The Text tag shows text that can be labeled. The text template is divided into the following segments:
- Information extraction: Includes NER and extracting relations among entities.
- Classification: Includes text classification and multi-class classification.
- Text summarization.
Specialized Templates
In addition to standard Text projects for NER, classification, and summarization, Generative AI Lab also provides several specialized text-based templates designed for advanced workflows:
-
HCC Coding (Text) – combines NER and classification to support medical coding and clinical risk adjustment. Annotators can link detected clinical entities to their corresponding HCC codes for validation and review.
-
LLM Evaluation Projects – designed to assess responses from Large Language Models (LLMs) using configurable rating criteria such as accuracy, coherence, and helpfulness.
Evaluators can score and compare generated outputs directly in the Lab interface. -
LLM Comparison Projects – enable side-by-side evaluation of responses from two or more LLMs, helping users benchmark performance or calibrate model output quality.
These projects support provider integrations including OpenAI, Azure OpenAI, Amazon SageMaker, and Anthropic Claude.
These specialized templates expand the capabilities of Text projects, allowing both annotation and evaluation workflows to coexist within the same platform.
Named Entity Recognition
Named Entity Recognition (NER) refers to the identification and classification of entities mentioned in unstructured text into pre-defined categories such as person names, organizations, locations, medical codes, time expressions, quantities, monetary values, percentages, etc.
The Generative AI Lab offers support for two types of labels:
- Simple labels for NER or assertion models;
- Binary relations for relation extraction models.
Assertion Labels
The syntax for defining an Assertion Status label is the same as for the NER labels, with an additional attribute - assertion which should be set to true (see example below). This convention is defined by Generative AI Lab users which we exploited for identifying the labels to include in the training and prediction of Assertion Models. A simple Labeling Config with Assertion Status defined should look like the following:
<View>
<Labels name="ner" toName="text">
<Label value="Medicine" background="orange" hotkey="_"/>
<Label value="Condition" background="orange" hotkey="_"/>
<Label value="Procedure" background="green" hotkey="8"/>
<Label value="Absent" assertion="true" background="red" hotkey="Z"/>
<Label value="Past" assertion="true" background="red" hotkey="X"/>
</Labels>
<View style="height: 250px; overflow: auto;">
<Text name="text" value="$text"/>
</View>
</View>
NOTE: Notice assertion=”true” in Absent and Past labels, which marks each of those labels as Assertion Status Labels.
Classification
The choices tag is used as part of the classification projects to create a group of choices. It can be used for a single or multiple-class classification. According to the parameters used along with the choices tag, annotators can select single or multiple choices.
Parameters
The Choices tag supports the following parameters/attributes:
| Param | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| required | boolean |
false |
Verify if a choice is selected |
| requiredMessage | string |
Show a message if the required validation fails | |
| choice | single | multiple |
single |
Allow user to select single or multiple answer |
| showInline | boolean |
false |
Show choices in a single visual line |
| perRegion | boolean |
Use this attribute to select an option for a specific region rather than the entire task |
<!--text classification labeling config-->
<View>
<Text name="text" value="$text"/>
<Choices name="surprise" toName="text" choice="single" required='true' requiredMessage='Please select choice'>
<Choice value="surprise"/>
<Choice value="sadness"/>
<Choice value="fear"/>
<Choice value="joy"/>
</Choices>
</View>

When using the perRegion attribute, choices can be defined for each chunk annotation as shown below:

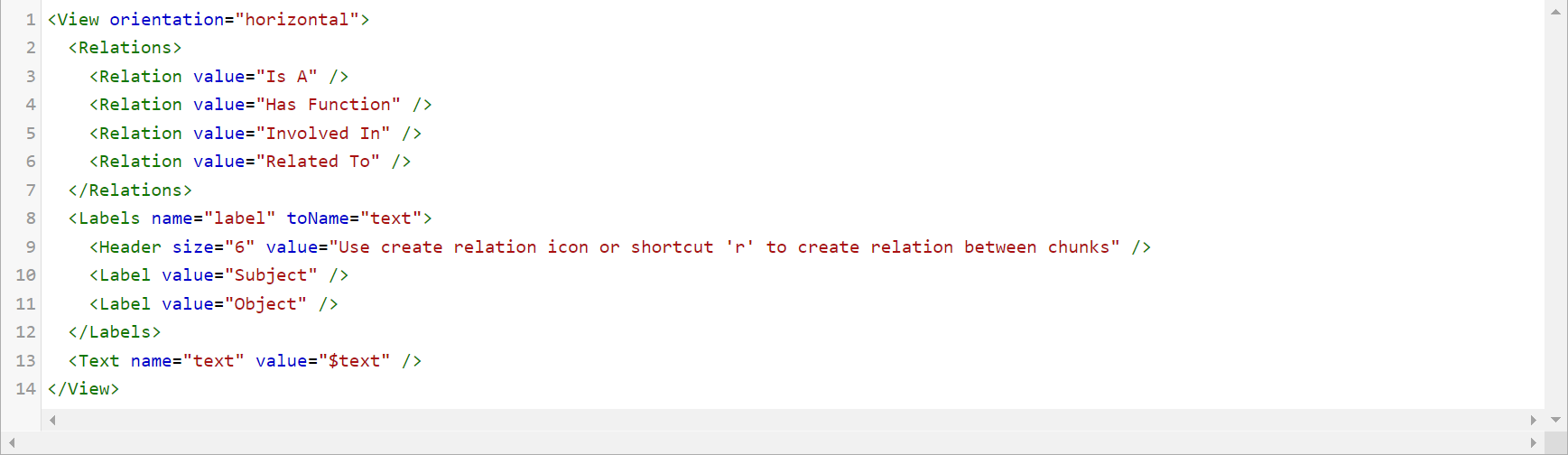
NER with Relation Extraction
Generative AI Lab also offers support for relation extraction. Relations are introduced by simply specifying their label in the project configuration.
<Relations>
<Relation value="CancerSize" />
<Relation value="CancerLocation"/>
<Relation value="MetastasisLocation"/>
</Relations>
Information Extraction
For simple NER related tasks, the configuration just needs the Text and Labels tags. The Labels tag provides a set of labels for labeling regions in your tasks. Use the Labels tag to create a set of labels that can be assigned to identified region and specify the values of labels to assign to regions. For example, you have the following JSON to label, as shown below.
{
"text": "The patient is a pleasant 17-year-old gentleman who was playing basketball today in gym. Two hours prior to presentation, he started to fall and someone stepped on his ankle and kind of twisted his right ankle and he cannot bear weight on it now. It hurts to move or bear weight. No other injuries noted. He does not think he has had injuries to his ankle in the past. He was given adderall and accutane.",
"title": "MyTestTitle"
}
The configuration in this case looks as shown below.
