Entity Extraction and Pre-Annotation via GPT Prompting
Generative AI Lab supports integration with external large language model (LLM) providers such as OpenAI, enabling a broader and more flexible range of prompts for pre-annotation.
This capability complements the existing Zero-Shot Entity and Relation Prompting options, allowing users to leverage advanced LLMs to generate high-quality pre-annotations even when no pre-trained model is available.
By combining GPT-based prompting with existing zero-shot and rule-based approaches, users can design more effective annotation workflows, quickly generate entity or relation suggestions, and improve overall annotation efficiency.
-
Broadens Prompt Possibilities: By integrating with Open AI LLM models, users can tap into a more diverse set of prompts, leveraging external expertise to craft pre-annotations, as an alternative pre-annotation solution or when pre-trained models are not available.
-
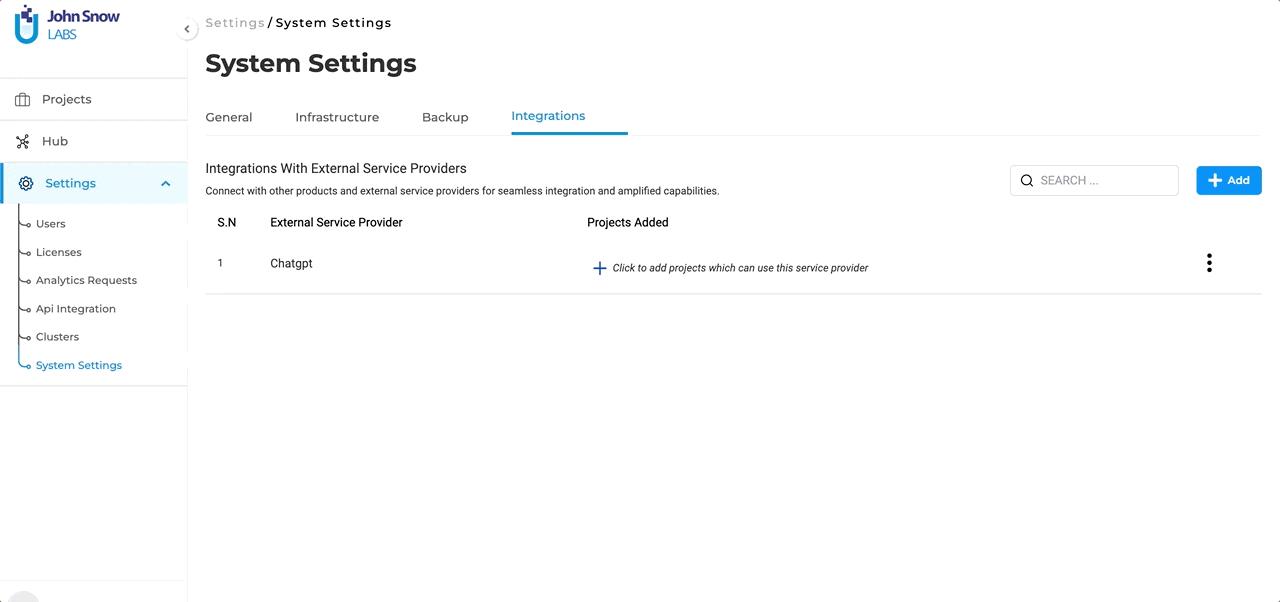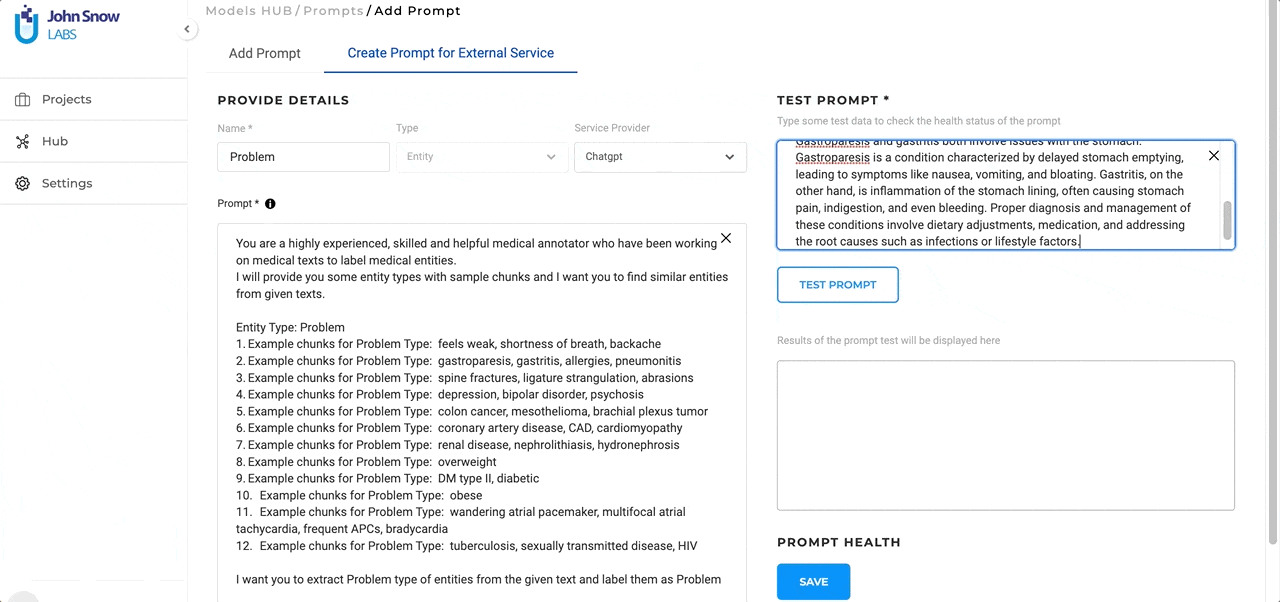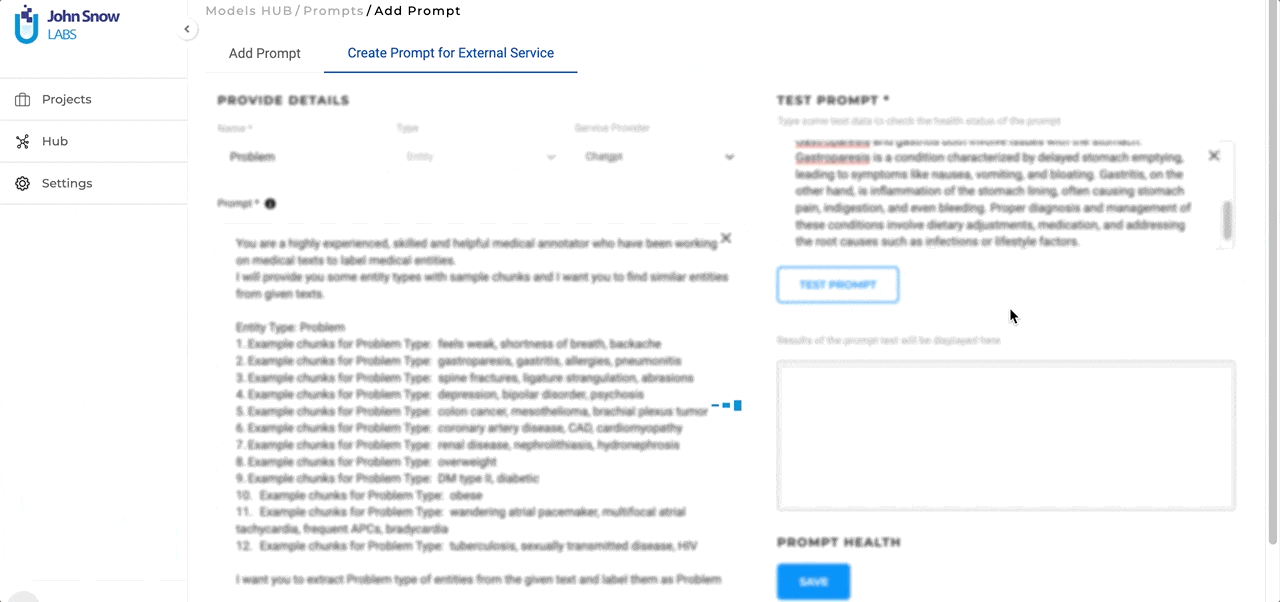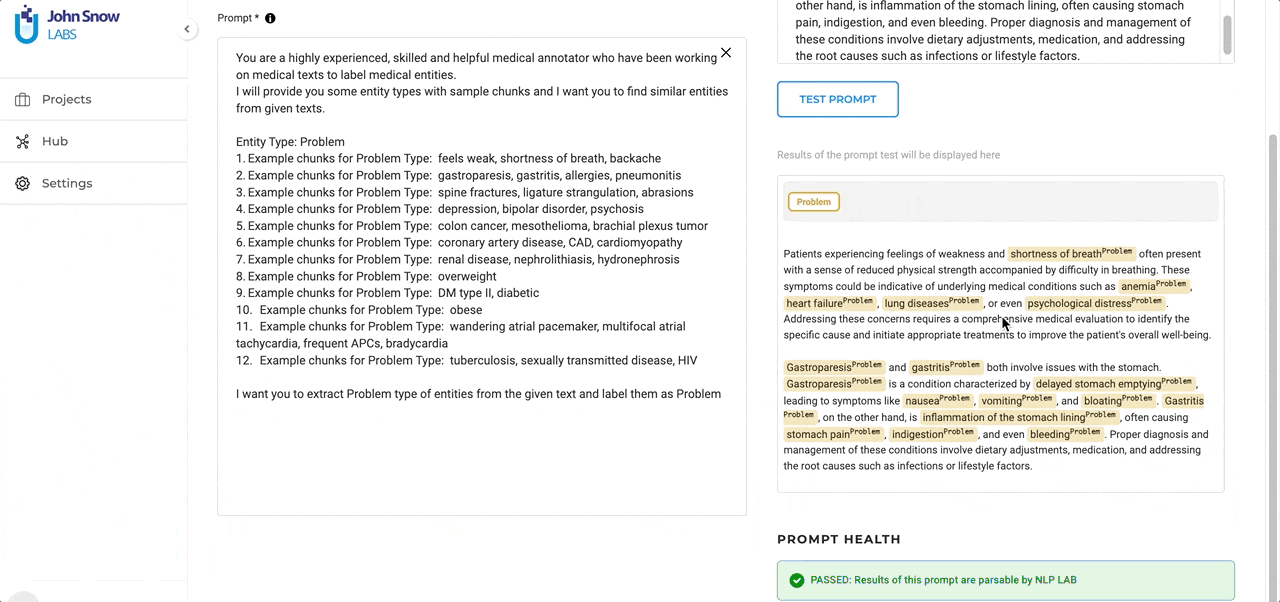
Efficient Entity Extraction: As current LLMs, GPT family included, are not very good at entity recognition tasks, Generative AI Lab included a post-processing step on the result provided by LLM. This improves entity identification and helps precisely locate the entities in the given text. These entities, carefully curated and aligned with Generative AI Lab pre-annotation requirements pave the way for a more efficient and streamlined annotation experience.
The following sections explain in detail how to define and use GPT prompts.
