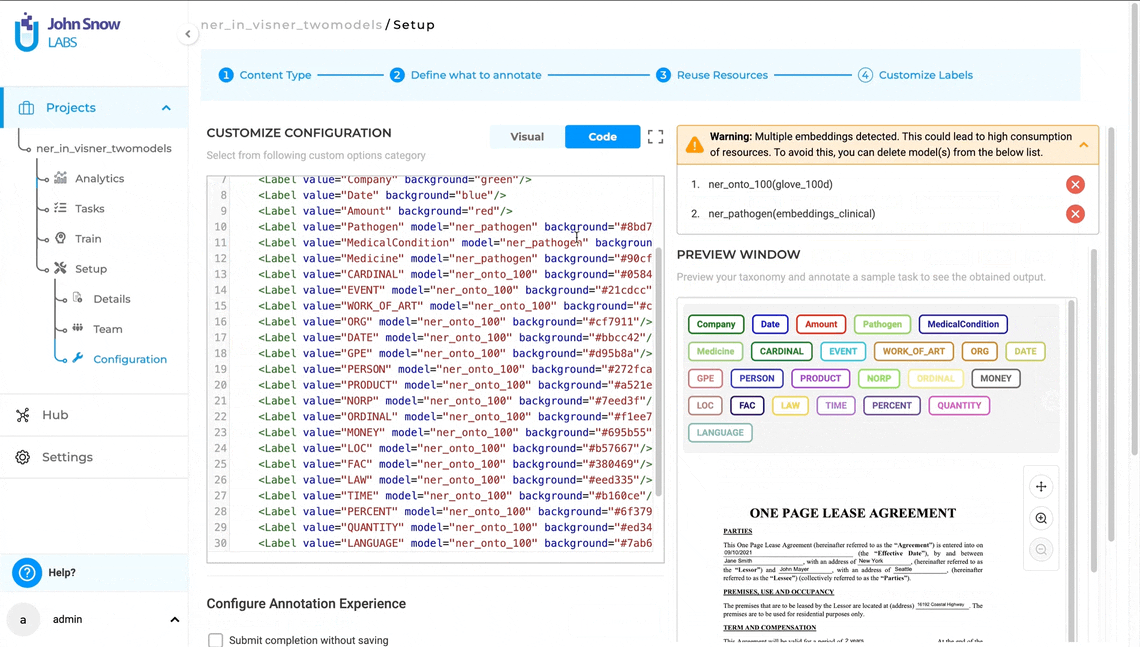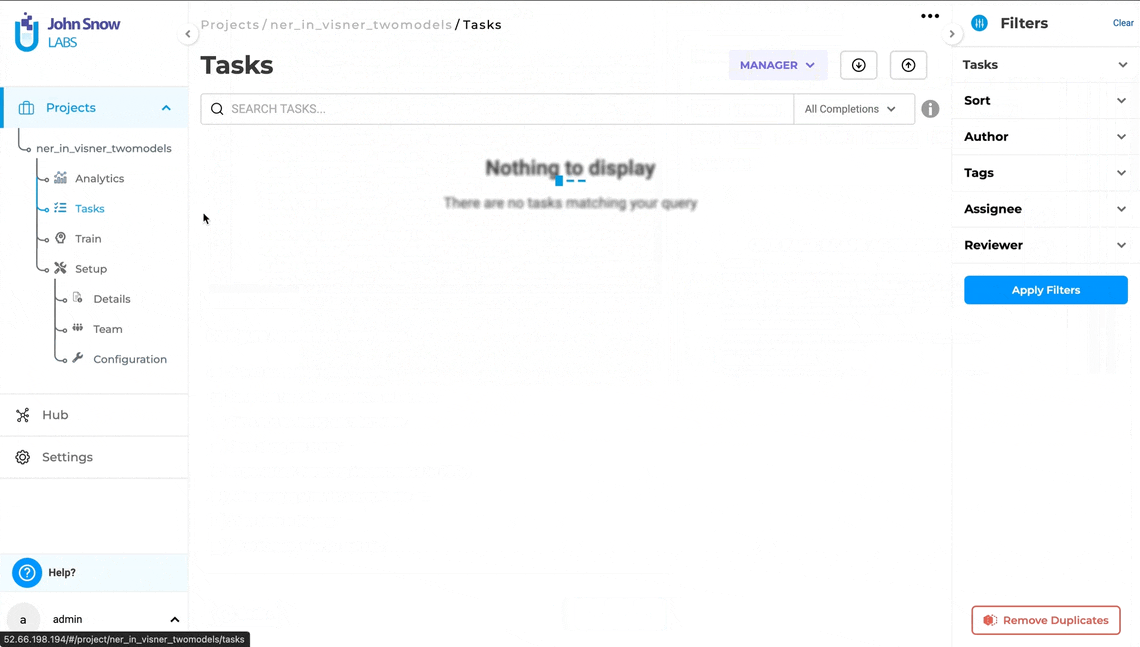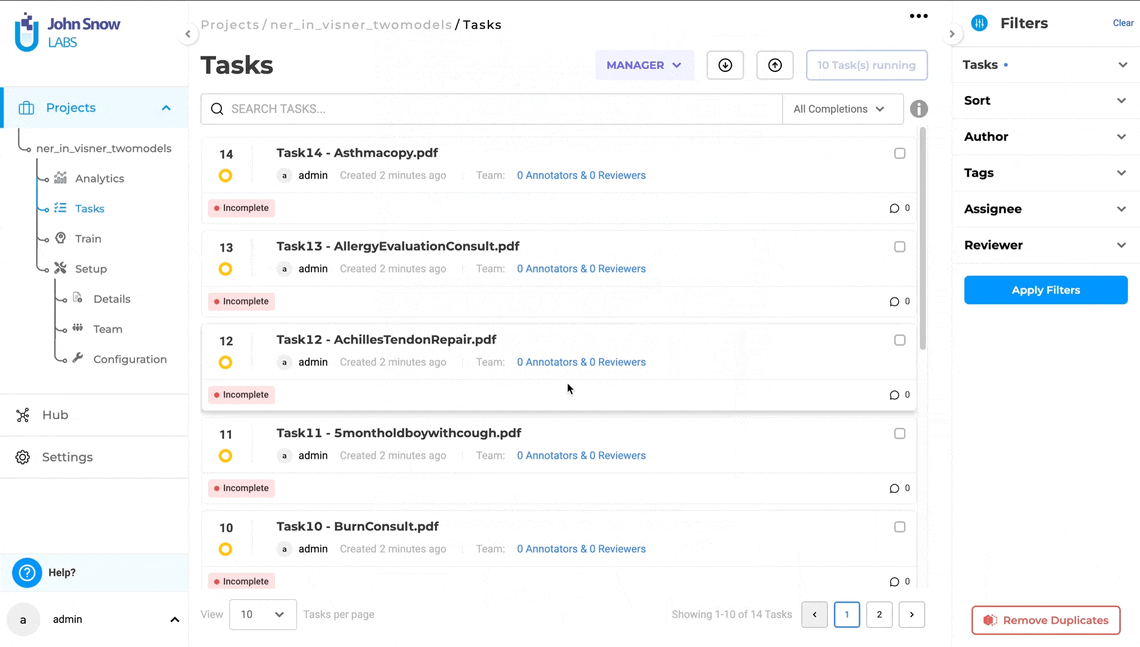
- Project Configuration: Begin by creating a new project and selecting the Visual NER Template during configuration. This sets the stage for seamless integration of NER models into your project.
- NER Model Selection: From the Re-use Resource page, navigate through the vast library of NER models and choose the one that best suits your project’s requirements. Once selected, save the project configuration to apply the chosen model.