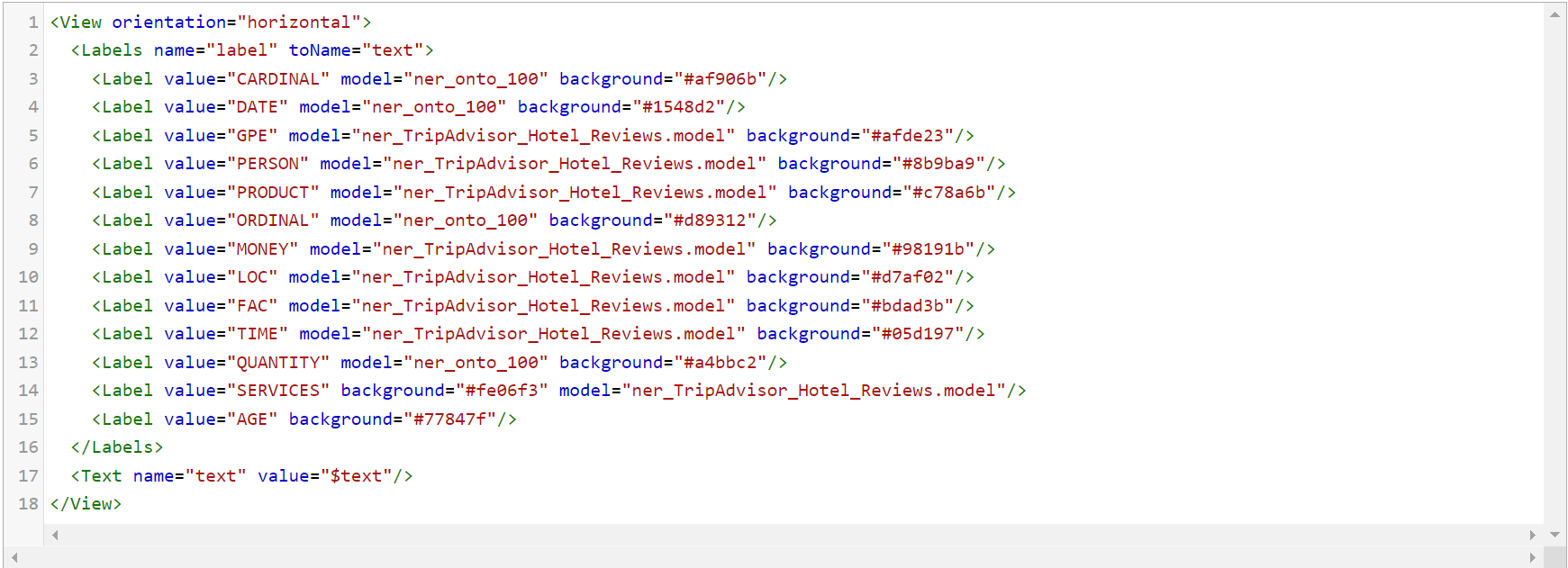
The model parameter in the Label tag must be specified whenever a pre-trained model is used in the project for pre-annotation purposes. It is automatically defined when a model is chosen from Reuse Resources.
For the case of relation extraction, the configuration additionally needs a Relations tag apart from Text and Labels. For the same input, the configuration would look as shown below.
Classification
For a classification task, the configuration needs the Text and Choices tags. For instance, you have the input JSON as shown below. The Choices tag is used to create a group of choices (a set of Choice tags), with radio buttons or checkboxes. It can be used for single or multi-class classification.
{
"text": "The patient is a pleasant 17-year-old gentleman who was playing basketball today in gym. Two hours prior to presentation, he started to fall and someone stepped on his ankle and kind of twisted his right ankle and he cannot bear weight on it now. It hurts to move or bear weight. No other injuries noted. He does not think he has had injuries to his ankle in the past. He was given adderall and accutane.",
"title": "MyTestTitle"
}
For simple single-class classification, the configuration is shown below.
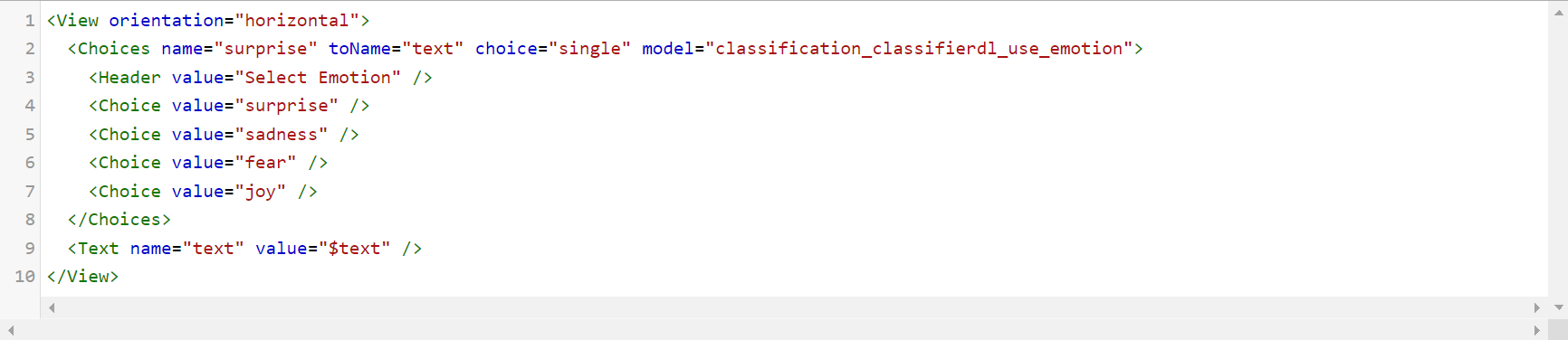
In the case of multi-class classification, the configuration would look as shown below.
