5.7.0
Release date: 12-21-2023
Training Relations Extraction Models and Support for OCR Pipelines in NLP Lab 5.7
NLP Lab 5.7 marks a significant milestone in the realm of natural language processing with the introduction of advanced Relation Extraction (RE) model training features and the support for Visual OCR Pipelines. In this release, users will discover a suite of powerful functionalities designed to enhance efficiency, collaboration, and customization. The new RE model training feature focuses on augmenting the capabilities for text analysis, offering an intuitive and flexible approach to building and managing custom RE models. Alongside this, the Visual OCR Pipelines bring a significant enhancement to pdf and image document handling in NLP Lab, ensuring accurate, consistent, and precise text extraction. This improves the OCR results on imported PDF and/or image tasks for NER and text Classification projects.
Furthermore, NLP Lab 5.7 introduces an exciting addition known as Interactive Help. This feature enhances the user experience by offering a more intuitive and readily accessible means of seeking help and finding information directly within the application. With Interactive Help, users can effortlessly navigate through the platform while effortlessly locating the support and guidance they require.
This new release demonstrates our continuous commitment to delivering advanced tools for text analysis and document processing, tailored to address our users’ evolving needs. Detailed descriptions of all new features and improvements are provided below.
Training Relations Extraction (RE) Model
We are excited to announce that NLP Lab 5.7 offers training features for Relation Extraction (RE) models. This new feature is augmenting our offerings for text analysis, providing users with a robust set of tools for building and managing custom RE models. Key benefits include:
- Customizable RE Model Development: Tailor RE models to your specific needs for text analysis, expanding the breadth of Model Training and Active Learning within NLP Lab.
- Optimization of Downstream Tasks: Apply trained RE models in pre-annotation workflows to significantly minimize manual labeling workload, thus expediting project timelines.
