5.5.0
Release date: 10-11-2023
Pre-annotations with Azure OpenAI Service, GPT Prompt Based Classification and Support for Free NER Rules in NLP Lab 5.5
We are thrilled to announce the release of NLP Lab version 5.5, marking another significant step forward in its Natural Language Processing capabilities. This update introduces integration with Azure OpenAI Service that provides organizations with access to OpenAI’s models with added layers of enterprise-grade capabilities, offering enhanced security, compliance, and governance features that are crucial for large organizations. This integration covers the already available NER pre-annotation and synthetic task generation but also a new feature: Prompt based Text Classification with GPT models.
Furthermore NLP Lab 5.5 adds support for FREE rule-based NER annotation, handy for cases where context can be ignored in pre-annotation scenarios (e.g. identification of email addresses, telephone numbers, list of cities, countries, etc.).
Aiming to streamline user experience, this version also brings a rich set of UI and workflow improvements that touch the project definition, annotation process, model publication to NLP Models Hub and many more. Dive into the details below to discover all that NLP Lab 5.5 has in store for you.
NEW: Integration with Azure OpenAI Service
NLP Lab 5.5 offers integration support for Azure OpenAI Service, expanding its existing pre-annotation and synthetic data generation capabilities. This new feature allows users to connect with a broader array of external service providers, providing an additional pre-annotation method in the absence of specific pre-trained models.
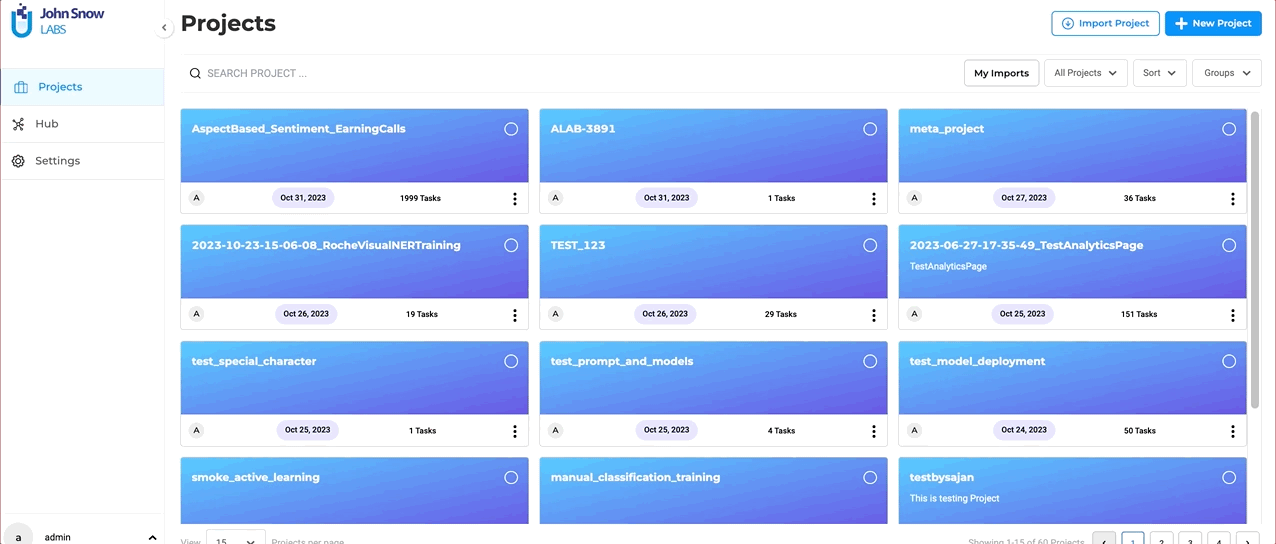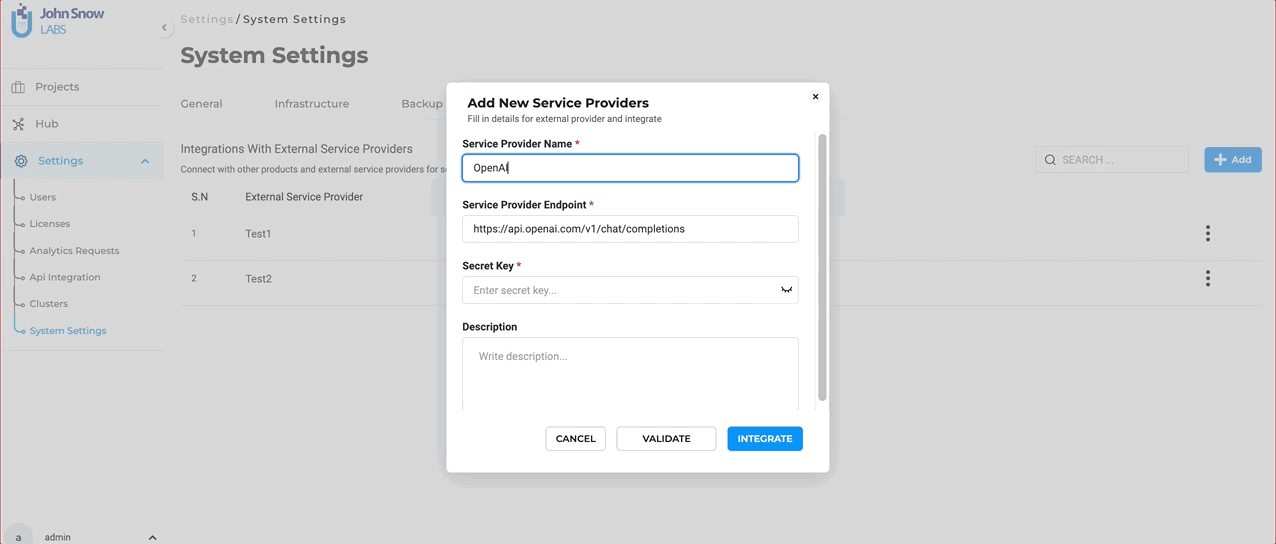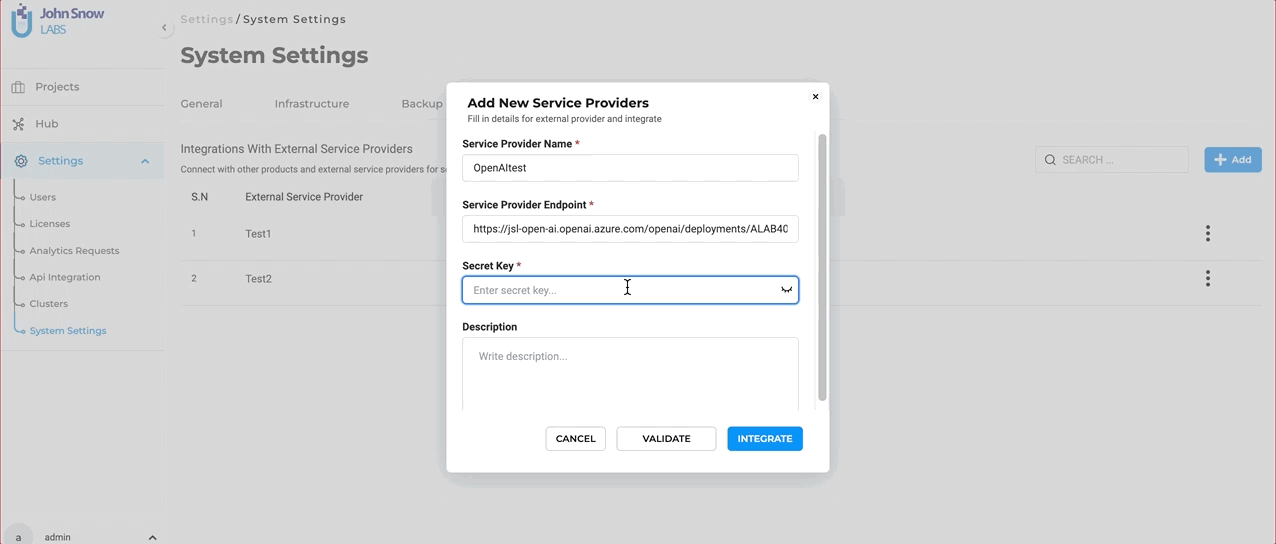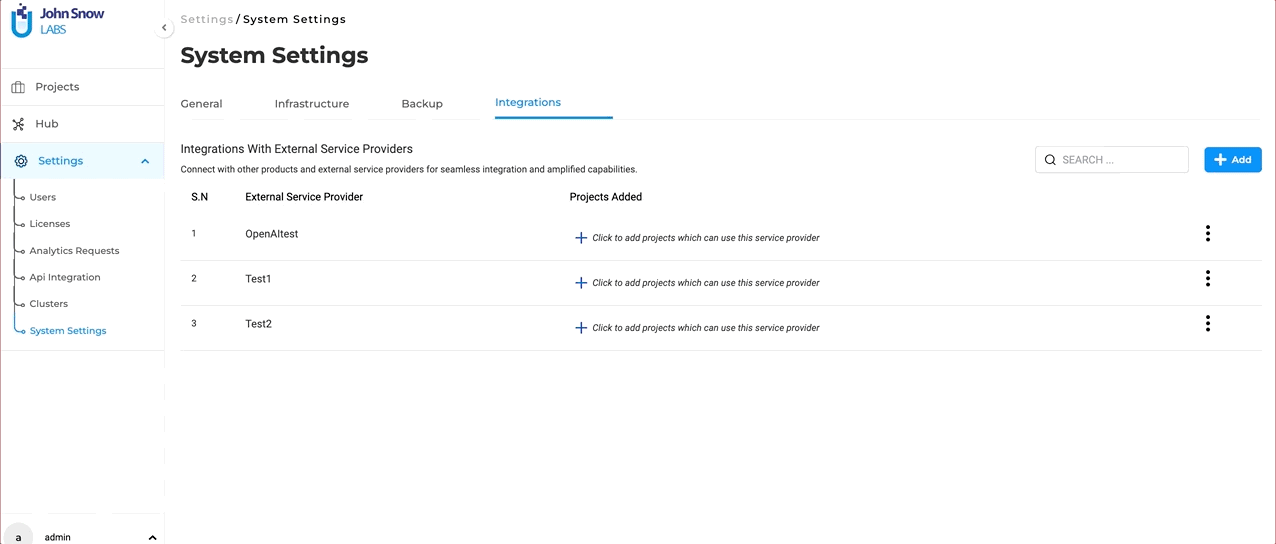
Begin by registering the external service provider with NLP Lab. Currently NLP Lab supports Azure OpenAI and OpenAI as service providers. Here’s a quick guide for this:
Getting Started
- On your NLP Lab instance, go to the “Settings” page and then click on the “Integrations” tab.
- Click the “Add” button, and fill in the required fields: “Service Provider Name” and “Secret Key.”
- Click “Validate” to ensure a successful connection between the service provider and NLP Lab.
- Click “Integrate.”
Creating and Testing NER Prompts:
After integrating the external service provider, you can create and test the NER prompt.
- Navigate to “Hub” and then to the “Prompts” page.
- Click the “+ Add Prompt” button.
- Select the “Create external LLM Prompt” tab.
- Provide a name for the prompt, select the entity from the type dropdown, and choose the desired service provider from the service provider dropdown.
- Enter the appropriate prompt in the “Prompt” text box.
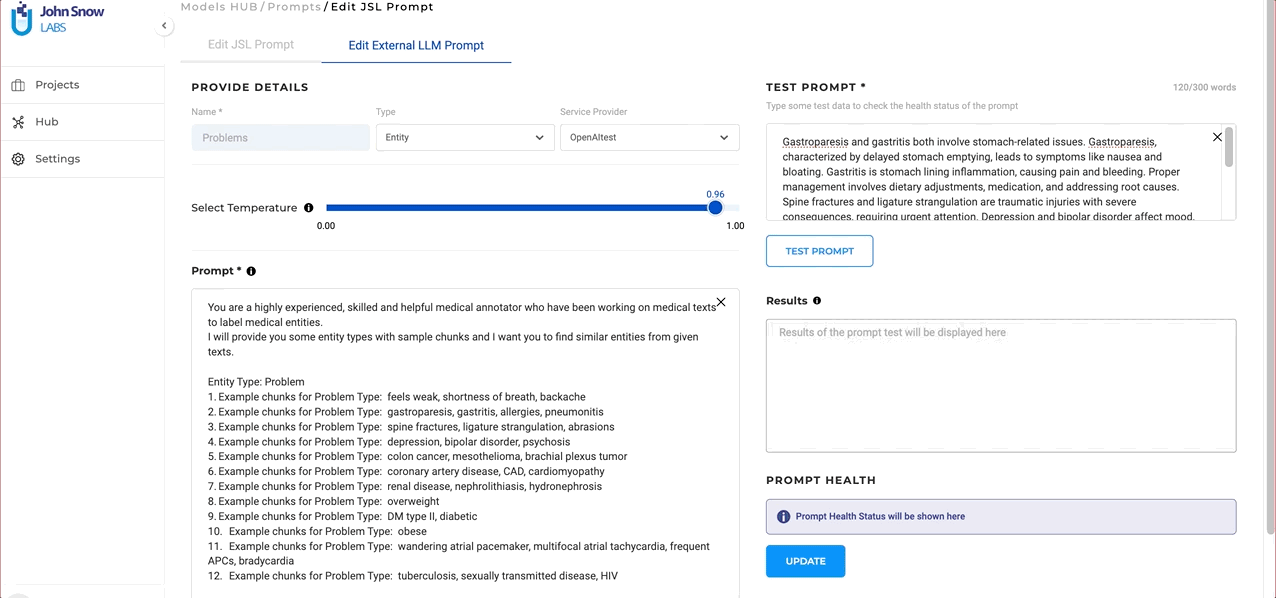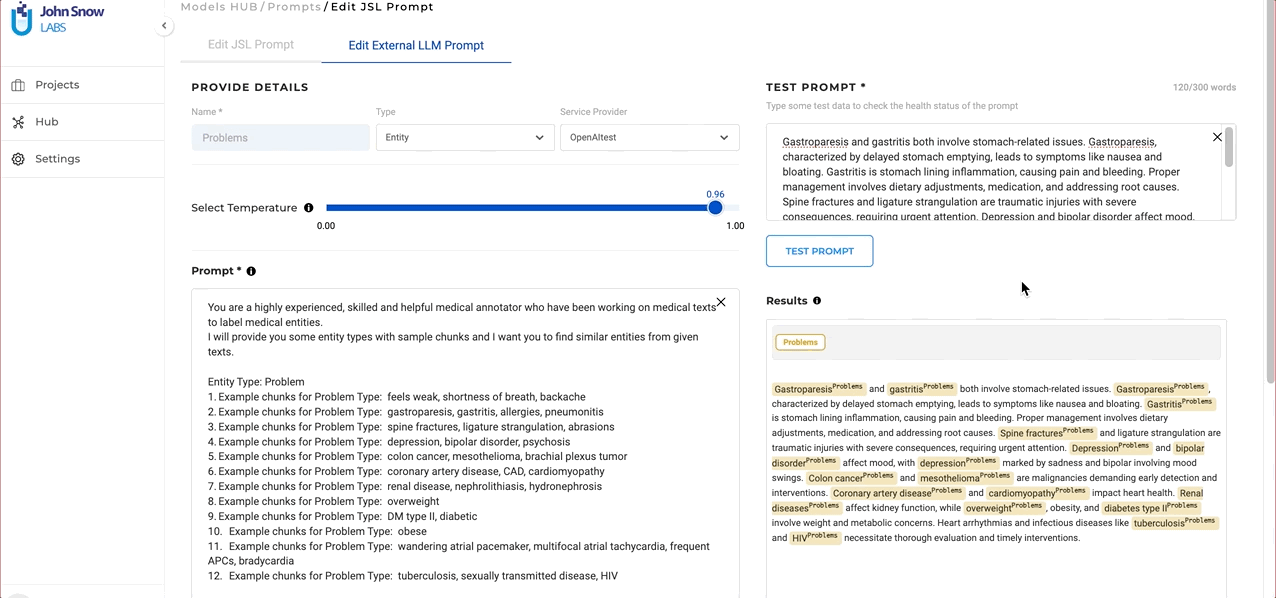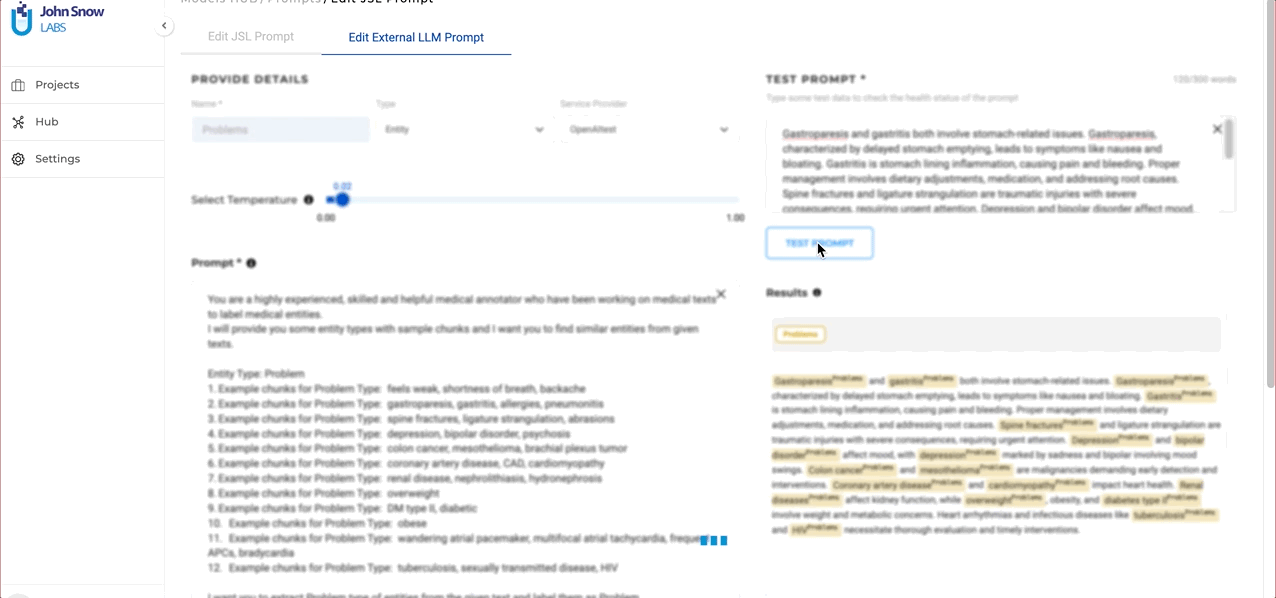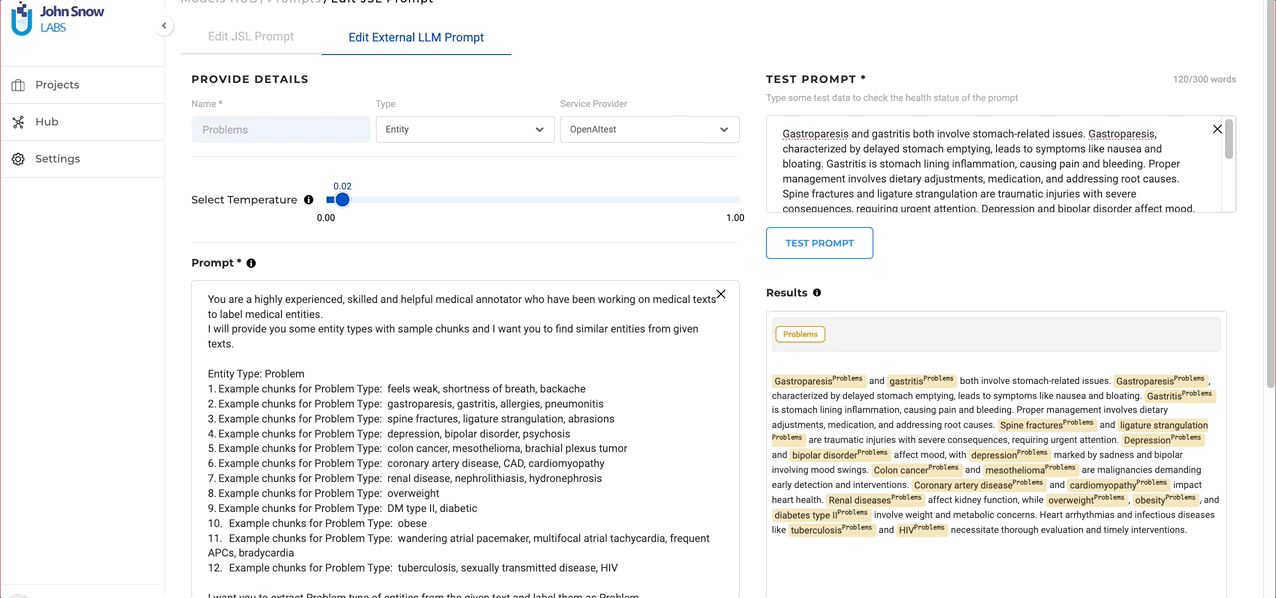
- Before saving the prompt, test it by entering text in the “Test Prompt” text box and clicking on the “Test” button.
- Experiment with different temperature values during testing to ensure the desired results.
- After testing and confirming that the prompt is working as expected, click on the “Save” button to save the prompt.