Setting Up the Integration with Open AI service
Integrating ChatGPT and Azure into the Generative AI Lab has been designed to be a straightforward process, ensuring users can harness the power of external expertise seamlessly. It consists of three easy steps:
Integrations Page: Navigate to the Integrations Page located within the System Settings. This is the hub where all external service providers, including Open AI’s GPT Models, can be defined and managed.
ChatGPT:
Azure:
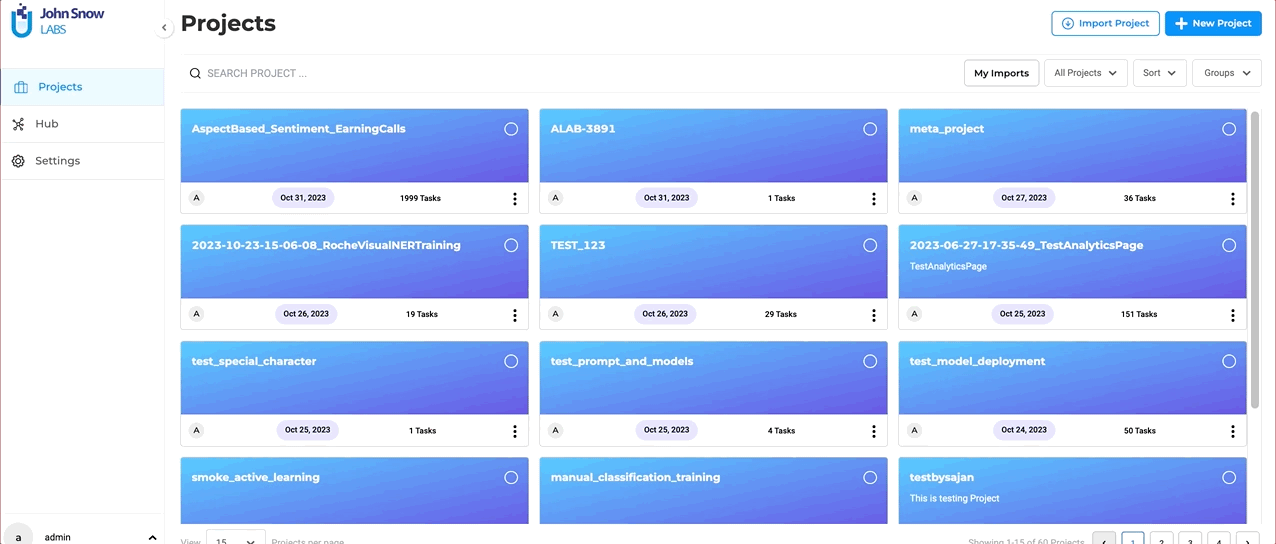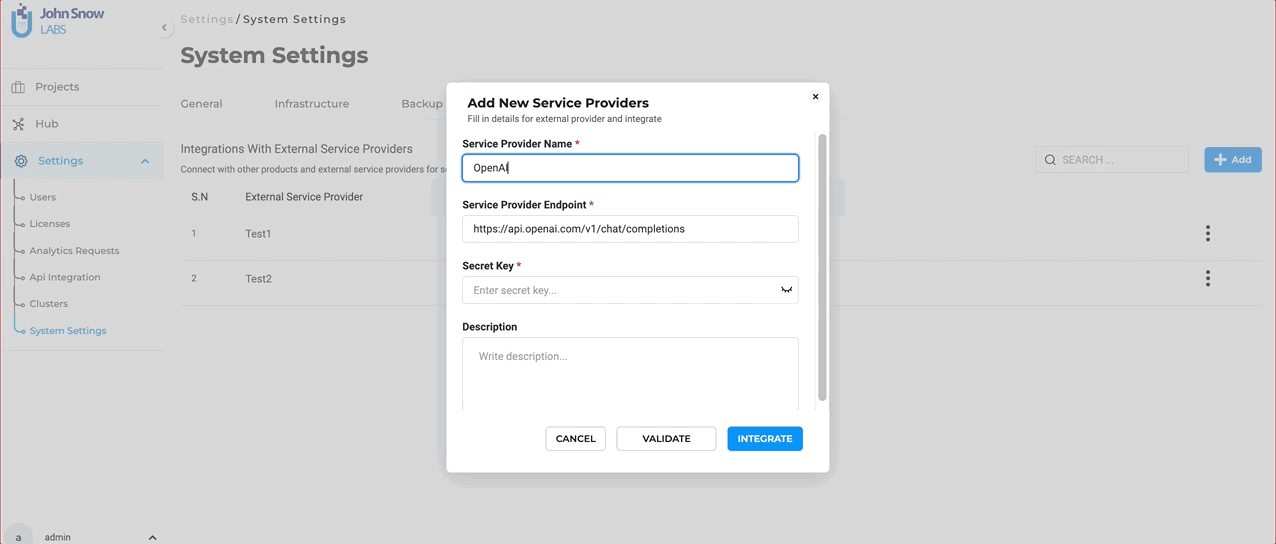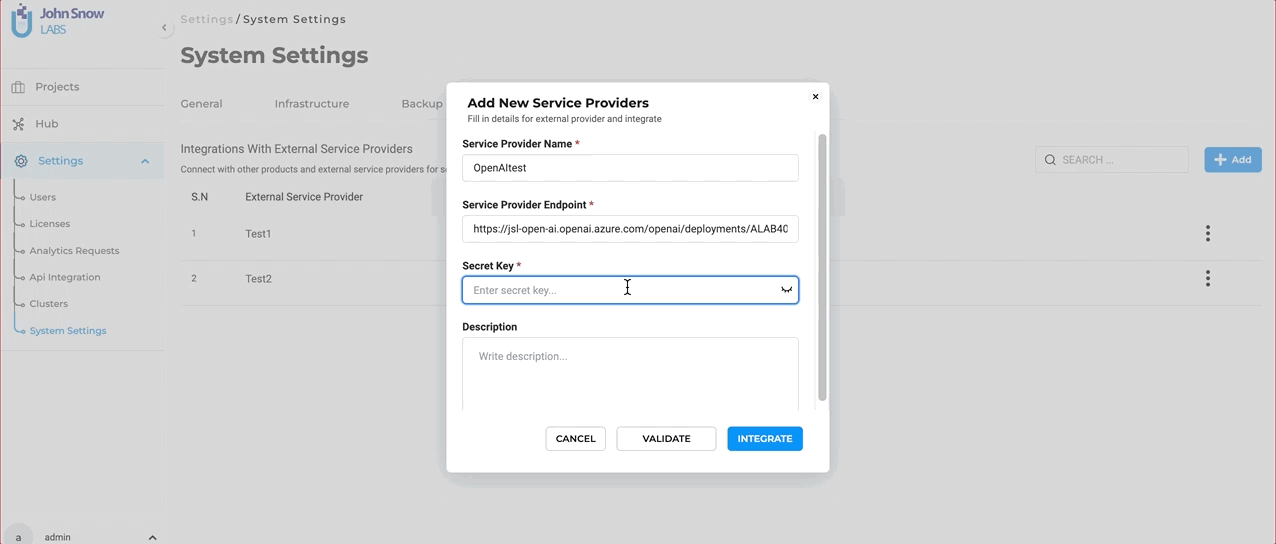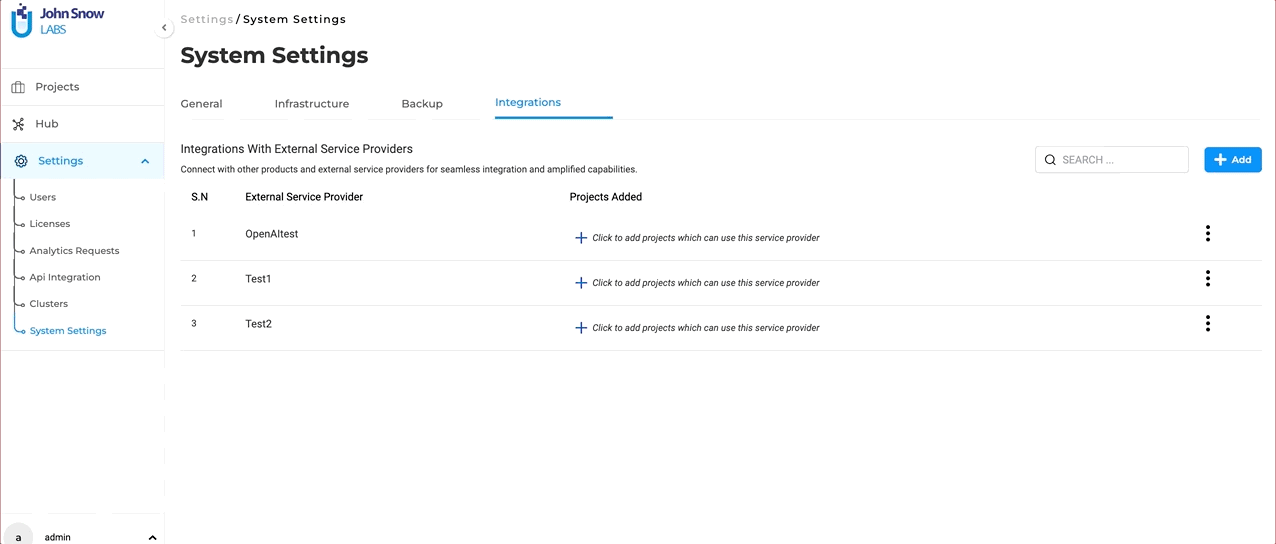
Define the Service Provider: To initiate the integration, users are required to provide specific details:
- Service Provider Name: This is the identifier for the external service, which in this case would be “ChatGPT” or any other name you prefer to use.
- Secret Key: Every external service comes with a unique Secret Key that ensures secure communication between the platforms. Enter the Secret Key associated with your Open AI subscription here. To ensure the integration process is error-free, users can validate the provided Secret Key directly within the form. This validation step ensures that the connection is secure and that the key is correct.
