5.3.2
Release date: 30-08-2023
NLP Lab 5.3 - A Leap Forward in Pre-Annotation through ChatGPT-Powered Entity Recognition
We’re excited to present NLP Lab 5.3, an exciting update that marks our foray into integrating Large Language Models (LLMs) into our platform. Leading the charge is the integration with ChatGPT family of models, the first in a series of LLM integrations we have planned for the future. This not only sets the stage for a new era of enhanced pre-annotation capabilities but also underscores our commitment to staying at the forefront of NLP innovation. By weaving ChatGPT’s prowess into our ecosystem, we’re offering users an expanded range of prompt possibilities and a refined entity extraction process. But that’s not all! Beyond the ChatGPT integration, we’ve made a series of enhancements across the board. From a revamped taxonomy customization experience for section-based projects to thoughtful improvements in OCR text formatting, every change in this release is designed to improve your annotation experience. Whether you’re a seasoned NLP Lab user or just getting started, we believe this update will offer you a blend of familiarity and fresh innovation, ensuring a smoother, more productive annotation journey. Dive into the details below to discover all that NLP Lab 5.3 has in store for you.
Entity Extraction and Pre-Annotation via GPT Prompting
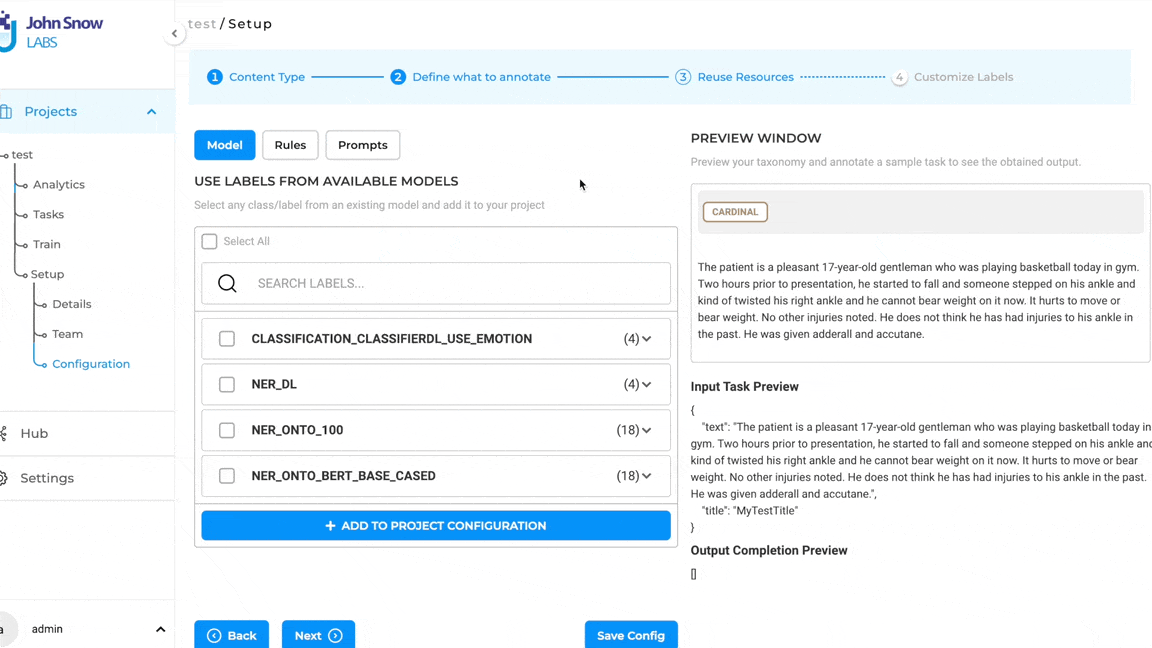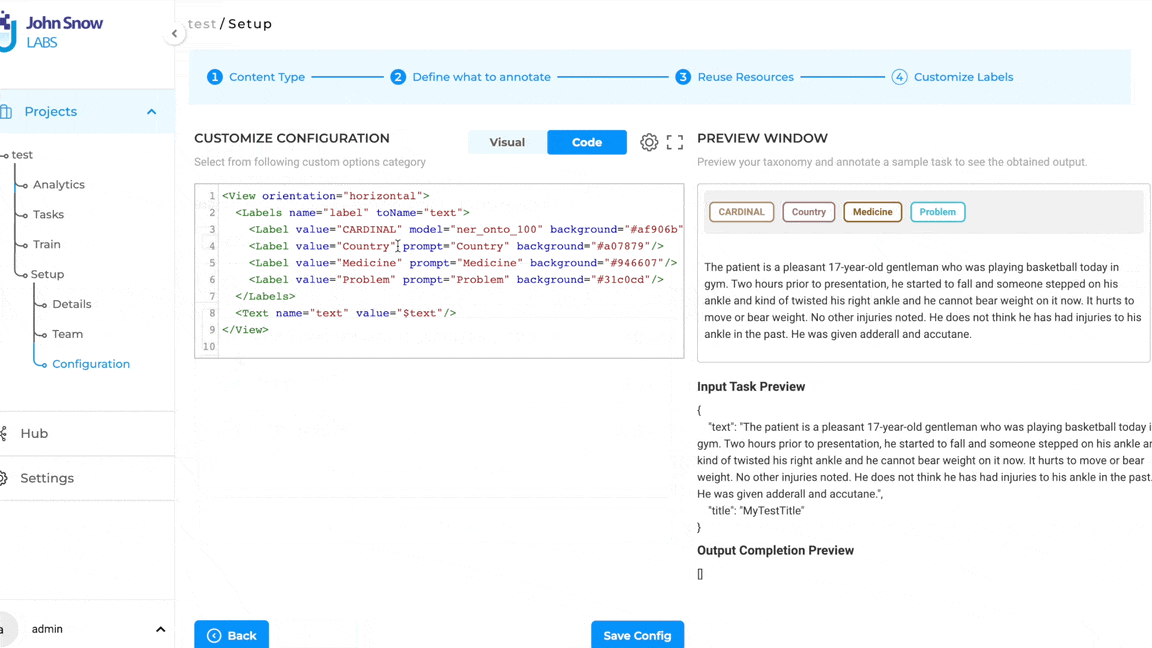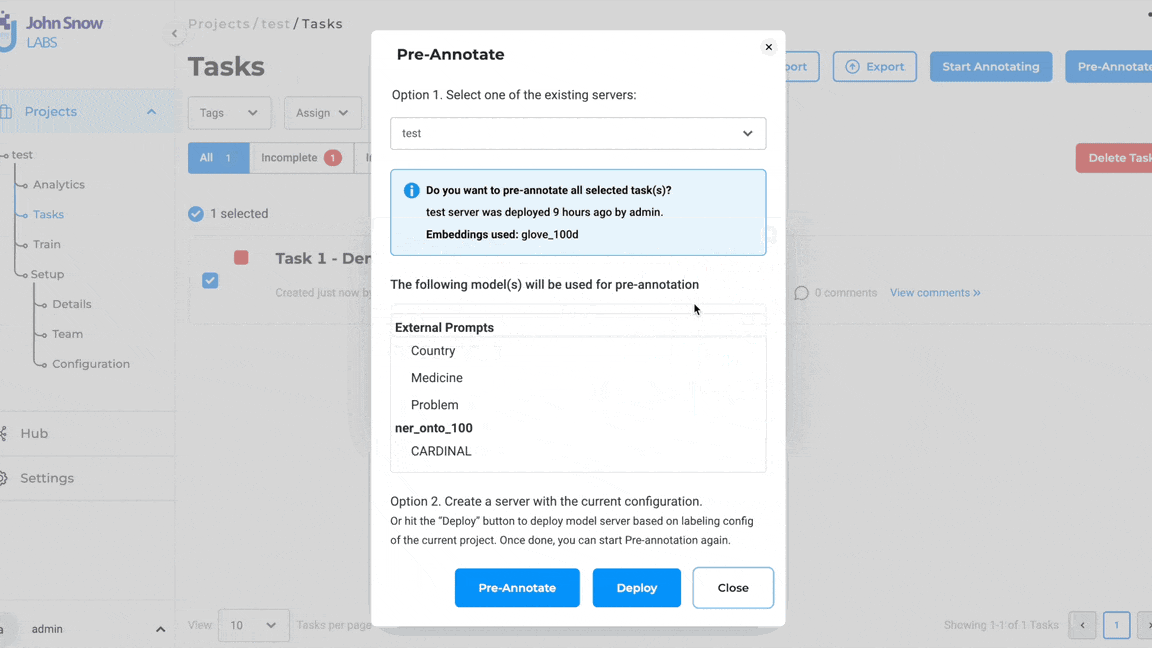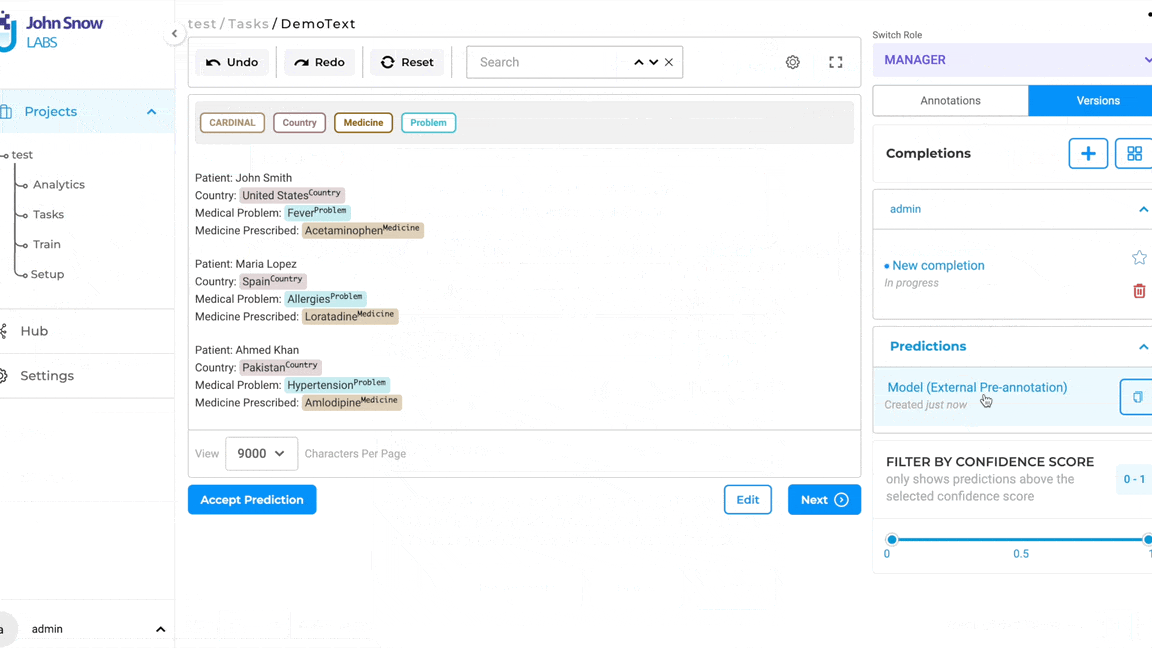
The highlight of this release is the integration with an external service provider, Open AI, to expand and deepen the range of prompts available for pre-annotation (in addition to the Zero Shot entity and relation prompts already supported). This feature:.
-
Broadens Prompt Possibilities: By integrating with Open AI LLM models, users can tap into a more diverse set of prompts, leveraging external expertise to craft pre-annotations, as an alternative pre-annotation solution or when pre-trained models are not available.