Using GPT Prompts in a Project
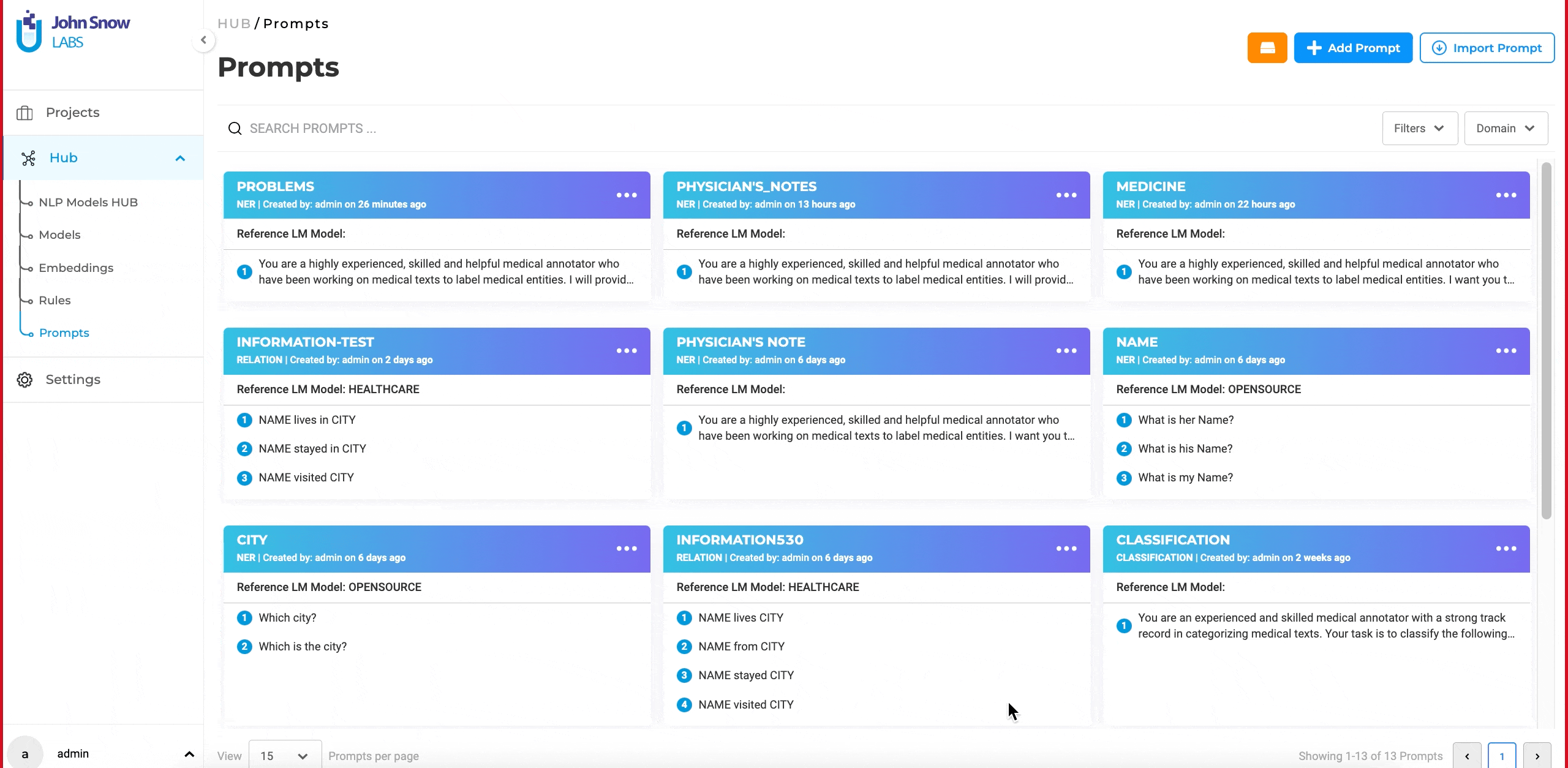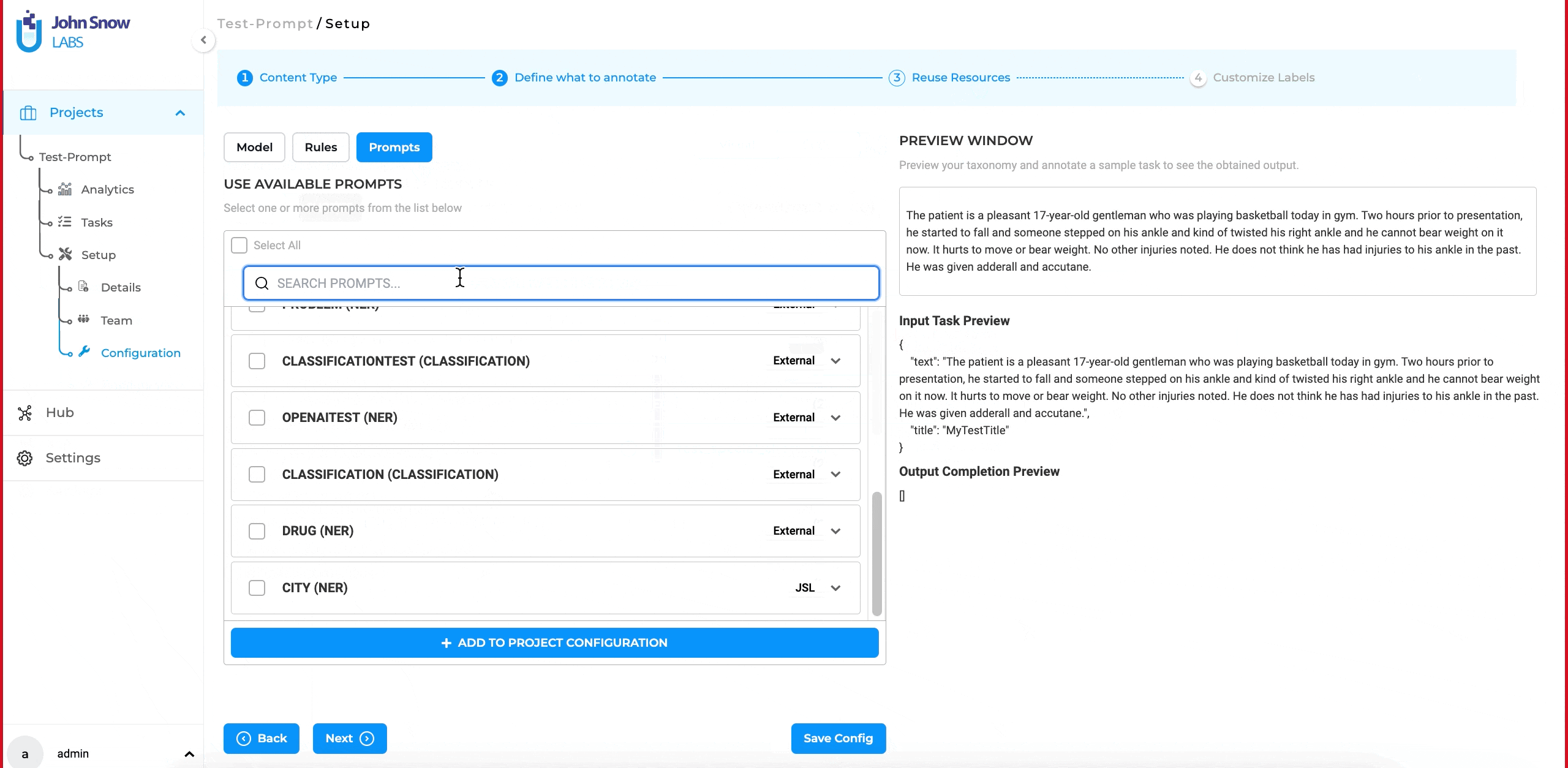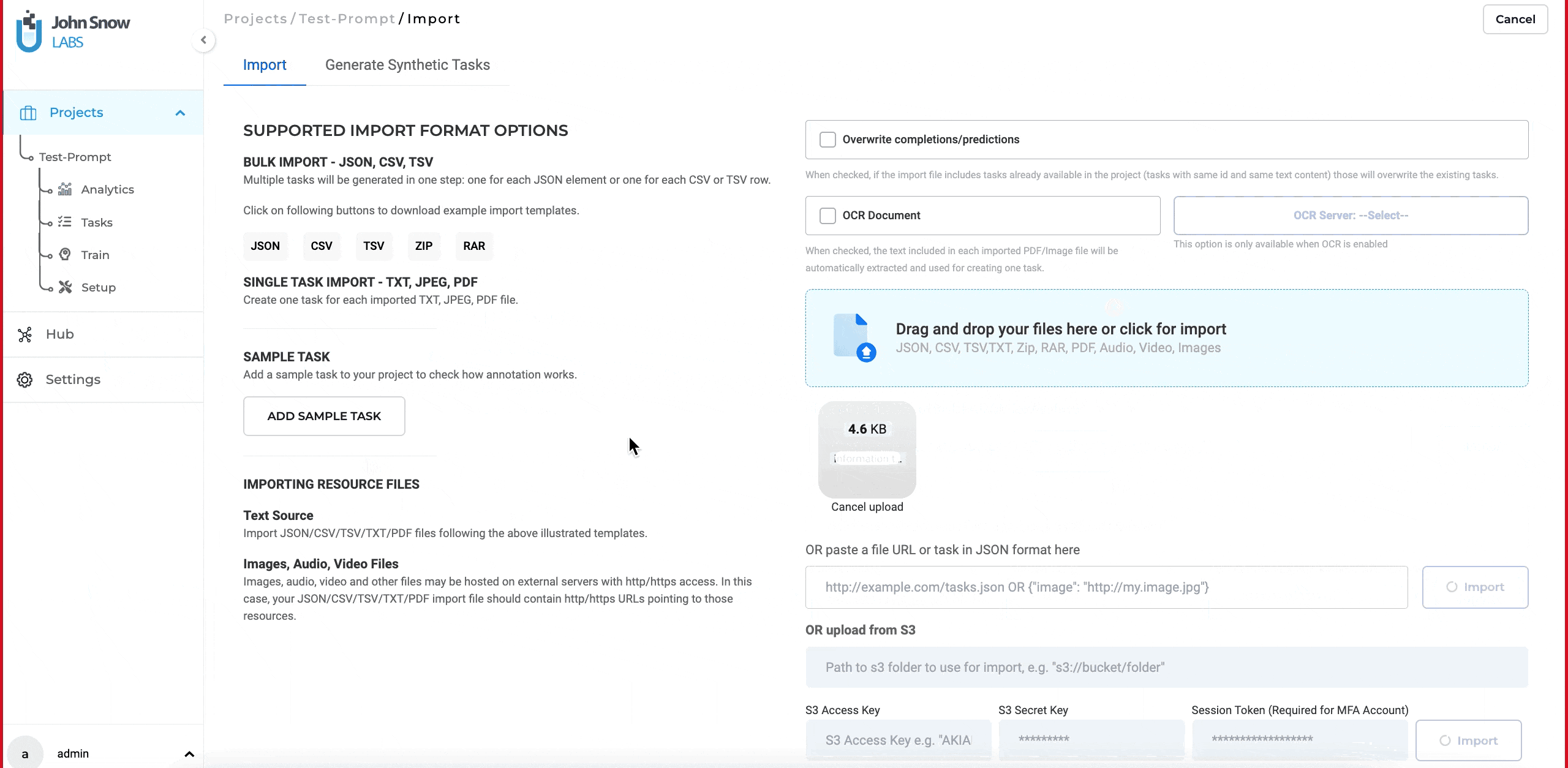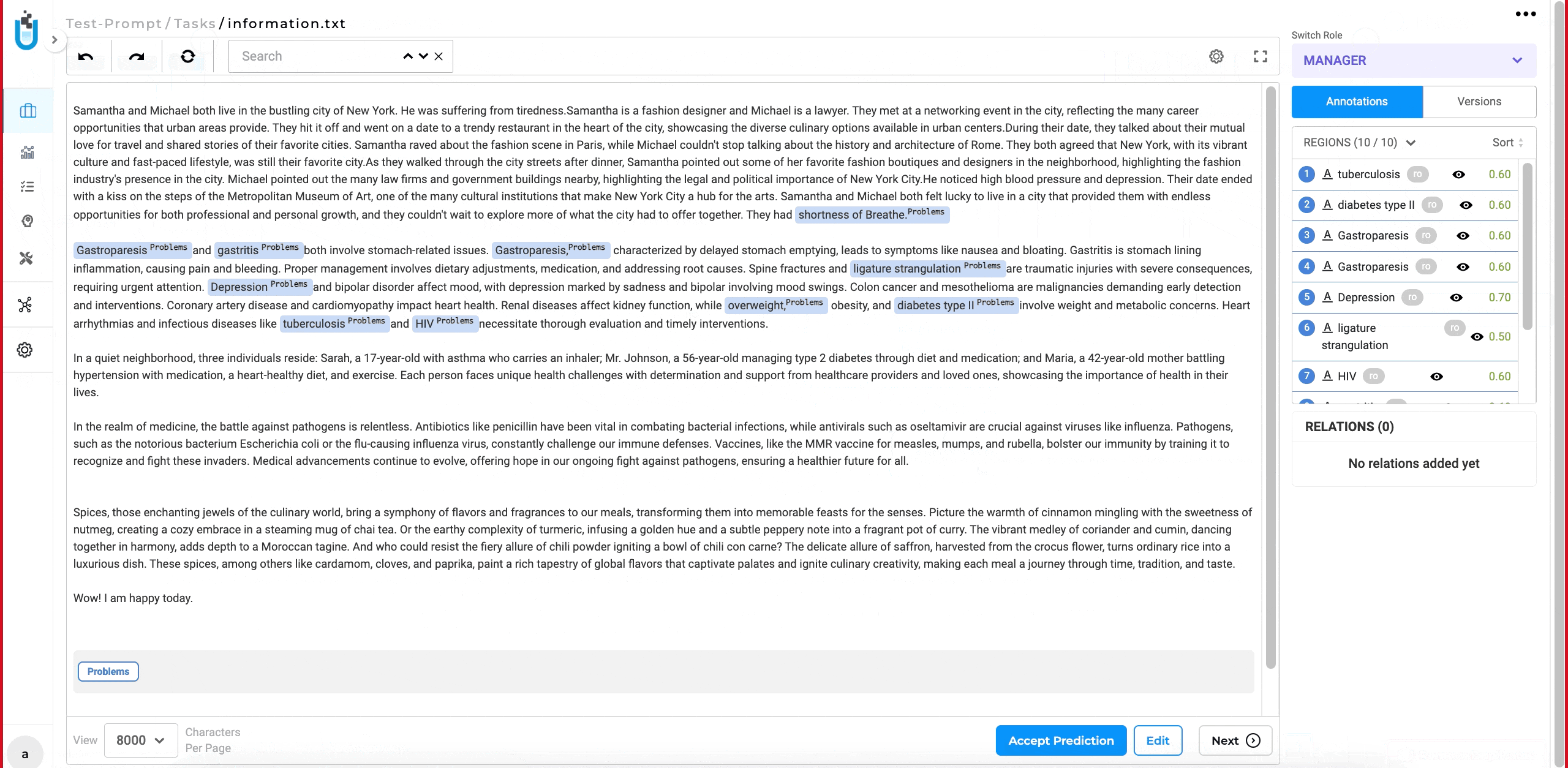
NER prompts can be used in a project just like regular Zero Shot prompts. You can find the prompt under the “Prompt” tab or the “Reuse Resource Page” in the project configuration. Add and use it for pre-annotation, similar to Zero Shot prompts, rules or models.
Generate synthetic tasks using Azure OpenAI
In addition to creating new prompts, Azure OpenAI can also be used to generate synthetic tasks. Here’s a quick guide:
Setting up and Validating the New Service Provider:
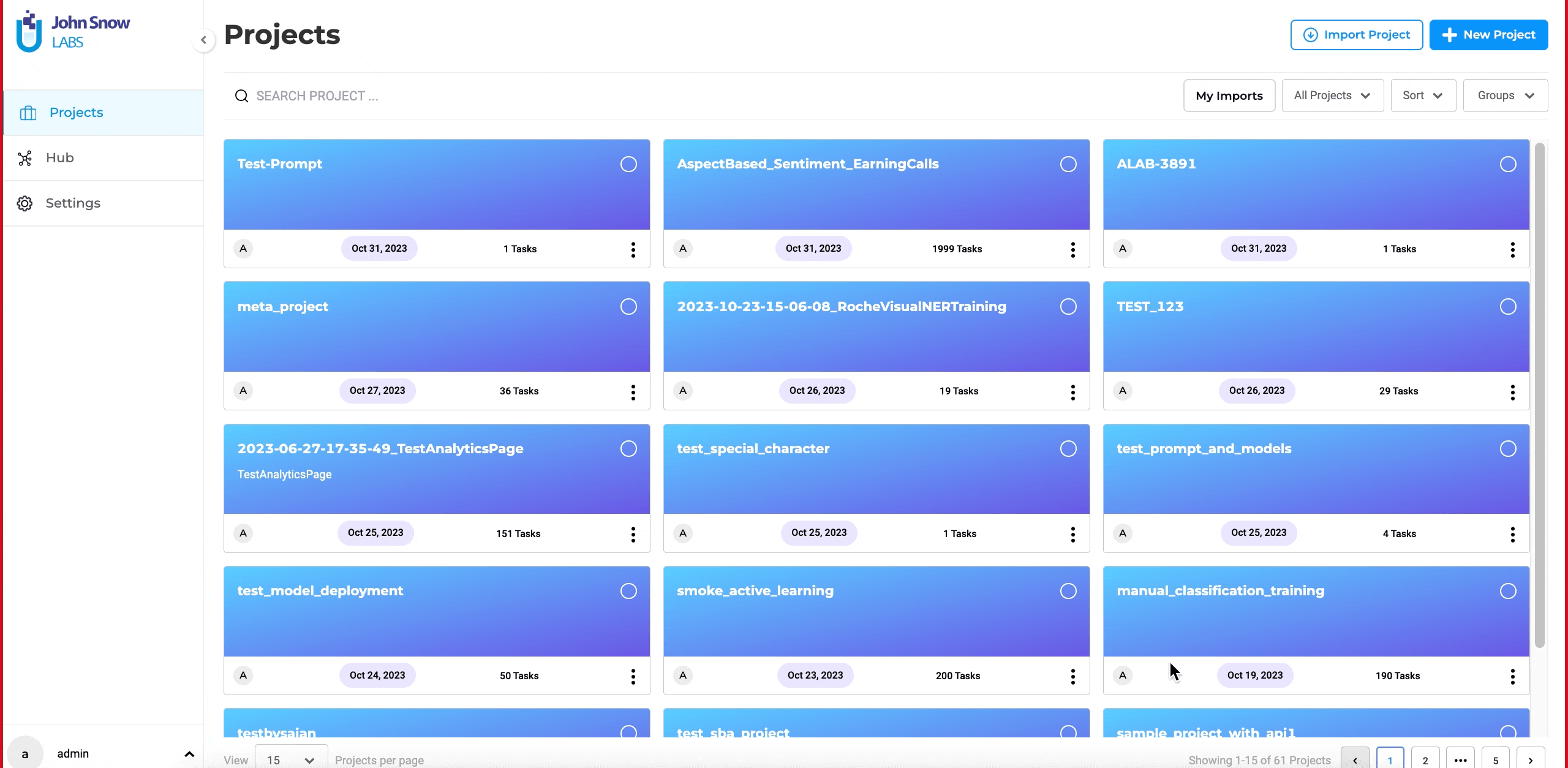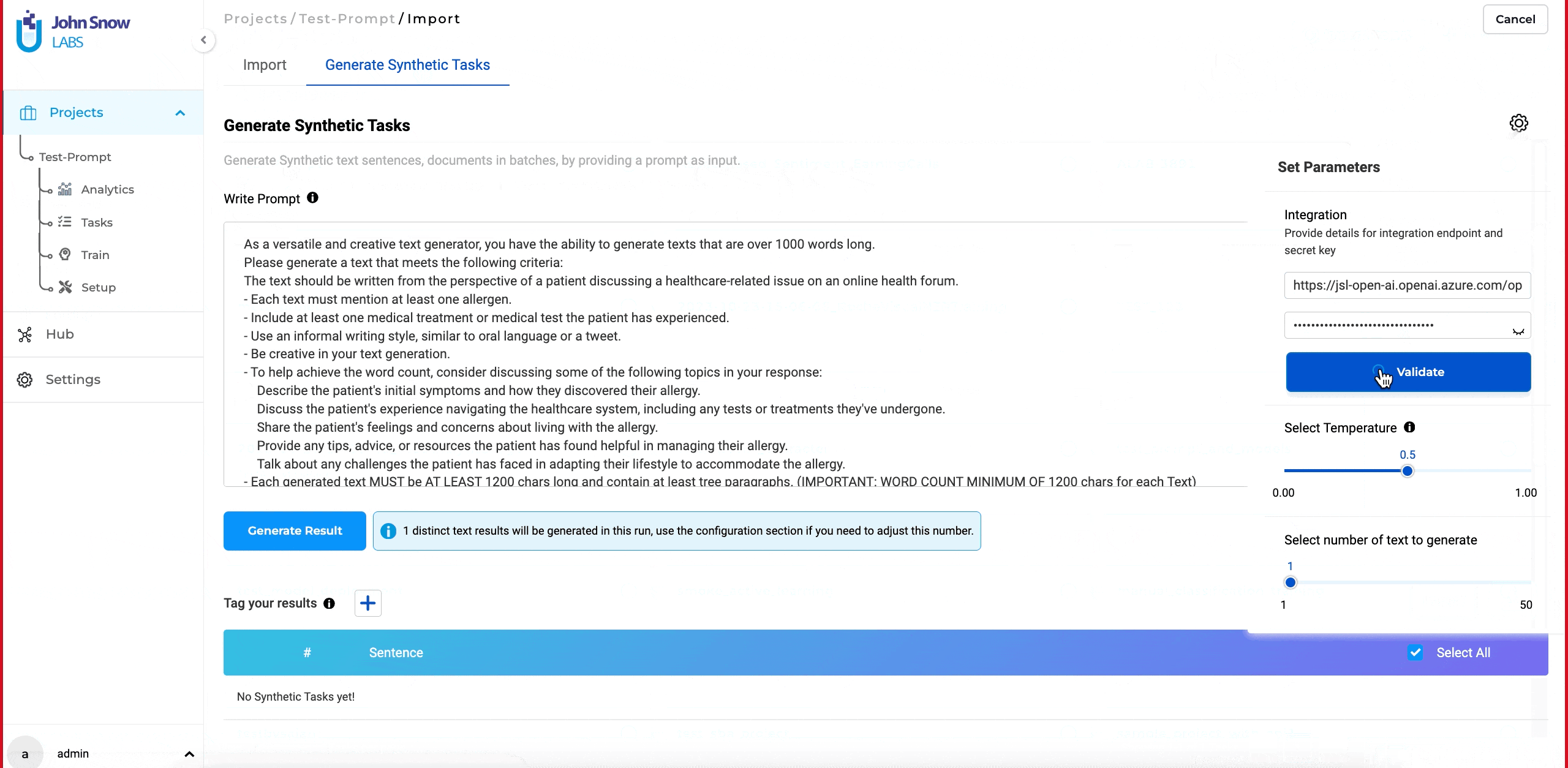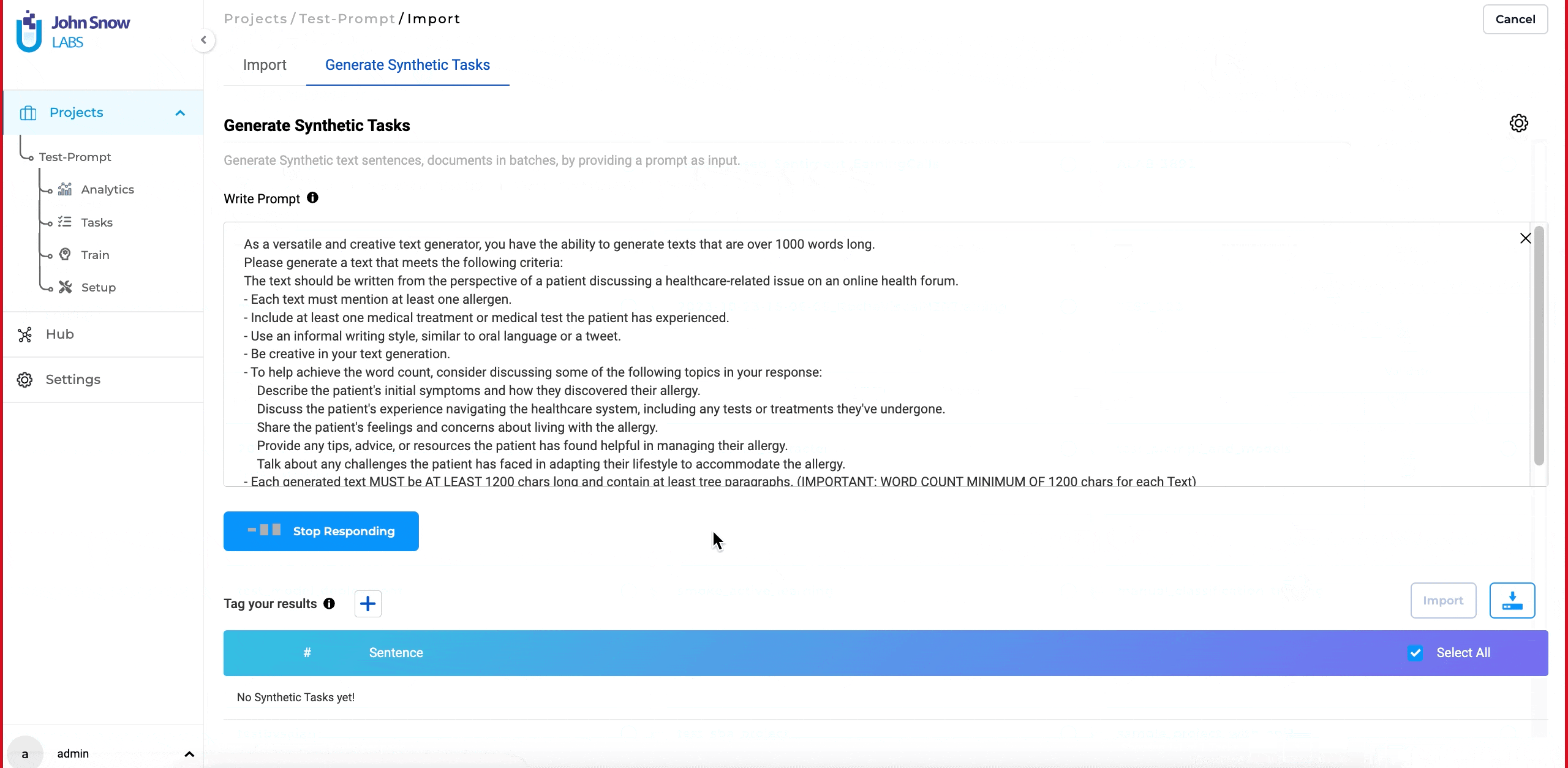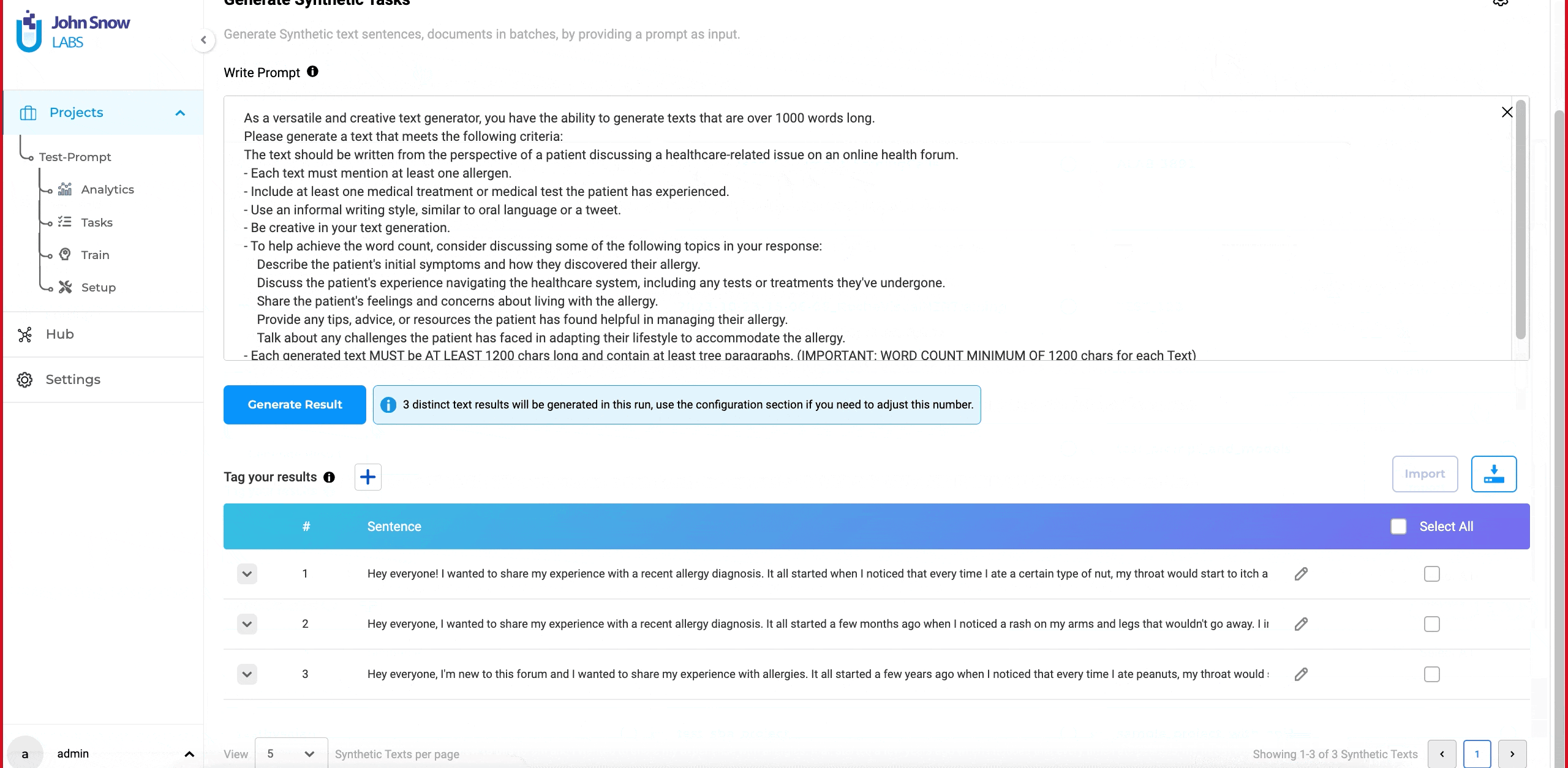
- From the task page, click on the “Import” button and navigate to the “Generate Synthetic Task” page.