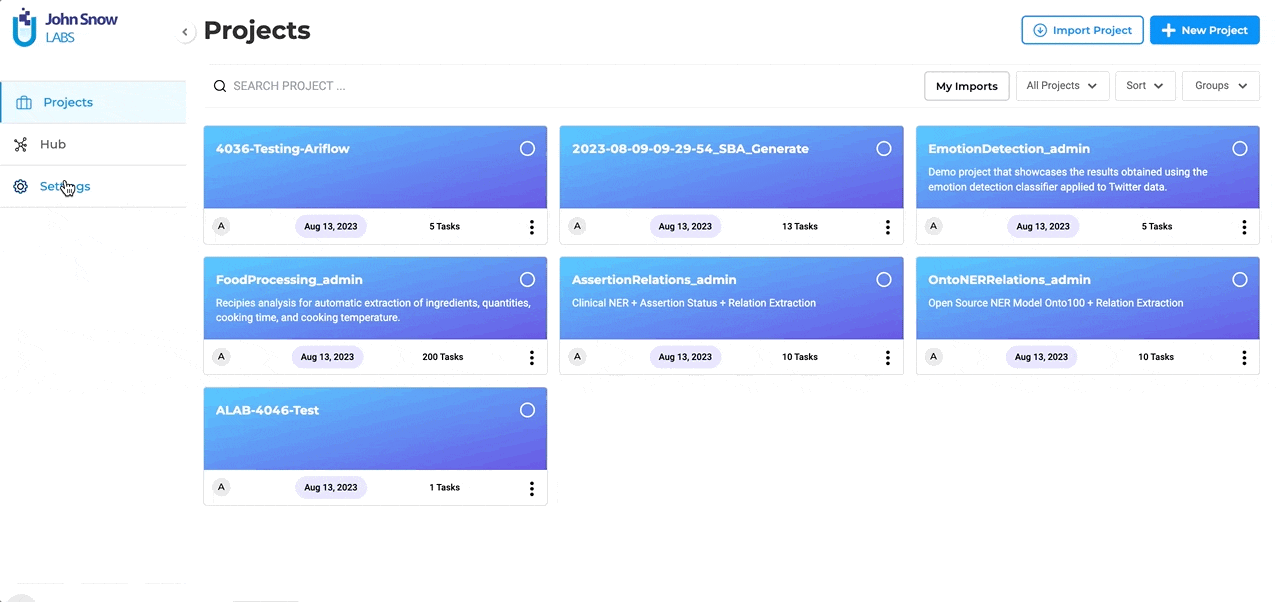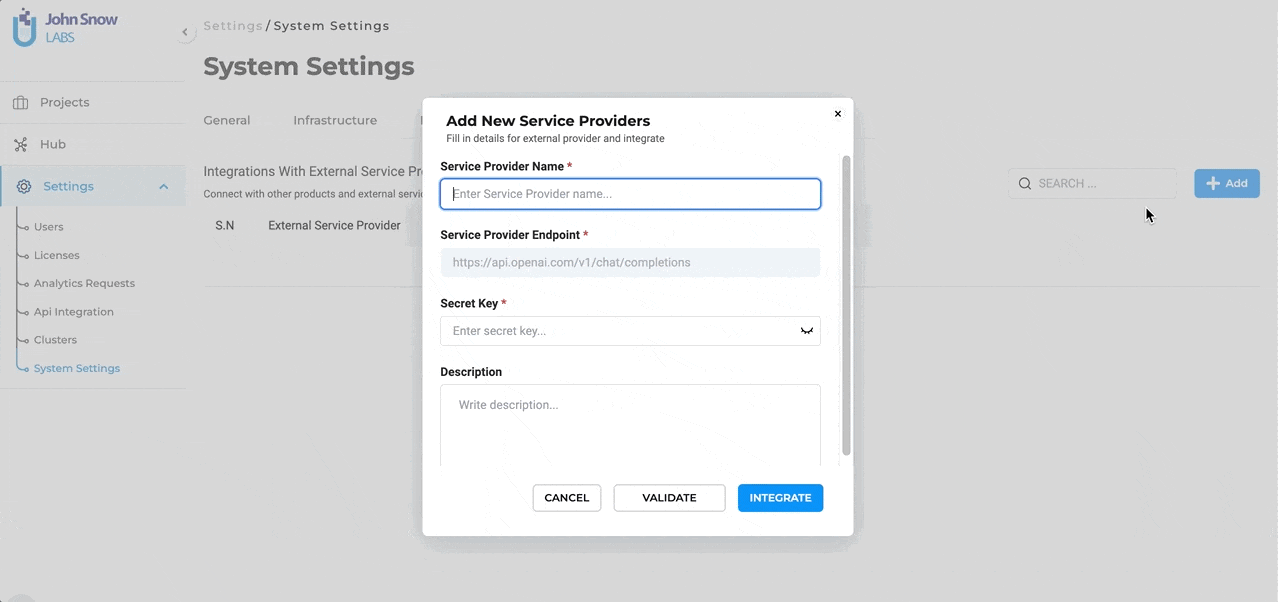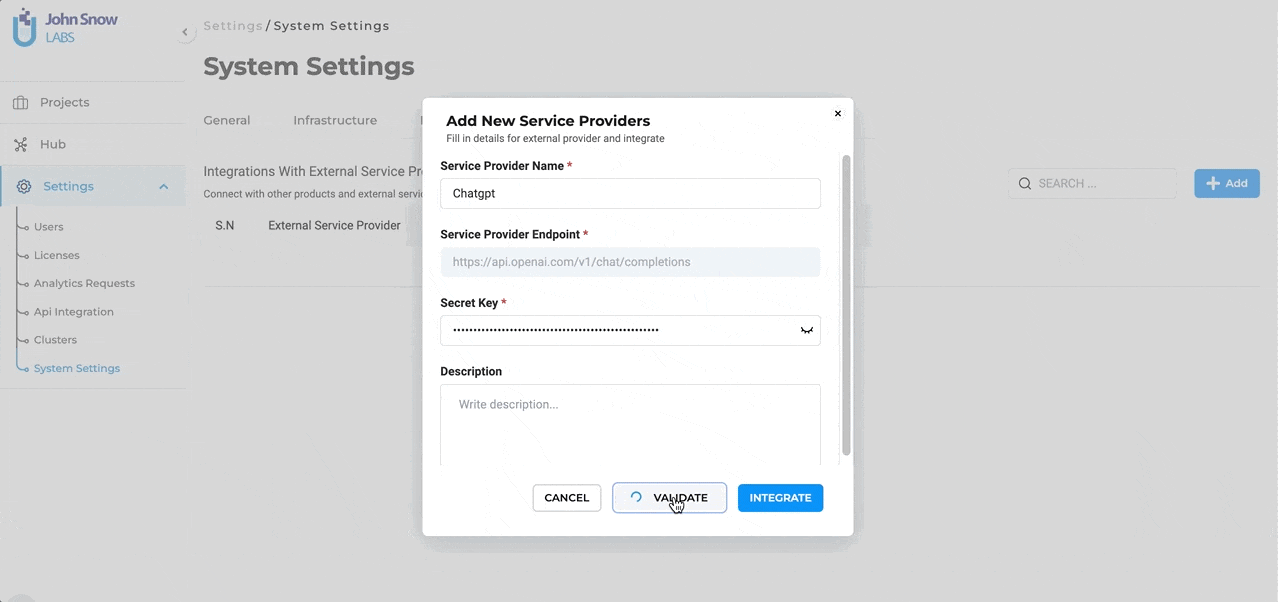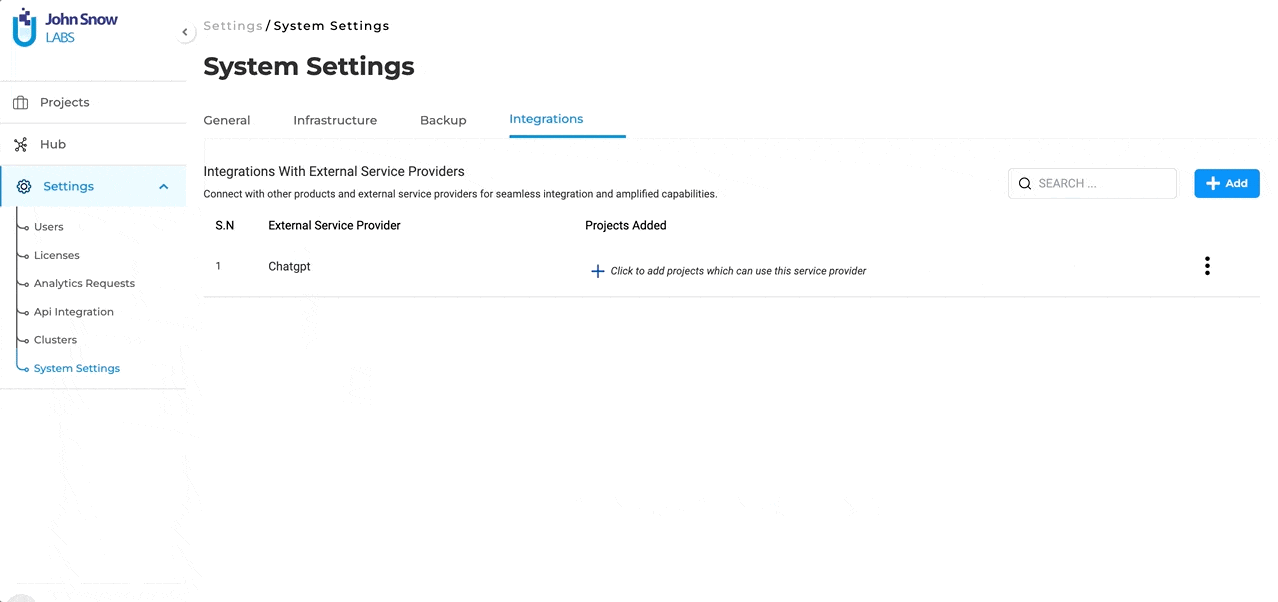
Project Association: Once a successful connection with “ChatGPT” (or any external LLM service provider) is established, it doesn’t end there. The integrated service will now be available for association with selected projects. This means users can decide which projects will benefit from the “ChatGPT” integration and enable it accordingly.
The Open AI integration allows users to tap into a vast reservoir of external expertise, enhancing the depth and breadth of their projects. We’ve ensured that the integration process is as intuitive as possible, allowing users to focus on what truly matters: crafting refined and effective pre-annotations.
Additional Supported Providers and Configuration Options
Generative AI Lab now supports integration with multiple external LLM providers:
- OpenAI (ChatGPT, GPT-4 family)
- Azure OpenAI Service
- Anthropic Claude
- Amazon SageMaker LLM Endpoints
Each provider can be added and configured from System Settings → Integrations using the same setup process. Users simply supply the required credentials (API key, access token, or endpoint) and validate the connection before linking the provider to specific projects.
Each integration form now includes generation control parameters that are consistent across providers:
- Temperature – Adjusts the randomness or creativity of the model output.
Lower values (e.g., 0.1) make responses deterministic, while higher ones (e.g., 0.9) yield more varied generations. - Max Tokens – Limits the maximum number of tokens generated in the response.
This setting helps control the verbosity and ensures annotations remain concise.
These parameters can be configured globally for a provider or fine-tuned per project when defining prompts.
They are saved along with the provider configuration and automatically applied during pre-annotation.
Prompt Definition and Testing
Users can generate LLM prompts on the dedicated Prompt page from the Hub of Resources. For ChatGPT and Azure Prompts, Generative AI Lab offers a dedicated definition interface. Here’s what to expect when creating a new LLM prompt:
-
Name the Prompt: Within this new tab, users will first be asked to provide a name for their prompt. This name will be used for pre-annotating identified entities. At this point, we recommend creating one prompt per target entity.
-
Select the Service Provider: Next, users can choose the specific service provider they’ve previously set up via the Integrations Page.
-
Test in Real-time: A standout feature is the ability to test ChatGPT prompts at creation time. As you craft your prompt, you can immediately see how it performs on some test data. This not only allows for immediate feedback but also ensures that the final prompt aligns perfectly with the user’s objectives.
The testing interface supports all integrated providers — users can preview and compare prompt responses from OpenAI, Azure, Anthropic Claude, and SageMaker models within the same workflow.
The output display and post-processing are consistent across providers, ensuring parity in prompt behavior and entity alignment.