-
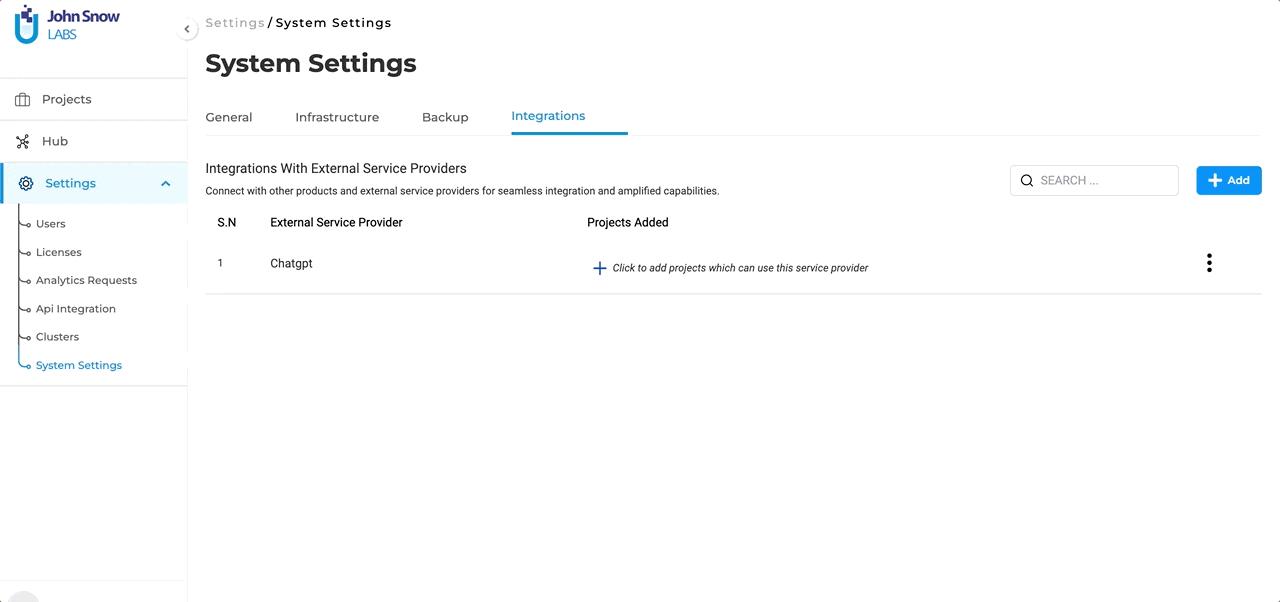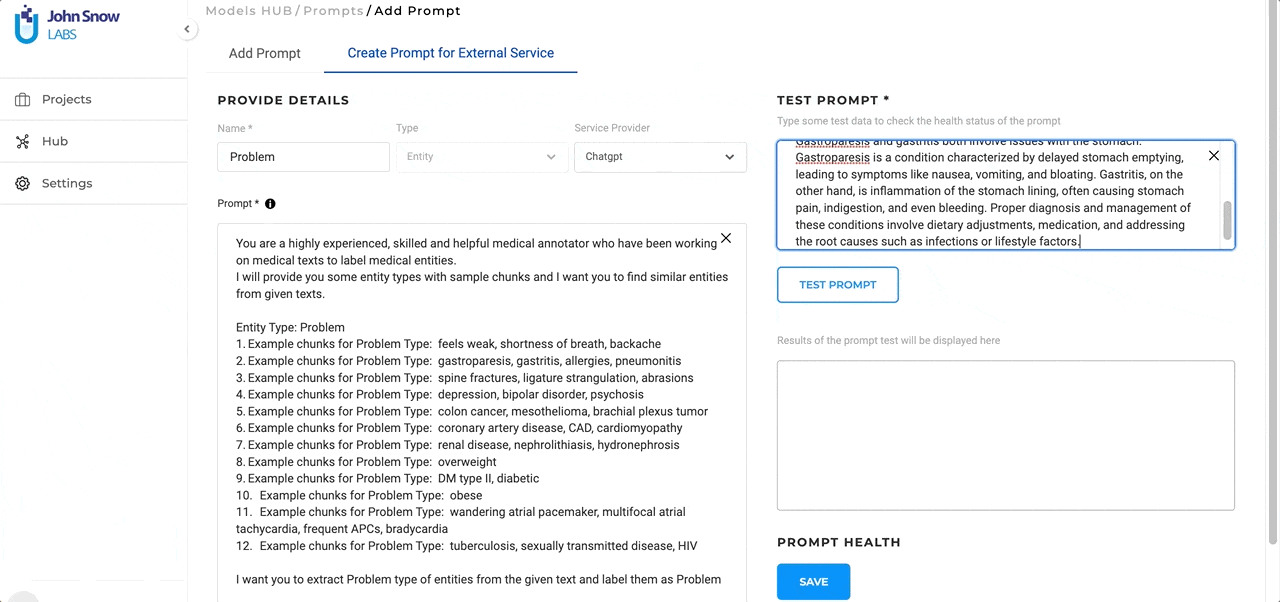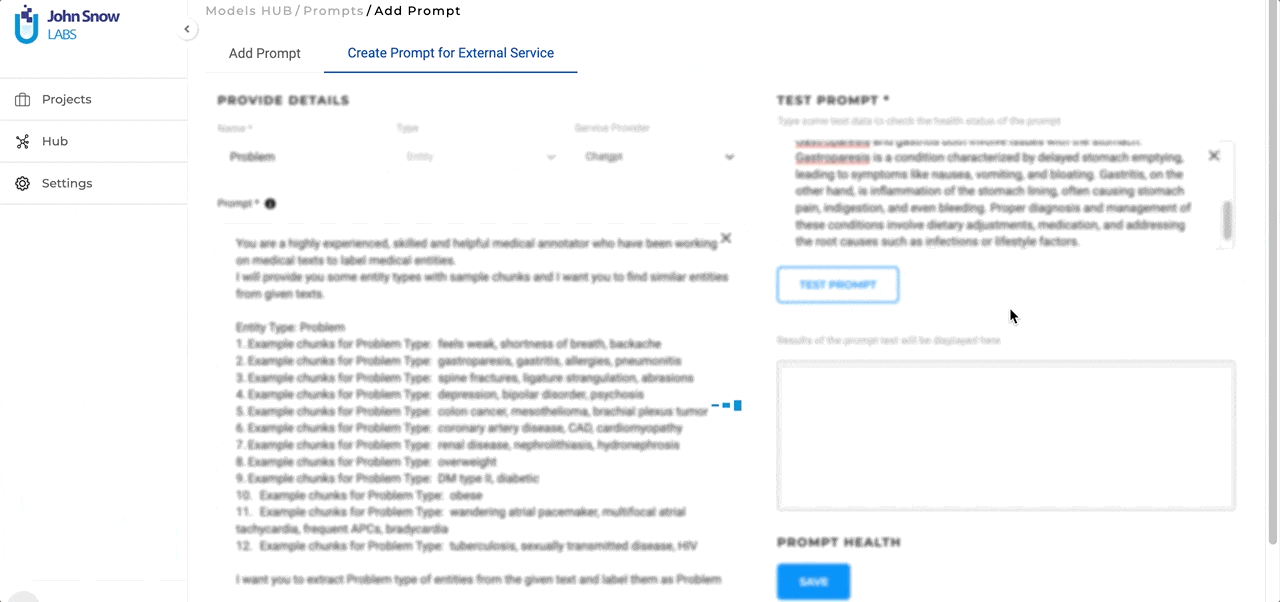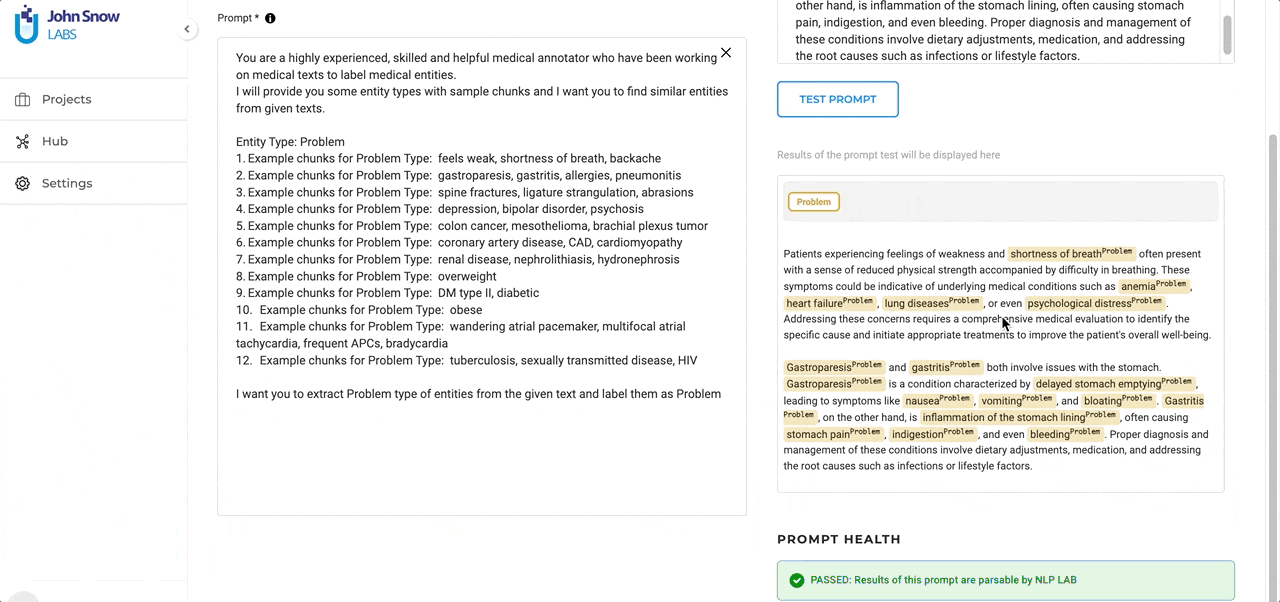
Efficient Entity Extraction: As current LLMs, GPT family included, are not very good at entity recognition tasks, NLP Lab included a post-processing step on the result provided by LLM. This improves entity identification and helps precisely locate the entities in the given text. These entities, carefully curated and aligned with NLP Lab pre-annotation requirements pave the way for a more efficient and streamlined annotation experience.
The following sections explain in detail how to define and use GPT prompts.
Setting Up the Integration with Open AI service
Integrating “ChatGPT” into the NLP Lab has been designed to be a straightforward process, ensuring users can harness the power of external expertise seamlessly. It consists of three easy steps:
Integrations Page: Navigate to the Integrations Page located within the System Settings. This is the hub where all external service providers, including Open AI’s GPT Models, can be defined and managed.