- Provide an appropriate prompt in the “Write Prompt” text box and click on the settings icon located on the right side of the page.
- Enter the API endpoint URL and secret key, then click on “validate.”
- After validating the connection, set the desired temperature and the number of tasks to generate.
- Click on the “Generate” button to create synthetic tasks.
It’s important to note that the user interface experience remains unchanged for import and pre-annotation. The application continues to provide the same user-friendly flow and experience as it always has.
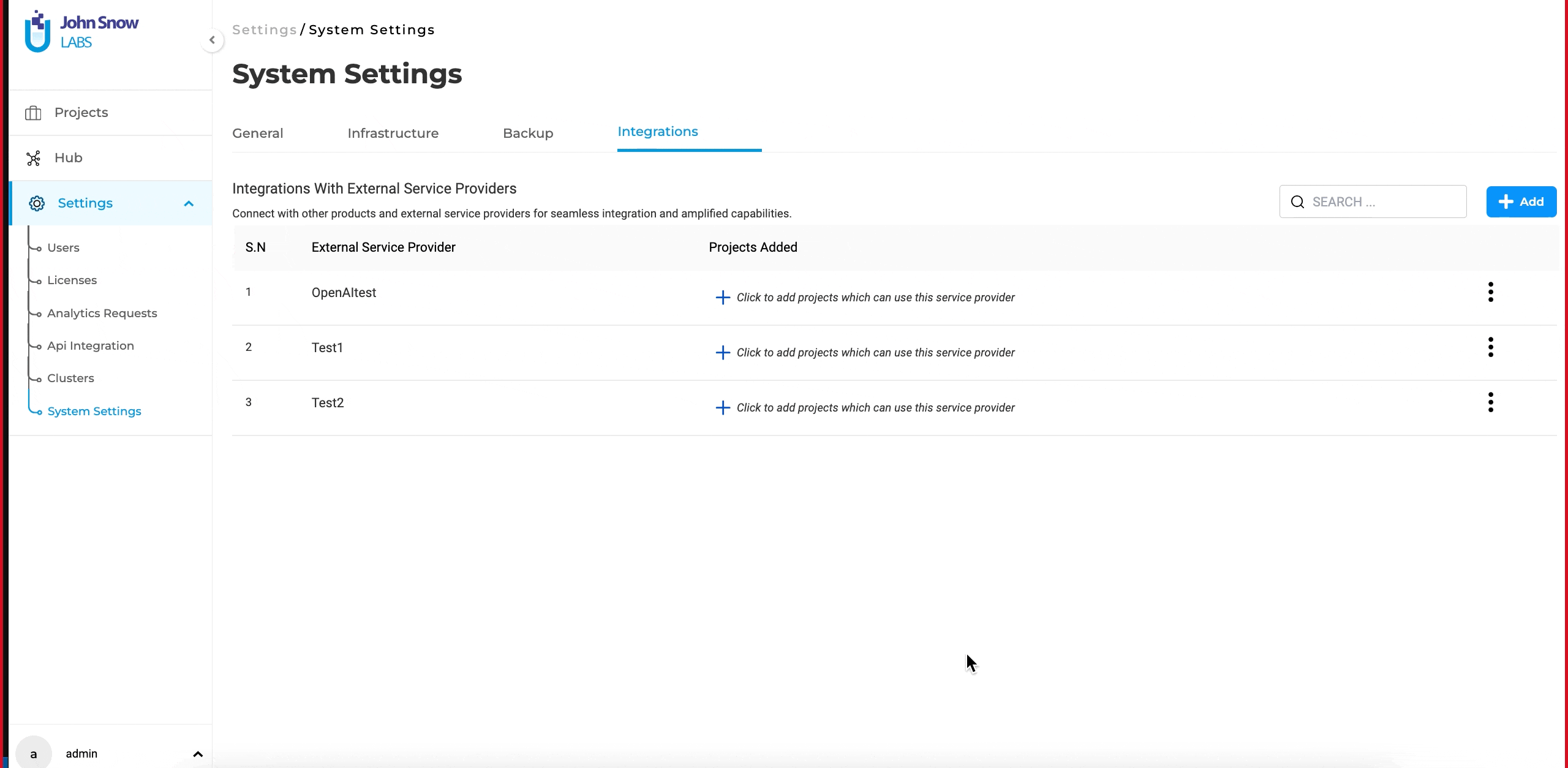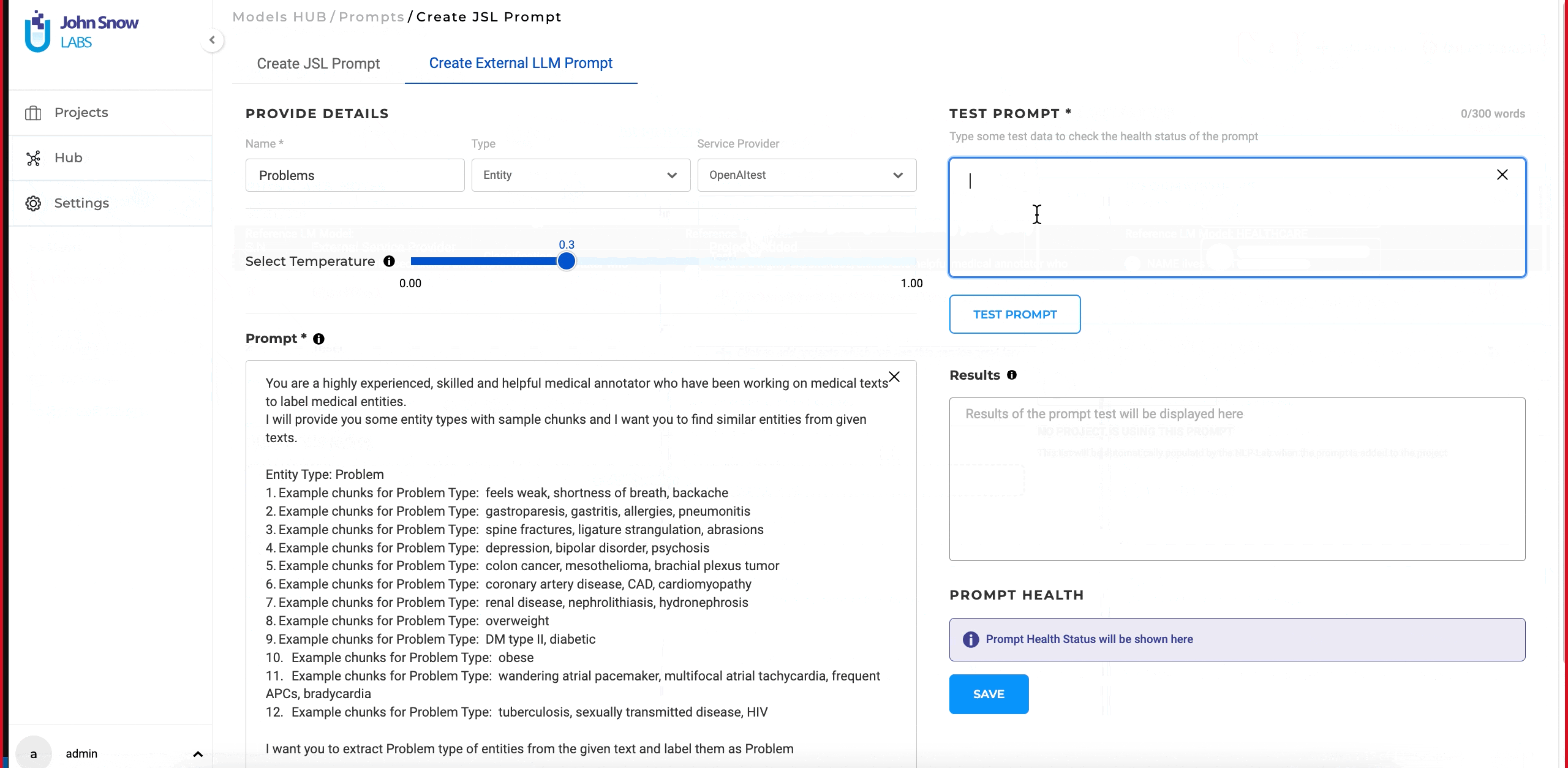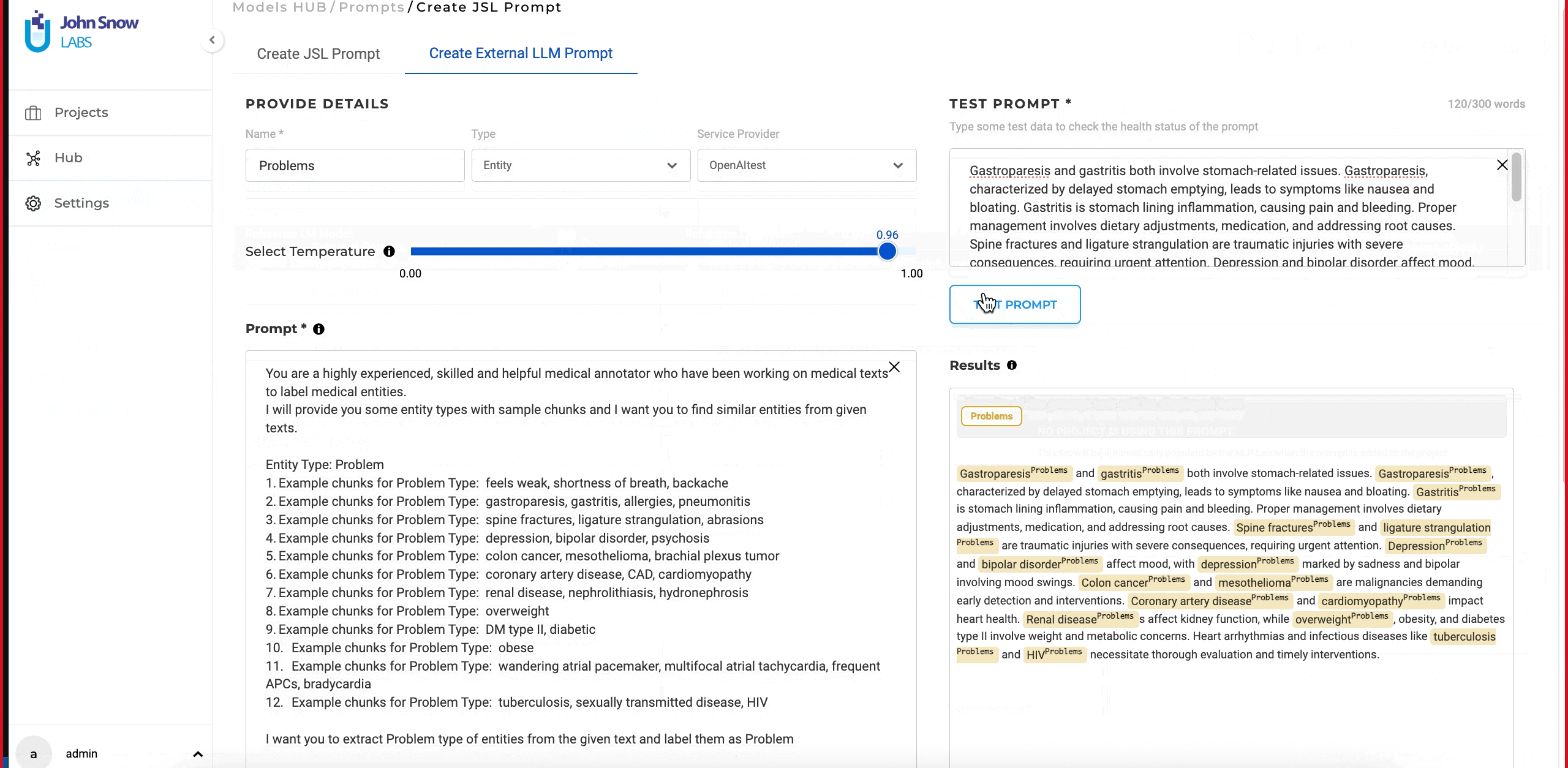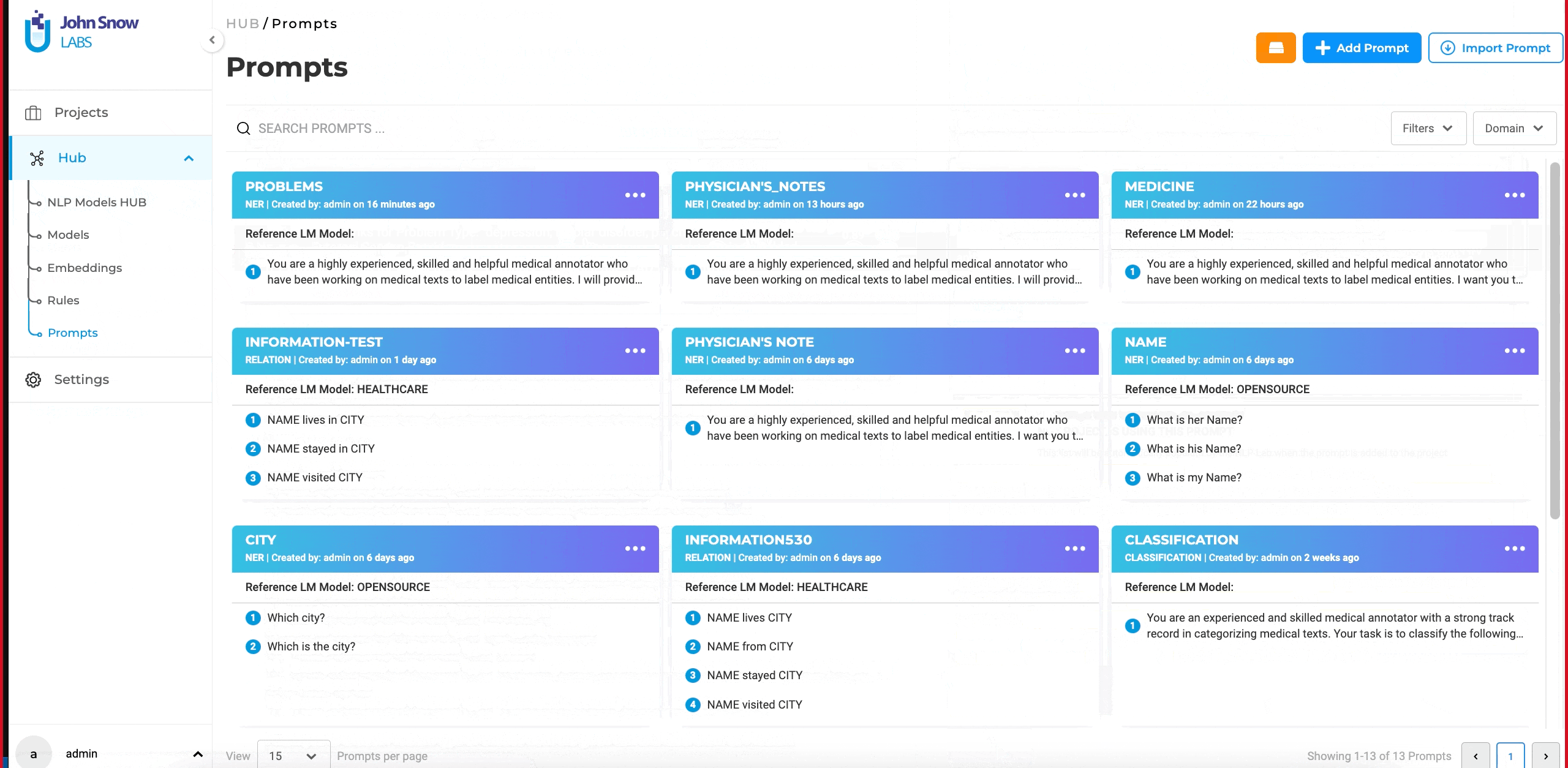
Adjustable Temperature Parameter for External LLM Prompts
In this version users can fine-tune the diversity of their output when creating GPT prompts. This is achieved through the use of a “temperature” parameter. This feature gives users control over the diversity of their prompt outputs: a higher temperature yields more varied responses, while a lower temperature produces more predictable results. This adjustability allows users to find the perfect balance for their specific needs and can be altered as necessary for fine-tuning prompt outputs. While creating GTP LLM prompts, users can experiment with different temperature settings to understand how it affects the output. Users can also edit the prompt and update the temperature as needed to make sure that the desired output is obtained. This flexibility empowers users to fine-tune their prompts to match their precise requirements.