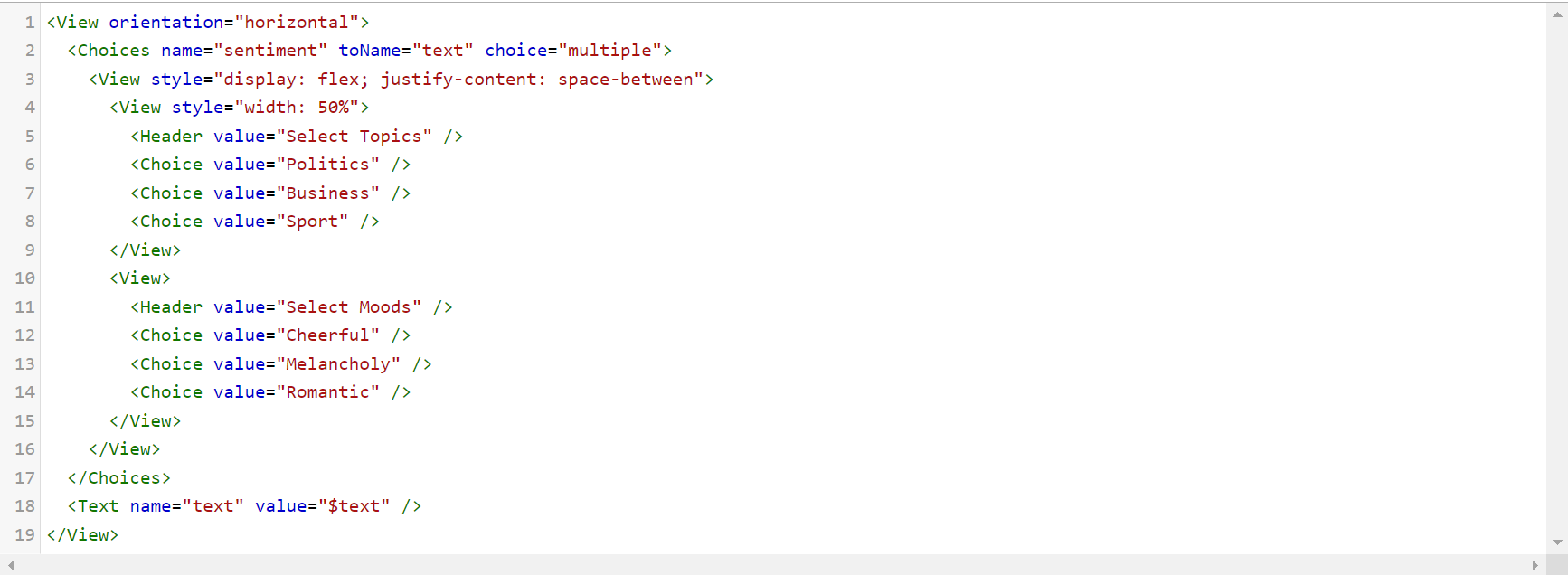
Text summarization
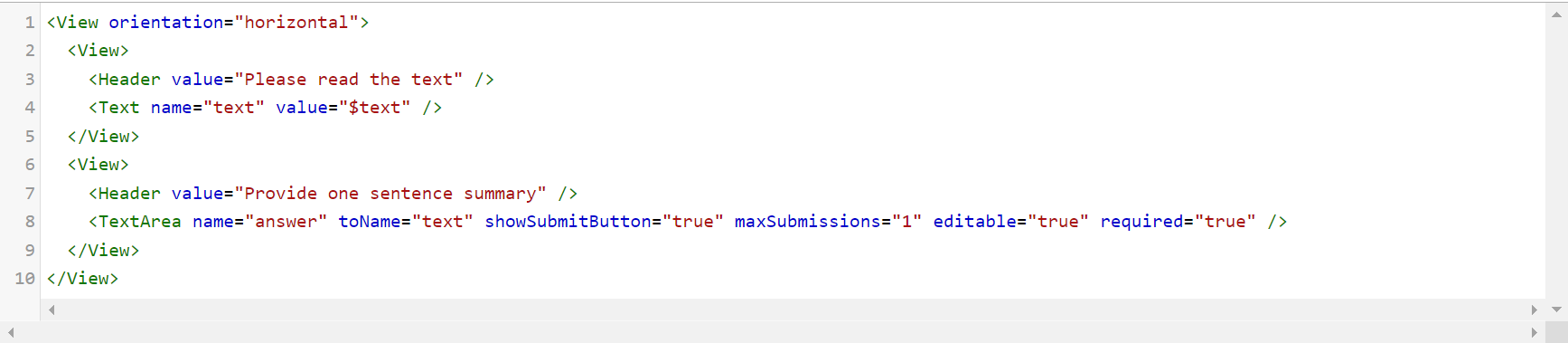
For a simple text summarization, the configuration just needs the Text and TextArea tags. The TextArea tag is used to display a text area for the user input. It is mainly used for transcription, paraphrasing, or captioning task.
Support for HCC Coding
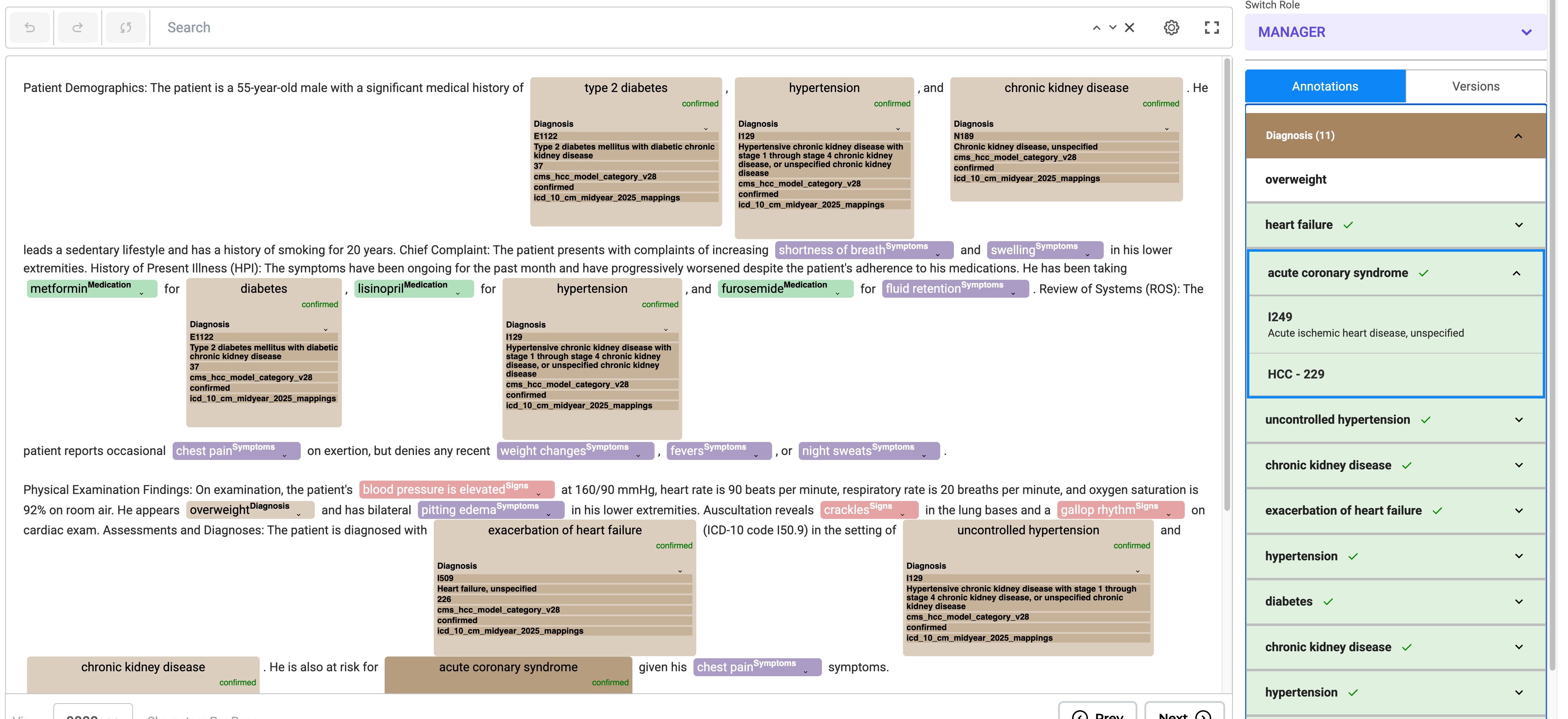
Generative AI Lab supports HCC (Hierarchical Condition Category) Coding for both text and PDF-based content.