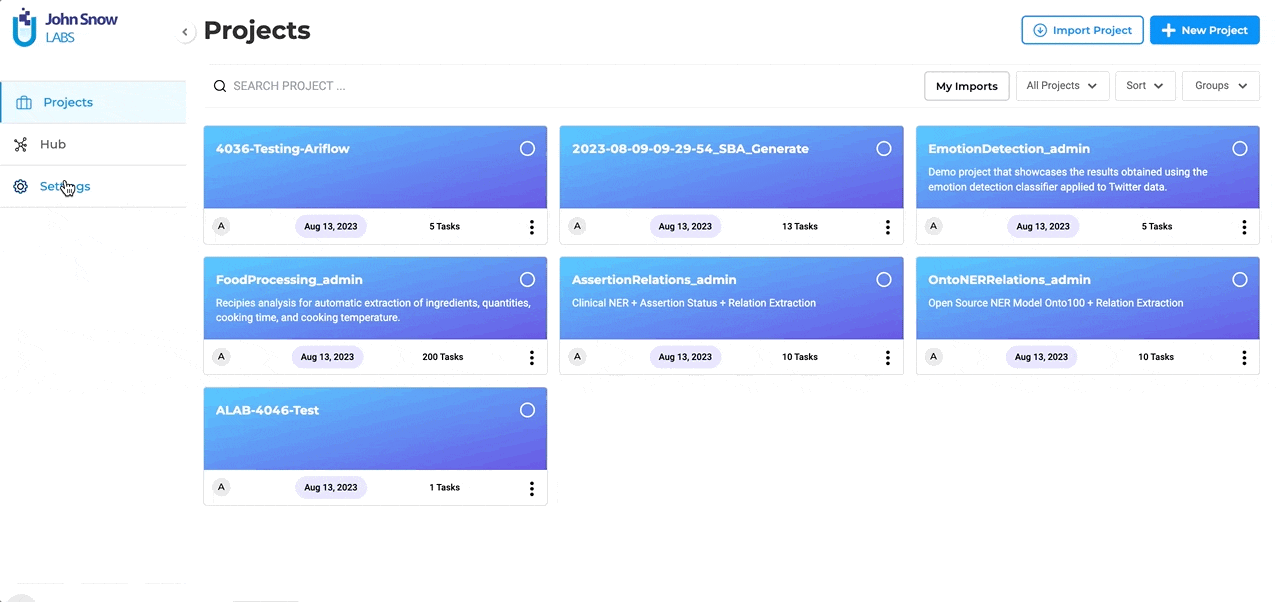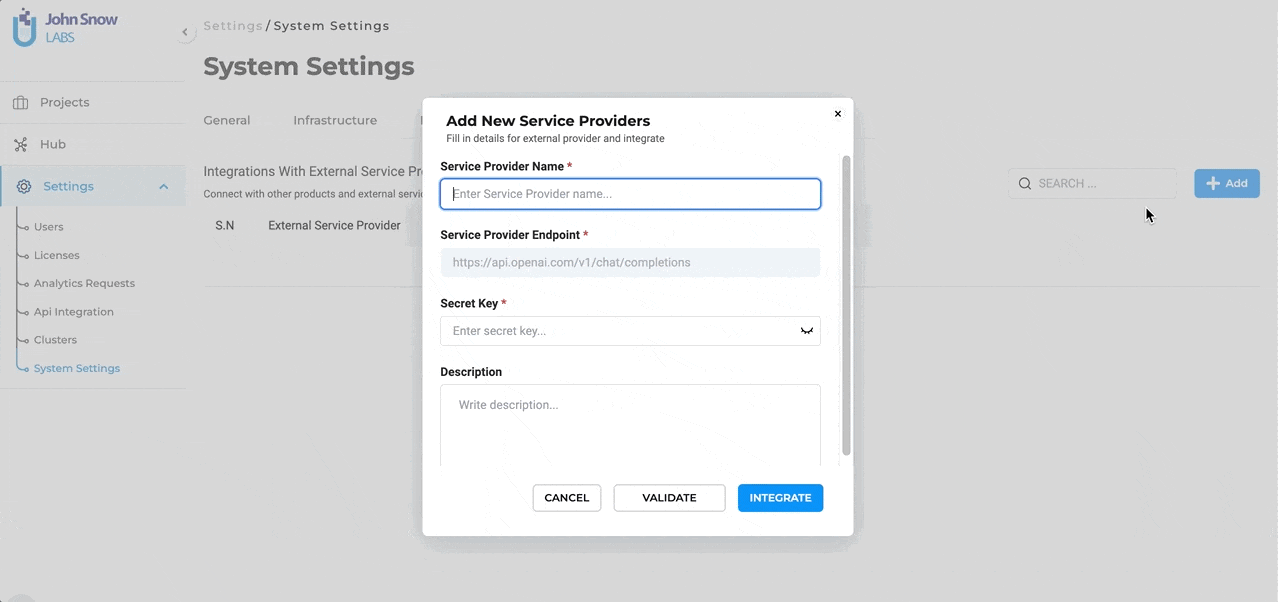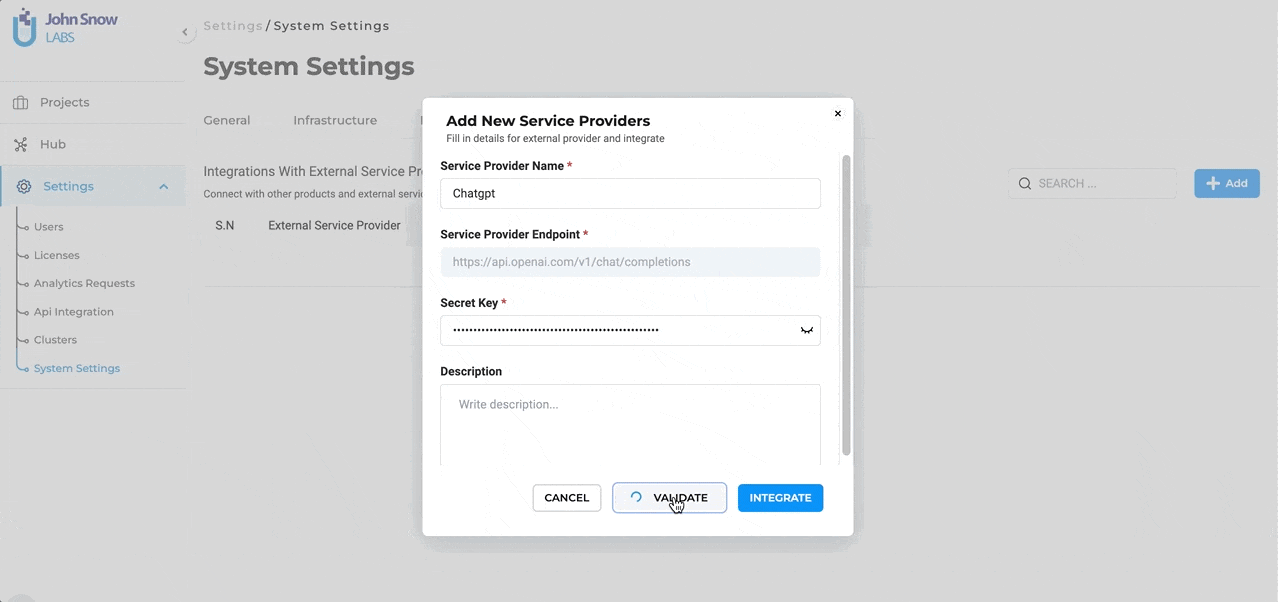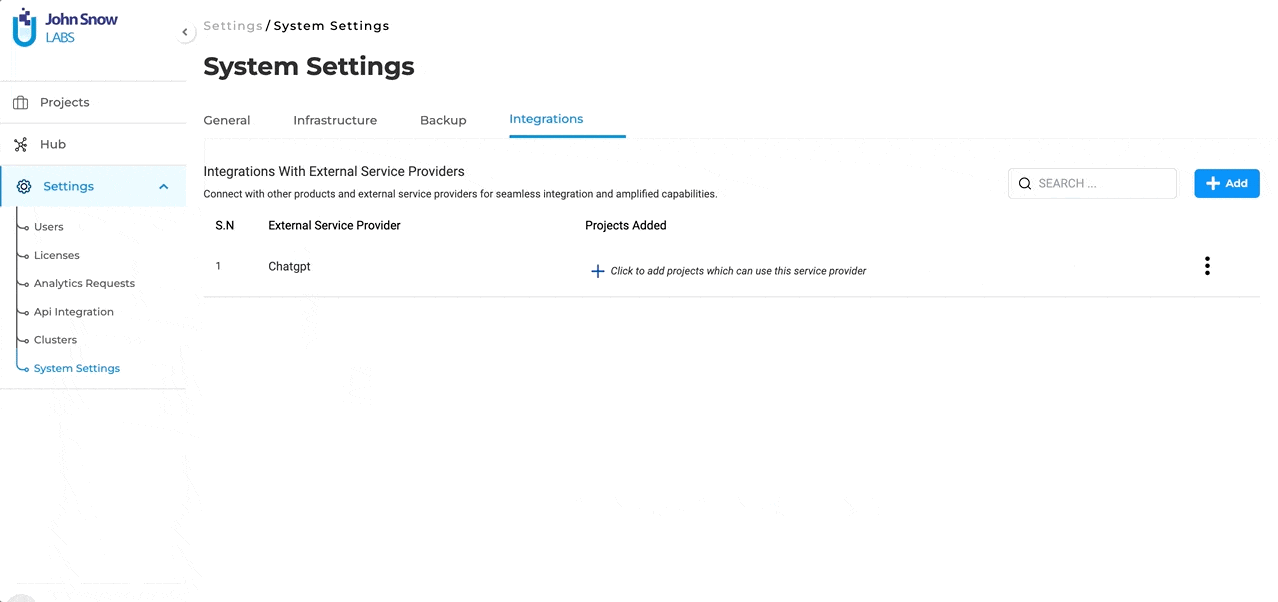
Define the Service Provider: To initiate the integration, users are required to provide specific details:
- Service Provider Name: This is the identifier for the external service, which in this case would be “ChatGPT” or any other name you prefer to use.
- Secret Key: Every external service comes with a unique Secret Key that ensures secure communication between the platforms. Enter the Secret Key associated with your Open AI subscription here. To ensure the integration process is error-free, users can validate the provided Secret Key directly within the form. This validation step ensures that the connection is secure and that the key is correct.
Project Association: Once a successful connection with “ChatGPT” (or any external LLM service provider) is established, it doesn’t end there. The integrated service will now be available for association with selected projects. This means users can decide which projects will benefit from the “ChatGPT” integration and enable it accordingly. The Open AI integration allows users to tap into a vast reservoir of external expertise, enhancing the depth and breadth of their projects. We’ve ensured that the integration process is as intuitive as possible, allowing users to focus on what truly matters: crafting refined and effective pre-annotations.
ChatGPT Prompt Definition and Testing
Users can generate LLM prompts on the dedicated Prompt page from the Hub of Resources. For ChatGPT Prompts, NLP Lab offers a dedicated definition interface. Here’s what to expect when creating a new LLM prompt:
-
Name the Prompt: Within this new tab, users will first be asked to provide a name for their prompt. This name will be used for pre-annotating identified entities. At this point, we recommend creating one prompt per target entity.
-
Select the Service Provider: Next, users can choose the specific service provider they’ve previously set up via the Integrations Page.
-
Test in Real-time: A standout feature is the ability to test ChatGPT prompts at creation time. As you craft your prompt, you can immediately see how it performs on some test data. This not only allows for immediate feedback but also ensures that the final prompt aligns perfectly with the user’s objectives.
This streamlined approach ensures that integrating and testing external prompts is as intuitive and efficient as possible.
Consistent Workflow with LLM Prompts
Even with the introduction of new features in NLP Lab’s 5.3.0 release, users can take comfort in the consistent experience offered when working with prompts. The addition of external service provider prompts brings a fresh layer to the annotation process, yet the core workflow you’re familiar with stays the same.
-
Familiarity Amidst Innovation: Despite the new integrations, the process of using available prompts remains as straightforward as ever. Whether you’re working with traditional prompts or the newly introduced ones, the experience is smooth and consistent.
-
Seamless Transition: Our commitment to user-centric design means that even as we innovate, we prioritize the ease of use you’ve come to expect. Transitioning to or incorporating external prompts is made effortless, with the interface and steps for prompt creation, selection, and integration remaining intuitive and unchanged.
With NLP Lab 5.3.0, you get the best of both worlds: exciting new features and the comfort of a familiar workflow.
Note: Pre-annotation of tasks using LLM Prompts does not require the deployment of the pre-annotation server. The pop-up to deploy the pre-annotation server is only shown if the project configuration consists of both LLM prompts and spark NLP models.
Improvements
Enhanced Taxonomy to Section Mapping
NLP Labs 5.3.0 brings significant upgrades to the taxonomy customization experience when dealing with Section-based projects.
Revamped Viewing Experience for Taxonomy Elements:
We’ve reimagined the way users view “Labels to Sections” associations:
- At-a-Glance Overview: Gone are the days of manually selecting each label to view its associations. Now, users can instantly see the complete mapping of Labels to Sections, providing a holistic view of the project’s current configuration.
- Efficient Updates: This consolidated view enables users to quickly grasp their current setup and make any necessary adjustments with ease, making the entire process more user-centric.