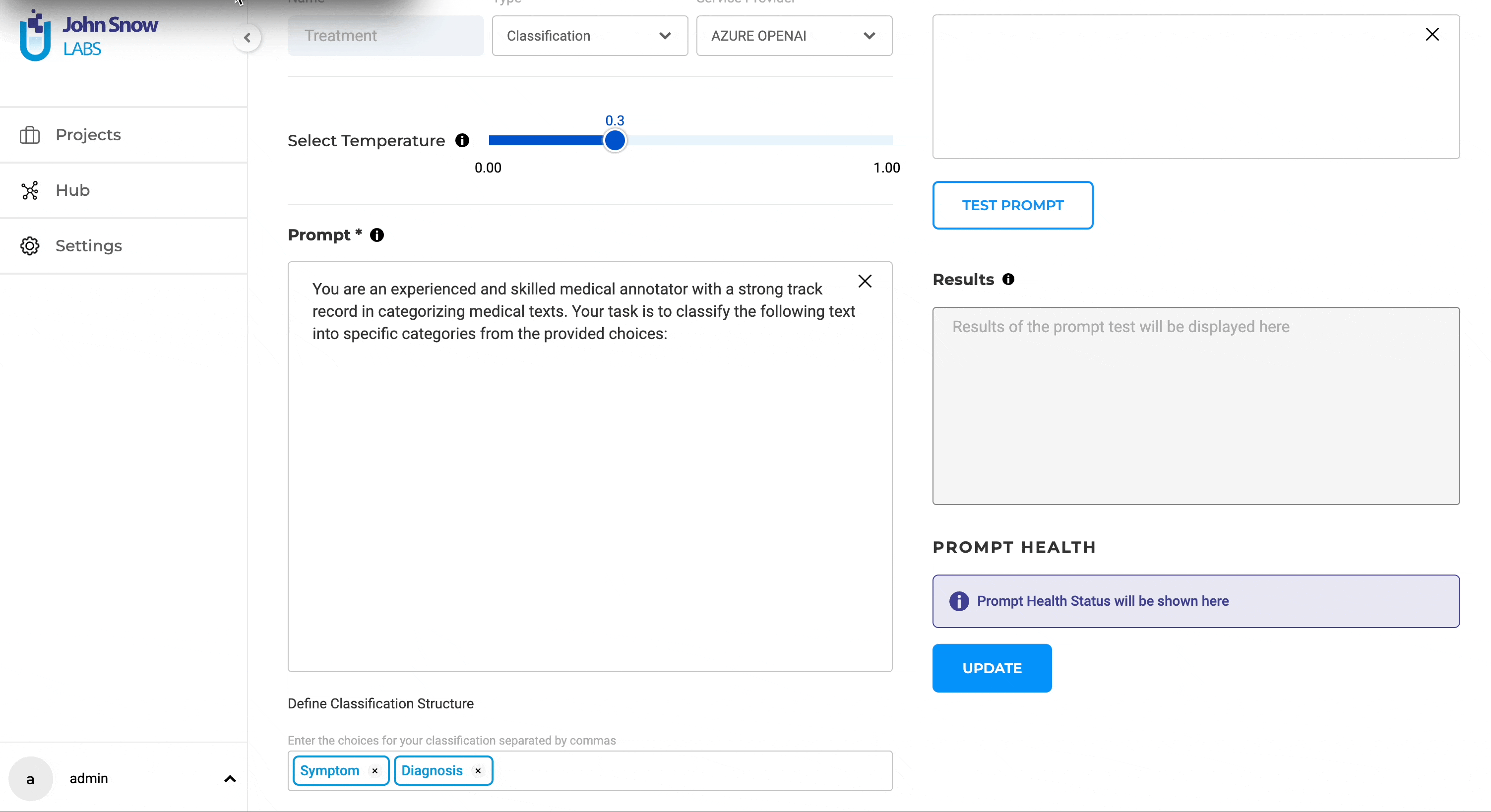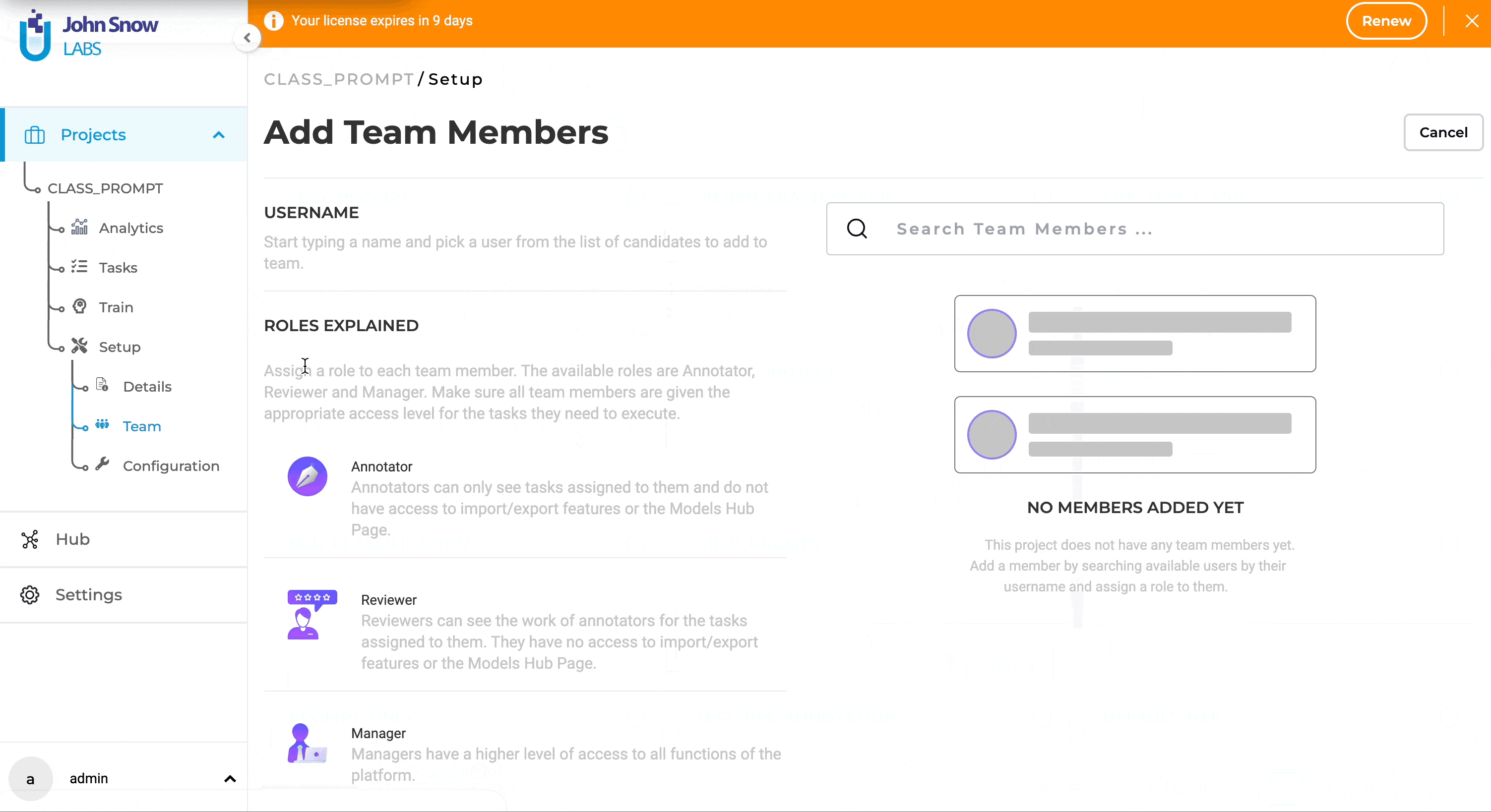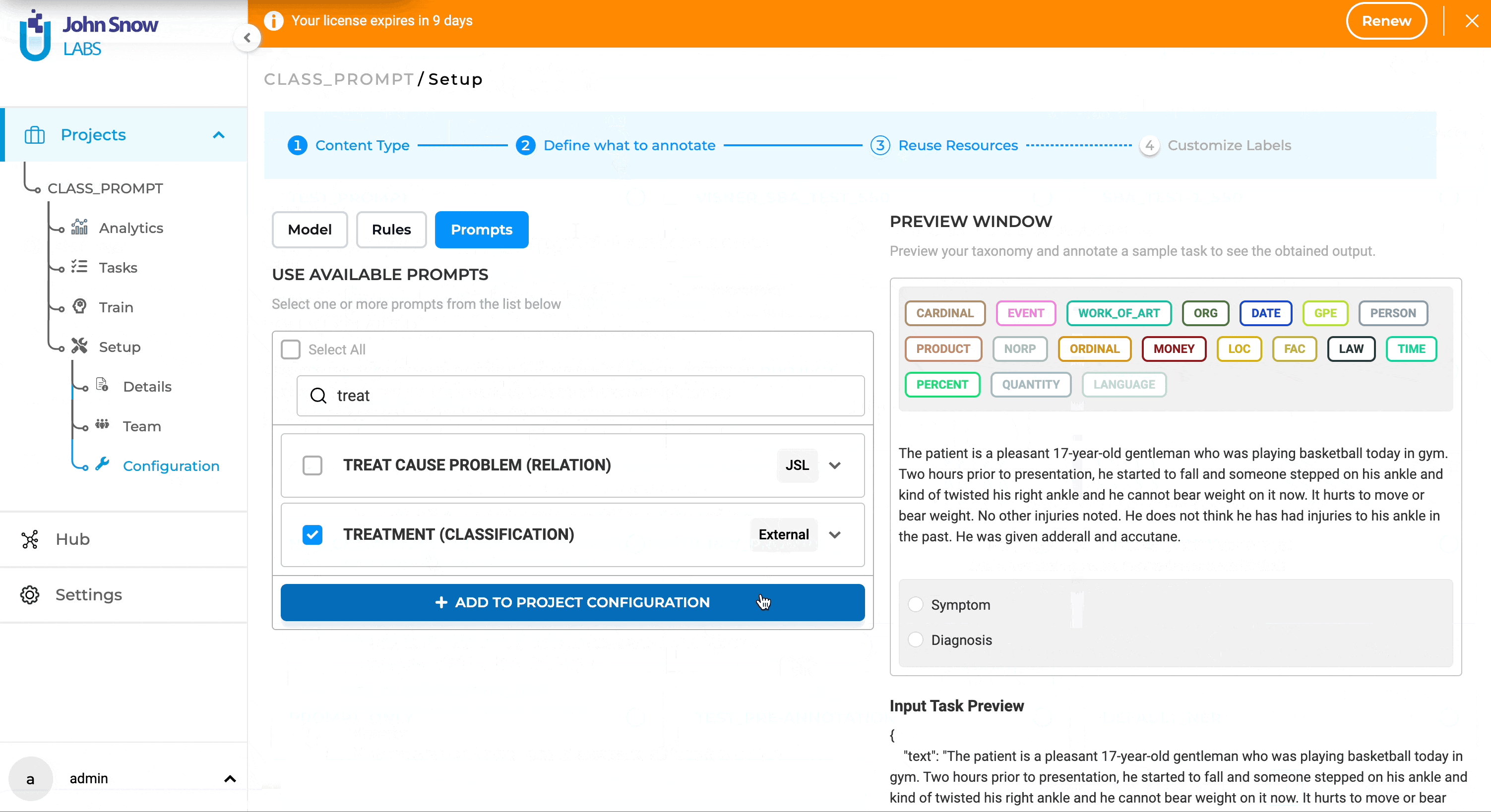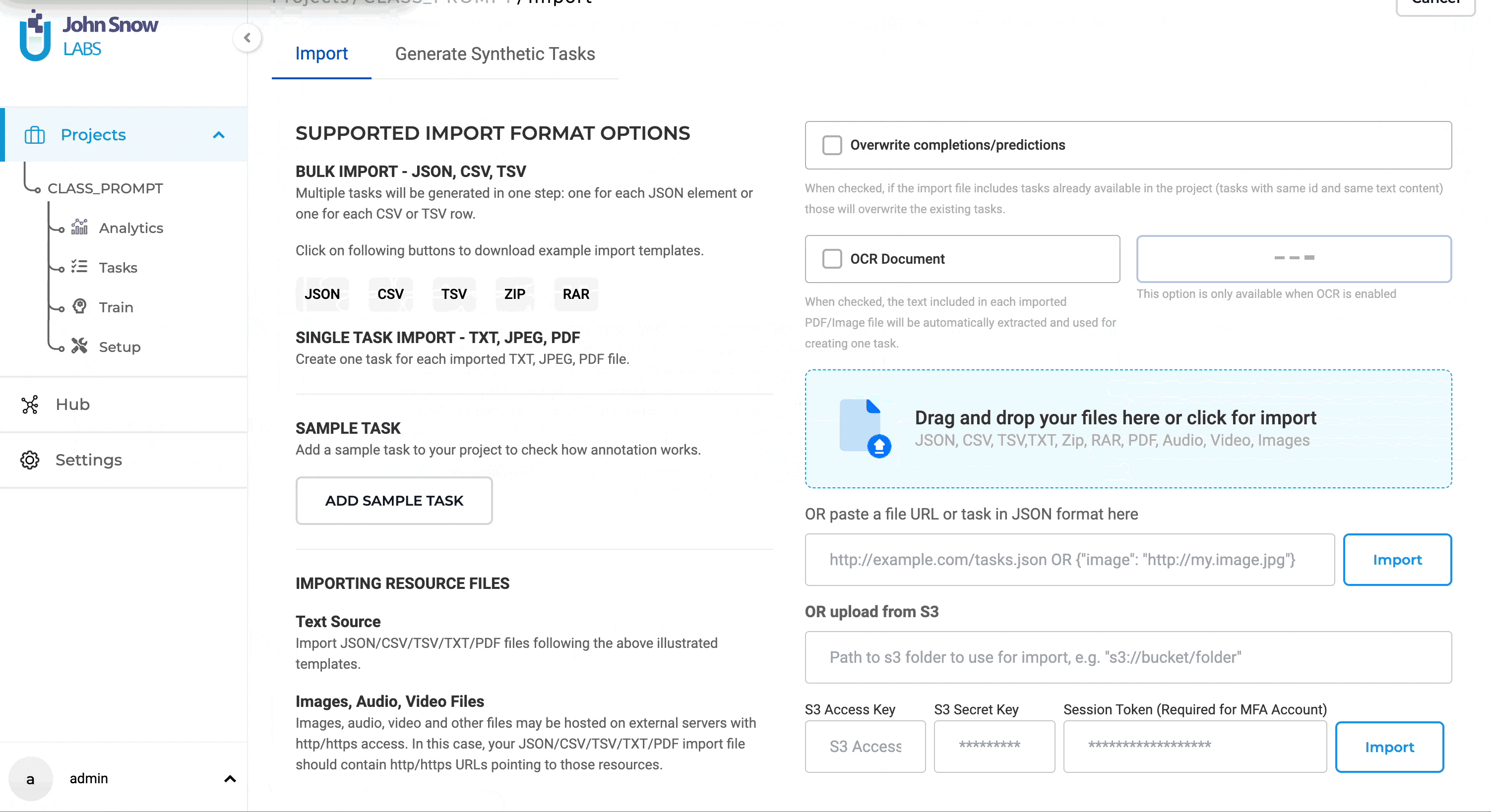
NEW: Prompt based Classification available with OpenAI and Azure OpenAI Services
NLP Lab 5.5 introduces Text Classification with LLM prompts using external services. This new feature empowers users to access a more diverse array of prompts, enabling them to harness external expertise for crafting pre-annotations. This feature becomes particularly valuable when pre-trained models are not readily available, serving as an alternative pre-annotation solution.
Classification prompts are supported by both Azure OpenAI and OpenAI service integrations.
Definition and Testing of Classification LLM Prompts:
Users can generate LLM prompts through the dedicated Prompt page within the Hub of Resources. Within the dedicated External LLM Prompt creation interface, the following details can be added to define the new LLM prompt:
- Name: Provide a clear and descriptive name that precisely conveys the prompt’s type and purpose.
- Type: Specify the type as “Classification.”
- Service Provider: Users can choose the specific service provider they have previously configured via the Integrations Page.
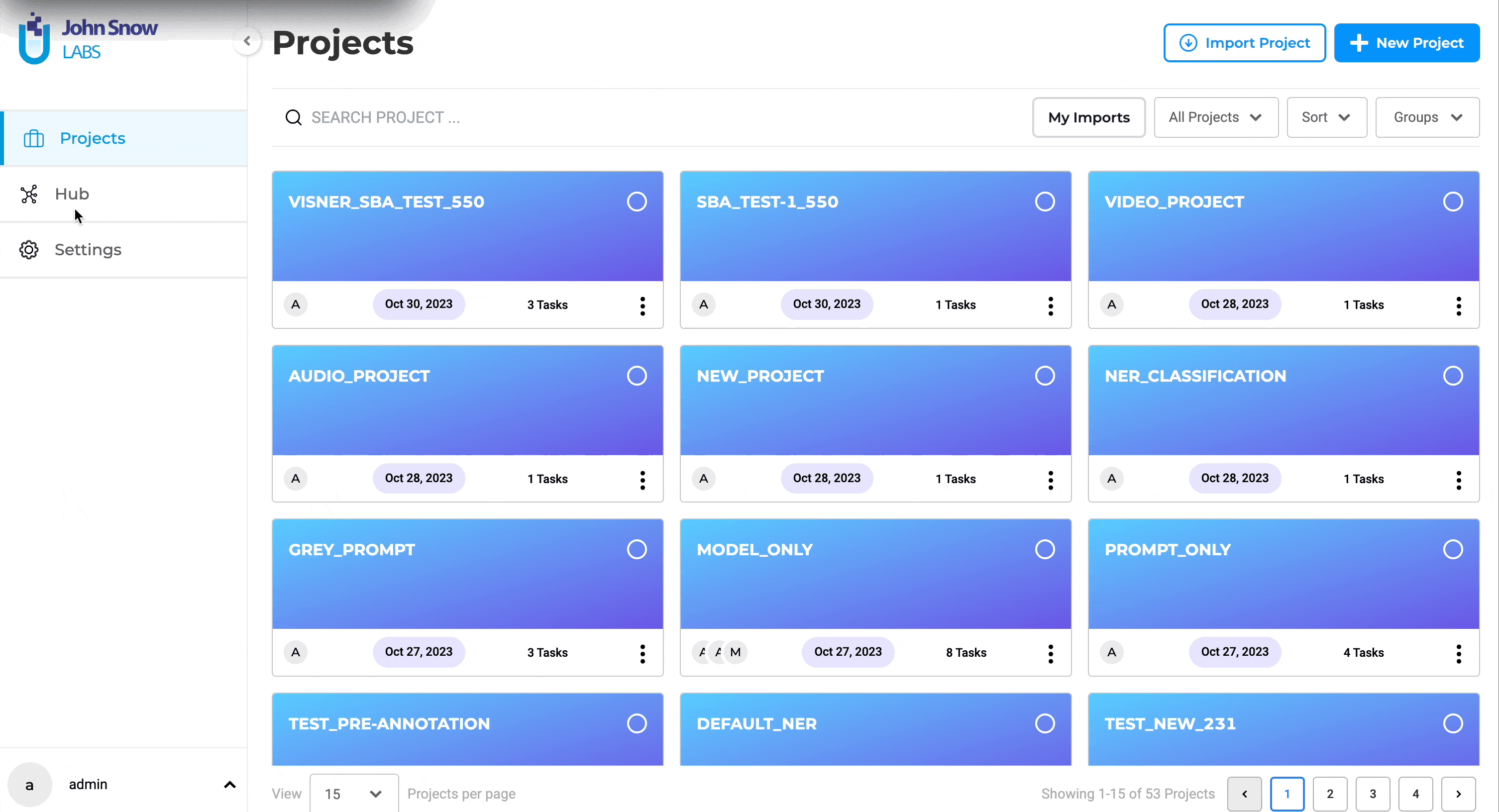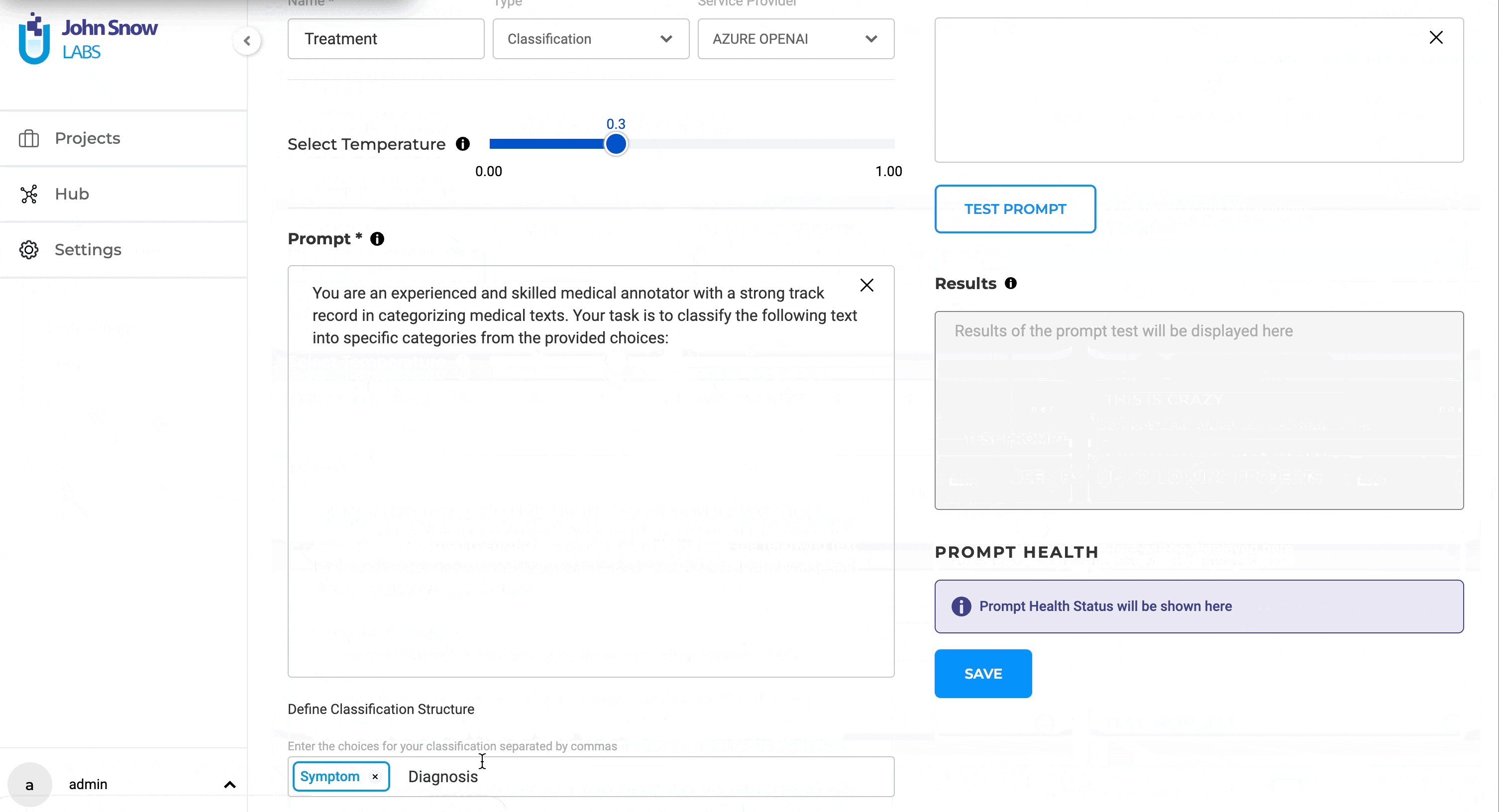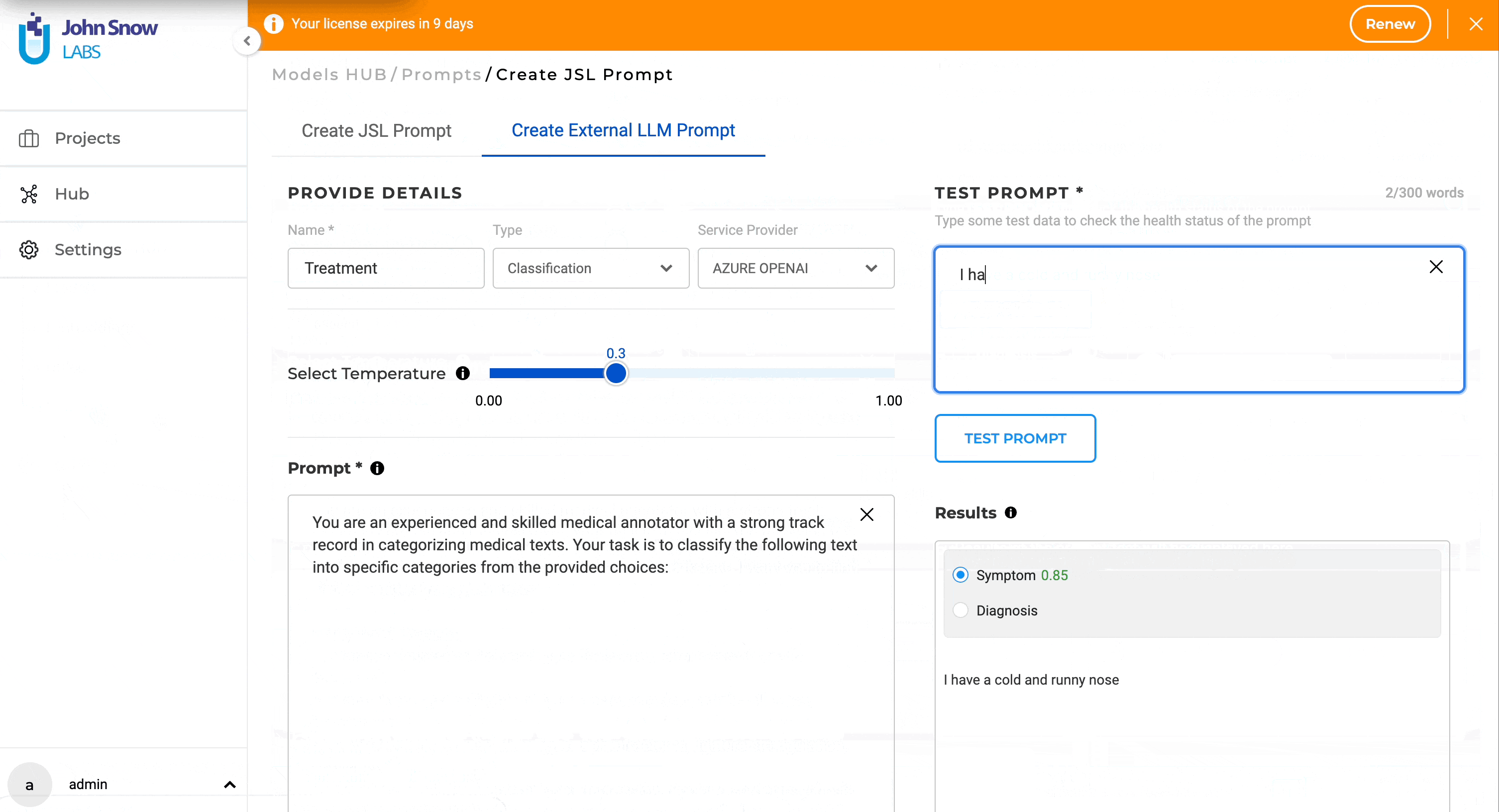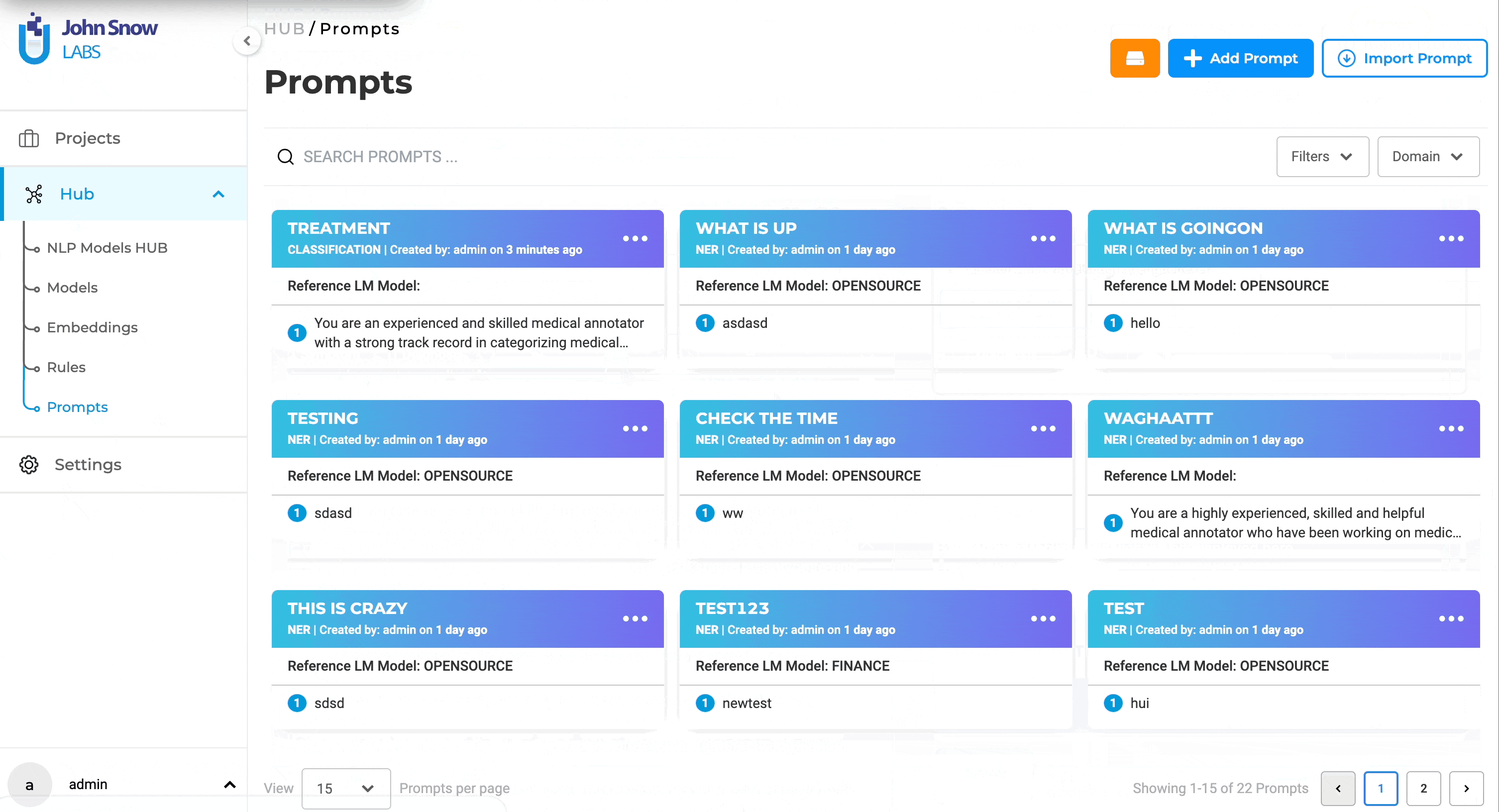
- Test in Real-time: The ability to test ChatGPT/Azure Open AI prompts in real-time during creation is provided right on the creation page. As prompts are crafted, users can immediately gauge their performance on test data. This not only facilitates immediate feedback but also ensures the final prompt aligns seamlessly with the user’s objectives.
The advantage of using external prompts lies in their simplicity and their power resides in the domain understanding incorporated in the GPT models used. Prompt crafting is user-friendly and can be done swiftly, which allows for rapid testing and integration into custom projects as necessary.
We continue to prioritize usability, ensuring a seamless transition or addition of external prompts. Incorporating external prompts is a straightforward process, with the interface and steps for prompt creation, selection, and integration retaining their intuitive and user-friendly design, much like the Entity Extraction with External Prompts. While classification prompts bring a layer of innovation to the annotation process, the core workflow remains unchanged and aligned with the existing experience.