- OCR Document Import: Import the OCR documents containing the data you wish to pre-annotate. These documents can be in PDF or image format, catering to a wide range of document types.
- Pre-annotation Automation: Leverage the selected NER model to automatically pre-annotate the imported OCR documents. This eliminates the need for manual labor and significantly expedites the pre-annotation process.
- Accuracy Verification: After pre-annotation, meticulously review the automatically generated annotations to ensure accuracy and address any discrepancies.
This feature empowers users to seamlessly integrate NER models into their Visual NER projects, fostering greater flexibility and efficiency in document annotation workflows within Generative AI Lab. By leveraging the power of NER models, users can streamline pre-annotation processes, reduce training time, and achieve enhanced accuracy, ultimately accelerating their data preparation efforts.
Rules
Pre-annotation of NER projects can also be done using
In the example below, we are reusing the available rules for pre-annotation.
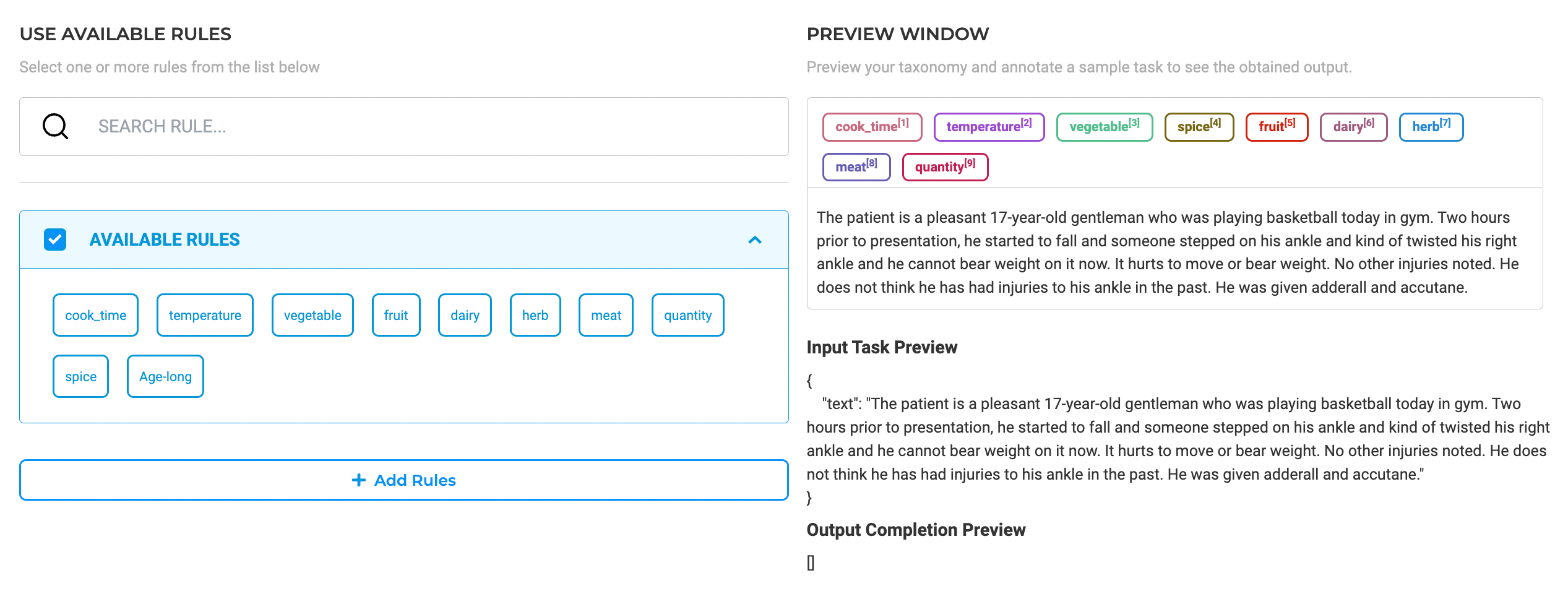

Read more on how to create rules and reuse them to speed up the annotation process here.
completion are now editable.