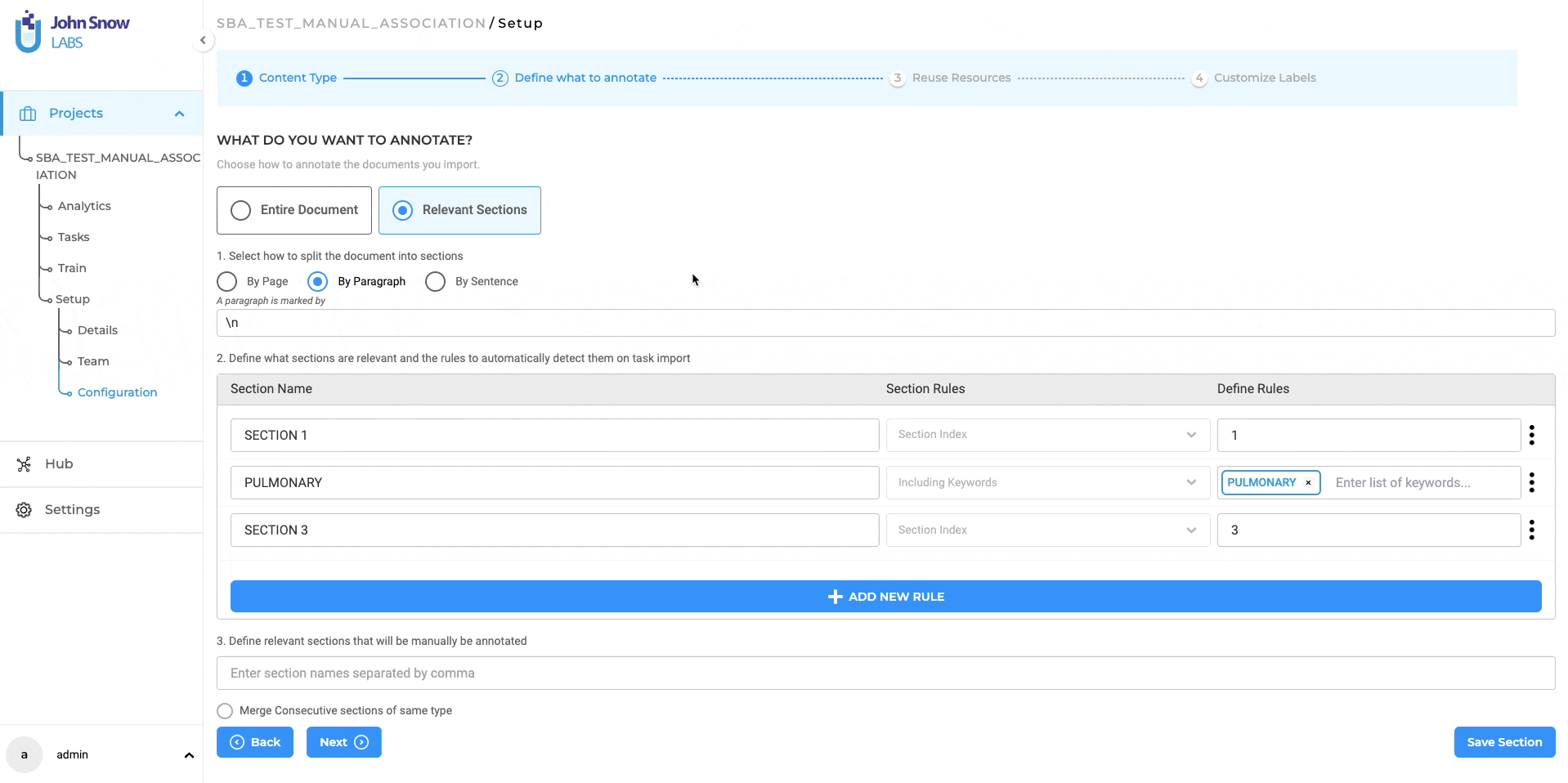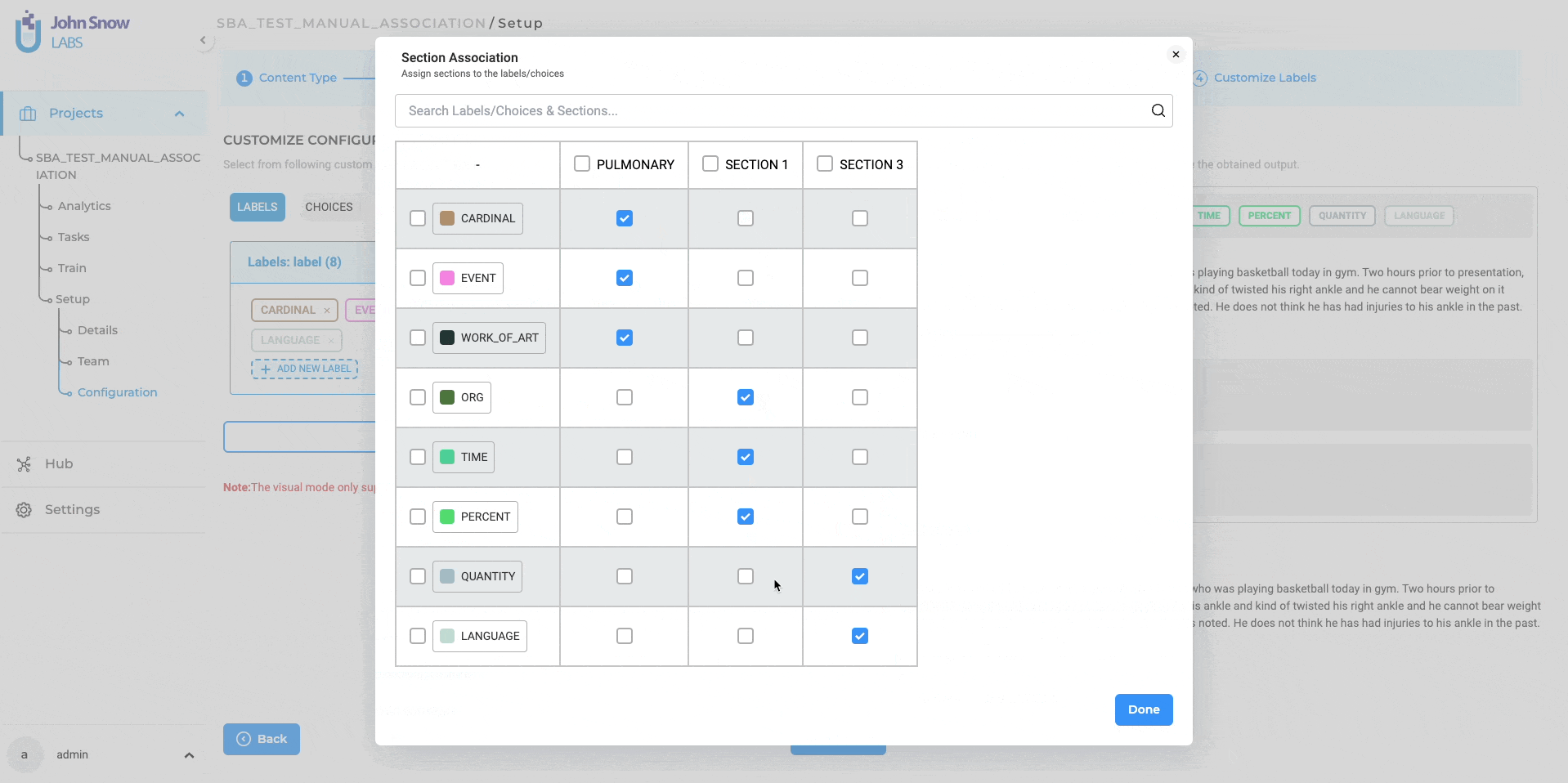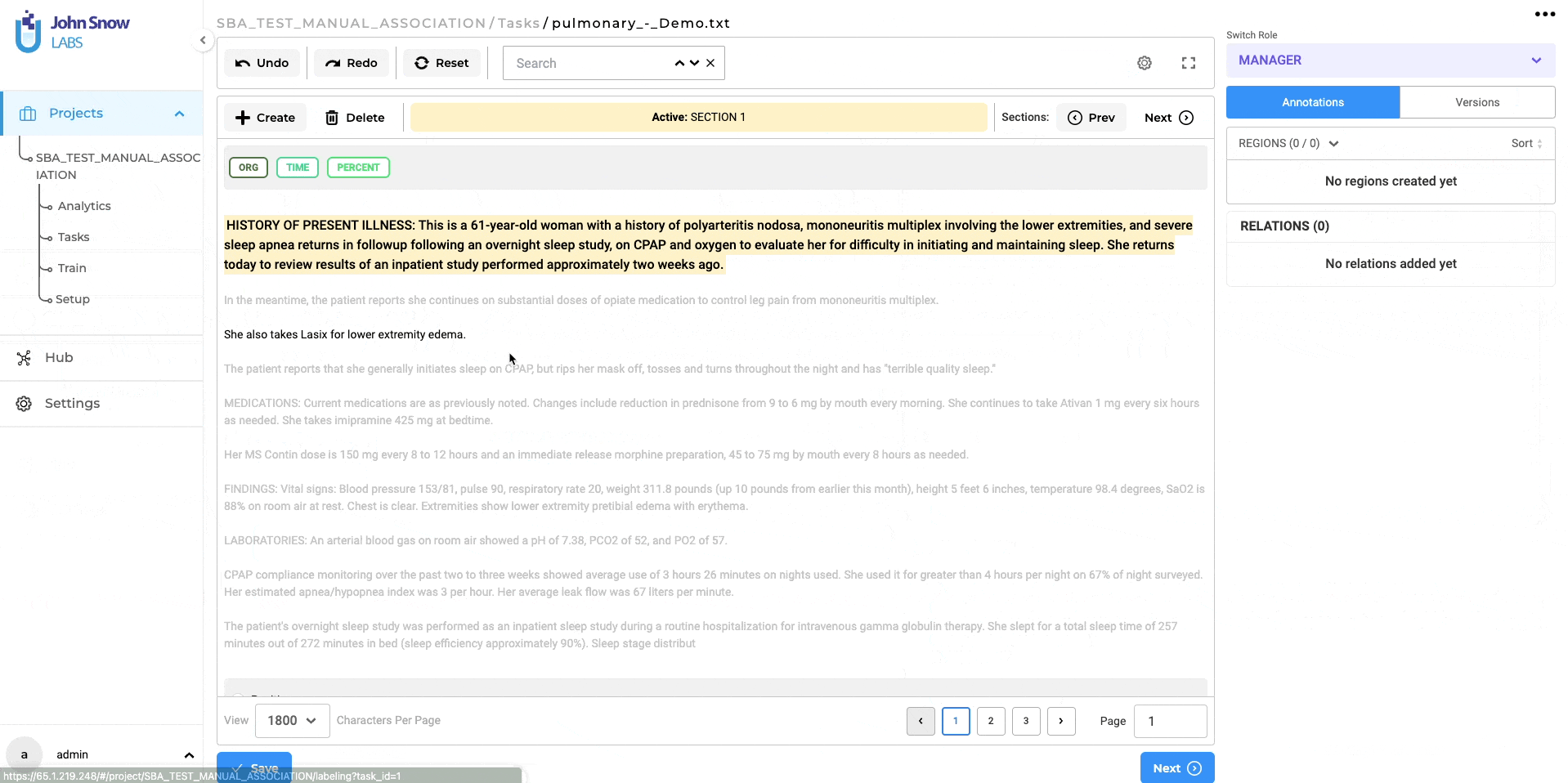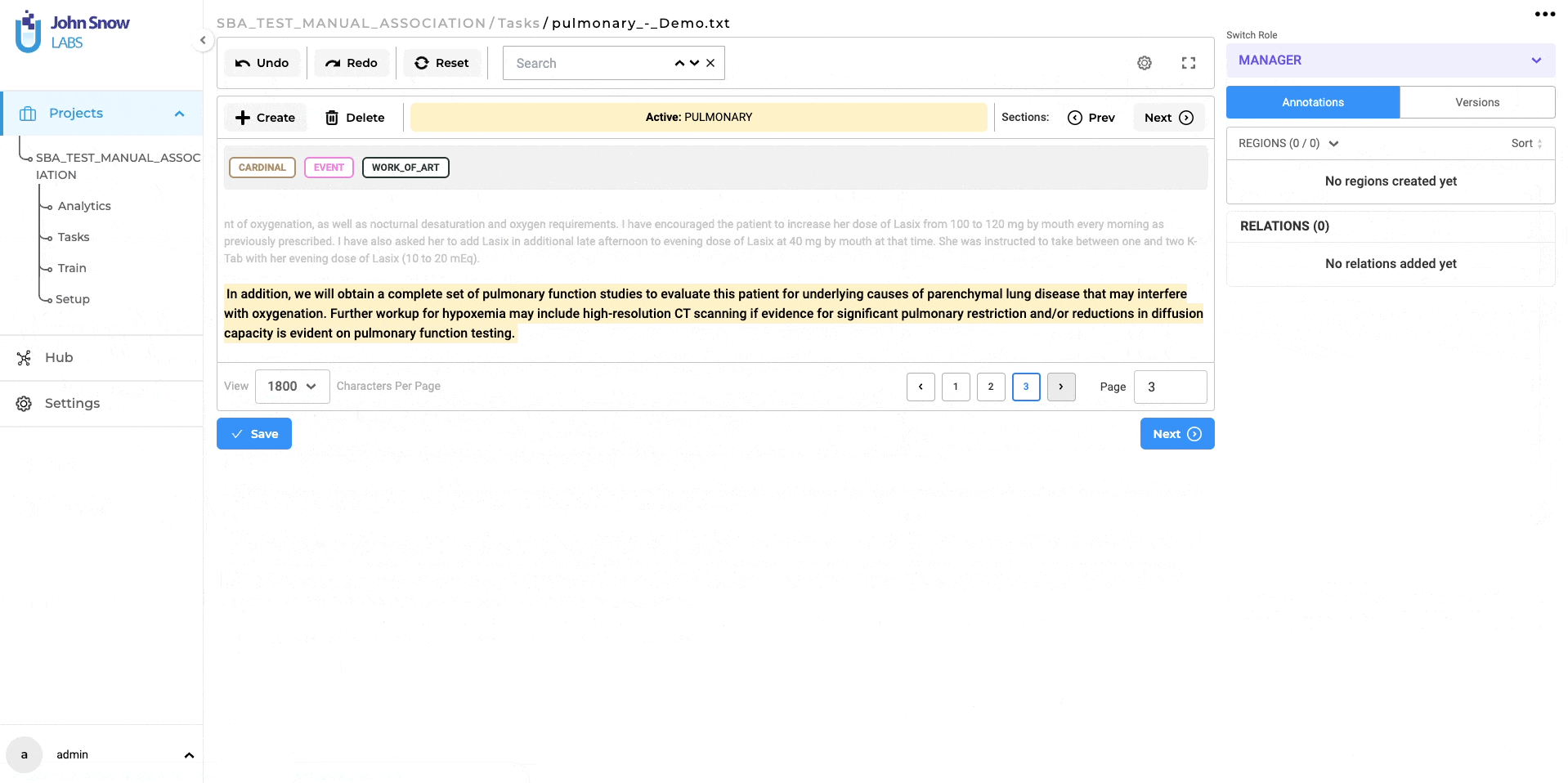
Bulk Association of “Labels/Choices to Section:
A standout enhancement is the ability to associate “Labels/Choices” to sections in bulk. Unlike the previous version, where users could only associate one label at a time, this update allows for simultaneous selection and association of multiple labels to various sections. This enhancement not only streamlines the project configuration and annotation process but also offers a more intuitive user experience, saving valuable time and effort.