Support for Free NER Rules
We are excited to announce the introduction of a new feature in version 5.5 of NLP Lab: Support for Free Rules. This feature enhances the capability of our product by allowing users to define and apply custom rules for pre-annotation, which can significantly accelerate the data annotation process.
Two types of rules are supported:
Regex-Based: Users can define a regex that will be used to identify all possible hit chunks and label them as being the target entity. For example, for labeling height entities the following regex can be used [0-7]'((0?[0-9])|(1(0|1))). All hits found in the task text that match the regex, are pre-annotated as heights.
Dictionary-Based: Users can define and upload a CSV dictionary of keywords that cover the list of tokens that should be annotated as a target entity. For example, for the label female: woman, lady, girl, all occurrences of strings woman, lady, and girl within the text of a given task will be pre-annotated as female. Make sure to include in the dictionary all possible forms of the target entity as only values in list will be pre-annotated.
Limitations:
The Free version of rules operates without support for contextual understanding. They are designed to recognize and annotate text based solely on the defined regex patterns or dictionary entries. While effective for many scenarios, users should note that without contextual support, there may be limitations in handling ambiguous cases where context is crucial for accurate annotation. Contextual rules are available in the presence of a healthcare license key. Any admin user can see and edit the rules under the Available Rules tab on the Models Hub page. Users can create new rules using the + Add Rules button.
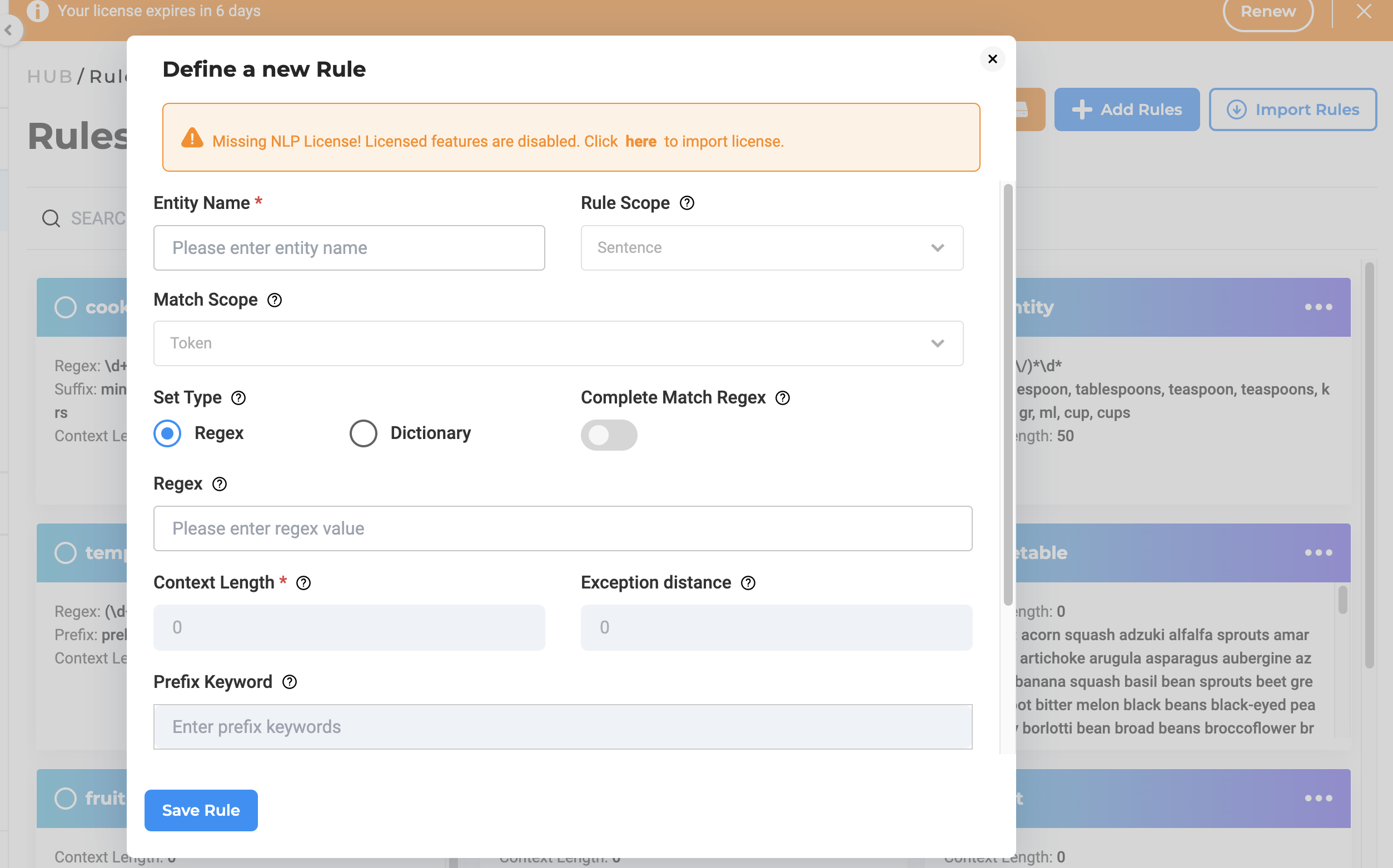
After creating a rule on the Models Hub page, the Project Owner or Manager can incorporate the rule into the project’s configuration where it is intended for use. This can be accomplished through the ‘Rules’ tab on the Project Setup page, located within the ‘Project Configuration’ tab. Additionally, the newly created rules can be tested in the playground.
Note:
- Free rules do not have access to context information like “Prefix Keyword,” “Suffix Keyword,” and Rule/Match Scope.
- If contextual rules are used within active projects in the presence of a healthcare license key and the later expires, the rules can remain operational but will no longer take context information into account.
Improvements
Enhanced Task Page Search: Focus on Ground Truth Completions
NLP Lab 5.5 enhances the search functionality on the tasks page by. Users now have the ability to narrow their search scope to either all completions or exclusively Ground Truth (GT) completions. This new feature retains all the existing search capabilities, and add a new Ground Truth filter for the results.
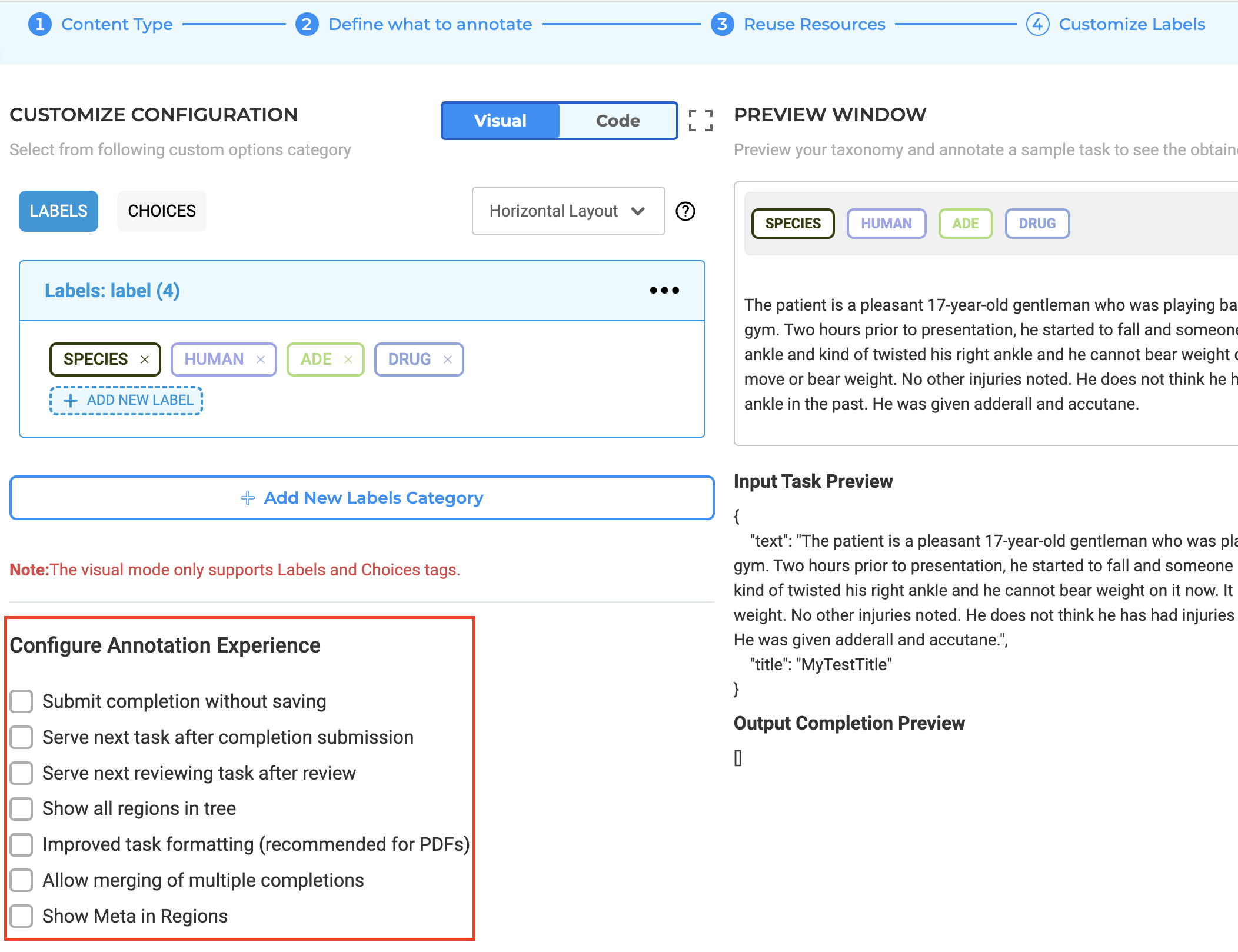
Annotation Experience Settings
Previously, at the conclusion of the setup process, a settings icon was provided which, upon interaction, displayed a configuration popup. This design presented a risk of users potentially missing the configuration options. To address this concern, we’ve introduced a compulsory confirmation step at the end of the configuration sequence. This ensures that users deliberately review and verify their settings choices before moving forward.
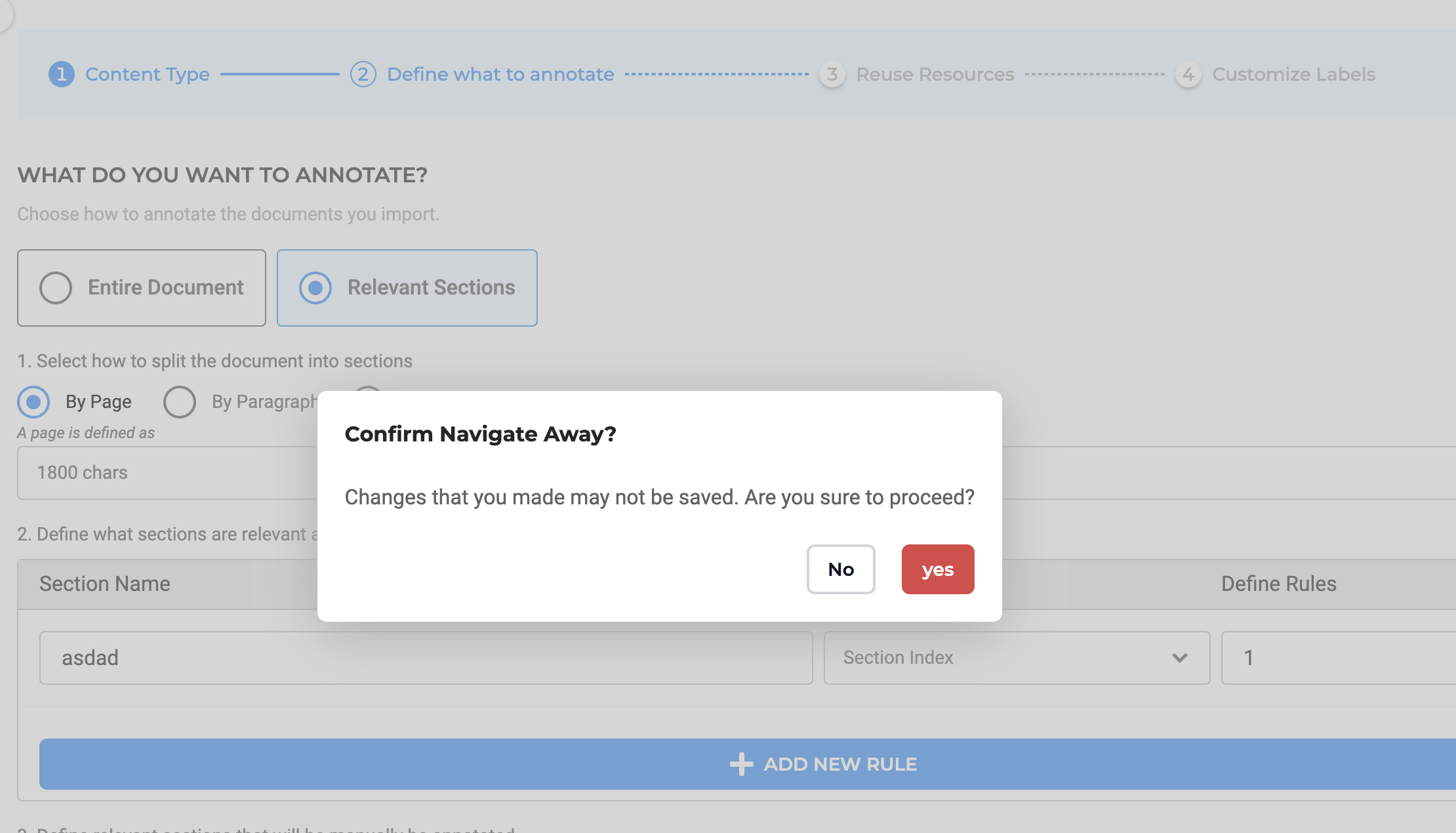
Confirmation Alerts for Unsaved Configuration Changes
A new alert system has been integrated into the configuration pages of NLP Lab 5.5. When users attempt to navigate away from a configuration page without saving their modifications, a pop-up warning will now display. This alert acts as a reminder to save any configuration changes to prevent accidental loss of unsaved work.
Redesigned Task Page for a Streamlined Experience
The task page in the latest NLP Lab version has been redesigned for a cleaner and more minimalist user interface. This design simplifies access to important information and enhances overall task management. The introduction of a dedicated Task Filter Slider Window complements this design update by providing robust filtering capabilities to swiftly locate specific tasks, thus optimizing task organization and management.
Expanded Labeling Page for Enhanced Annotation Workflow
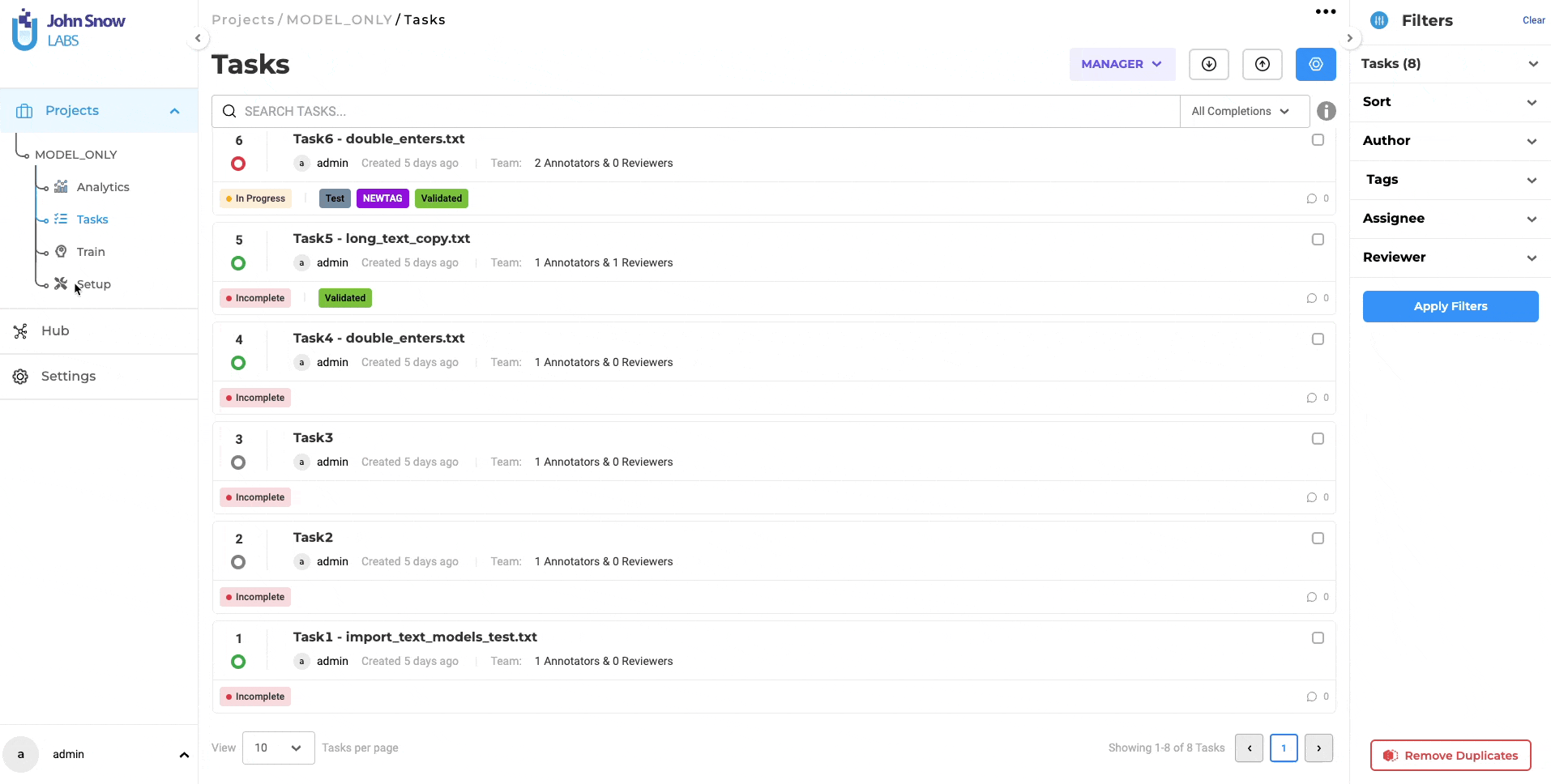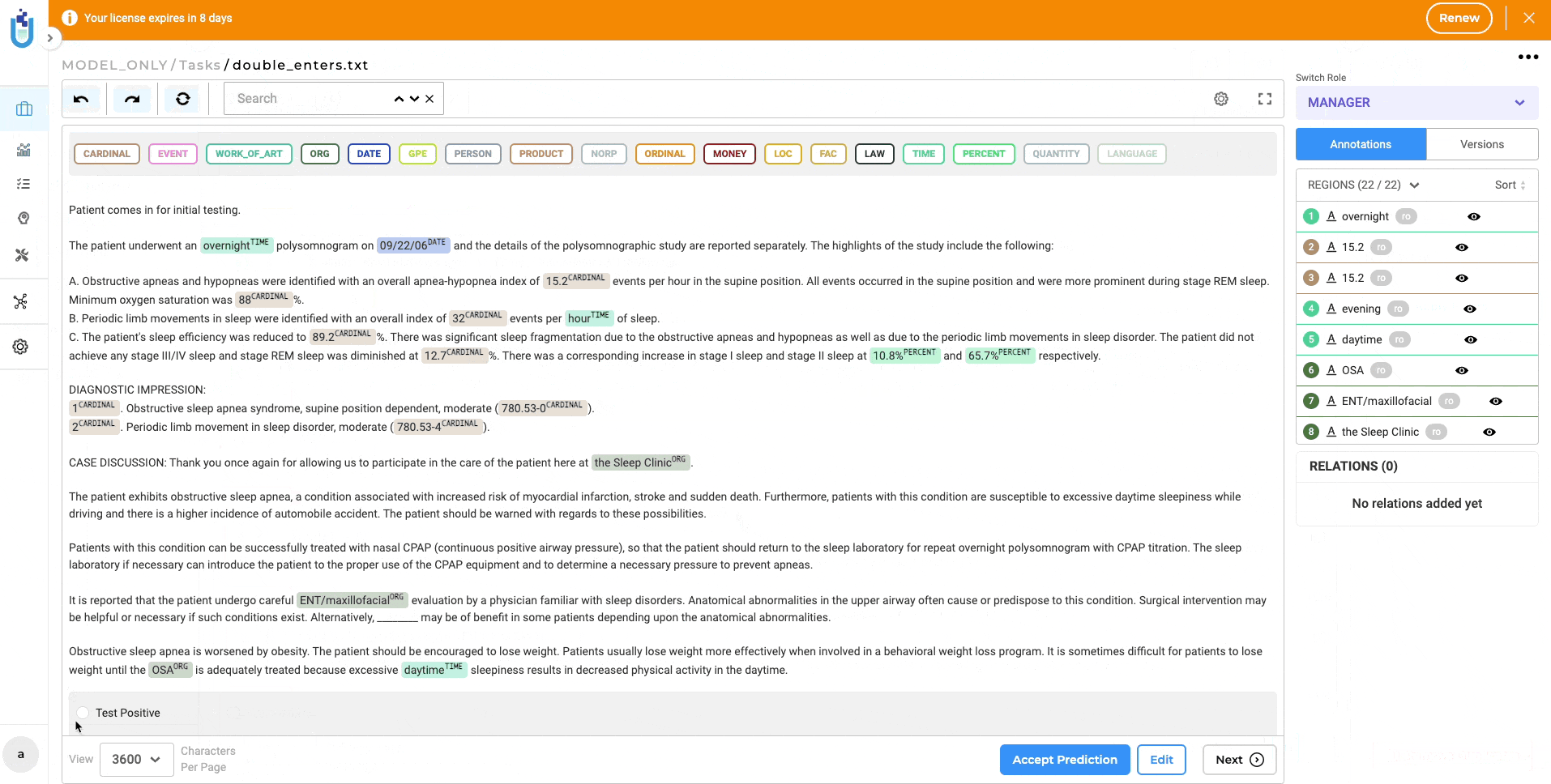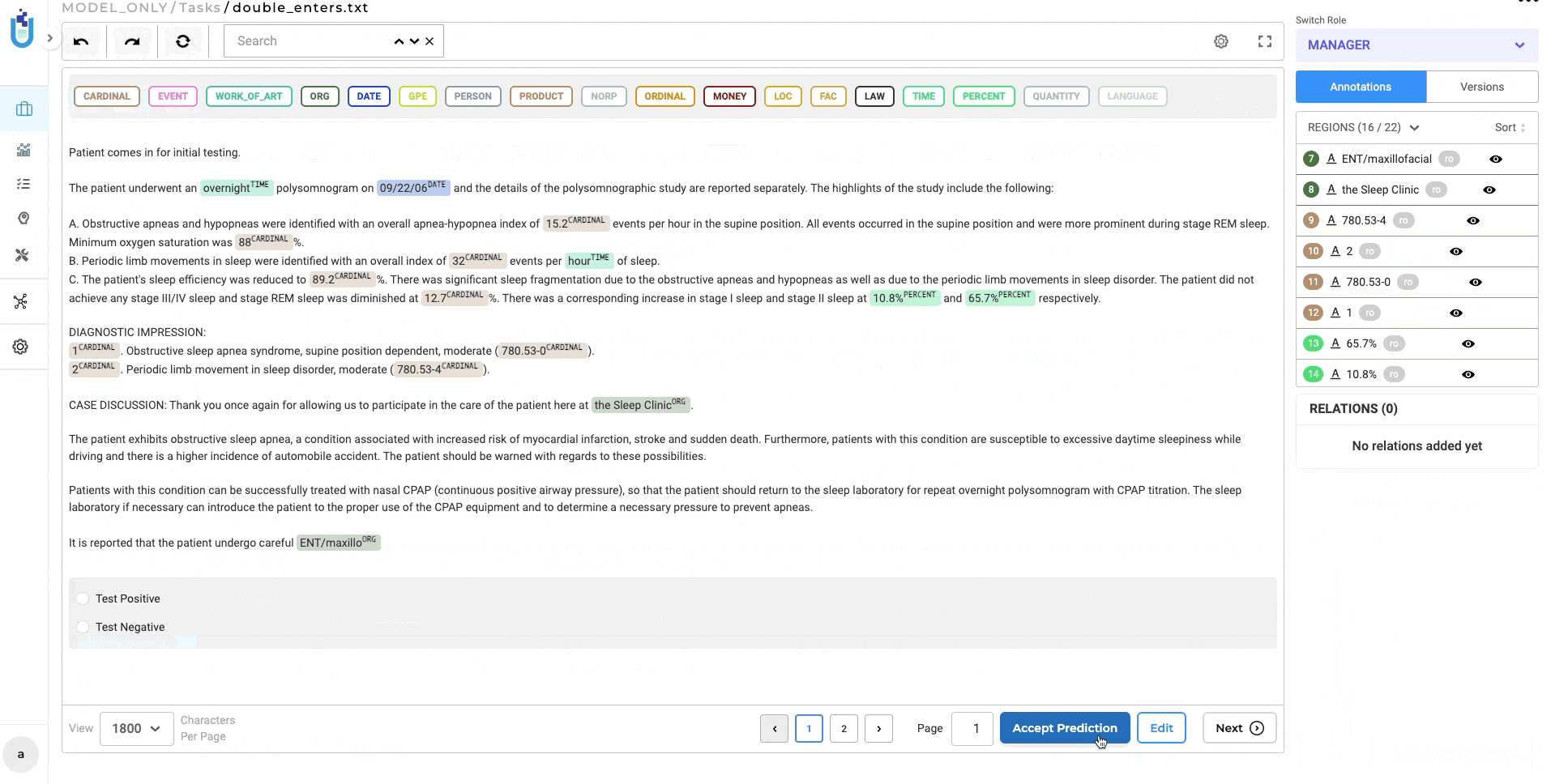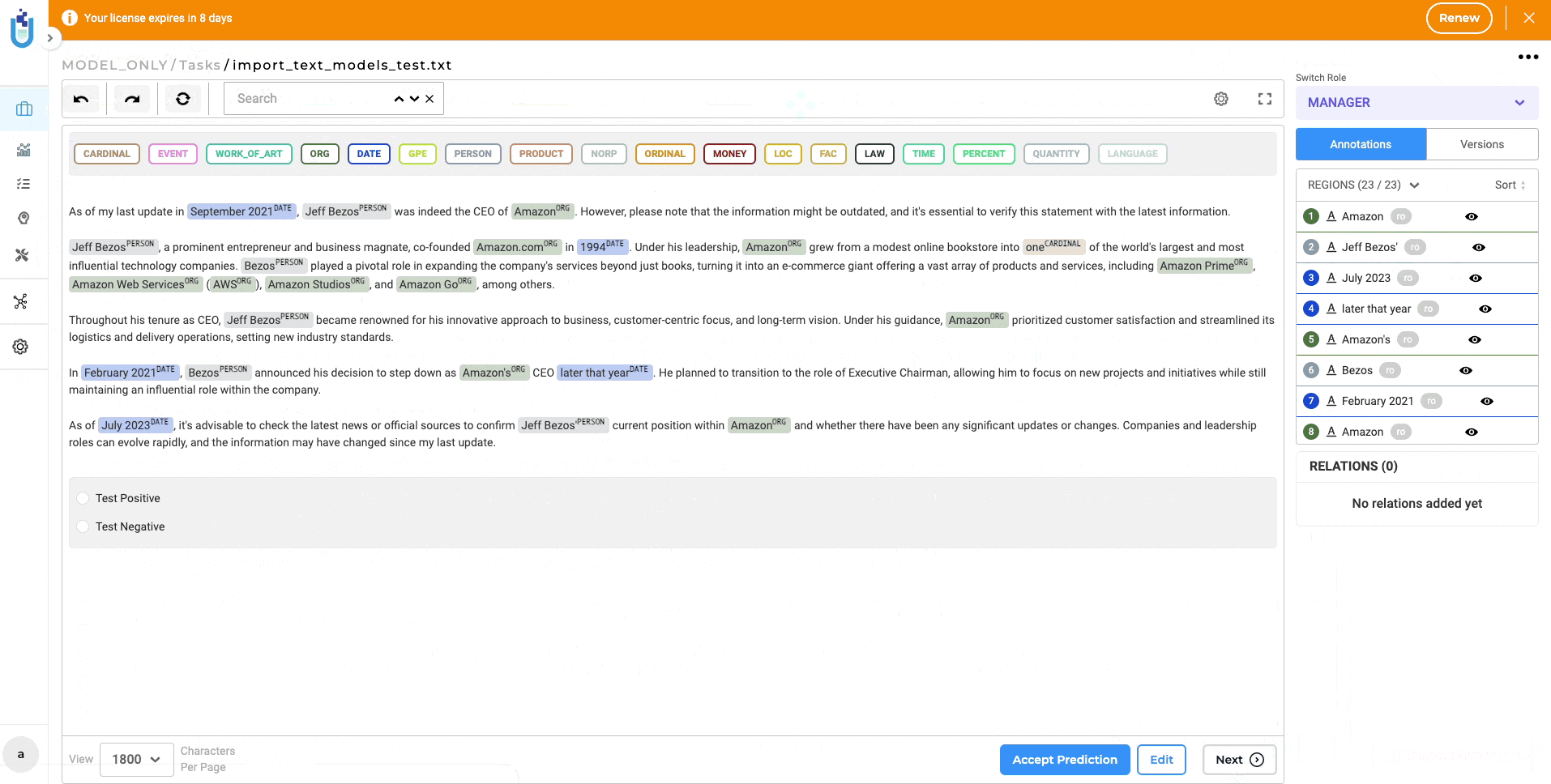
To further empower annotators, the labeling page’s workspace has been expanded, maximizing the use of screen space. This redesign aims to streamline the annotation process, allowing annotators to work more effectively with a layout that’s both functional and intuitive while maintaining the workflow’s familiar feel.