These project types streamline clinical risk adjustment and insurance verification workflows by mapping detected ICD-10 diagnosis codes to their corresponding HCC categories.
Available Project Types
- HCC Coding for Text – supports text-based annotation, allowing users to label and map clinical findings directly to HCC codes.
- HCC Coding for PDF + Text (side-by-side) – provides a dual-view interface for reviewing the original PDF alongside extracted text during annotation.
These templates allow users to associate HCC codes with annotated clinical entities using preconfigured lookup datasets, reducing manual input and improving consistency in medical coding.
Usage Instructions
To enable HCC Coding Support, follow these steps:
To enable HCC Coding Support, follow these steps:
- Project Setup
- Select either of the new project templates during project creation.
- Choose the HCC Coding for PDF and Text (side by side) option if you need a visual representation of the original document while performing HCC coding.
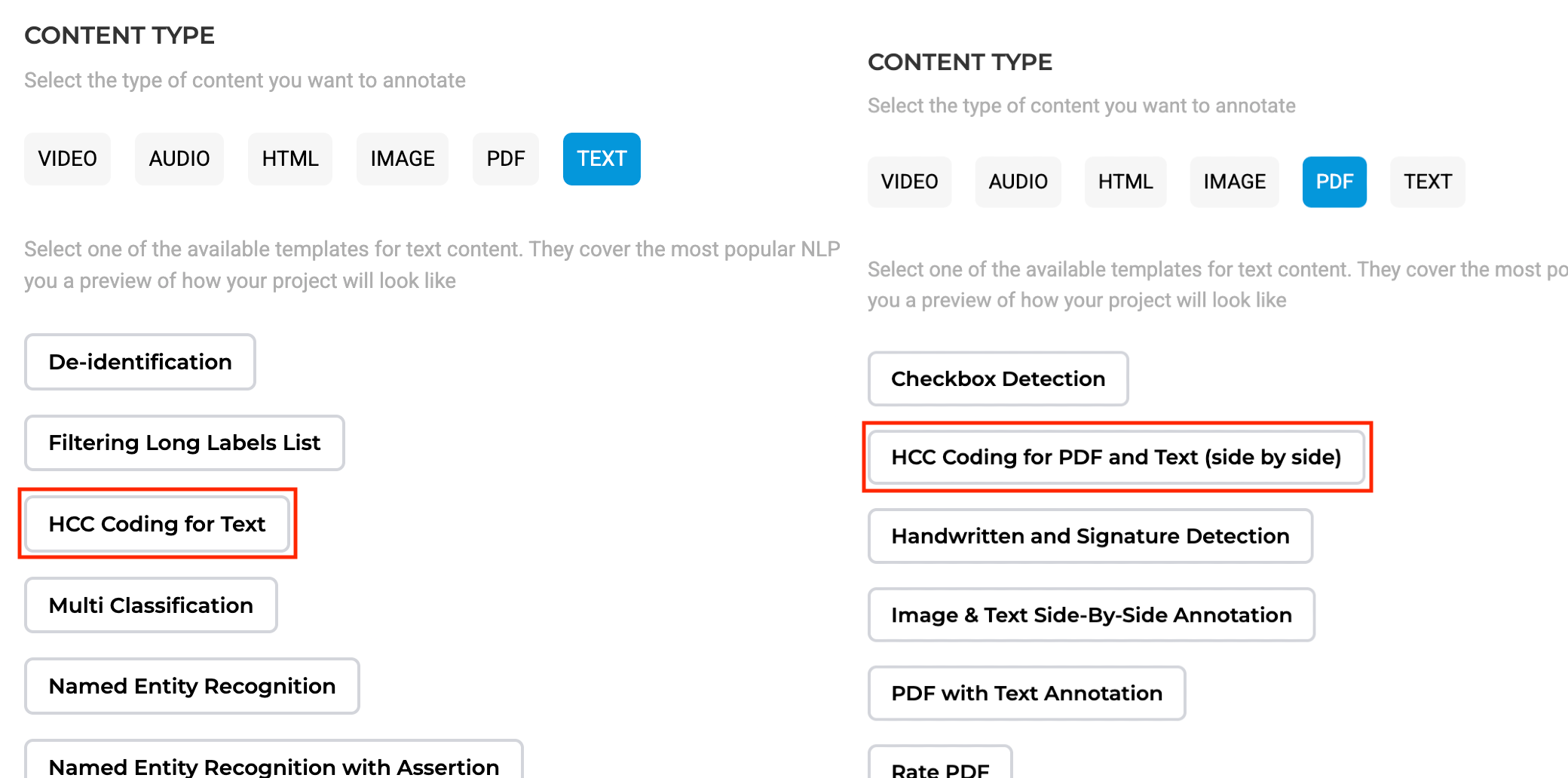
- Label Customization - On the Customize Labels page, users can either:
- Apply a lookup dataset globally, to all labels in your taxonomy at once.
- Assign Lookup options to specific labels.