To facilitate these new features, we have made minor adjustments to the project configuration page in NLP Labs. Under the “Customize Labels” tab, you can now find a new button named “Associate Sections”. Clicking on this button allows users to quickly access the tabular form of the mapping, making it easier to manage Labels/Choices linkage with specific sections. For both “Labels” and “Choices”, we have provided the dedicated “Associate Sections” button on their respective configuration tabs. These new improvements are supported in all section-based annotation-enabled projects, including Visual NER projects.
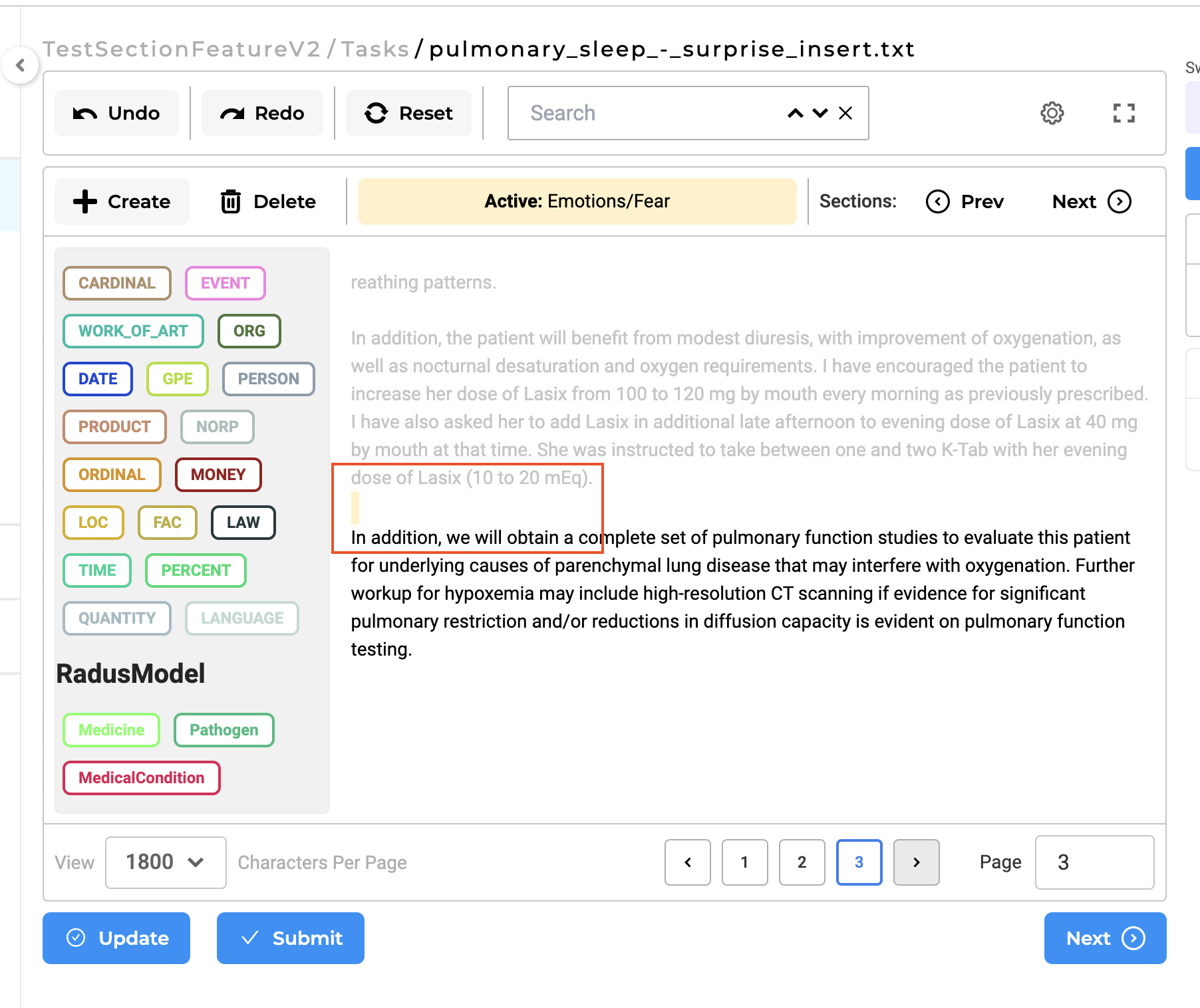
Section-Based Annotation: automatically disregard empty sections
In earlier iterations of the section-based annotation project feature, users noticed that some empty sections were marked as relevant when automatically splitting content into paragraphs. Recognizing this issue, version 5.3.0 brings a thoughtful enhancement: sections without any textual content are now automatically disregarded. This ensures a more streamlined annotation process, omitting empty sections like the examples provided below.
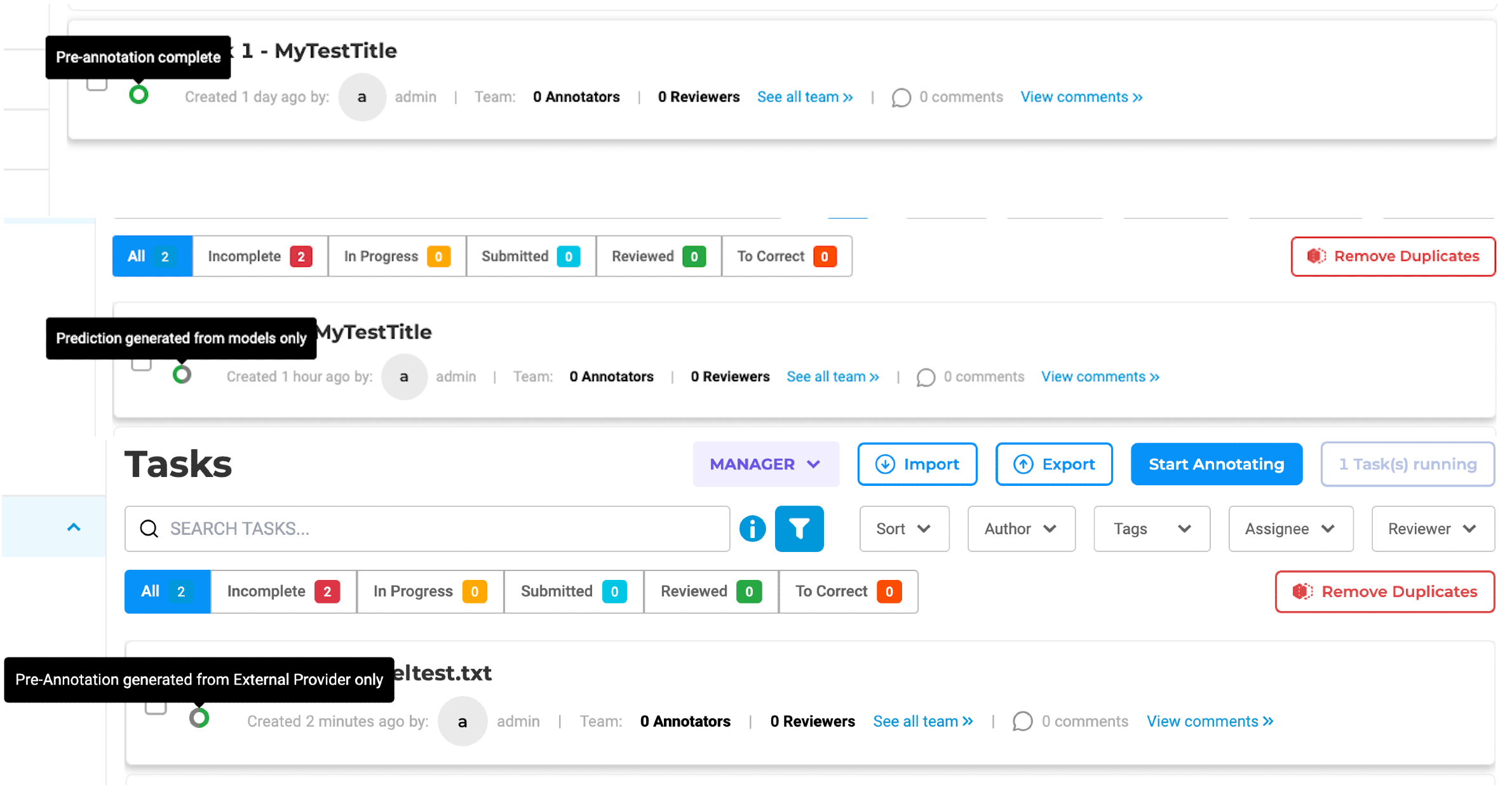
Updated Pre-annotation Status indicator on task page
In the past, the pre-annotate status exclusively indicated whether a prediction was marked as “generated,” “not generated,” or if the pre-annotation process had encountered a failure.