Improved Model Publication to NLP Models Hub
Automatic generation of results for Model Upload form
Version 5.5 simplifies the procedure for uploading trained models to the NLP Models Hub. Now, users can provide sample text during the model training phase, which the system will use to automatically generate expected results samples in the model upload form, eliminating the need for manual input during model publication.
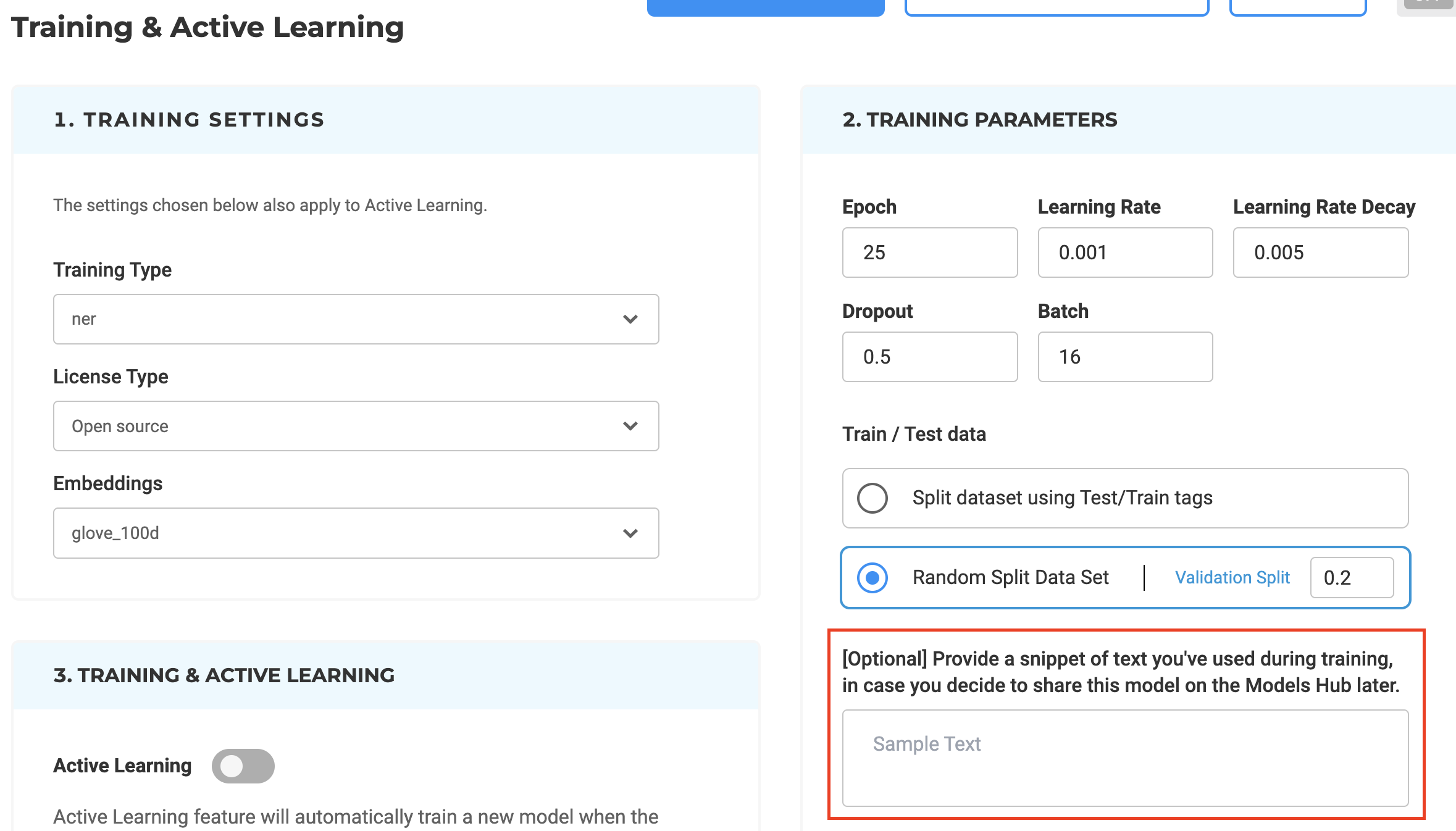
Automated Python Code Generation for Model Hub Publications
With the aim of further streamlining the model upload workflow, the Python code required for publishing models to the Models hub will now be auto-generated and inserted into the Publish Model Form. Users have the option to edit this code to suit their unique requirements.
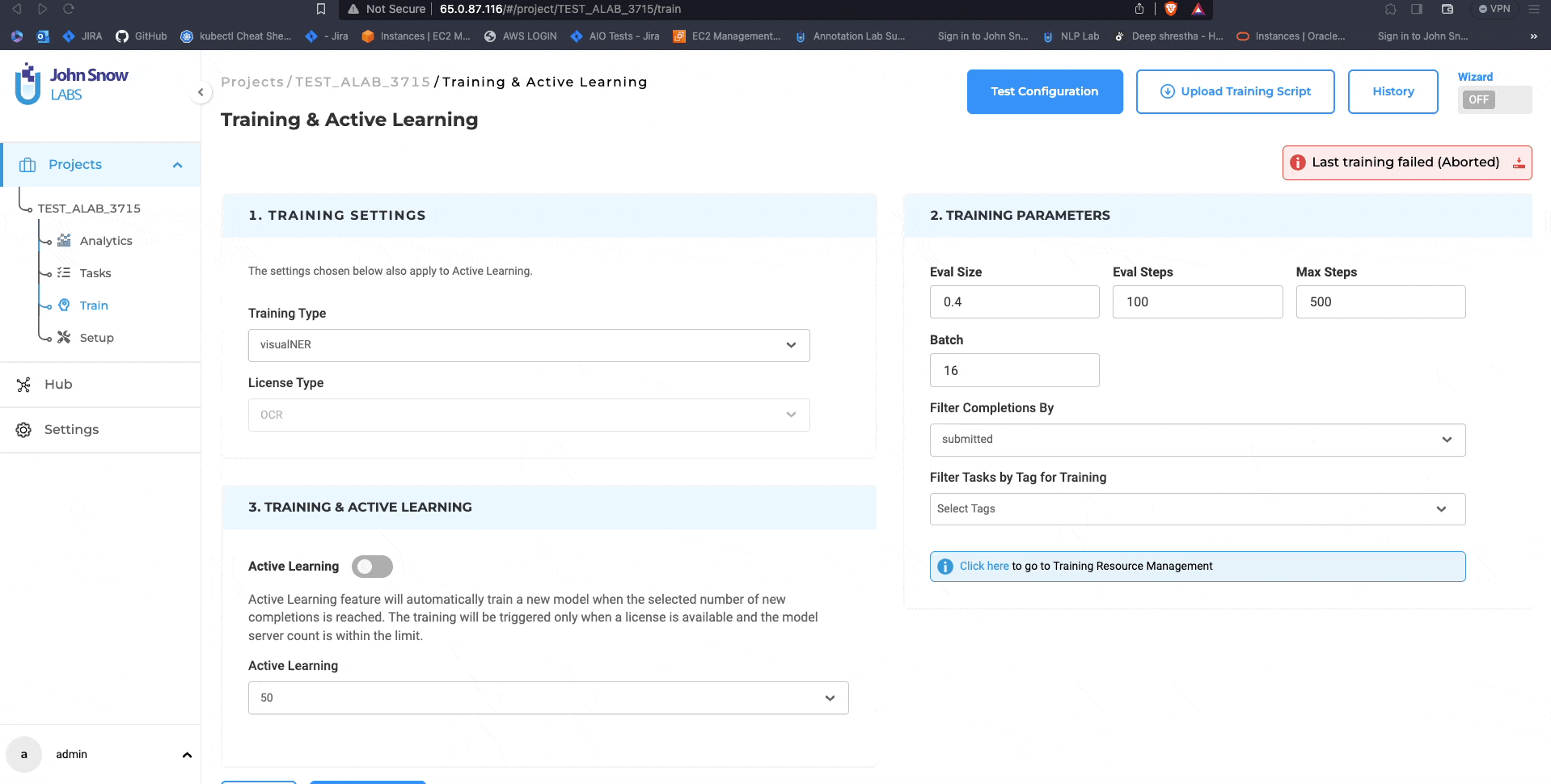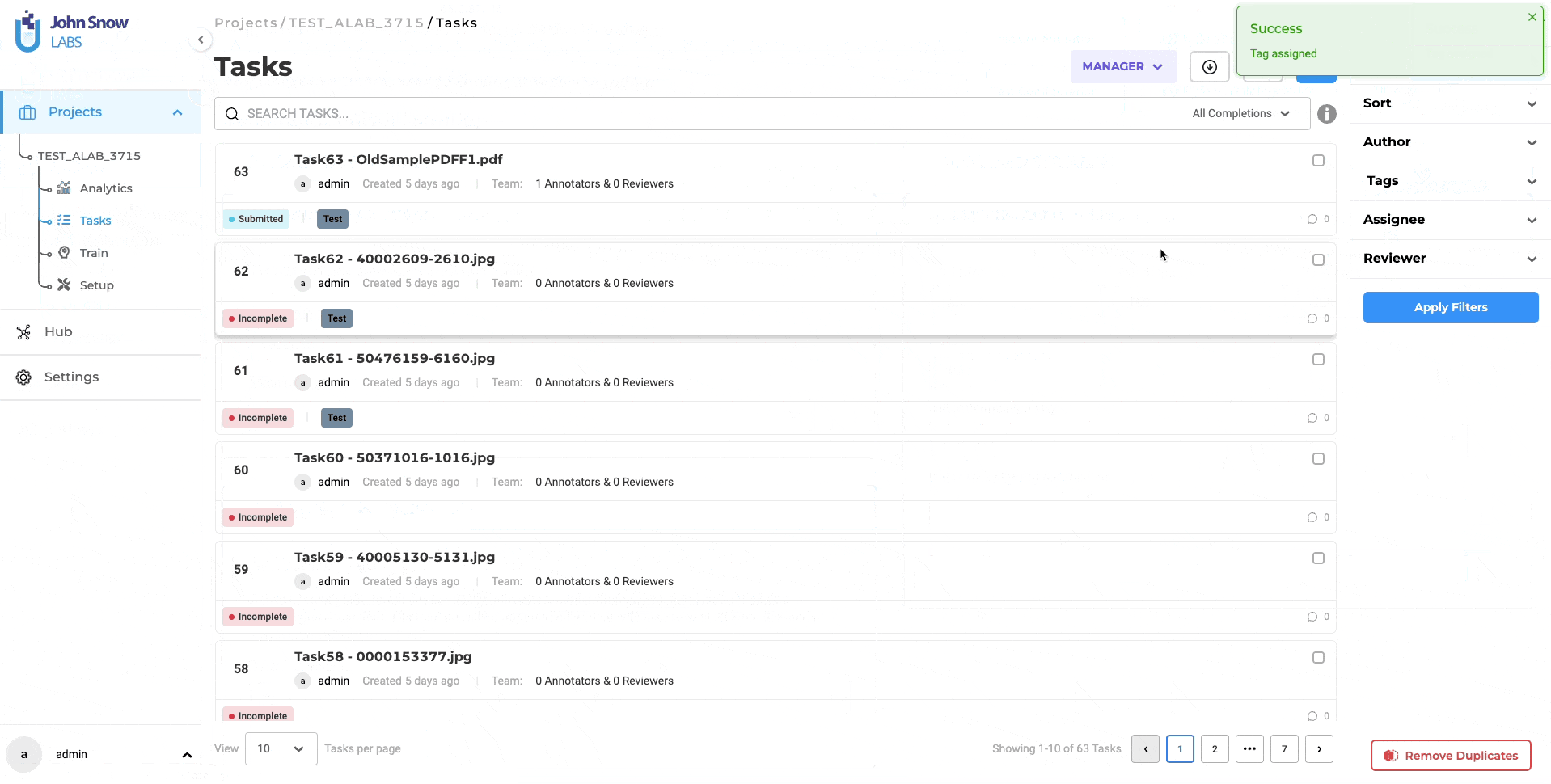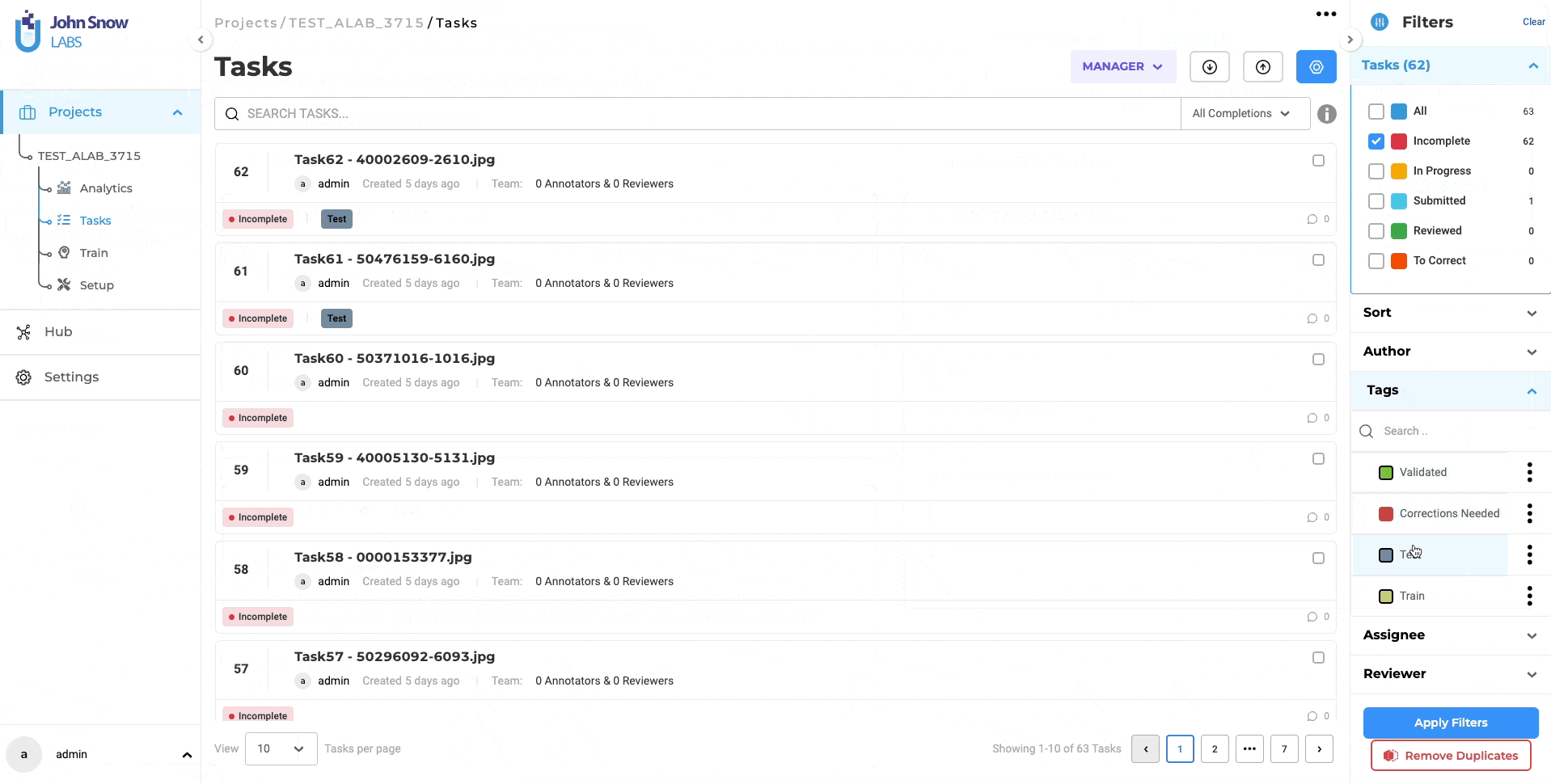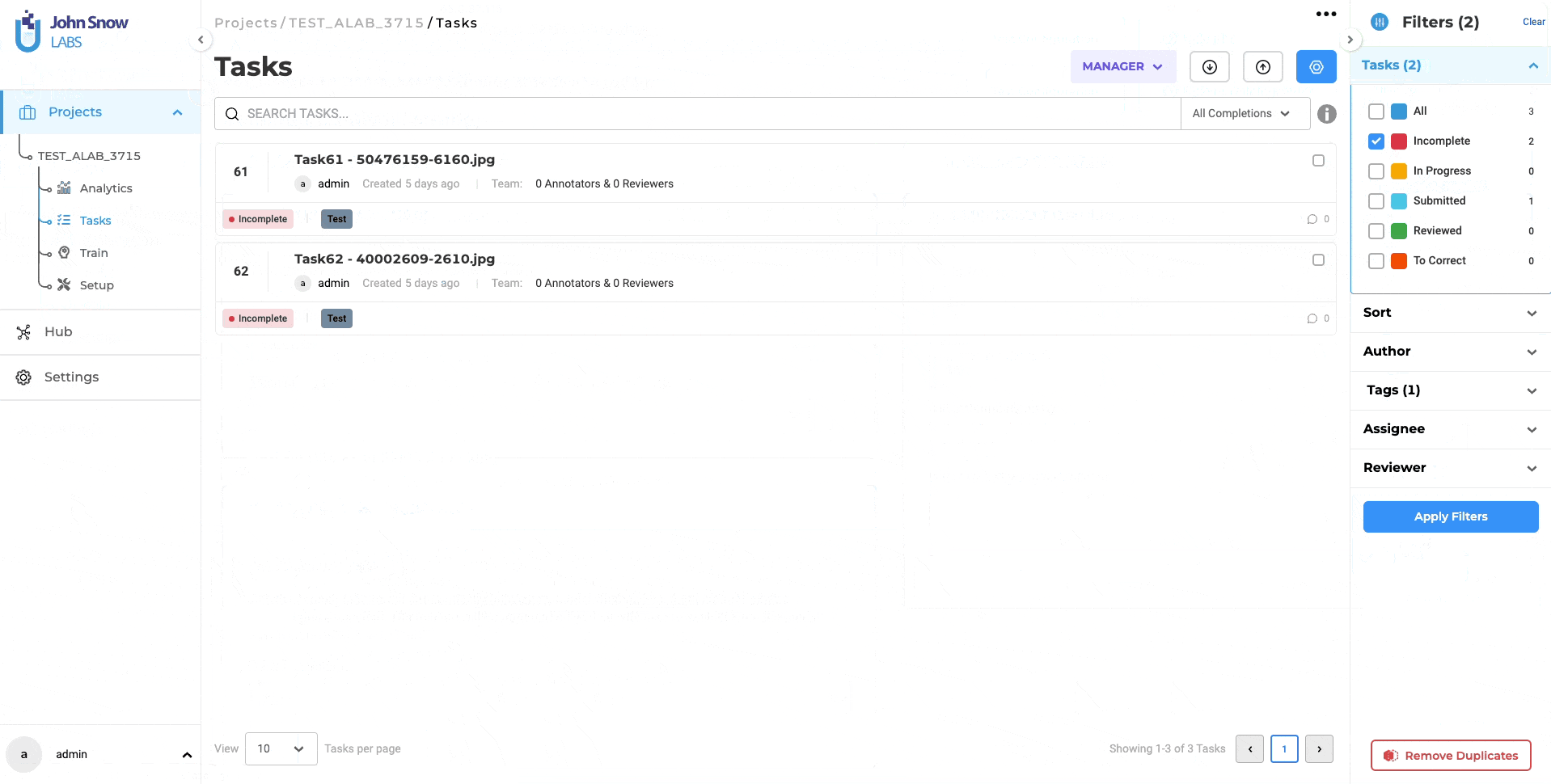
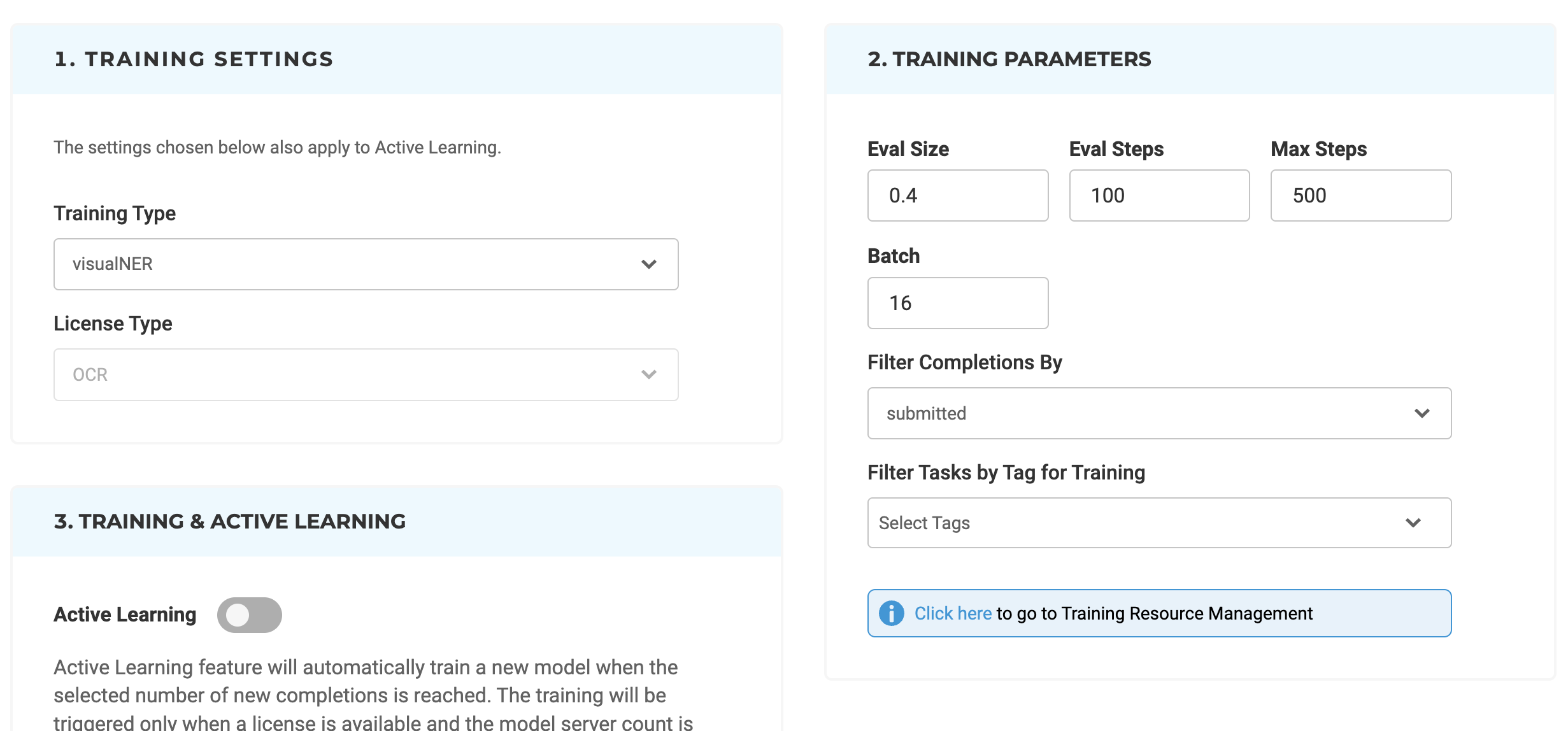
Visual NER Training Parameters Update
Version 5.5 of the NLP Lab offers the ability to train Visual NER models faster, apply active learning for automatic model training, and pre-annotate image-based tasks with existing models to accelerate the training process. From the Training Settings sections, users can tune the training parameters “Eval Size”, “Eval Steps”, “Max Steps” and “Batch”
- Eval Size: Eval Size refers to the size of the dataset that is reserved for evaluating the model’s performance during training. This dataset, often referred to as the test split, is essential for assessing how well the model generalizes to new, unseen data.