Visual Pre-annotation
For running pre-annotation on one or several tasks, the Pre-Annotate button from the upper right side of the

Known Limitations:
- When bulk pre-annotation runs on many tasks, the pre-annotation can fail due to memory issues.
- Pre-annotation currently works at the token level, and does not merge all tokens of a chunk into one entity.
Pre-Annotation Using Prompts in Visual NER Projects
Generative AI Lab supports zero-shot prompting for Visual NER projects, enabling pre-annotation of image and PDF documents through natural language instructions.
Previously available only for text-based projects, prompt-based pre-annotation now extends to visual tasks, allowing you to describe the entities you want identified directly in plain language.
For example, you can use a prompt like “Highlight all medication names and dosages in the document” to automatically generate labeled regions within OCR-extracted text or visual elements.
By leveraging prompts, users can:
- Expand Pre-Annotation Flexibility: Apply zero-shot entity extraction across both text and visual data without requiring a pre-trained model.
- Improve Annotation Efficiency: Automatically generate annotations for relevant entities, reducing manual labeling time.
- Ensure Consistency: Use standardized prompt definitions across projects to maintain uniform labeling logic between text, PDF, and image-based workflows.
This feature streamlines setup and increases coverage for projects that rely on Visual NER, enabling teams to combine model-based and prompt-based pre-annotation within the same environment.
Configure and Pre-annotate tasks using Prompts:
- Create a Visual NER Project
- Navigate to Reuse-Resource Page and add desired zero shot prompts (relation prompts and external prompts are not supported, currently)