- Fostering Collaboration and Knowledge Sharing: Reuse models across projects, facilitating knowledge transfer and enhancing task performance.
- Efficient Model Management: Effortlessly download, upload, and publish trained RE models for collaborative use and wider community access through the Models Hub.
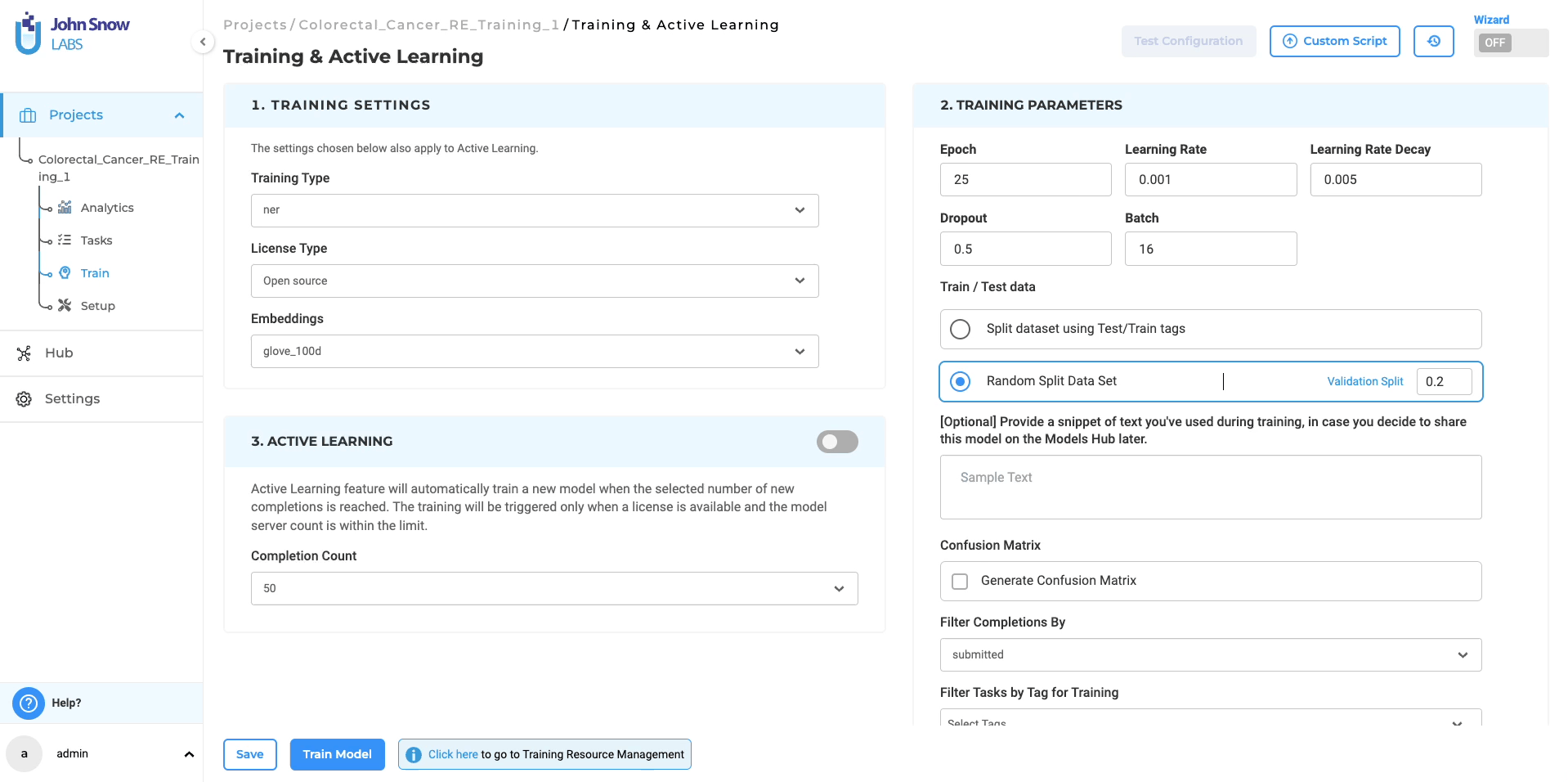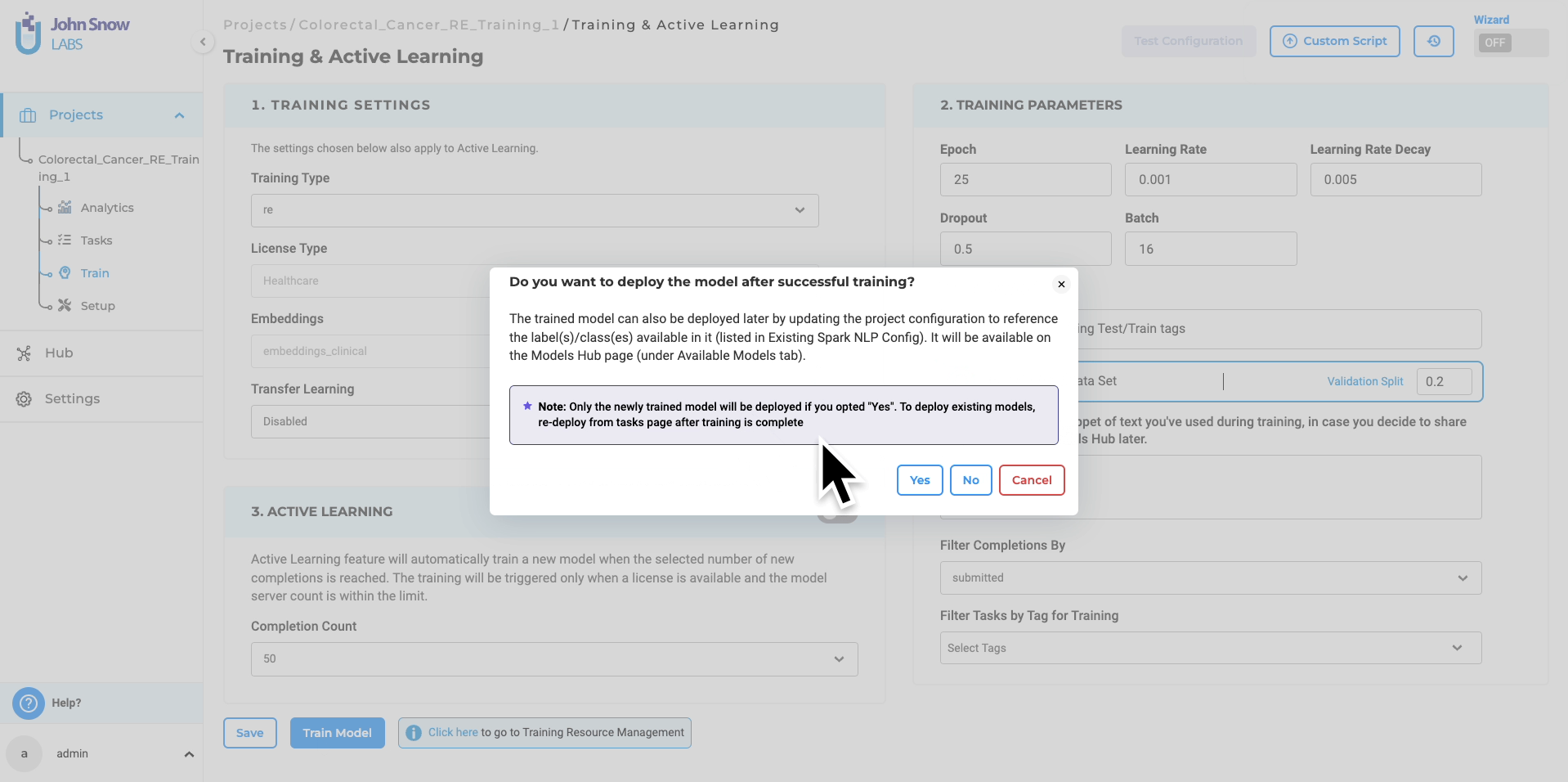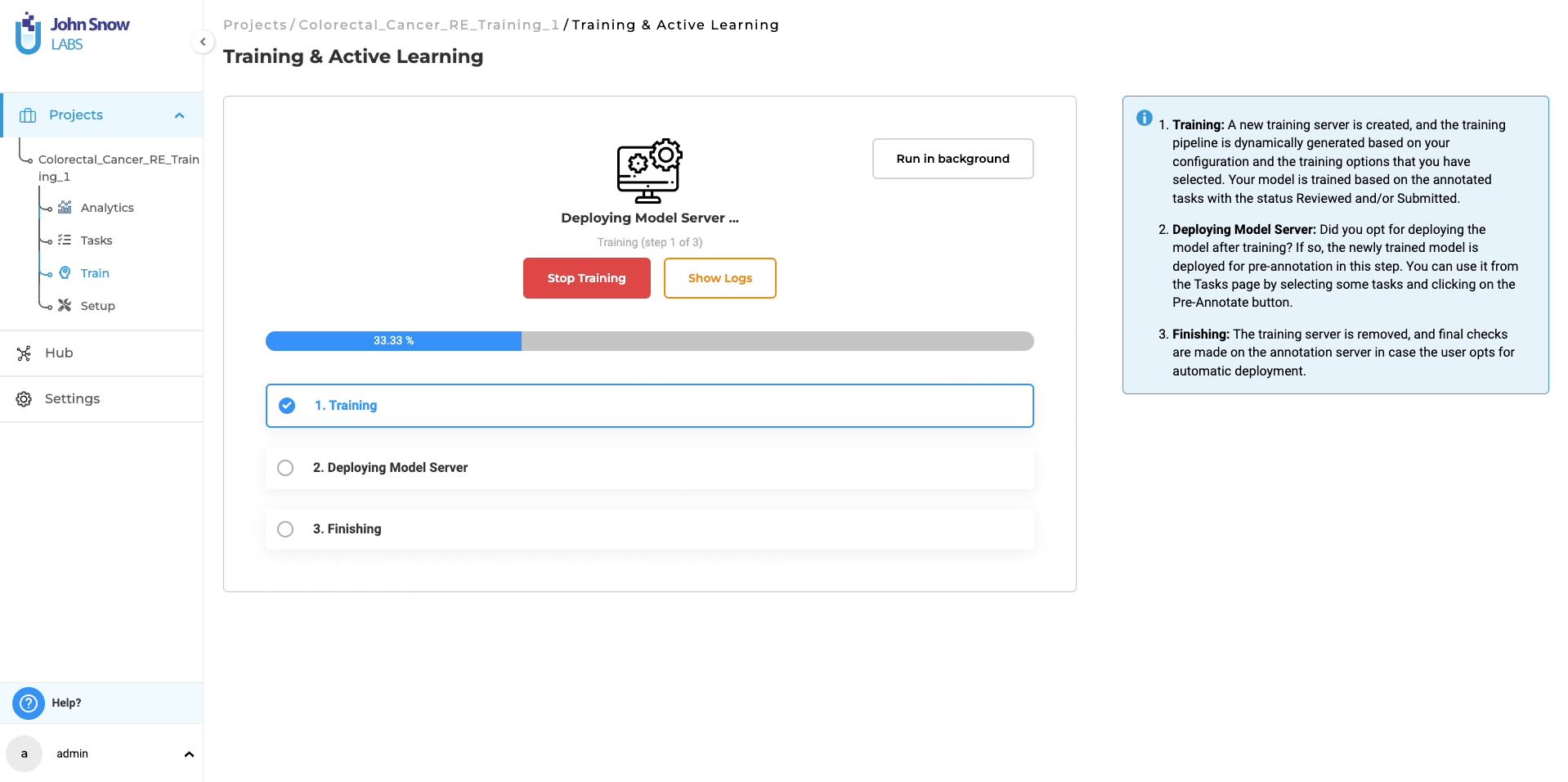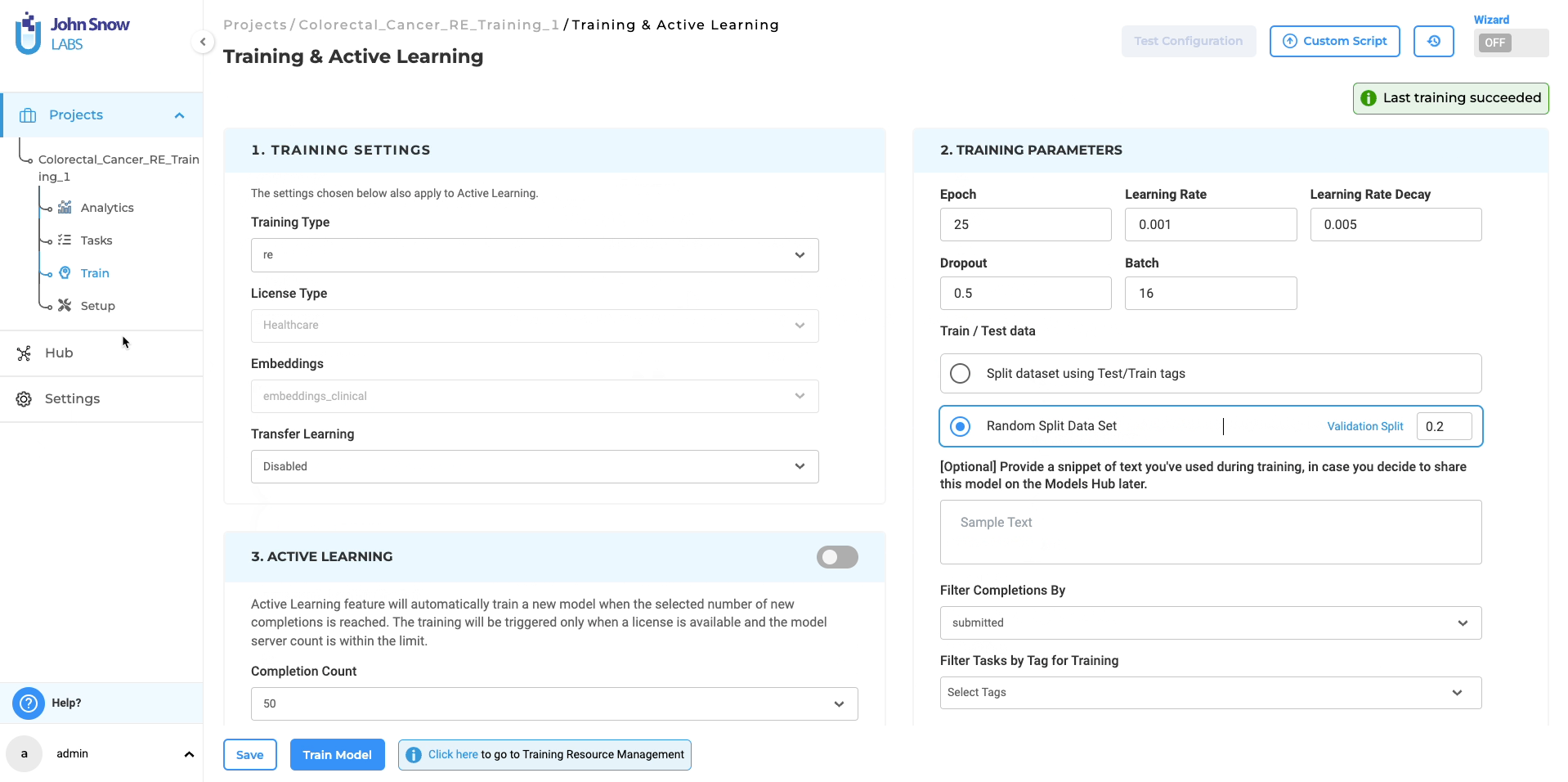
Note: The RE model training feature is accessible exclusively for NER text projects. It becomes available when a NER text project is created, and the Relation section is configured, activating the “re” option in the Training Type dropdown.