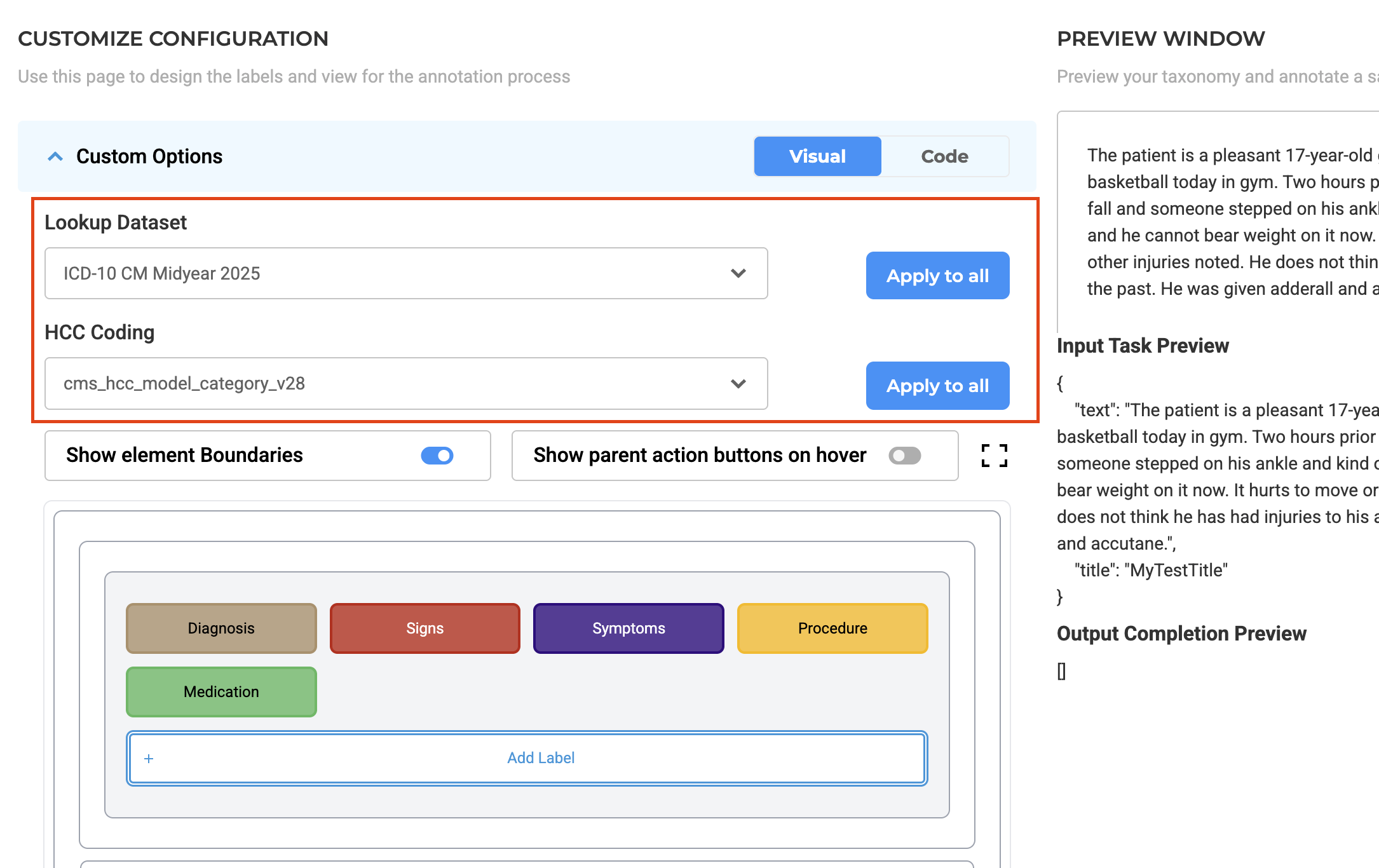
- Annotation Process
- Annotate entities and assign codes using the annotation widget.
- Edit codes inline or through the Annotation Widget from the right panel.
- Annotated chunks are listed under their respective labels. Users can expand labels by clicking the down arrow to view all chunks associated with them.
- Lookup code can be edited or updated directly from labeled tokens or via the labeling section by clicking the edit button.