With the integration of pre-annotations derived from ChatGPT, the updated approach to preannotation status will encompass statuses for both SparkNLP predictions and ChatGPT predictions. Specifically, for projects involving both SparkNLP models and prompts generated through ChatGPT as an external provider, a revamped pre-annotation circle has been reimagined as a ring divided into two halves. The first half of the ring will showcase the pre-annotation status derived from SparkNLP, while the second half will depict the status of predictions stemming from ChatGPT.
Enhanced Formatting for OCR Text
For text projects using PDF/Image processing via Visual NLP, we’re excited to introduce an enhanced format feature.
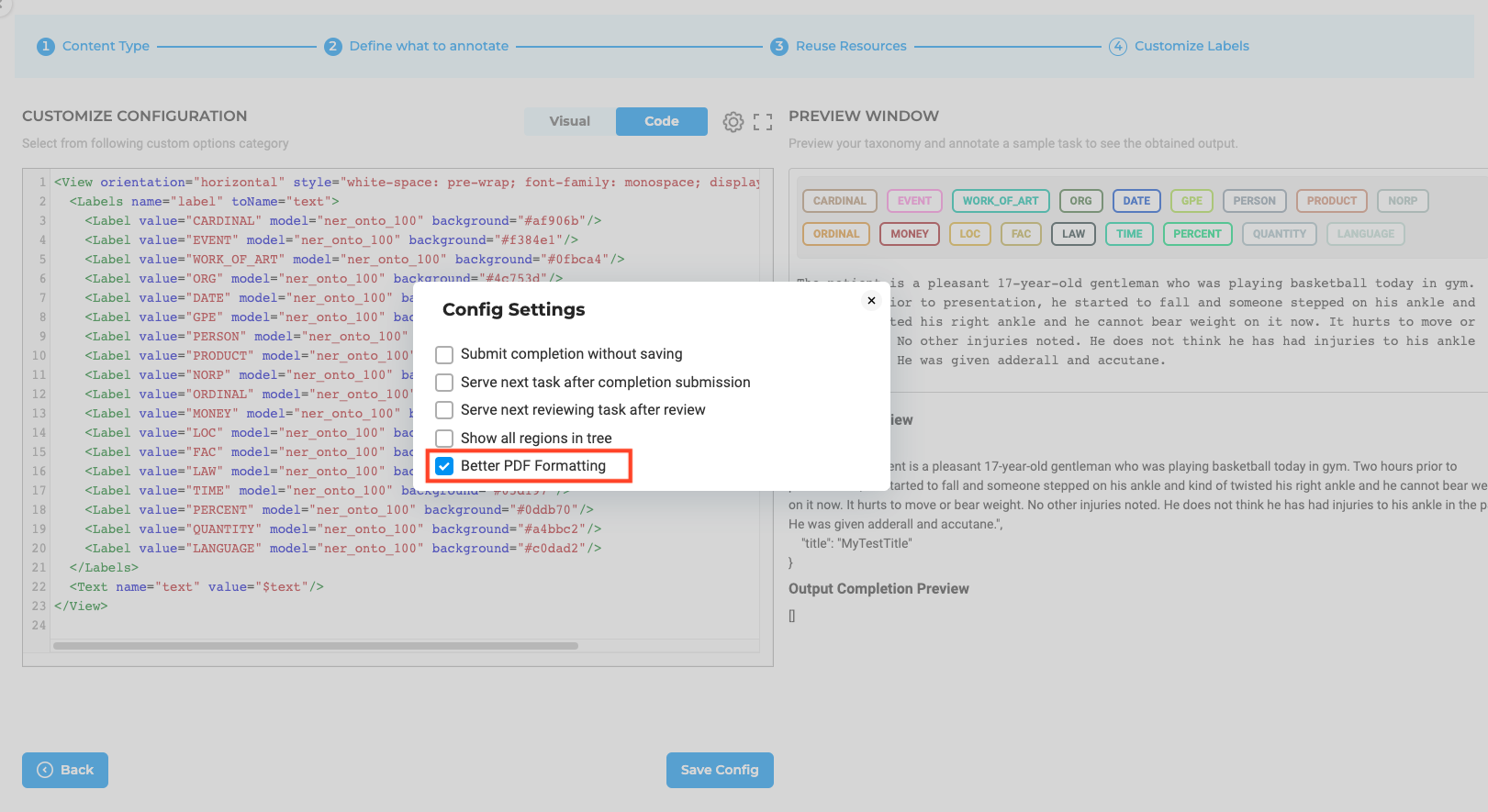
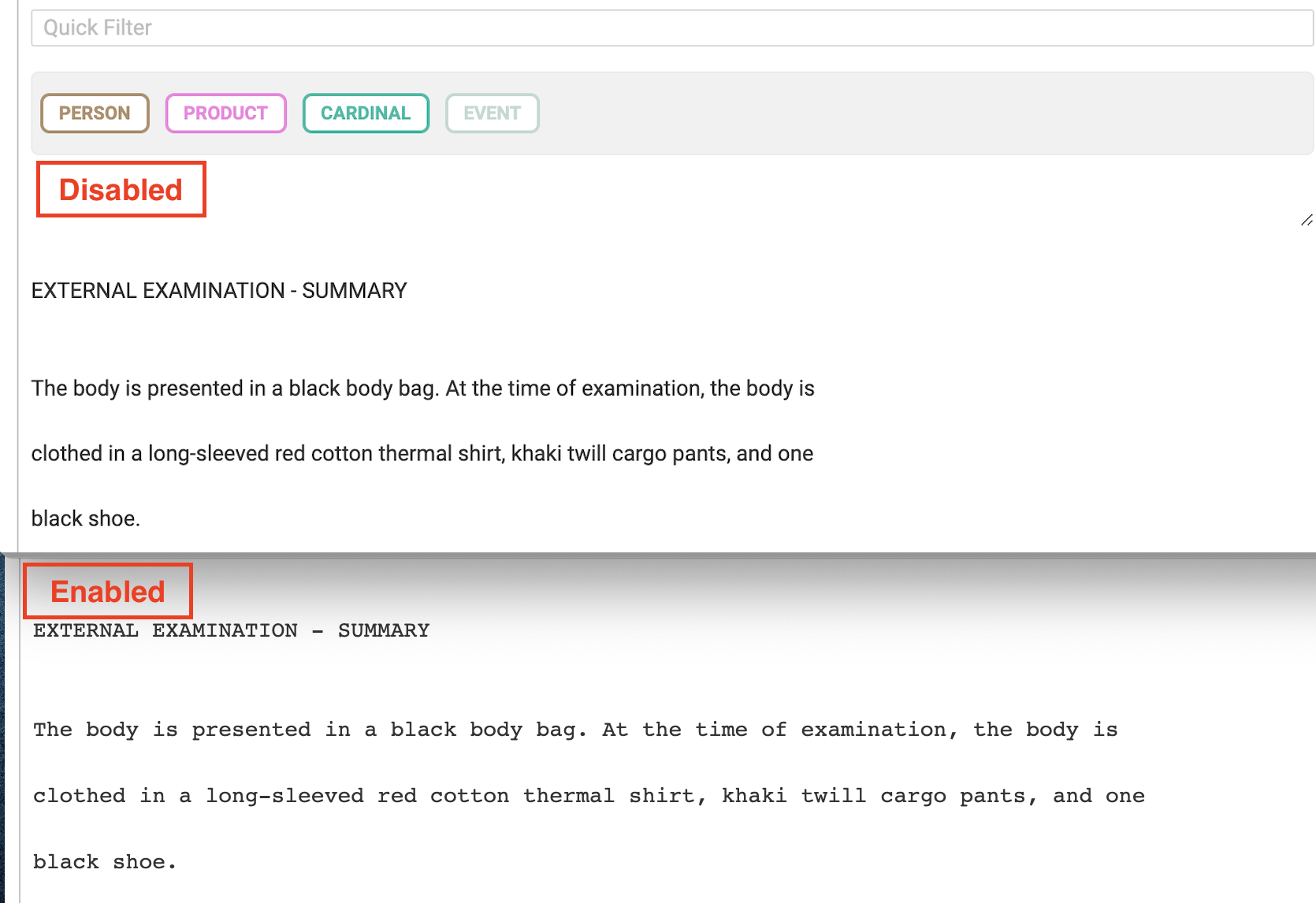
Once this feature is activated, the imported text is reformatted to offer better clarity and spacing within the annotation interface. Our goal with this enhancement is to foster a clearer, more spacious workspace, ensuring precision and ease during text annotation.
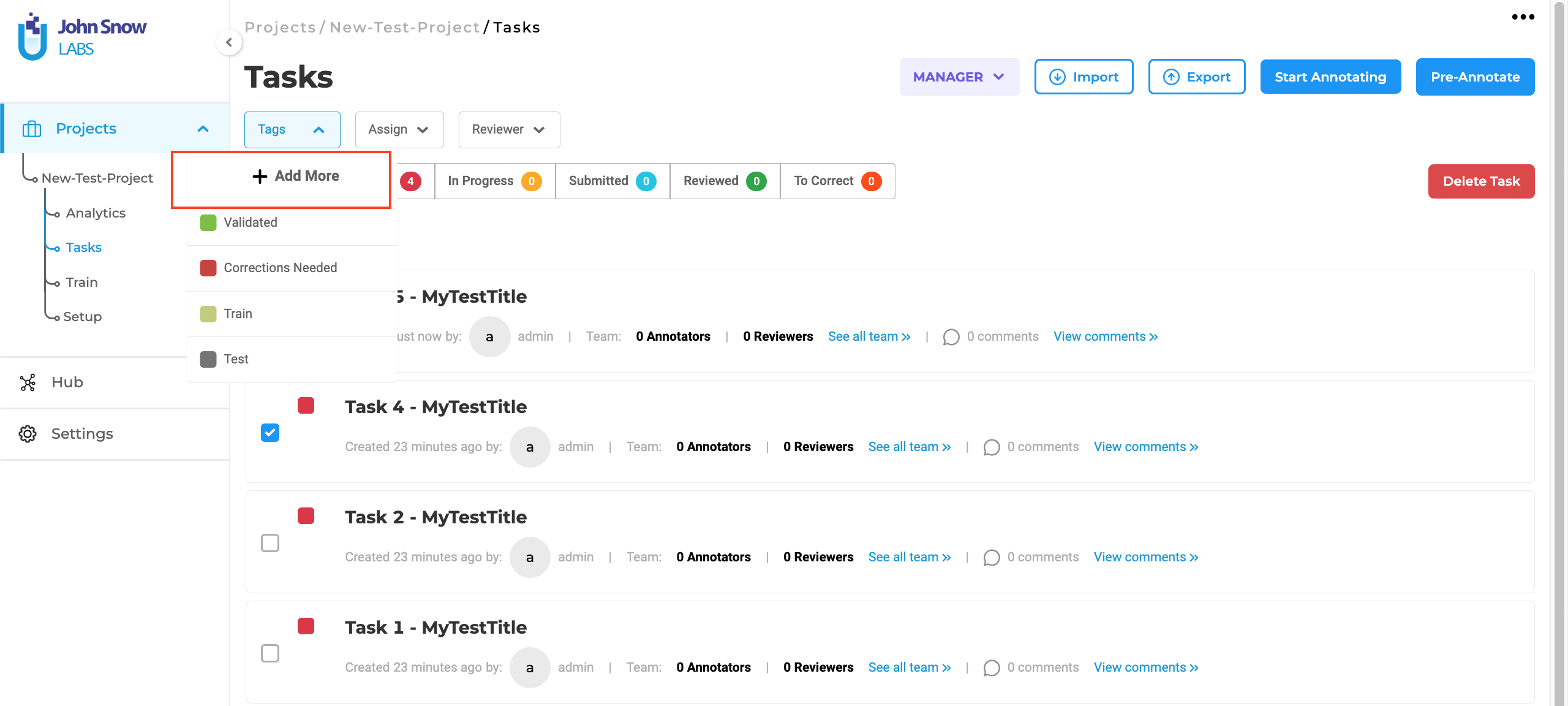
Tags Definition Button was moved on the Tasks Page
In version 5.3.0, the “Add More” option for task tags was moved. Based on user feedback, we’ve moved the “Add More” button to a more accessible location at the top of the Tags dropdown list. Along with its new position, the button now sports a “+” icon and a refreshed design, while retaining its original functionality. Importantly, the button’s functionality remains consistent with its previous purpose.