- Eval Steps: Eval Steps indicate when the model should be evaluated during training. It defines the number of training steps (iterations) that occur before the evaluation process is triggered.
- Max Steps: Max Steps represents the maximum or total number of training steps the model will undergo during the training process. It sets an upper limit on the training duration.
- Batch: Batch size refers to the number of data samples that are processed together in a single forward and backward pass (iteration) through training
Information on the training progress is shown in the top right corner of the Model Training tab. Users can check detailed information regarding the success or failure of the last training.
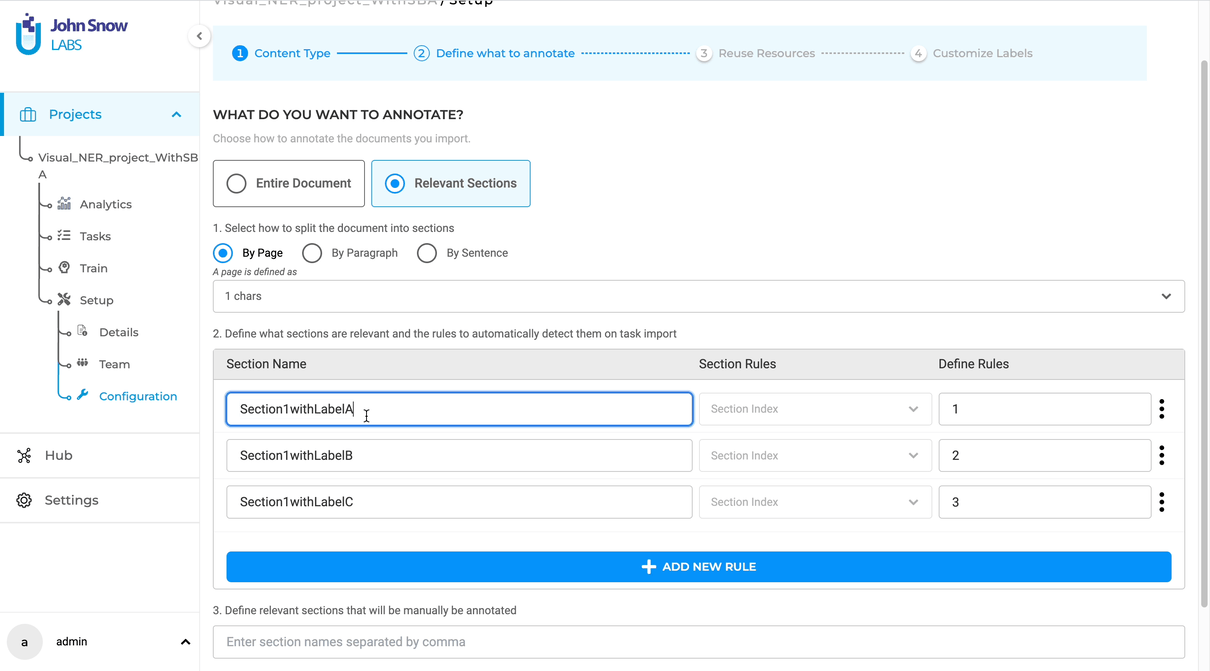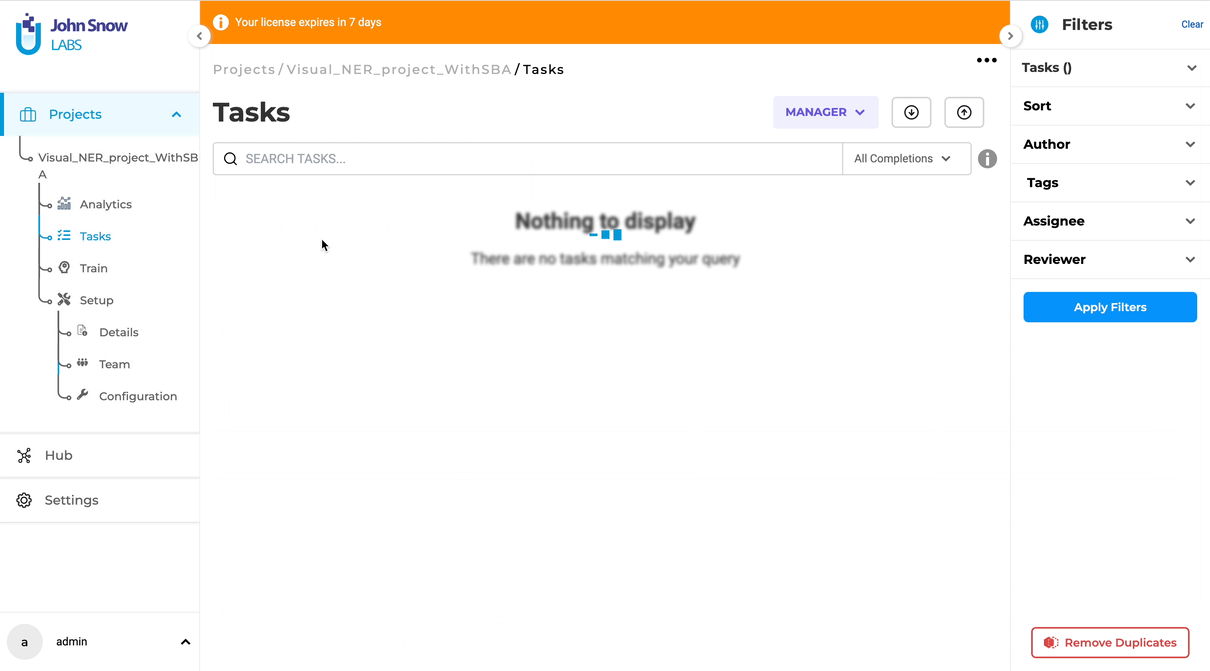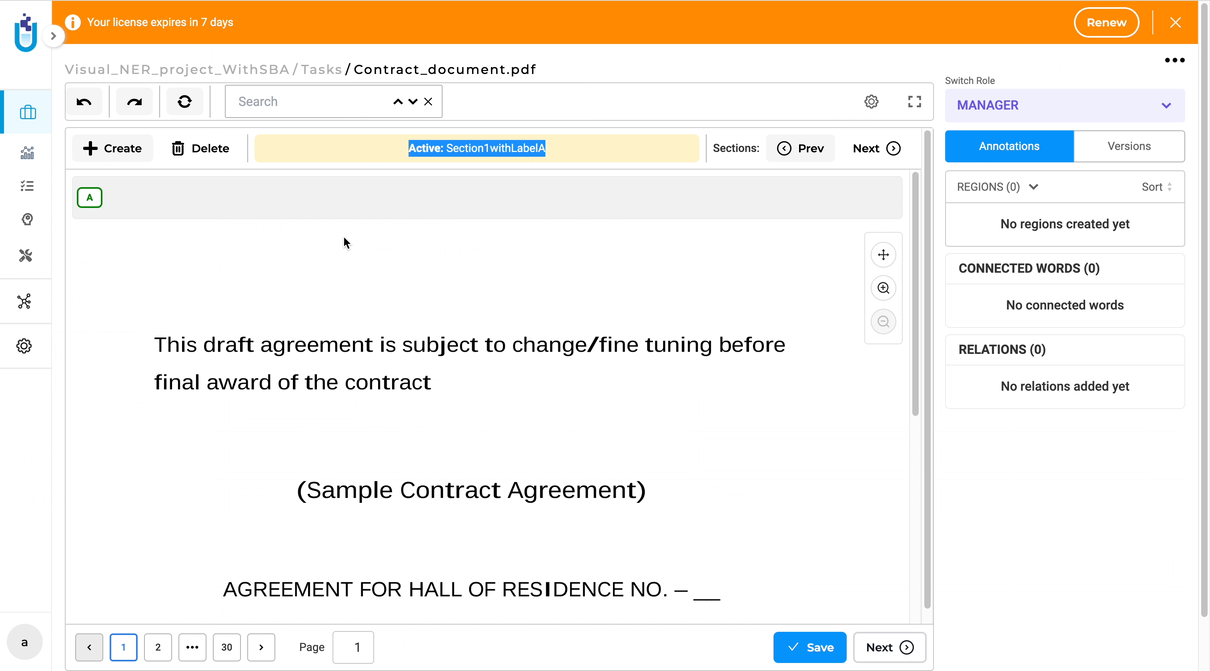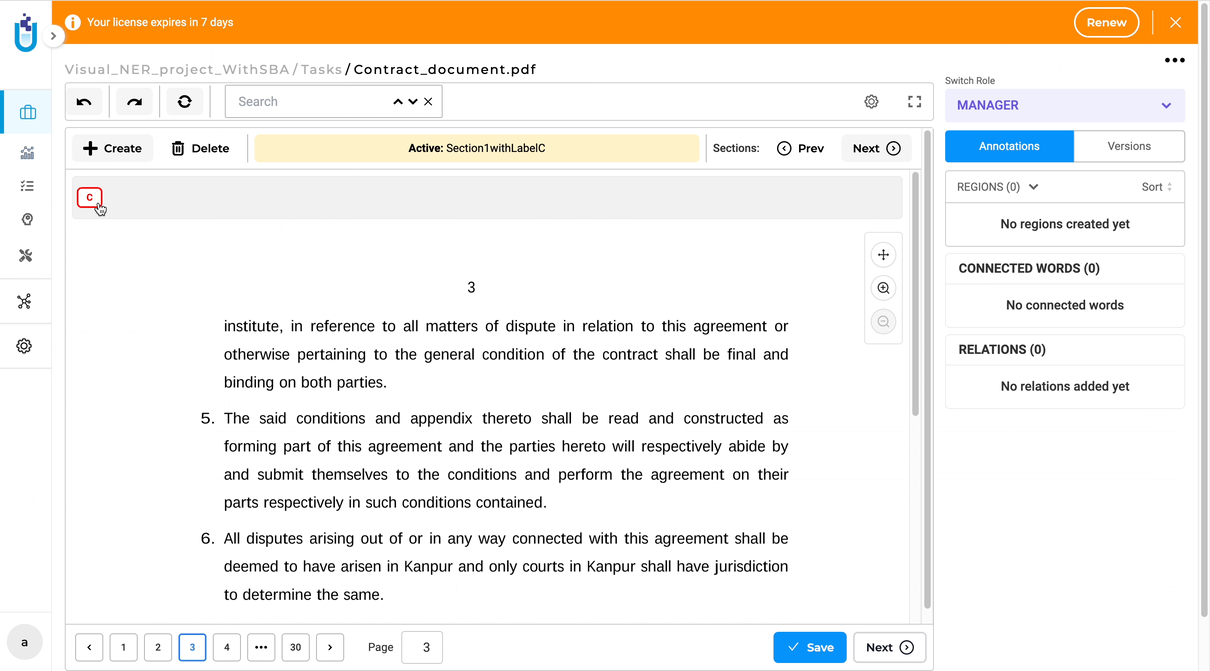
Customizable Section-Specific Taxonomies for Visual NER Projects
We’ve refined our section-based annotation features, allowing for more granular control over label display in Visual NER projects. On the project configuration page, users can now assign labels to appear in designated sections through an enhanced visual interface. This ensures that Visual NER labels are only visible in relevant sections, aligning pre-annotation labels with the user’s predefined settings.
By tailoring label visibility at the section level, annotation efforts are more targeted and efficient for PDF and image documents. This customization results in a streamlined annotation process, optimizing time and resource expenditure and supporting the production of high-quality, task-specific annotations.
Bug Fixes
-
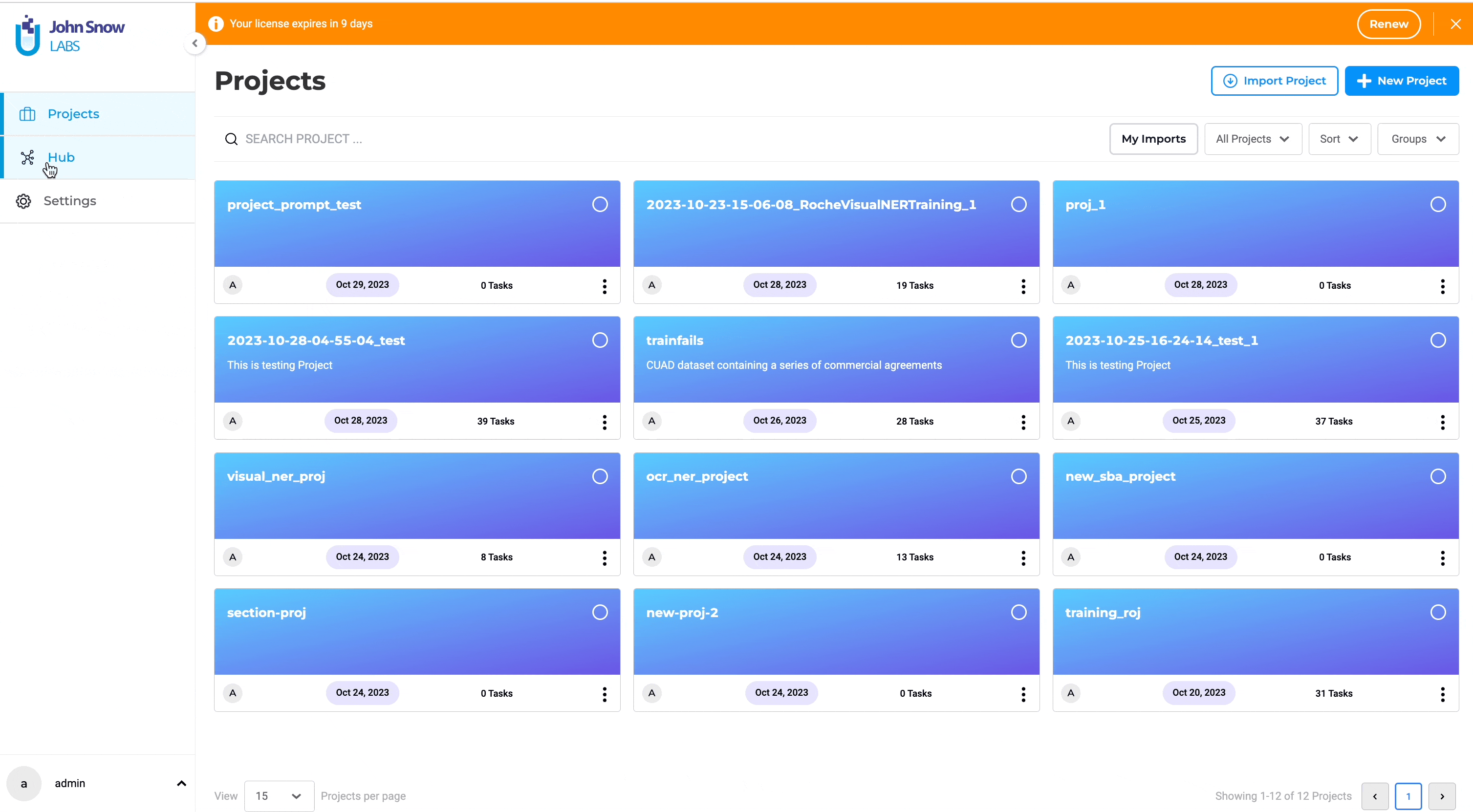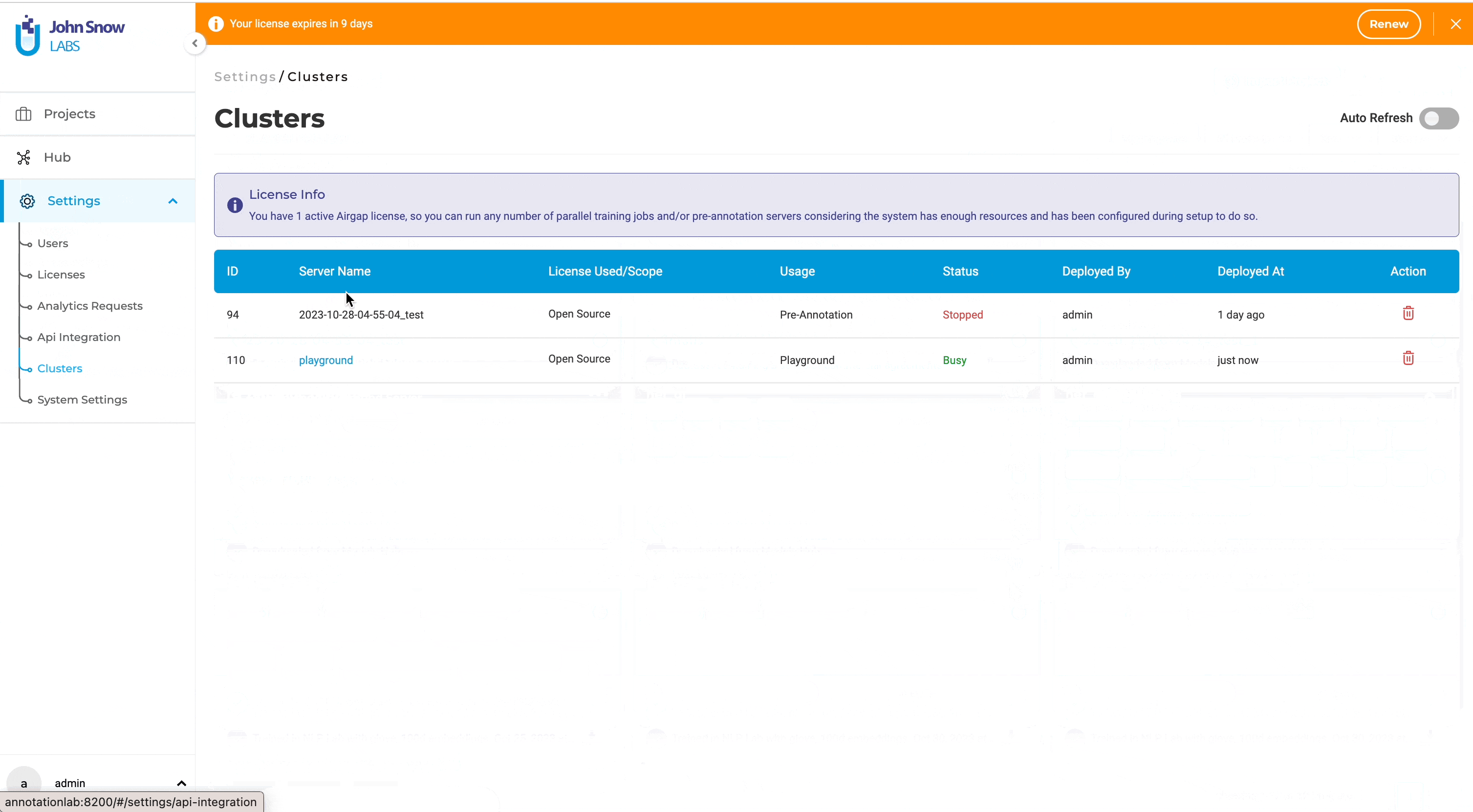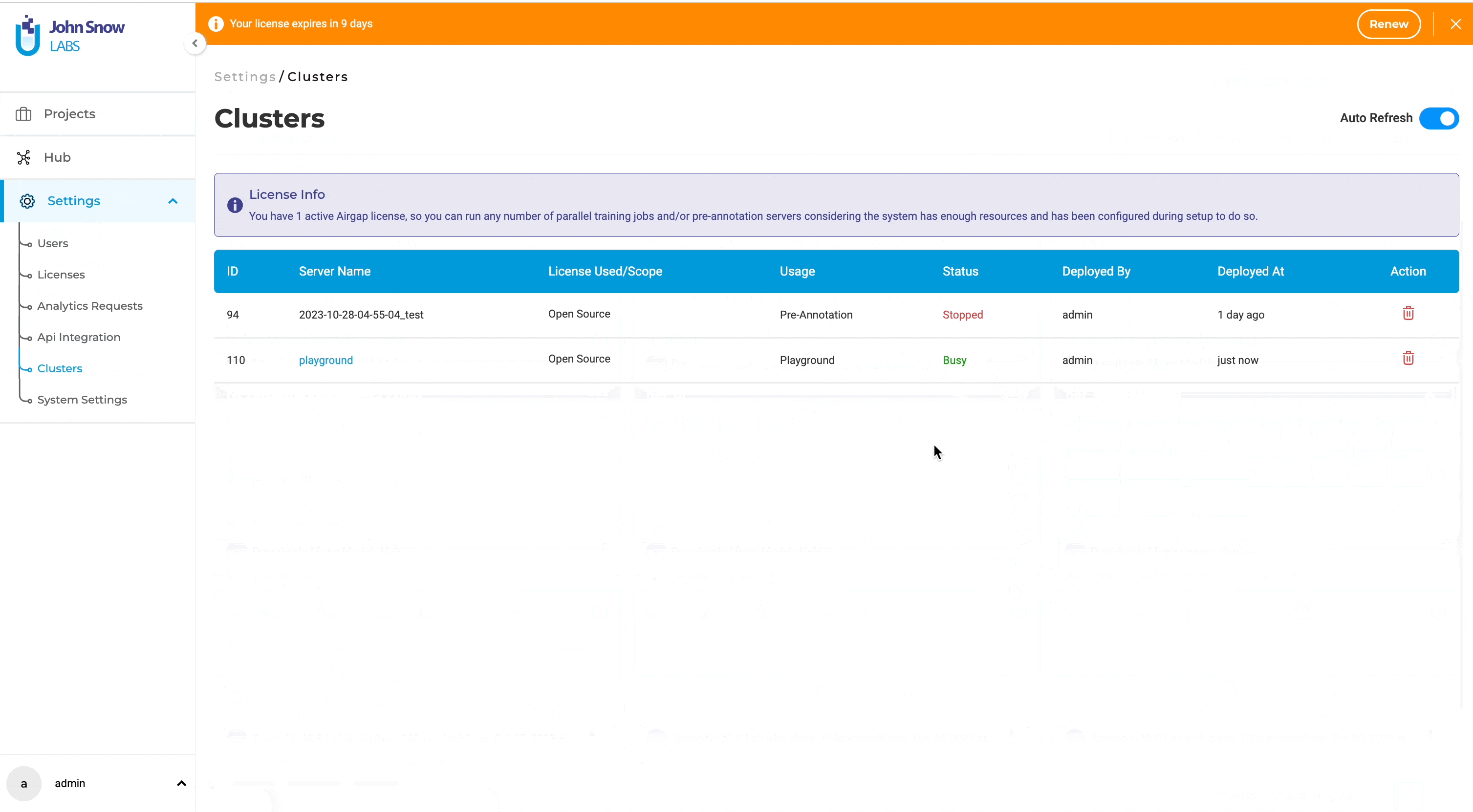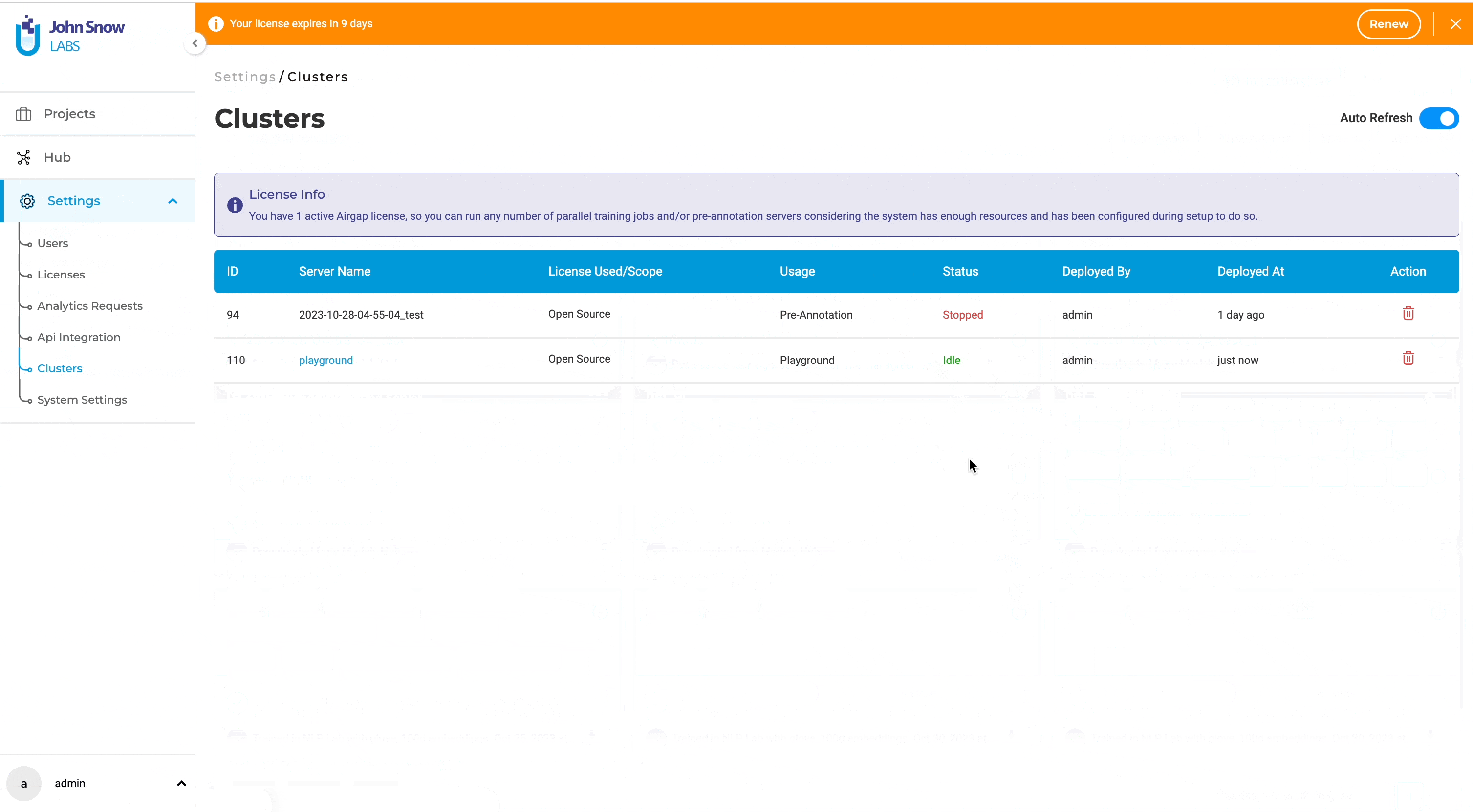
Status of the model server deployed from the playground is not updated
Following the deployment of the model in the playground server, its status transitions to “Idle,” signifying readiness for preannotation.