This streamlined approach ensures that integrating and testing external prompts is as intuitive and efficient as possible.
Consistent Workflow with LLM Prompts
Generative AI Lab maintains a familiar and streamlined experience when working with LLM-based prompts.
Even with the addition of new integrations and external LLM providers, the prompt workflow remains intuitive and consistent across all project types.
-
Familiar Interface: The process of creating, selecting, and applying prompts follows the same simple steps users are accustomed to, whether using built-in templates or external LLM-powered prompts.
-
Seamless Integration: External prompt providers can be added without changing existing workflows. The interface for managing and applying prompts remains unified, allowing teams to adopt new capabilities without retraining or workflow disruptions.
-
Saved Parameters and Analytics Support:
When used in projects, prompts retain their custom Temperature and Max Token settings automatically.
The analytics module also includes LLM-related metadata, allowing reviewers to correlate evaluation results with model configuration for transparency.
With Generative AI Lab, you get the best of both worlds: exciting new features and the comfort of a familiar workflow.
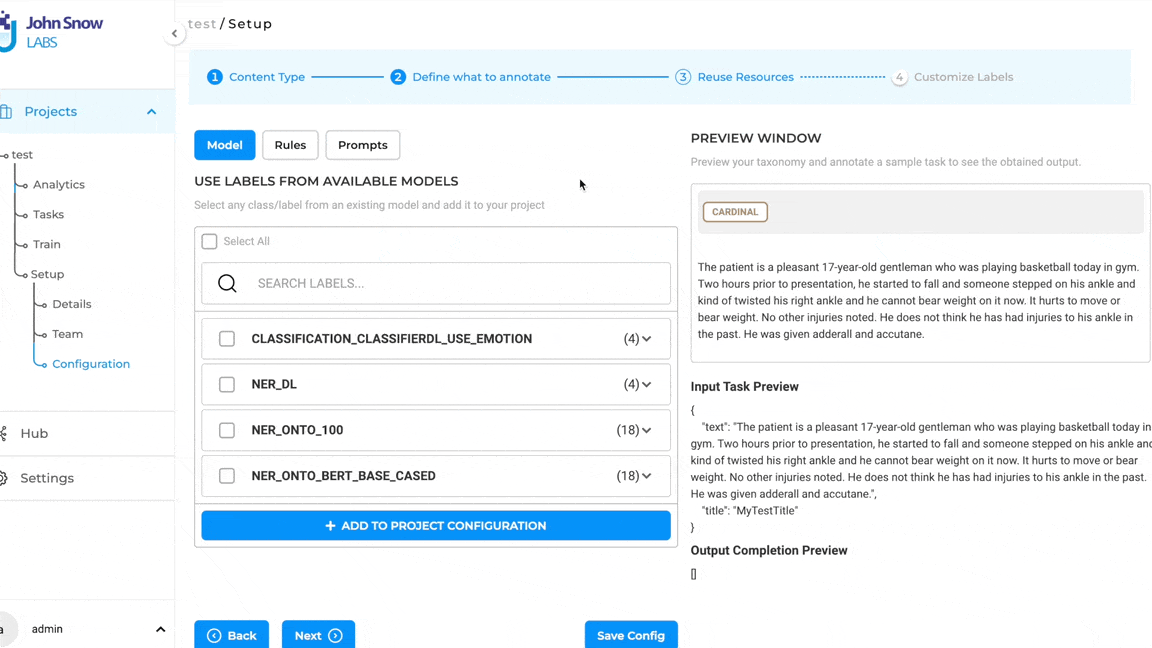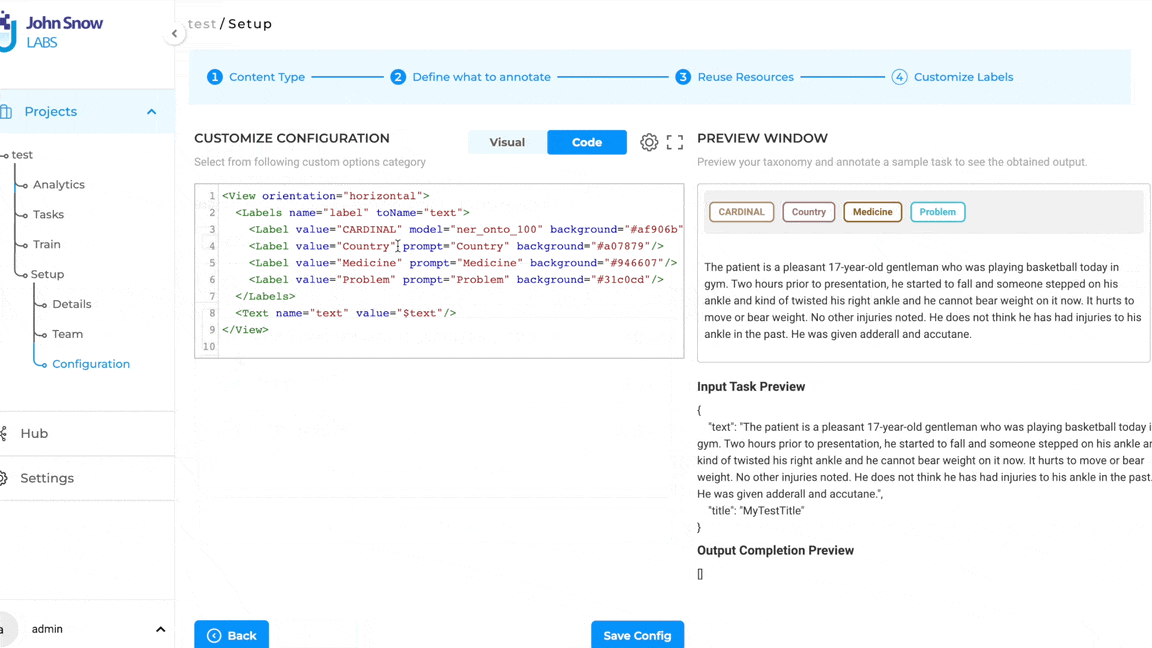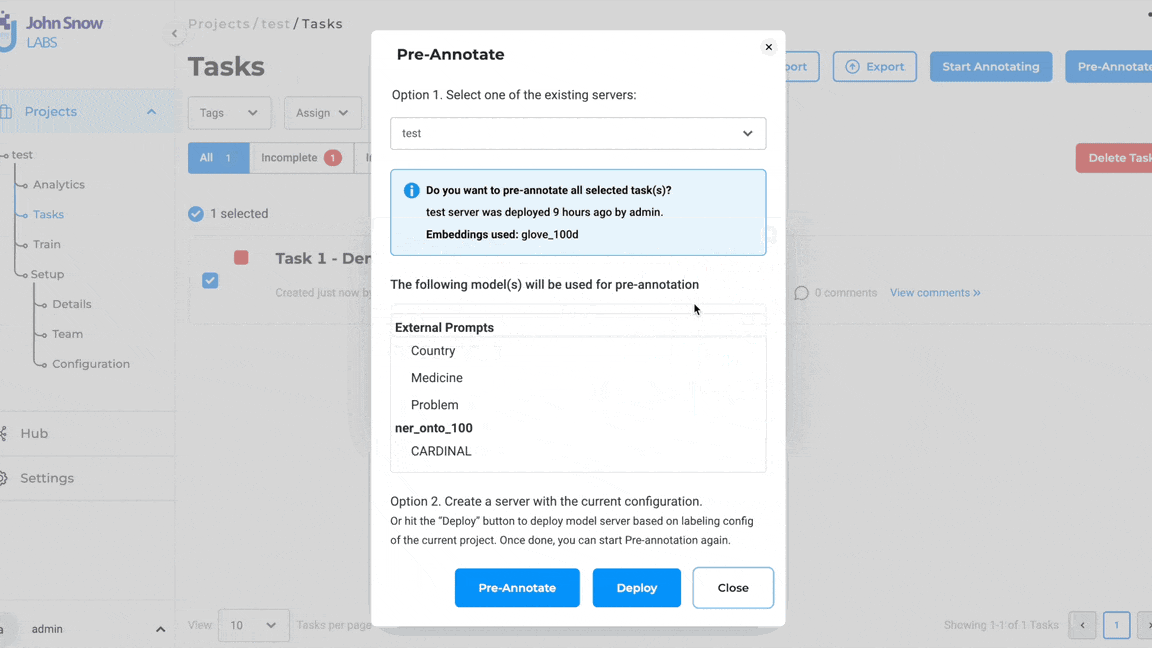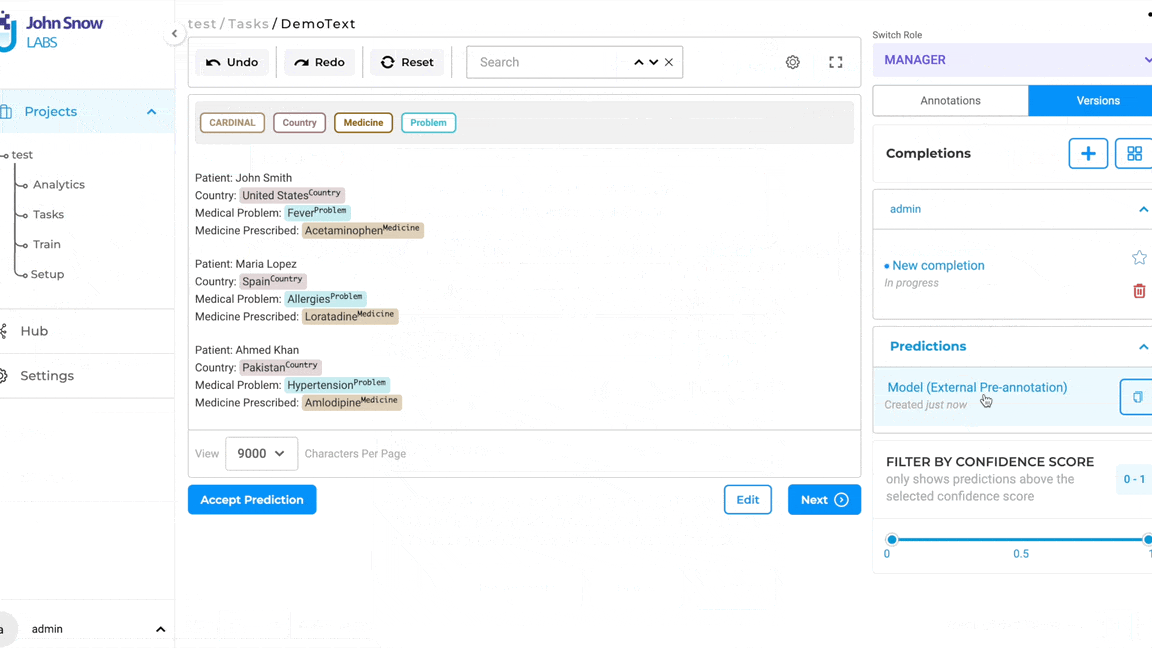
Note: Pre-annotation of tasks using LLM Prompts does not require the deployment of the pre-annotation server. The pop-up to deploy the pre-annotation server is only shown if the project configuration consists of both LLM prompts and spark NLP models.