- Once project configuration is saved, pre-annotate the tasks using the prompt.
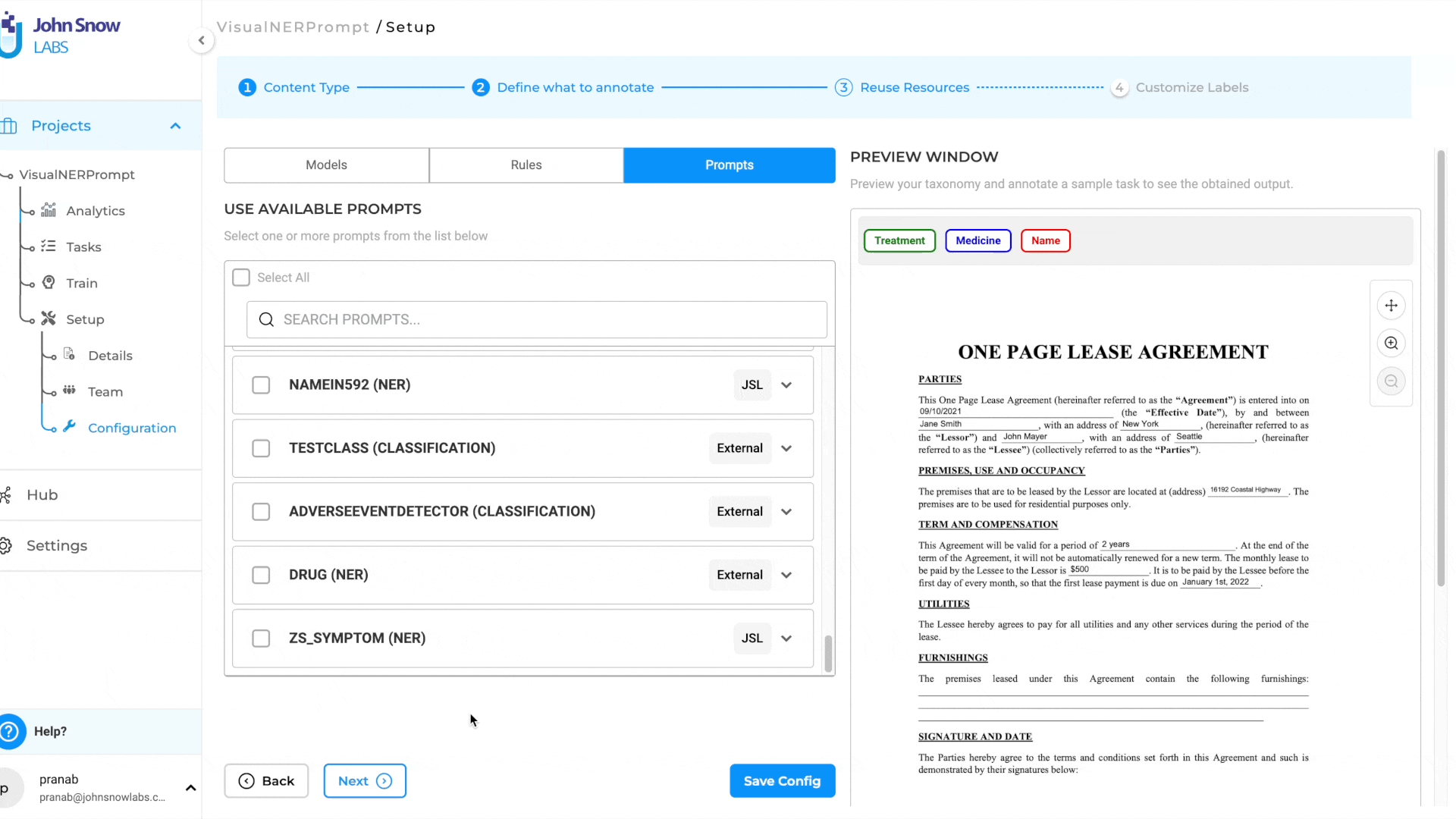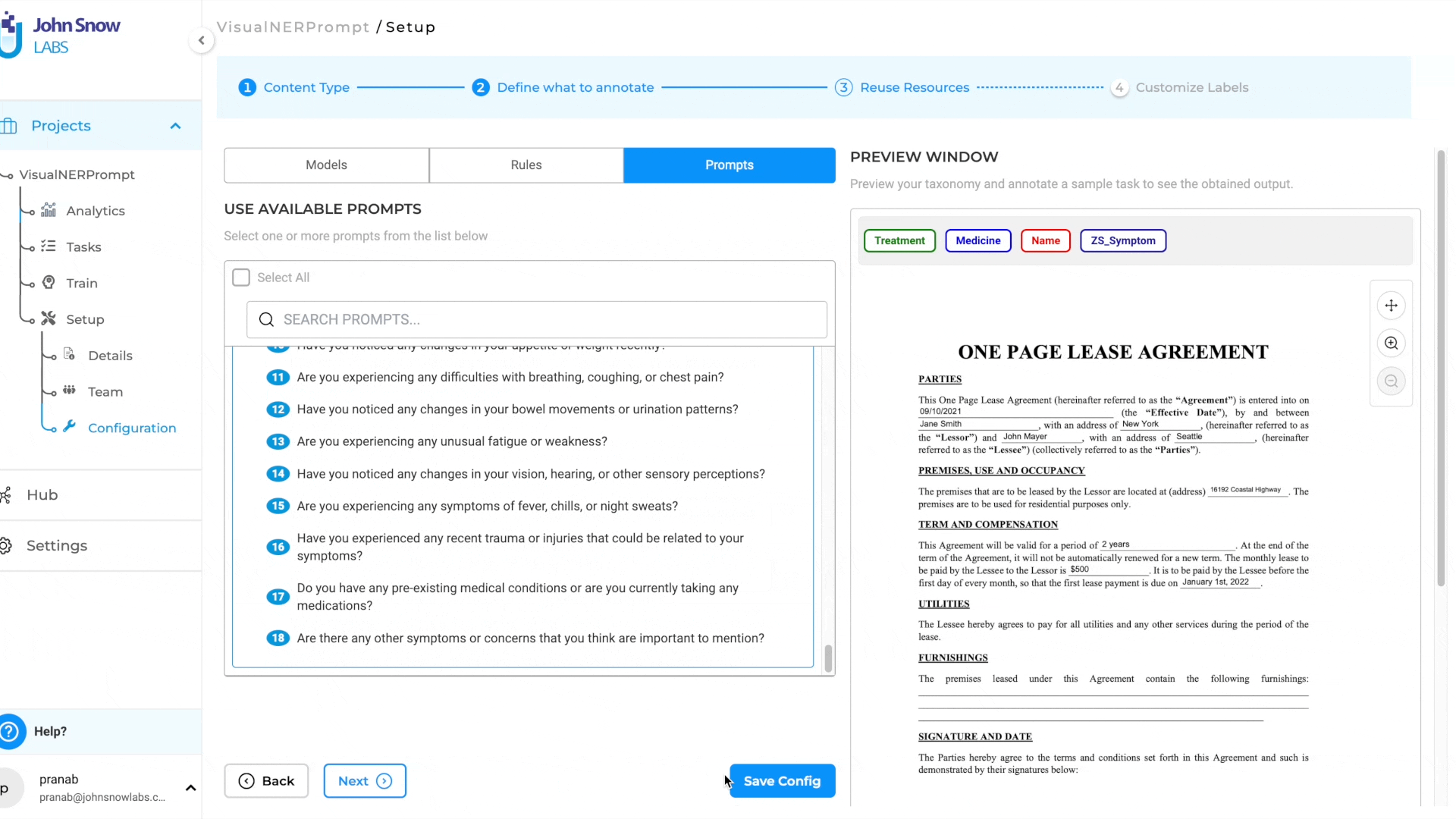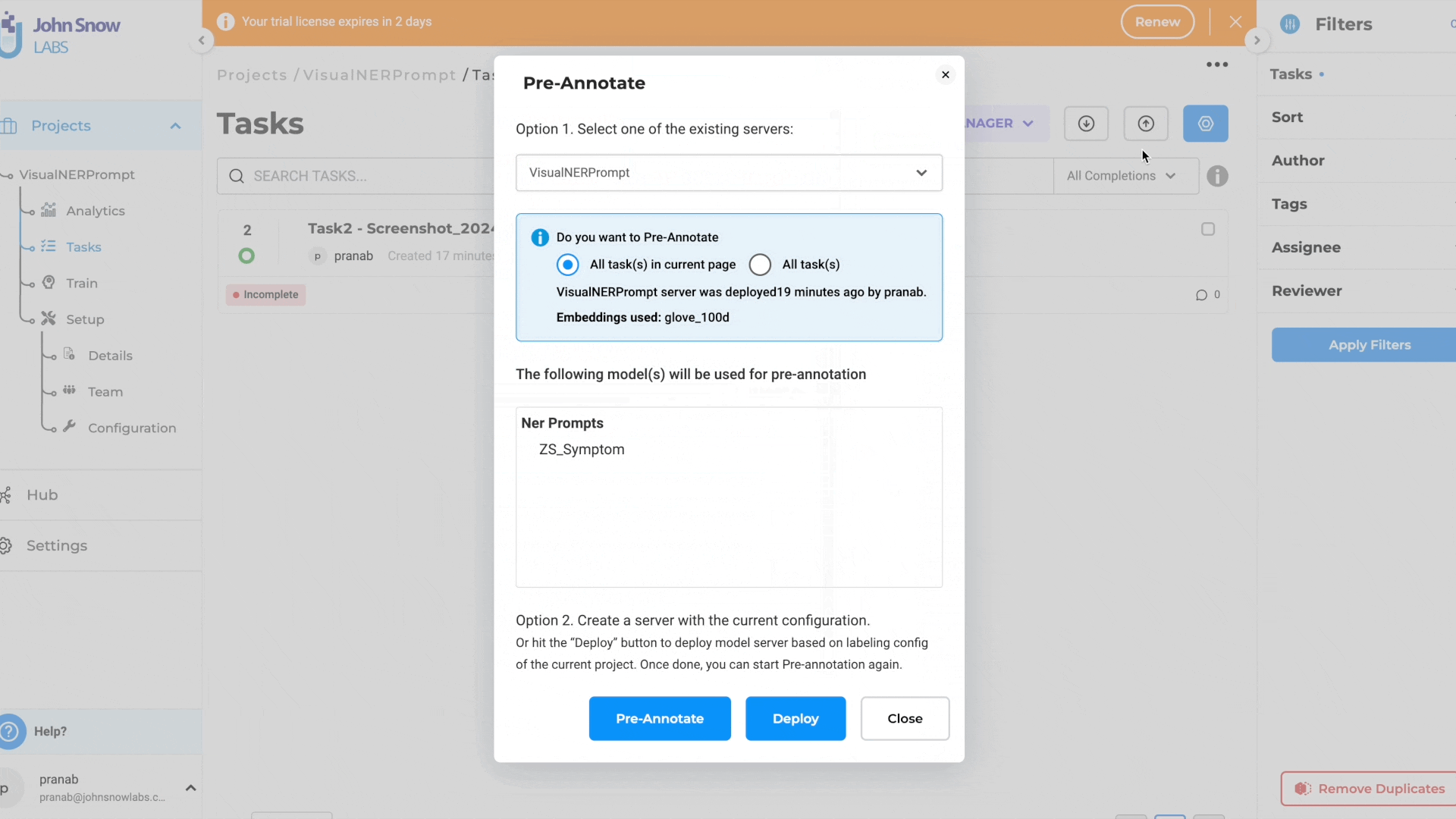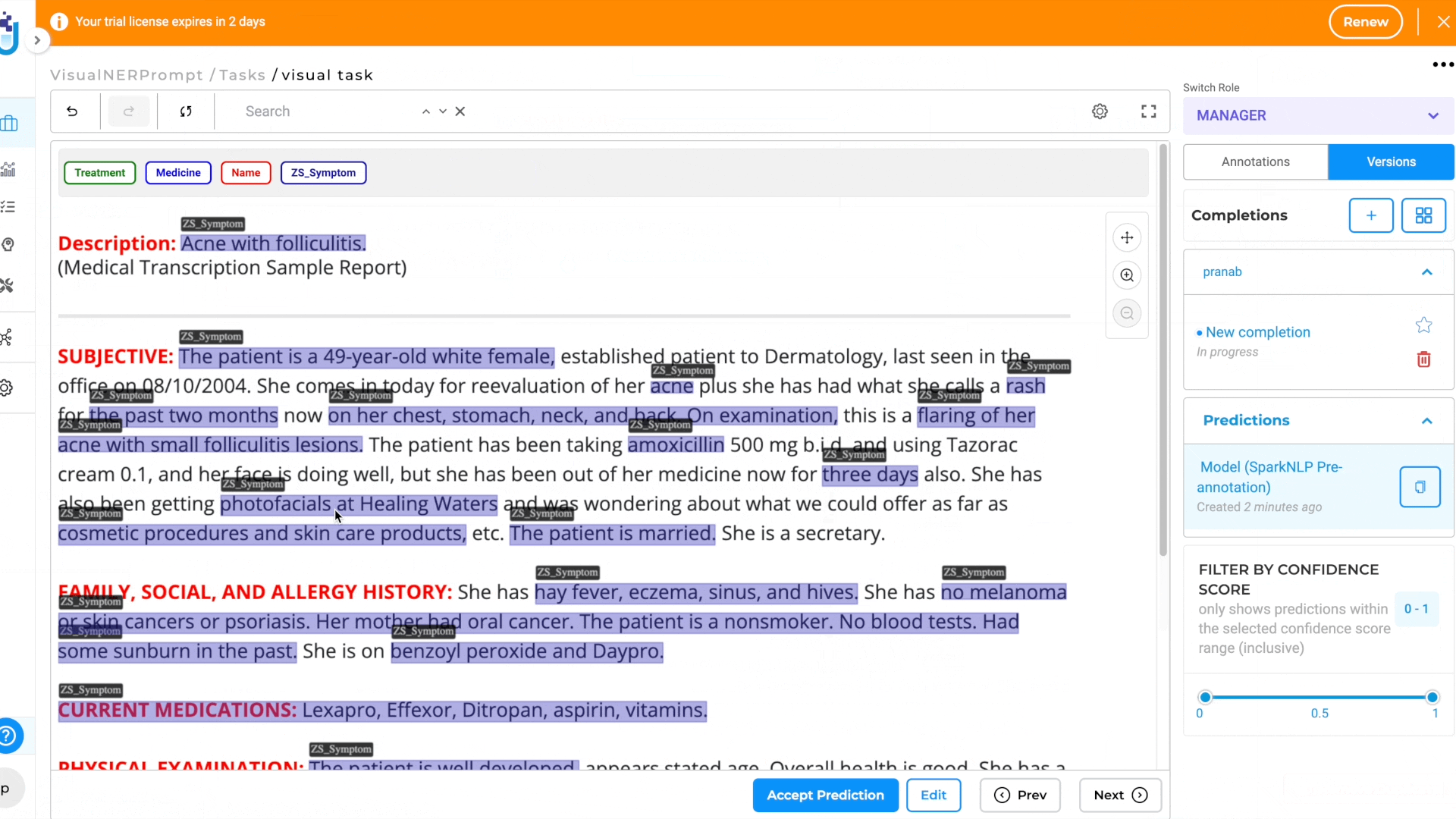
This new feature streamlines the pre-annotation process and extends the benefits of prompts to Visual NER projects, empowering users to annotate tasks more effectively across various document types.
Pre-Annotation Using Rules in Visual NER Projects
Generative AI Lab supports the use of Rules for pre-annotation in Visual NER projects, enabling automated labeling of PDF and image-based documents based on user-defined patterns and conditions.
This enhancement extends the rule-based pre-annotation framework beyond text projects, allowing you to combine visual and textual information when defining entity