Bug Fixes
-
For HTML sources projects replace the dialogue in PREVIEWS with the JSL link
The preview format for HTML Dialogues & Conversations projects has been enhanced to feature a JSL link in place of the traditional ‘Dialogues’.
-
Tags are not consistently assigned to Tasks
Previously, tasks generated from external providers lacked assigned tags, posing challenges for users in distinguishing imported tasks’ sources. To address this, tags are now consistently assigned when clicking on the edges of tag options or the color indicators instead of only being assigned when clicking directly on the tag name.
-
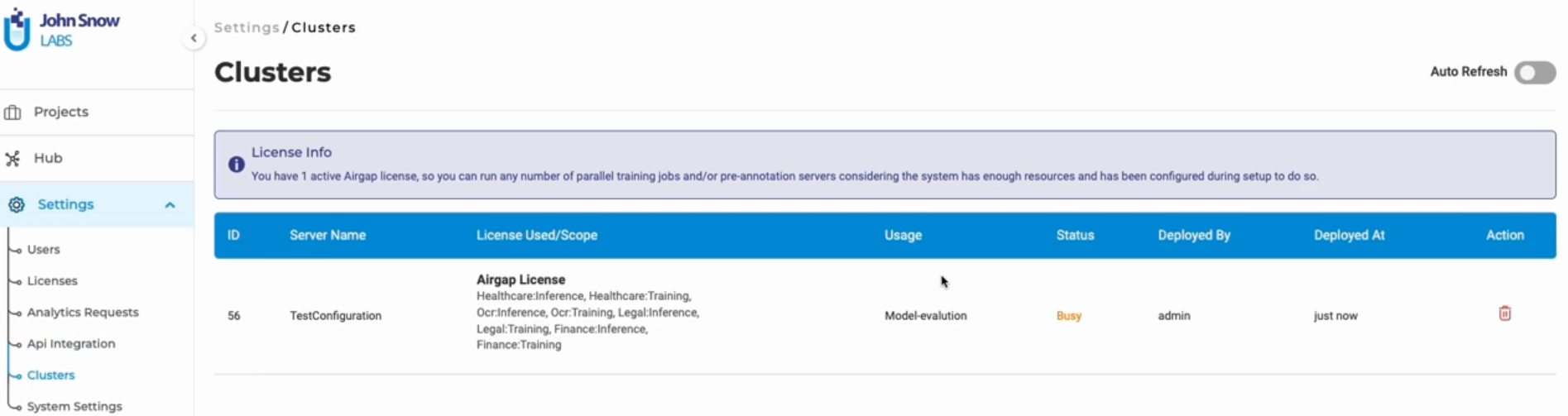
Model evaluation starts before the required resources are available when the maximum server count is reached
In the previous version, model evaluations would commence even if the necessary resources were unavailable or if the maximum server count had been reached. To address this, a new approach has been implemented. When a model evaluation is in progress, a dedicated server is generated on the cluster page. This server is designed to be automatically removed once the evaluation concludes. Furthermore, should the maximum server count be reached and a user initiates an evaluation, an error message indicating “Maximum Model Server Limit Reached” will be displayed.
Additionally, users have the option to delete an evaluation server from the cluster page. This action results in the evaluation being aborted on the Train page, accompanied by a notification banner indicating the aborted evaluation.
-
For all Search Fields, White Space before/after the “search keyword” causes the search action to return no results
Previously, in all Search Fields, having white space before or after the “search keyword” resulted in the search action yielding no results. Consequently, a change has been implemented to ensure that search results are displayed accurately regardless of any leading/trailing whitespace around the search keyword. This enhancement is universally applicable to all search fields within the application.
-
The duplication error for Section Field does not resolve if the user changes/deletes the value of the other duplicate field
Previously, if a Section-based Rule with a duplicate name was added, the error would still show as if the first originally named rule was edited to a different name. With Version 5.3.0, the duplication error will now be resolved if any of the rules that fall under the duplication case are edited to be unique. -
Incorrect active section name is shown in the top bar for pages without relevant section
In the case of a multi-page task that does not have relevant sections, the previously active section will no longer appear at the page’s top. Additionally, if a page contains no pertinent sections, the Active tab on the task’s upper part will be displayed in a subdued manner.
-
Tasks imported in Visual NER Project are not visible until the tasks page is refreshed
The issue of the OCR task imported in Visual NER projects not appearing on the Tasks page and the Import button staying disabled until manually refreshed has been resolved in this version.
-
Clicking on undo button in the playground resets every detail of the rule deployed
Previously, using the Undo button in the playground didn’t restore rules to their original state after modifications. The Undo action cleared all aspects (suffix, rule type, content length) from deployed playground rules. This problem has now been addressed.
-
Section Based Annotation: Merger of consecutive sections of the same name
Previously, when the option “Merge Consecutive sections of the same type” was chosen, any two sections created by the rule that appeared consecutively were combined into a single section. This approach posed a challenge as it could result in an elongated chain of sections if all sections were consecutive.