-
Visual NER Training fails due to out-of-memory error
NLP 5.5 incorporates Visual NLP 5.0.1, which brings optimizations to the Visual NER training process. As a result of this update, the out-of-memory error has been successfully addressed and resolved.
-
Updating classifier section rules in the project configuration generated an error related to cluster limit
With this release, the user can now deploy the section server without encountering a cluster limit error, provided that the preannotation server of the same project is deployed, and vice versa.
-
In the NER project with RE, Assertions, and NER pre-trained models, when the model is trained and deployed, pre-annotation fails
Pre-annotation failed when a project with RE, Assertion, and NER models was trained and deployed in earlier versions. Now the issue has been resolved and tasks can be pre-annotated using the deployed model without any issue.
-
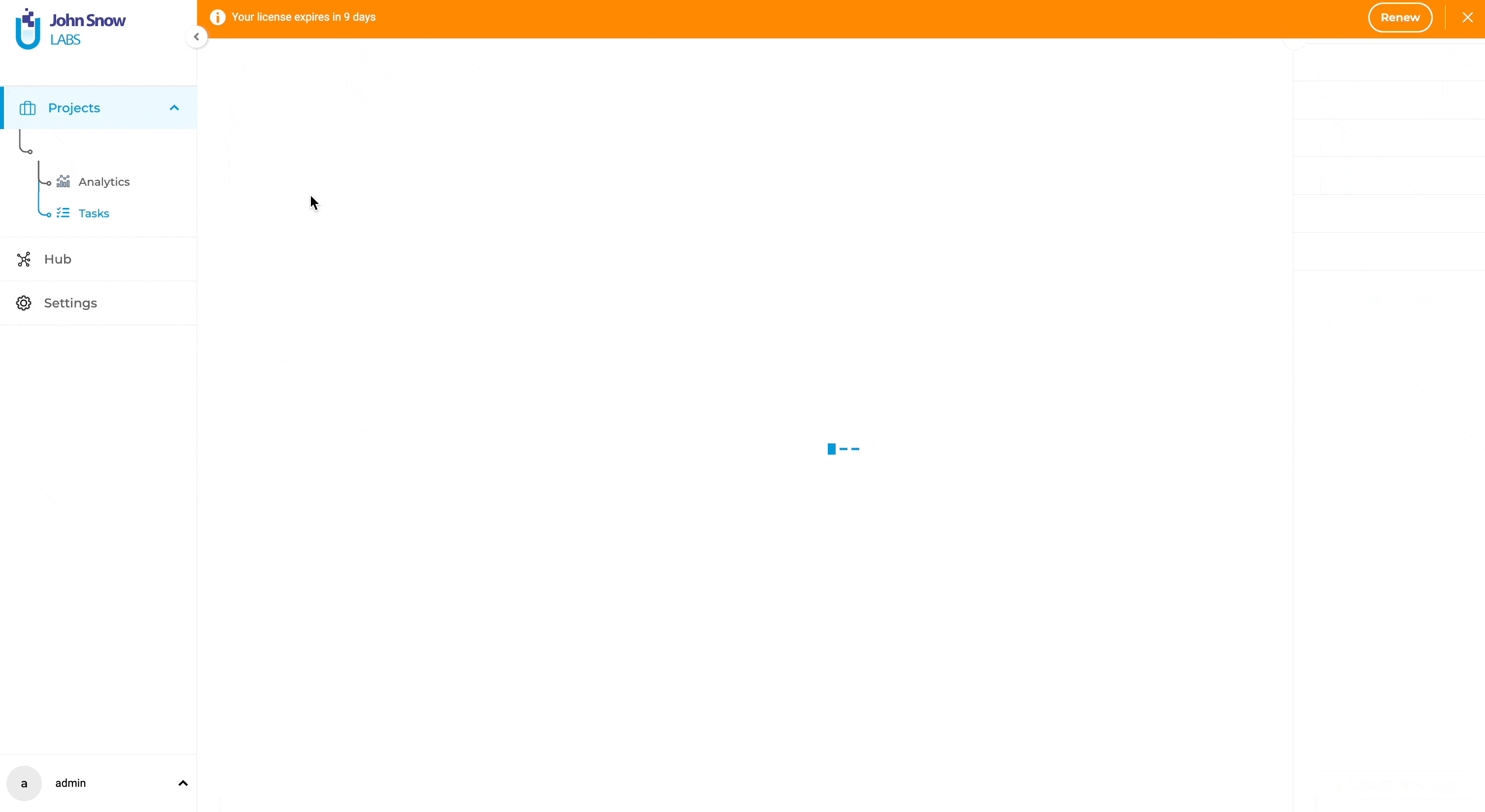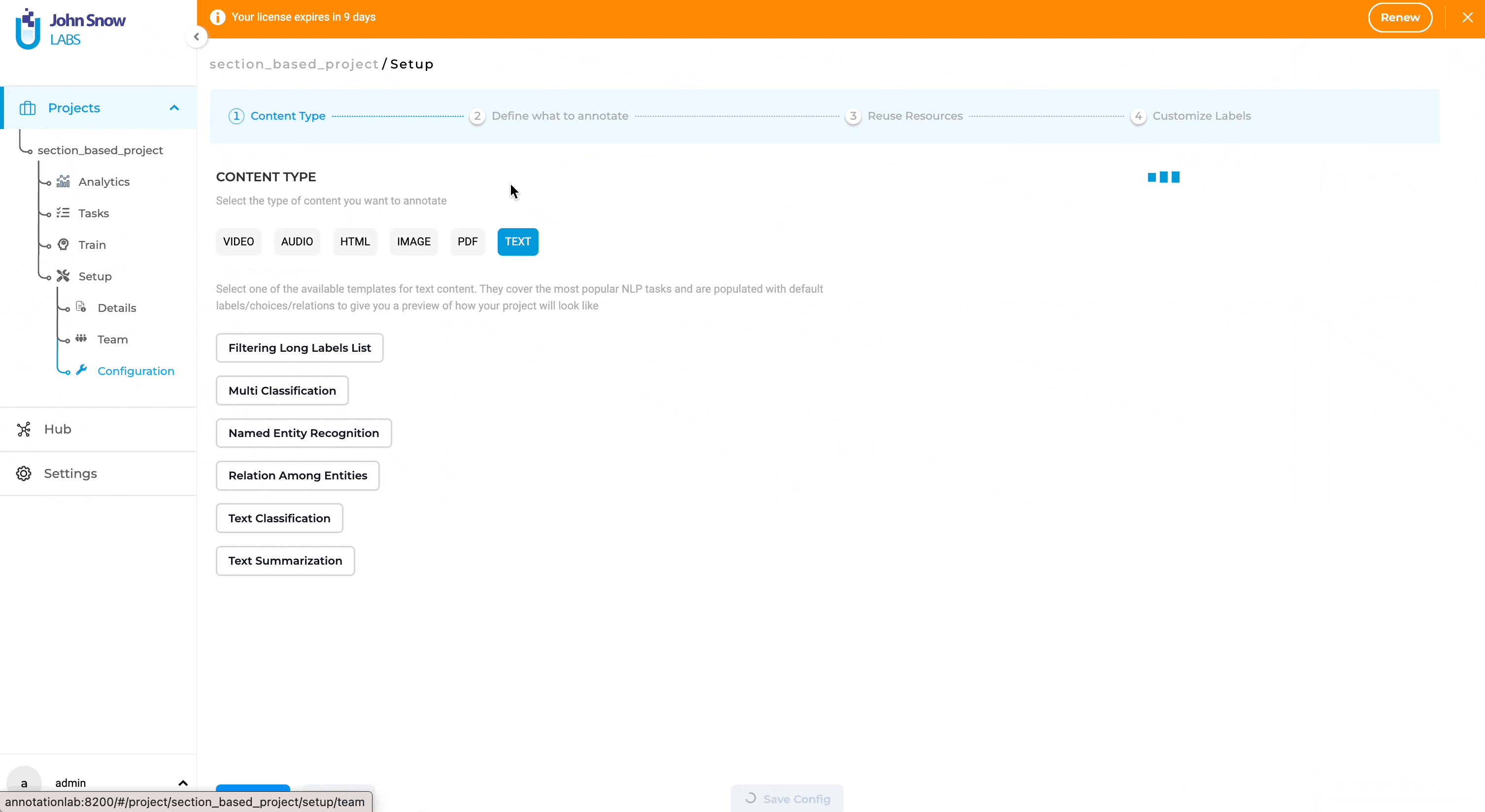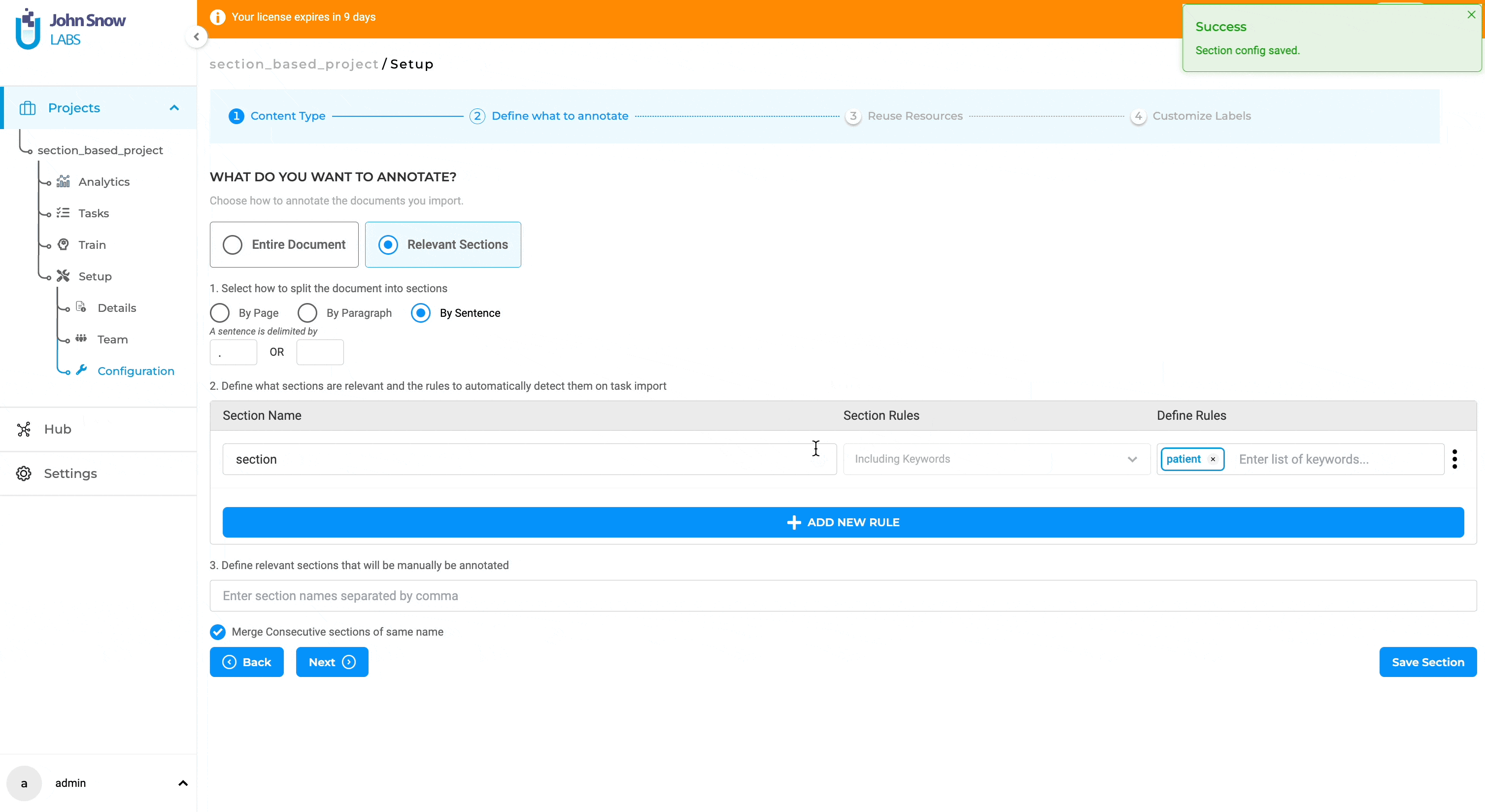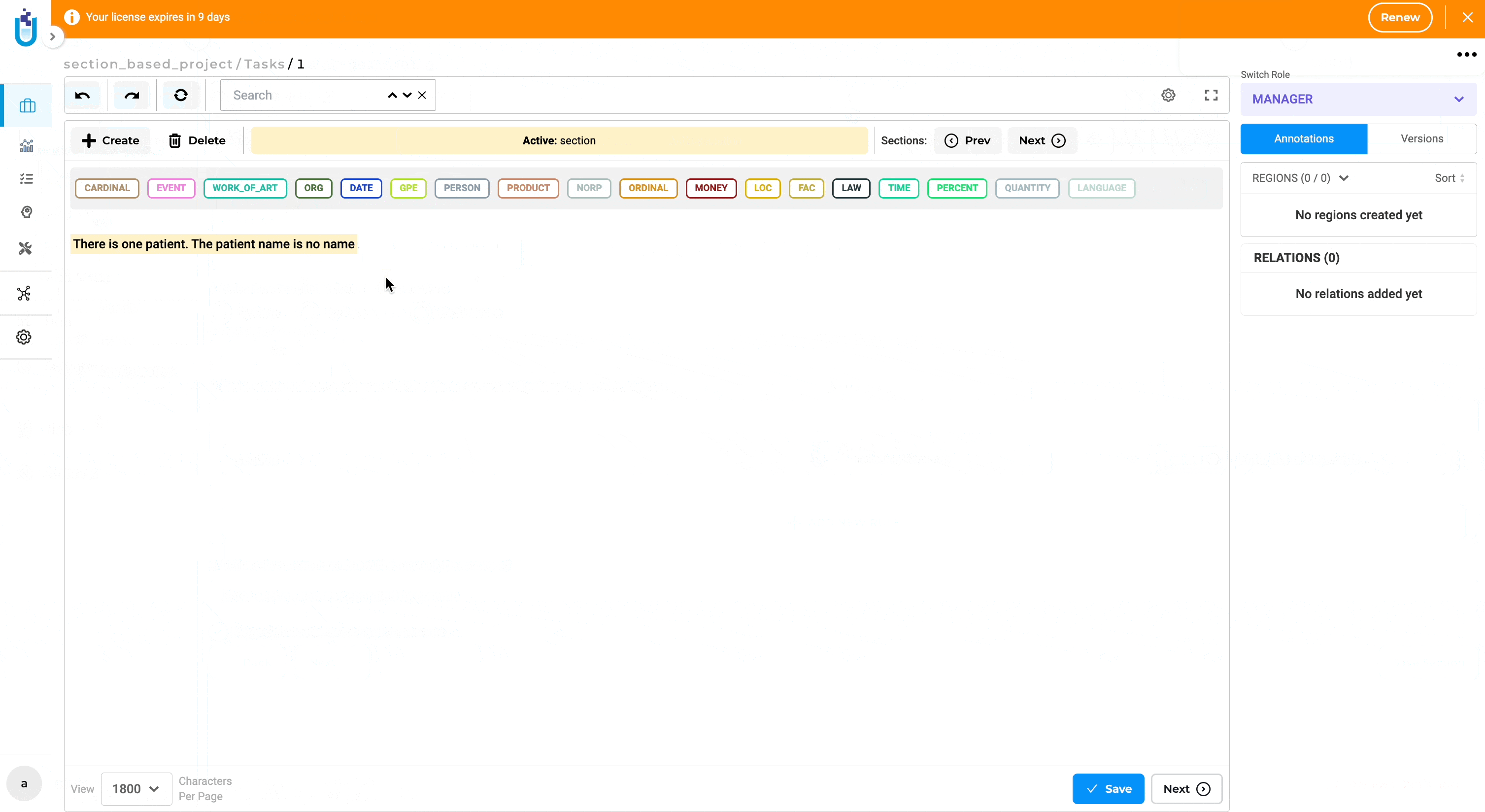
Filtered pre-annotation result is not shown when “merge consecutive section” is enabled
With this release, the consecutive sections with the same section name are merged when “merge consecutive section” is enabled.
-
Adding a style attribute to enable the does not enable “Improve PDF formatting” checkbox
Fixed an issue where adding style attribute itself to
Tag would show "Improve PDF Formatting" as enabled. -
OCR Deployment for Visual NER Projects is shown as loading even after it is completed
Previously, users were required to manually refresh the page to view the deployed OCR server. This issue has been resolved, and now the deployed OCR server is automatically refreshed, eliminating the need for manual intervention.
-
State of Generate Result button is reset after navigating to a different page
Fixed an issue where the continuous updating is not resumed when results generation is still ongoing and the user navigates back to the synthetic tasks page
-
Prompt created with an external service provider, returning Internal Server Error during import
Prompts using an external service provider can be imported to NLP Lab with a valid service provider URL.
-
User can add Predicted Entities manually along with the ones automatically populated while uploading the model via NLP lab UI
With this release, the issue where the predicted entities were editable is fixed. The field is read-only and displays only the entities extracted from the model that is being published.
-
When using manually created Prompts, Rules, and External Provider Prompts together for pre-annotation, tasks are pre-annotated based on external prompts only.
External Provider Prompts can be used together with other models, rules, prompts for pre-annotation. Results from all the pre-annotations are merged.
-
Pre-annotation using Rules is failing for some tasks
With this release, preannotation rules now accommodate text containing newline characters (“\n”). It’s a convenient enhancement for handling multiline text during the preannotation process.
-
Trying to delete embedding from Embeddings page is returning Internal Server Error
Previously, when the user tried to delete an embedding from Embeddings page, the page returned Internal Server Error. In this latest version, the issue has been fixed and users can now delete the embeddings easily.
-
Duplicate predicted entities are seen when pre-annotating with external providers
The external provider prompt previously made predictions for a token only once, regardless of its repetition within the task. This issue has been resolved, and now duplicate predictions are no longer observed.
-
Data Backup Settings: Adding/Editing and saving the S3 Backup settings is not working properly
An issue previously existed when attempting to save S3 backup settings from the settings page, particularly when pre-filled values were already present. This issue has been successfully resolved, allowing users to now effortlessly configure their backup settings.
-
Sticky layout for labels is not working for Visual NER tasks
In the earlier version, users were unable to employ the horizontal-sticky label/choices layout for their Visual NER projects. This limitation has been addressed and rectified in the most recent version.
-
Application shows critical server error when trying to change the configuration of the project from Relevant Section to Entire Document
Users were unable to change the project settings to Entire Document if Relevant Sections were saved already. In this version, the issue has been resolved and users can update the configuration without any issues or errors.
-
UI freezes when attempting to edit a project group
In the previous version of NLP Lab, the UI froze and had to be closed or refreshed when trying to edit the project groups. Now the issue is resolved and project groups can be edited and updated.
-
Improvement on different representations of the pre-annotation statuses for both Model-based and External Service pre-annotations
We addressed an issue where the pre-annotation statuses displayed did not align accurately with the actual results. Now, whether you’re working with Model-based Pre-annotations or external Prompts, the pre-annotations in the task list page are represented precisely in line with the actual results. This update ensures that users can rely on the status information provided, regardless of the type of pre-annotation used. Moreover, the system is now capable of handling both Model-based and external Prompts pre-annotations simultaneously, presenting users with precise and reliable status indicators for a more streamlined workflow.
Versions
- 7.7
- 7.6.0
- 7.5.1
- 7.5.0
- 7.4.0
- 7.3.1
- 7.3.0
- 7.2.2
- 7.2.2
- 7.2.0
- 7.1.0
- 7.0.1
- 7.0.0
- 6.11.3
- 6.11.2
- 6.11.1
- 6.11.0
- 6.10.1
- 6.10.0
- 6.9.1
- 6.9.0
- 6.8.1
- 6.8.0
- 6.7.2
- 6.7.0
- 6.6.0
- 6.5.1
- 6.5.0
- 6.4.1
- 6.4.0
- 6.3.2
- 6.3.0
- 6.2.1
- 6.2.0
- 6.1.2
- 6.1.1
- 6.1.0
- 6.0.2
- 6.0.0
- 5.9.3
- 5.9.2
- 5.9.1
- 5.9.0
- 5.8.1
- 5.8.0
- 5.7.1
- 5.7.0
- 5.6.2
- 5.6.1
- 5.6.0
- 5.5.3
- 5.5.2
- 5.5.1
- 5.5.0
- 5.4.1
- 5.3.2
- 5.2.3
- 5.2.2
- 5.1.1
- 5.1.0