extraction logic. Rules can be used to automatically identify specific terms, expressions, or patterns detected within OCR text, and apply the corresponding labels directly on the visual content.
By integrating rules into Visual NER workflows, you can:
- Automate Visual Annotations: Apply pattern-based labeling to image and PDF documents using the same rule sets as text projects.
- Enhance Annotation Consistency: Ensure uniform application of labeling logic across different content types.
- Increase Efficiency: Reduce the need for manual annotation by leveraging deterministic rules for pre-annotation on visual data.
This capability gives teams greater flexibility in designing hybrid annotation strategies that combine model-based, rule-based, and prompt-based automation for both text and visual projects.
Configure and Pre-annotate tasks using Rules:
- Create a Visual NER Project
- Navigate to Reuse-Resource Page and add desired rules.
- Once project configuration is saved, pre-annotate the tasks using the rules.
Pipeline Limitations
For optimal performance and resource management, each pre-annotation server supports a maximum of five models per deployment. This limit ensures efficient memory usage and stable operation when performing large-scale or concurrent pre-annotations.
Additionally, all models used within the same project must be compatible in terms of their underlying embeddings. Mixing models trained on different embeddings within one project is not supported. If incompatible models are selected, the Labeling Configuration will display a validation error, and deployment will be prevented until the configuration is corrected.
These safeguards help maintain consistent model performance and prevent runtime issues during pre-annotation.