With the recent improvement, only the relevant sections with matching section names are merged. For instance, if there are sections named S1, S1, S3, S1, S2, S2 created consecutively, only the first occurrence of S1 and the final instance of S2 will be merged into a single section, while S3 will remain unaffected.
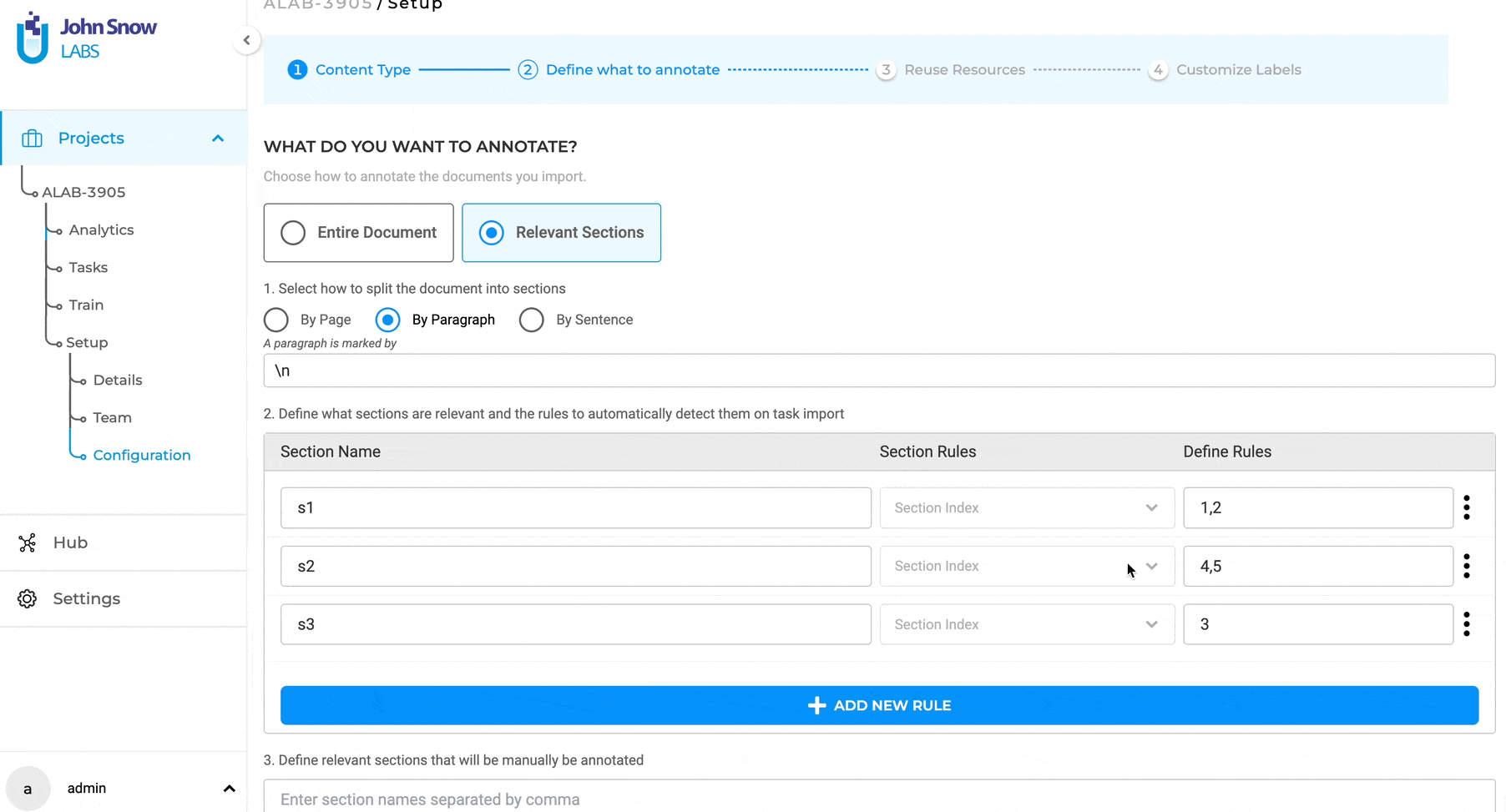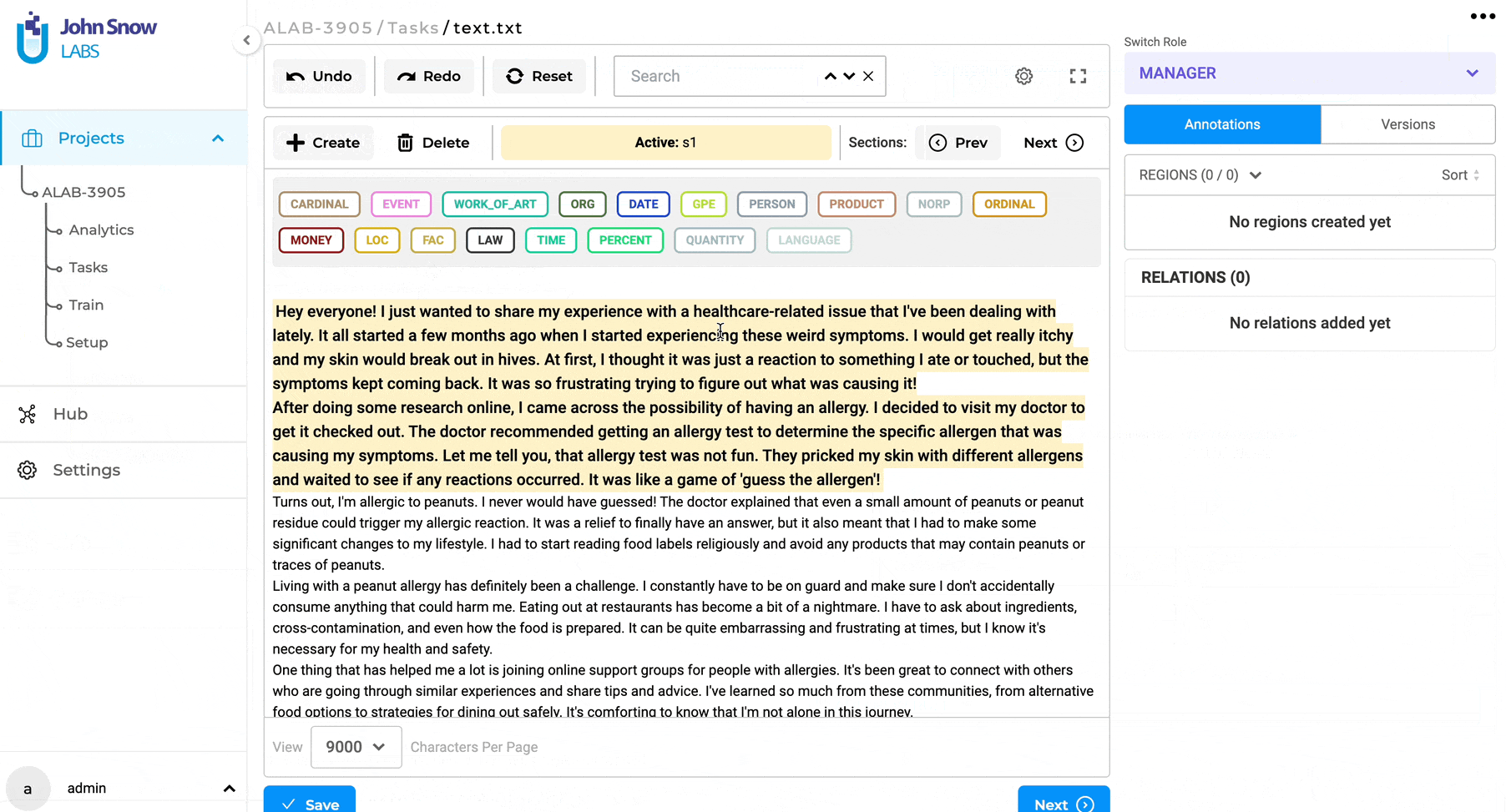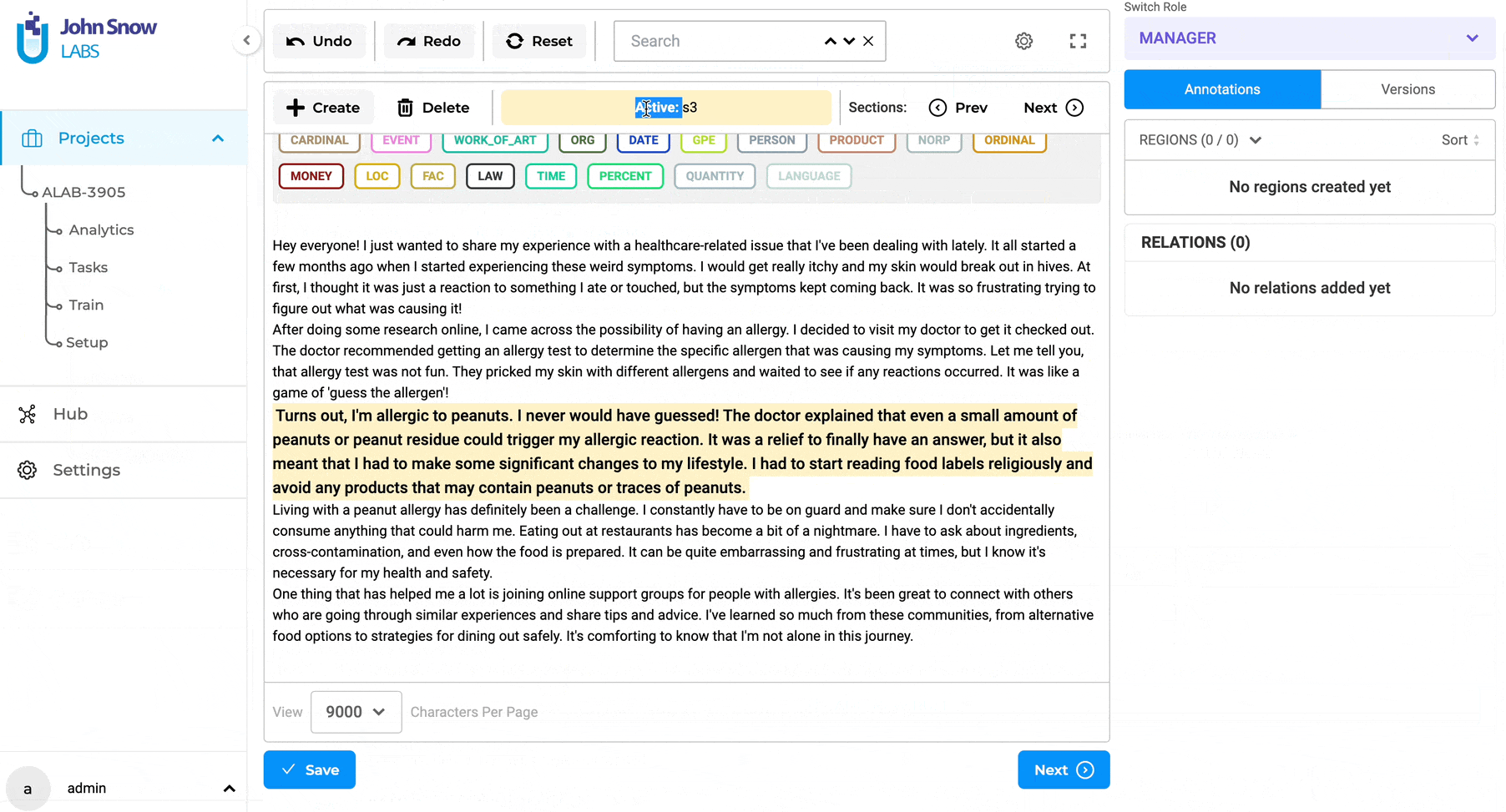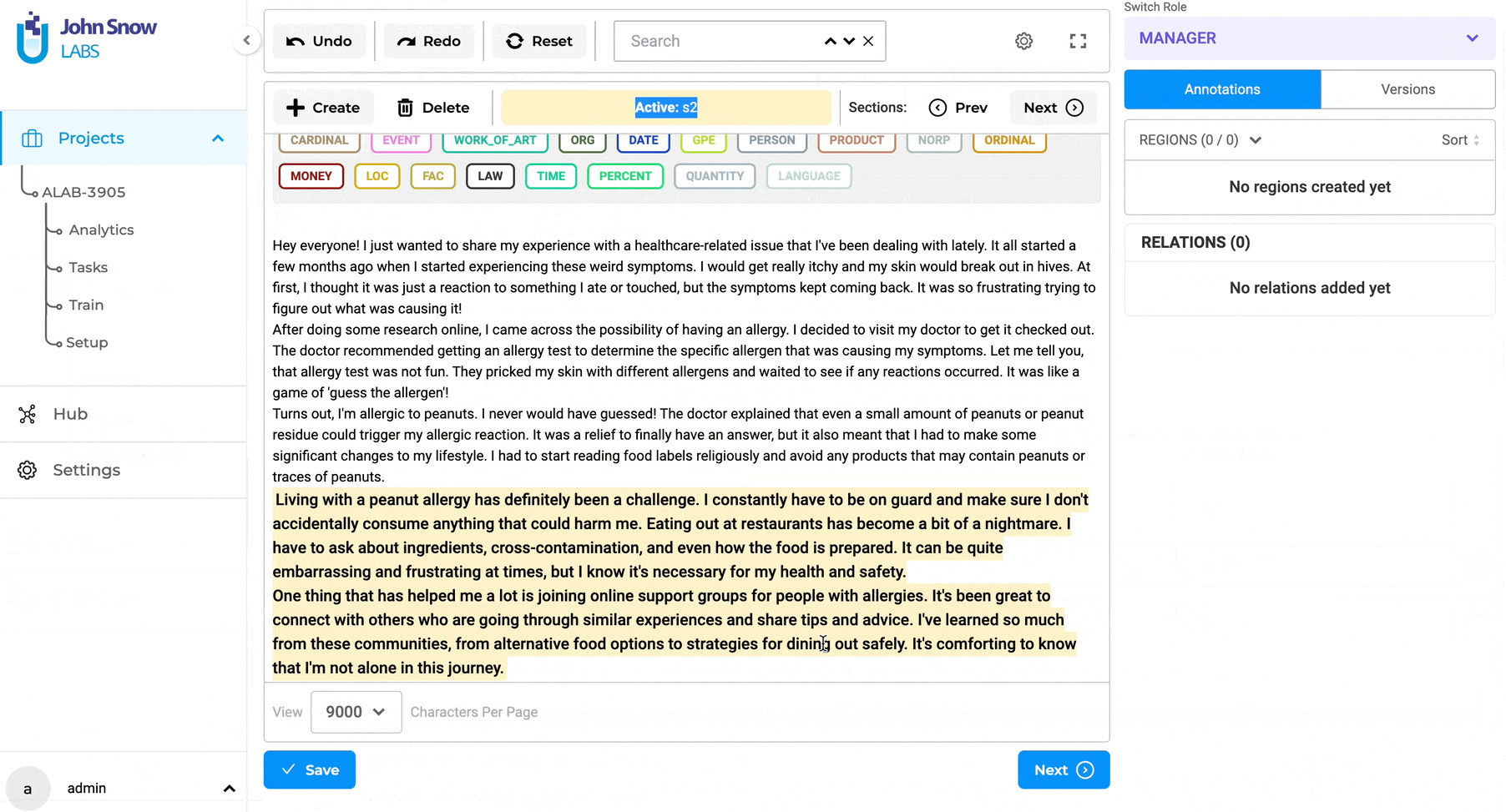
-
Section Based Annotation: Model is redeployed if the same classifier is modified for the same project
The sections classifier no longer undergoes redeployment each time classifier options are modified for the same model. Additionally, the section classifier remains unaffected when an additional classifier rule using the same classifier is introduced. Consequently, in scenarios involving task importation, newly added classifier rules are integrated into the new tasks.
However, the section classifier is automatically deployed in situations where a new classifier server is added and the previous one is subsequently removed.
-
“Filter pre-annotations according to my latest completion” shows predictions for deleted sections in SBA-enabled project
There was an inconsistency when applying “Filter pre-annotations according to my latest completion” for SBA enabled task. The problem of the filter not functioning correctly, resulting in predictions for deleted sections, has been resolved in version 5.3.0.
-
RE prompts using NER Prompts cannot be deployed in the playground
Previously, errors were encountered in the playground when deploying the Relation prompt using the NER prompt in the playground. With this update, these issues have been resolved.
-
Generate Synthetic Text: Unable to import generated text if the SBA project has Classification Rules
There was a singular case for Section-based Projects, where adding classification section-based rules to create sections prevented the import of the generated synthetic text. In version 5.3.0, this has been fixed and now users can import the synthetic tasks after or even while the classification model for the section rules is being deployed.
-
Validation missing when deleting section rule which is already associated with label/choice in the Configuration > Customize Labels page Previously, when a user tried to delete the section rule that was associated with label/choice, there was no warning suggesting user that the section is linked to labels/choices in the configuration. The issue has now been resolved and users are given a warning dialog box about the link between the section and the labels/choices and he/she can either proceed and delete the section or cancel it and make necessary changes in configuration.
-
Filter XML code does not filter labels for the NER project
Before, the Filter XML function failed to filter the label/assertion list effectively. This issue has now been resolved. When a project’s taxonomy contains a substantial number of NER/Assertion labels, the display of the taxonomy consumes significant screen space, impeding annotators’ navigation through the labels. To address this, Annotation Lab has introduced a search feature for labels within NER projects, offering an autocomplete search option.
For incorporating the search bar targeting NER Labels or Choices, utilize the Filter tag as exemplified in the subsequent XML configuration. This filtering mechanism is also applicable to Visual NER filters.

Versions
- 7.8.2
- 7.8.1
- 7.8
- 7.7
- 7.6.0
- 7.5.1
- 7.5.0
- 7.4.0
- 7.3.1
- 7.3.0
- 7.2.2
- 7.2.2
- 7.2.0
- 7.1.0
- 7.0.1
- 7.0.0
- 6.11.3
- 6.11.2
- 6.11.1
- 6.11.0
- 6.10.1
- 6.10.0
- 6.9.1
- 6.9.0
- 6.8.1
- 6.8.0
- 6.7.2
- 6.7.0
- 6.6.0
- 6.5.1
- 6.5.0
- 6.4.1
- 6.4.0
- 6.3.2
- 6.3.0
- 6.2.1
- 6.2.0
- 6.1.2
- 6.1.1
- 6.1.0
- 6.0.2
- 6.0.0
- 5.9.3
- 5.9.2
- 5.9.1
- 5.9.0
- 5.8.1
- 5.8.0
- 5.7.1
- 5.7.0
- 5.6.2
- 5.6.1
- 5.6.0
- 5.5.3
- 5.5.2
- 5.5.1
- 5.5.0
- 5.4.1
- 5.3.2
- 5.2.3
- 5.2.2
- 5.1.1
- 5.1.0