- Predictions can be copied to generate a completion, allowing the HCC code to be reviewed using the annotation widget on the right.
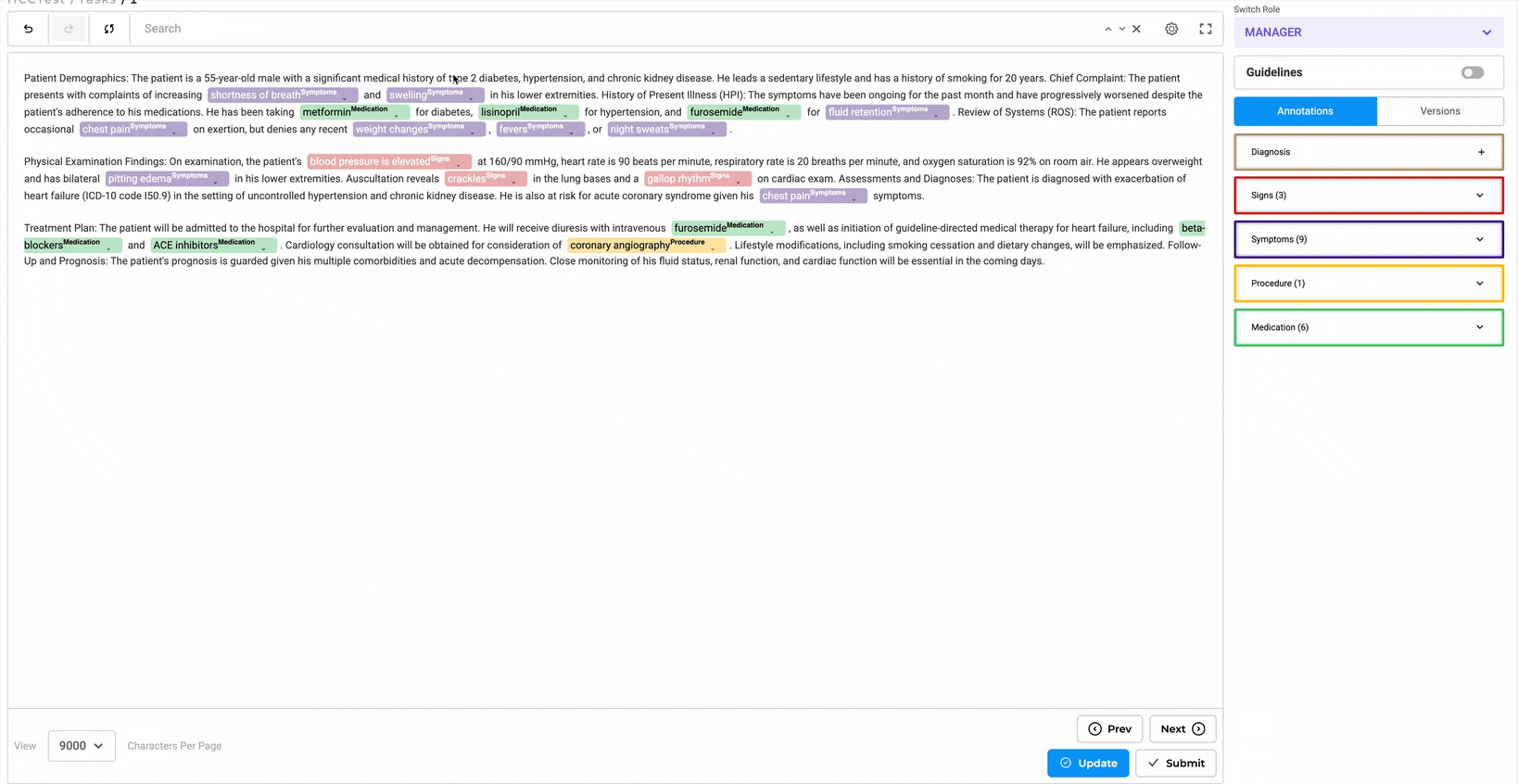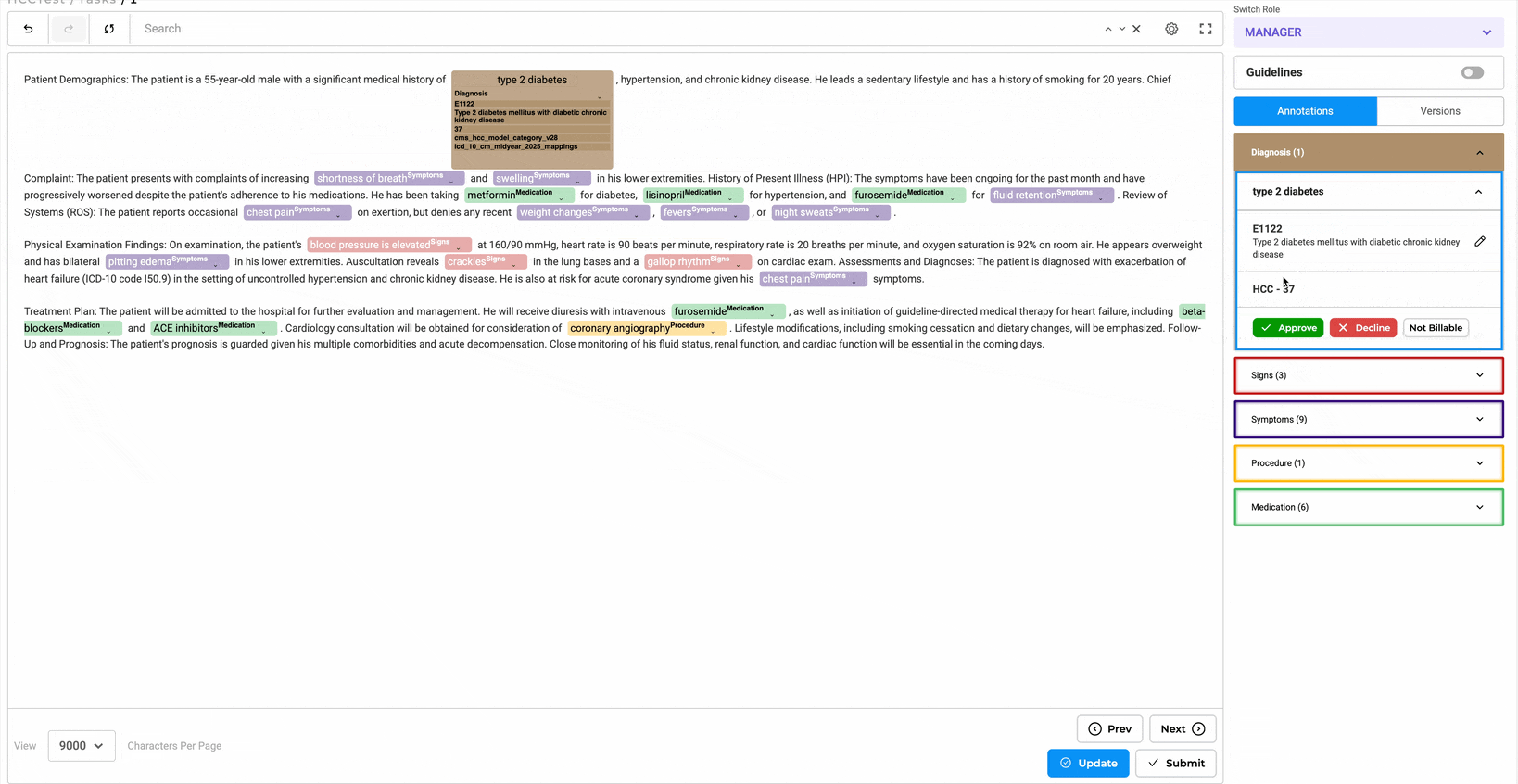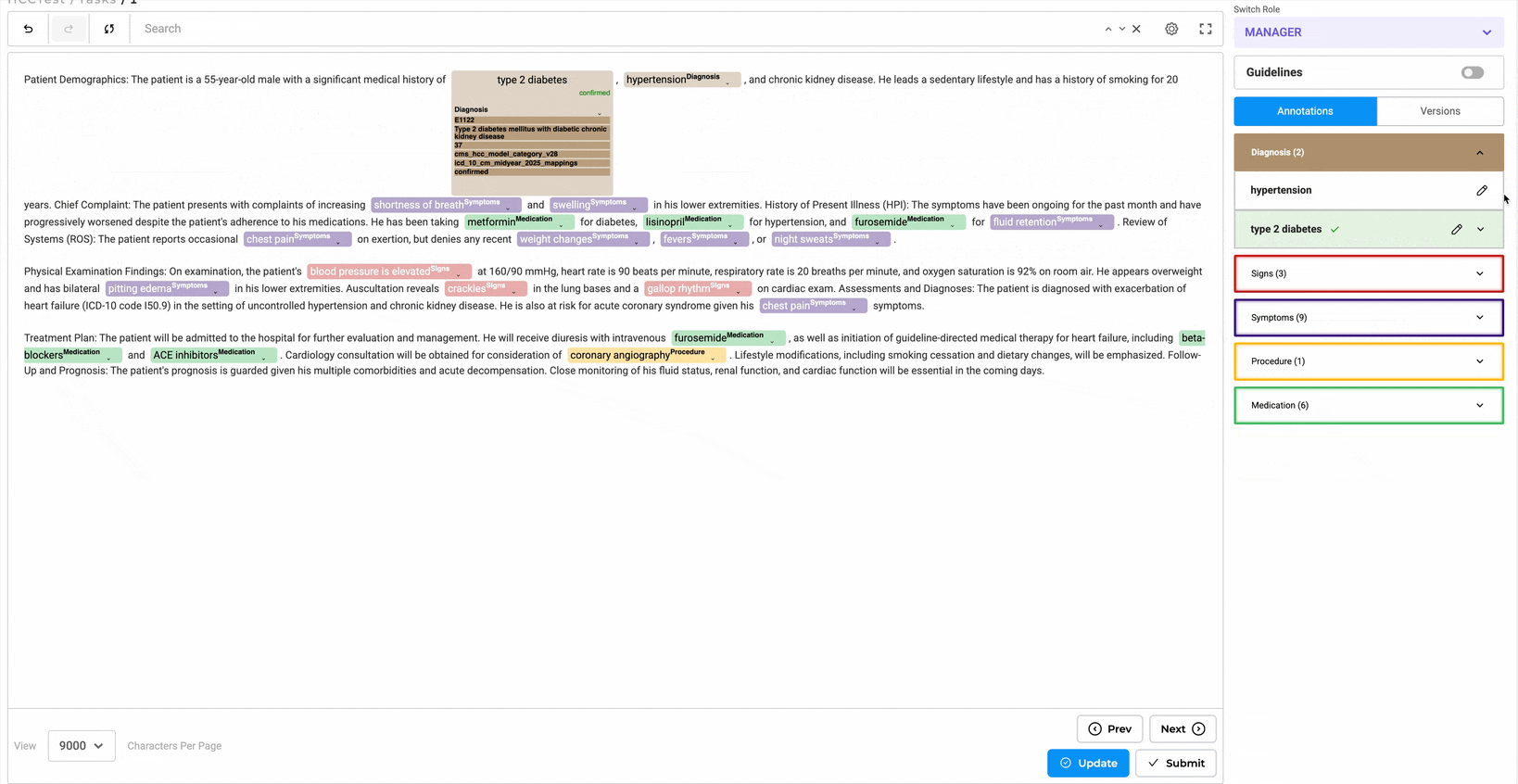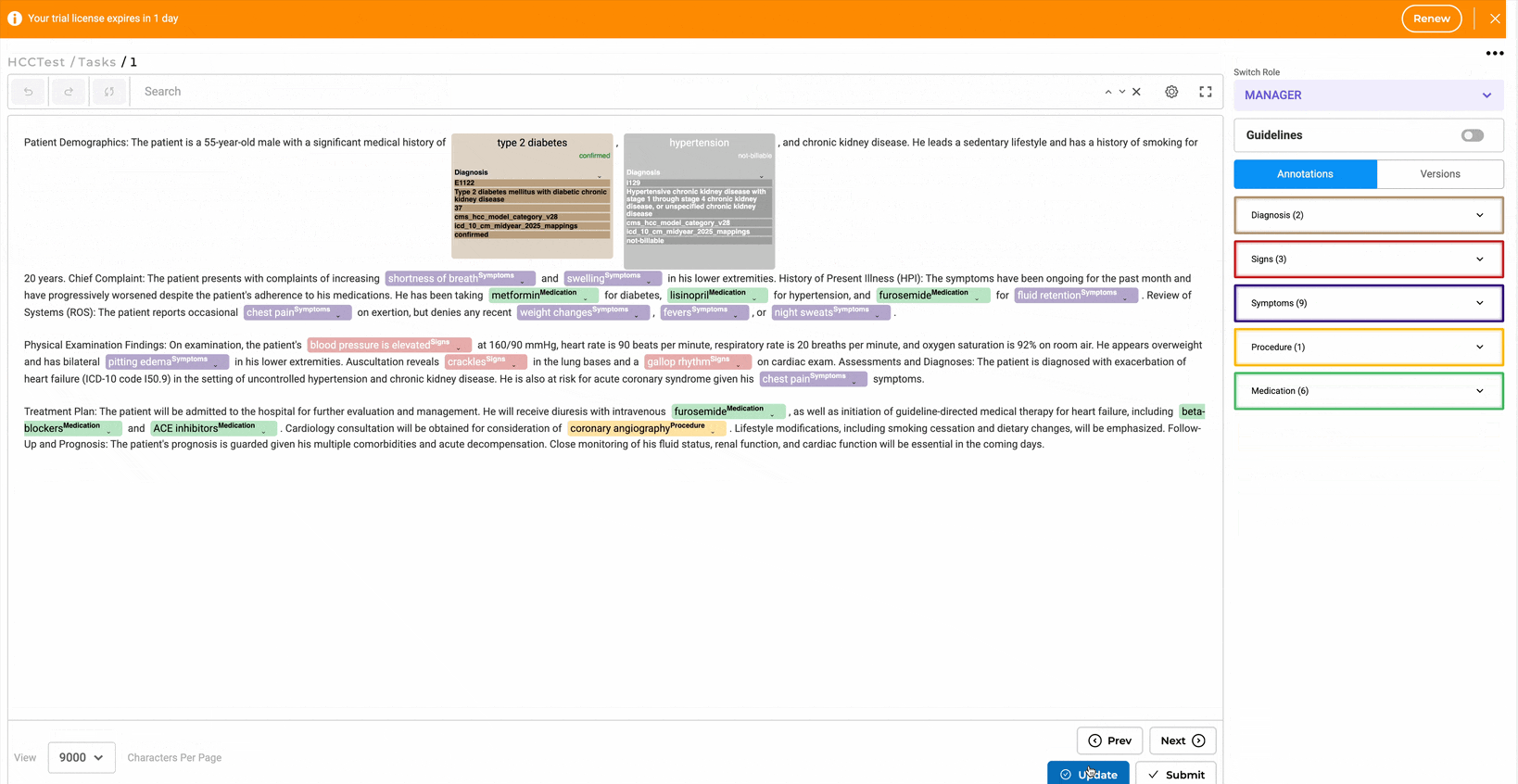
- Review and Confirmation
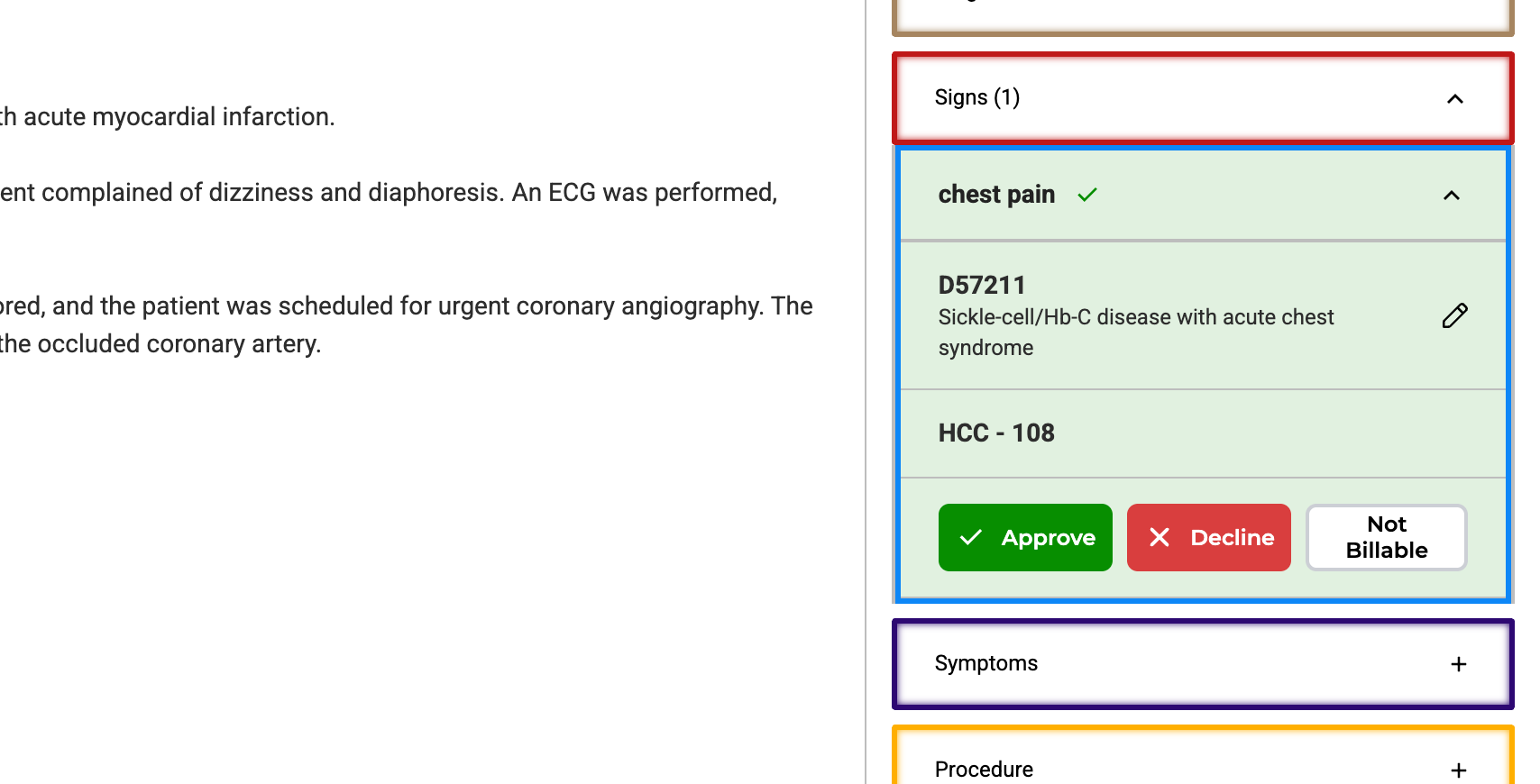
Once a task is labeled and lookup codes are assigned along with HCC Codes, reviewers have the following options:
- Accept and confirm the labeled text.
- Decline and remove the labels.
- Tag the label as non-billable, if necessary.
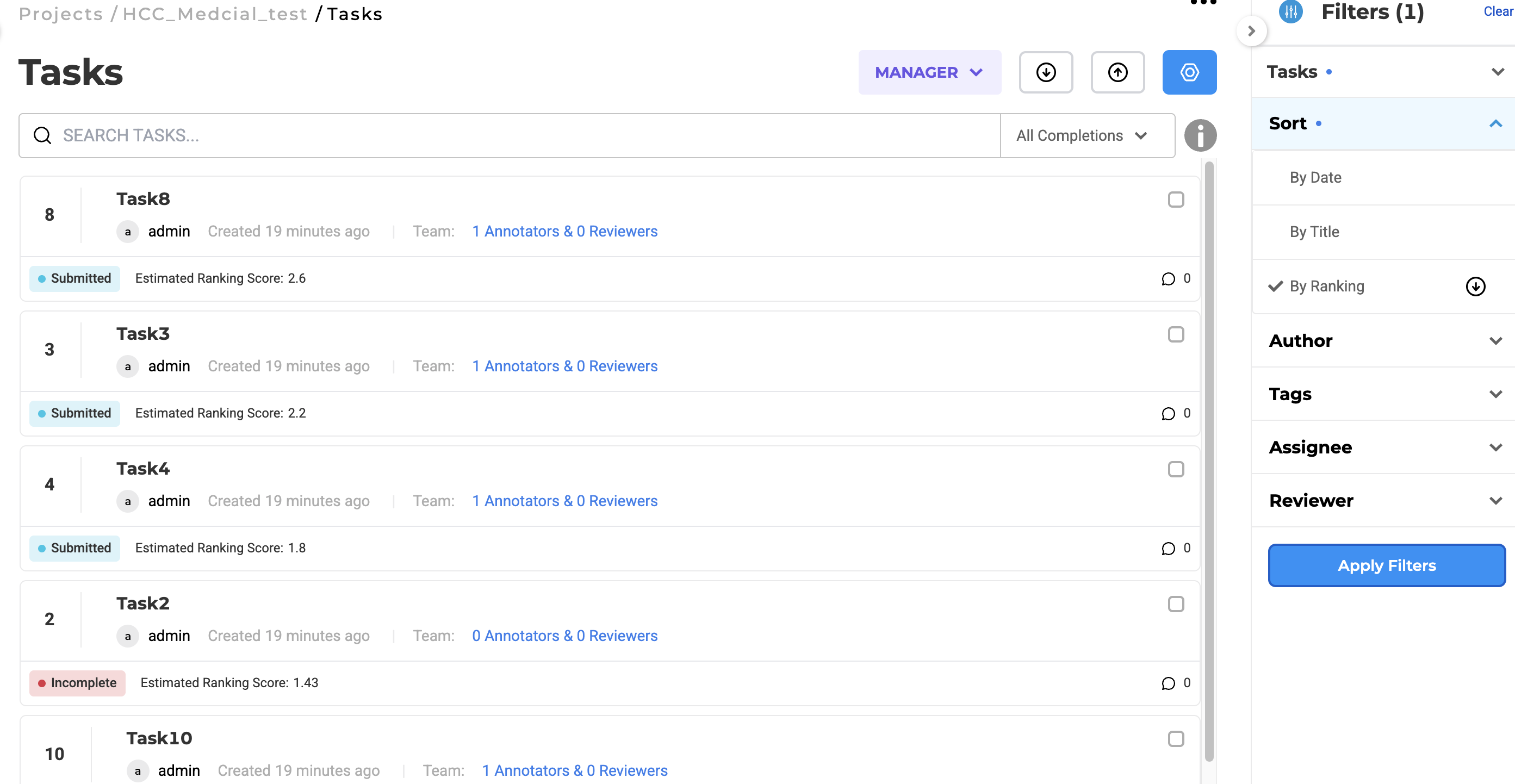
Raking Score Integration
Tasks can include ranking scores to support triaging and prioritization, allowing users to manage large annotation datasets more effectively. When importing tasks, users can associate each task with a ranking score that reflects its clinical significance or urgency. These scores are then displayed in the task list and can be used to sort and filter tasks dynamically. This functionality is particularly beneficial in risk adjustment workflows where prioritizing complex or high-impact cases is critical. Ranking scores also integrate with the HCC coding workflow, enabling annotators and reviewers to systematically focus on the most relevant cases for validation.