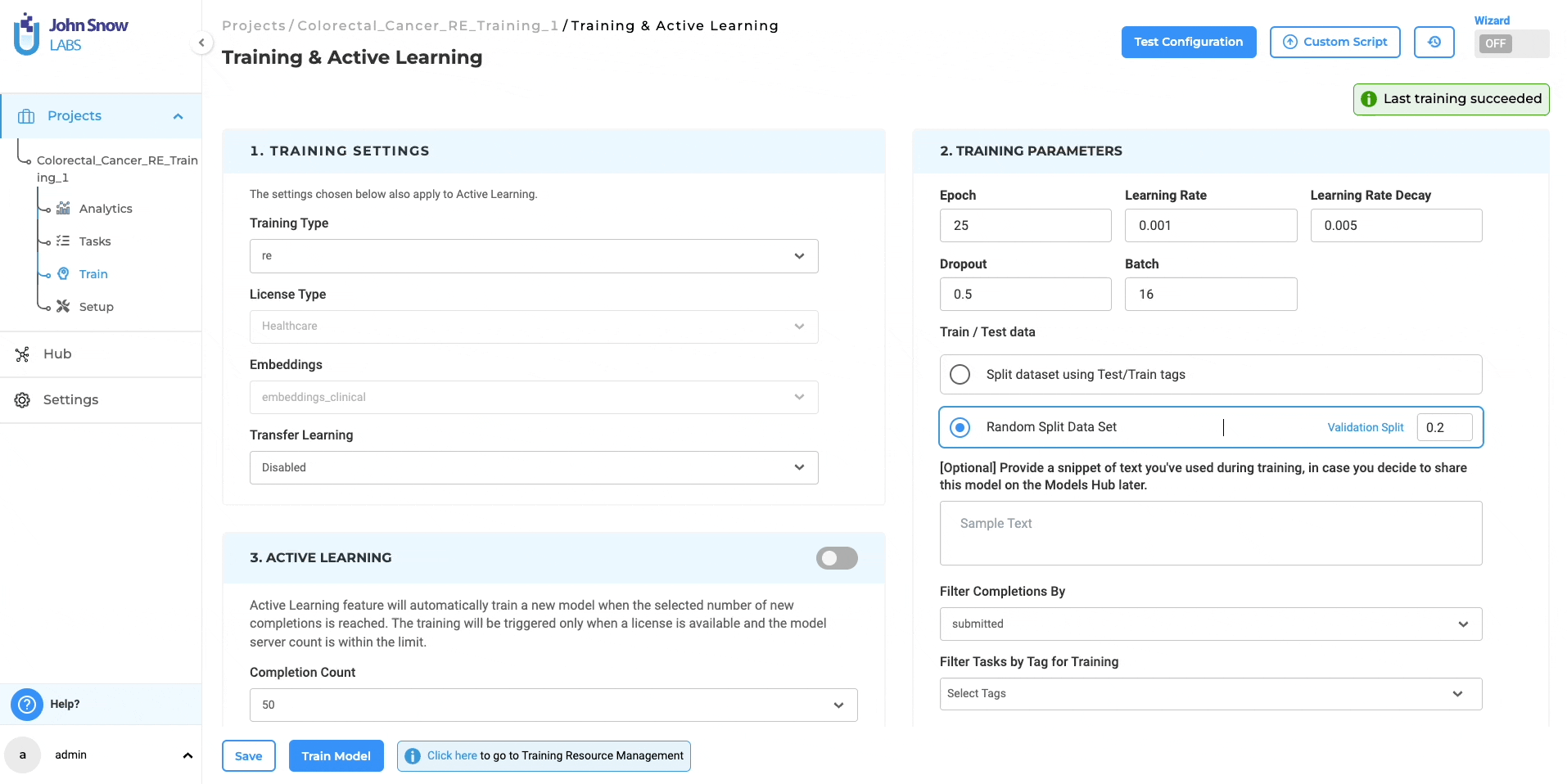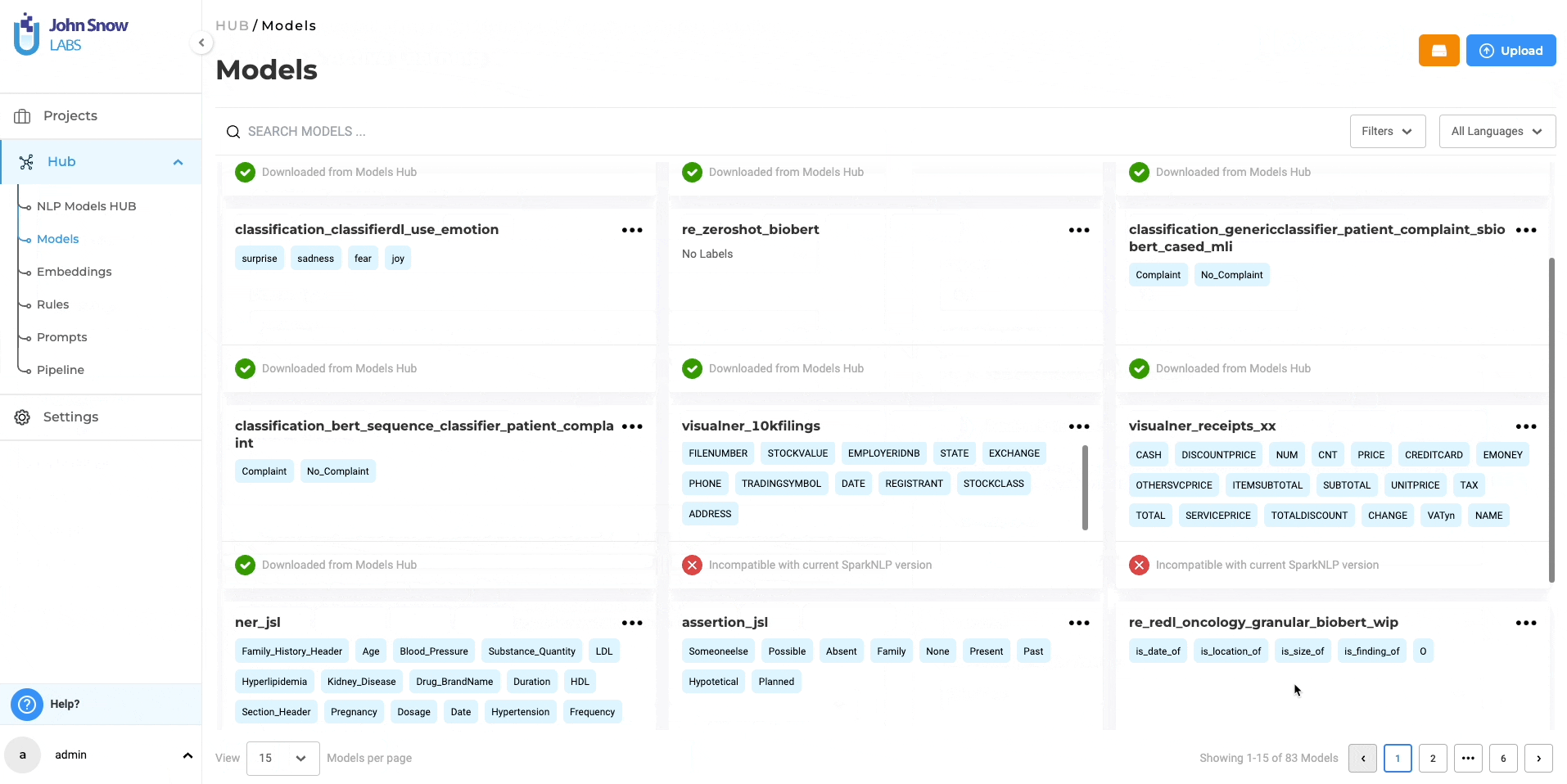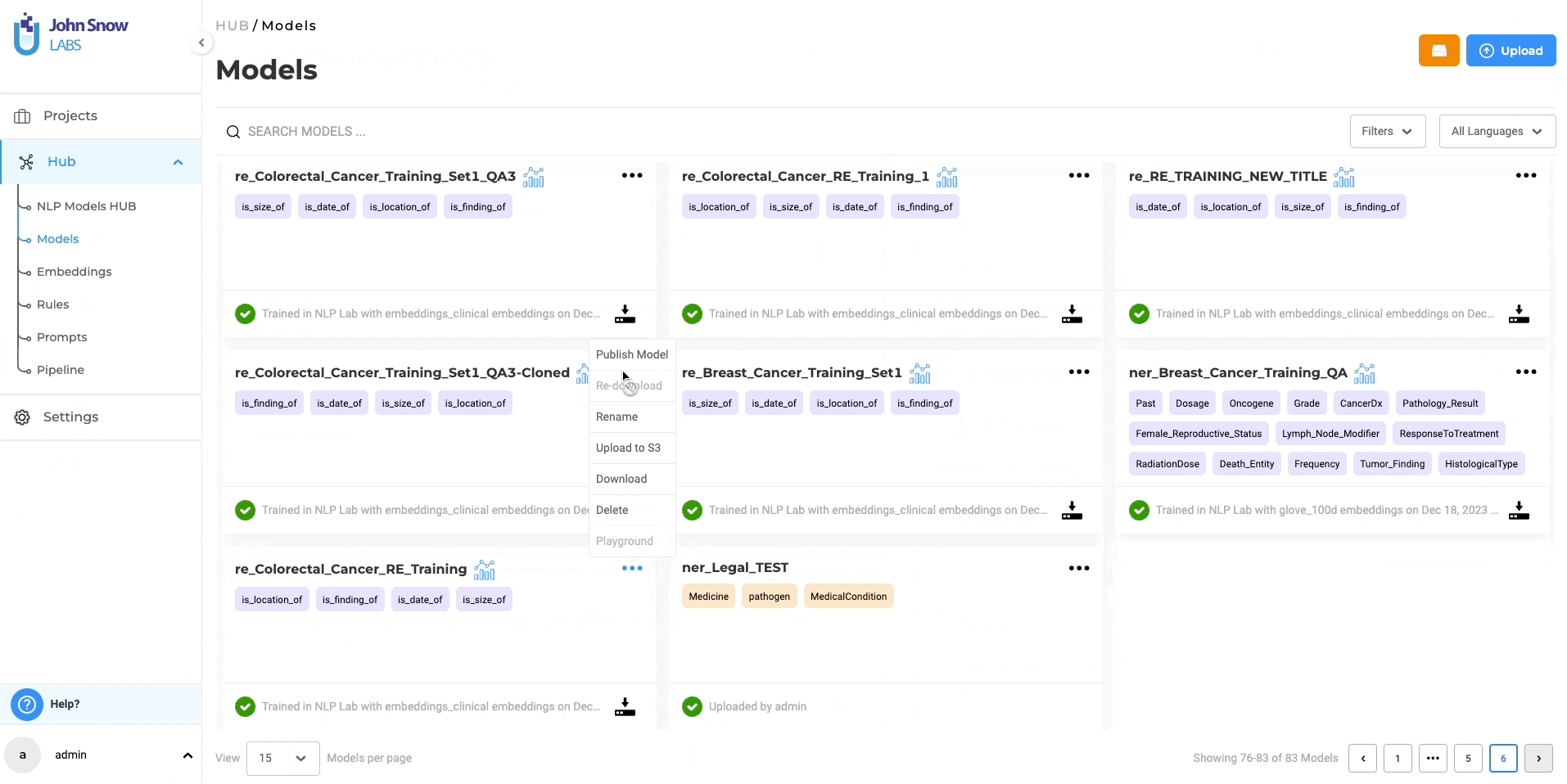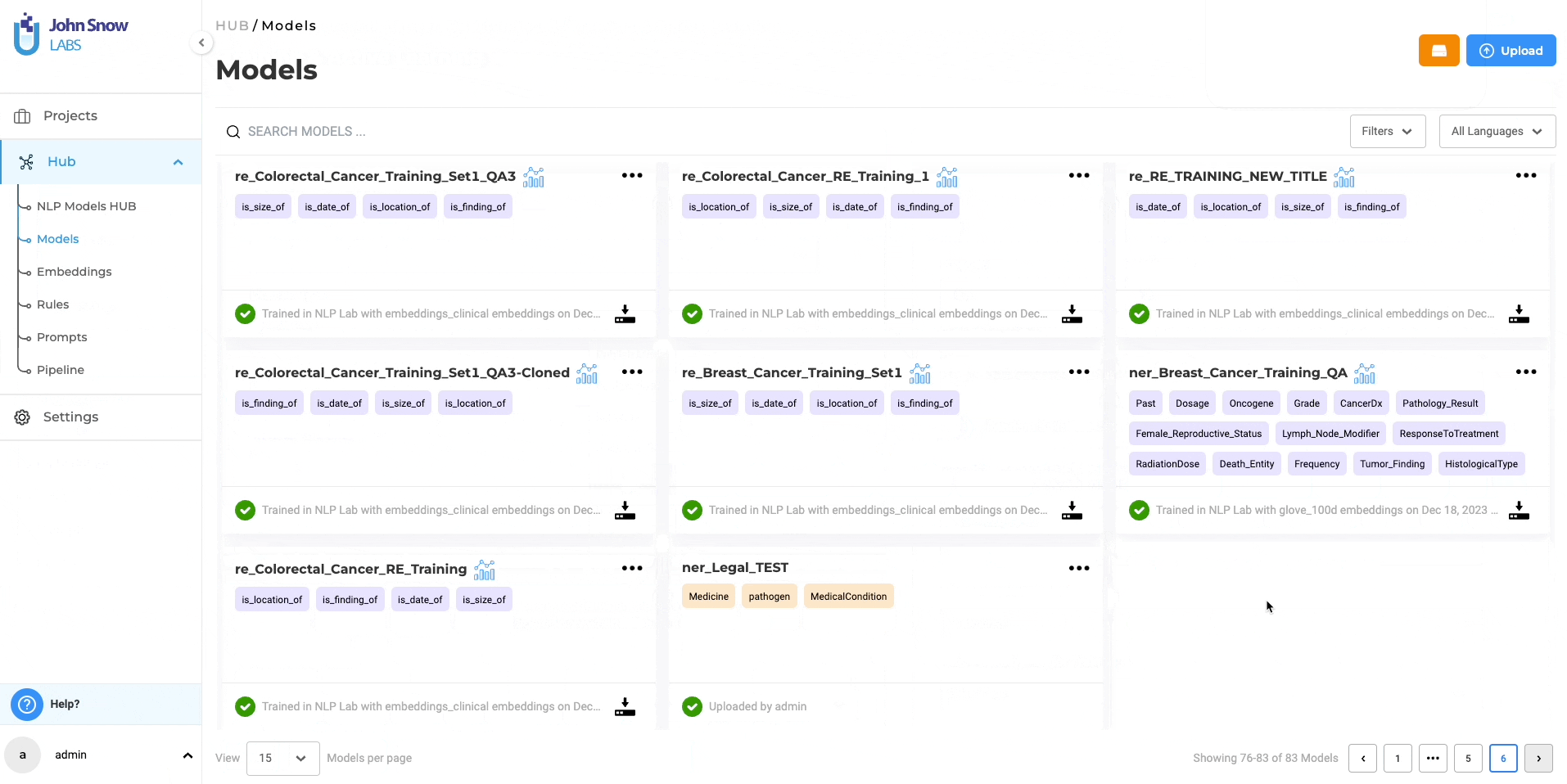
Initiating the Relations Extraction (RE) Training Job:
- Access Training Page: Navigate to the “Train” page within the Project Menu to set up and start model training jobs.
- Select Training Type: Choose “re” from “Training Type” for RE model training.
- Automated Configuration: Selecting “re” auto-configures “Embeddings Field” and “License Type” to “embeddings_clinical” and “Healthcare” respectively.
- Configuration Customization: Modify training parameters as needed and save your settings.
- Start Training: Initiate the training with a step-by-step wizard, allowing real-time monitoring of progress and logs.
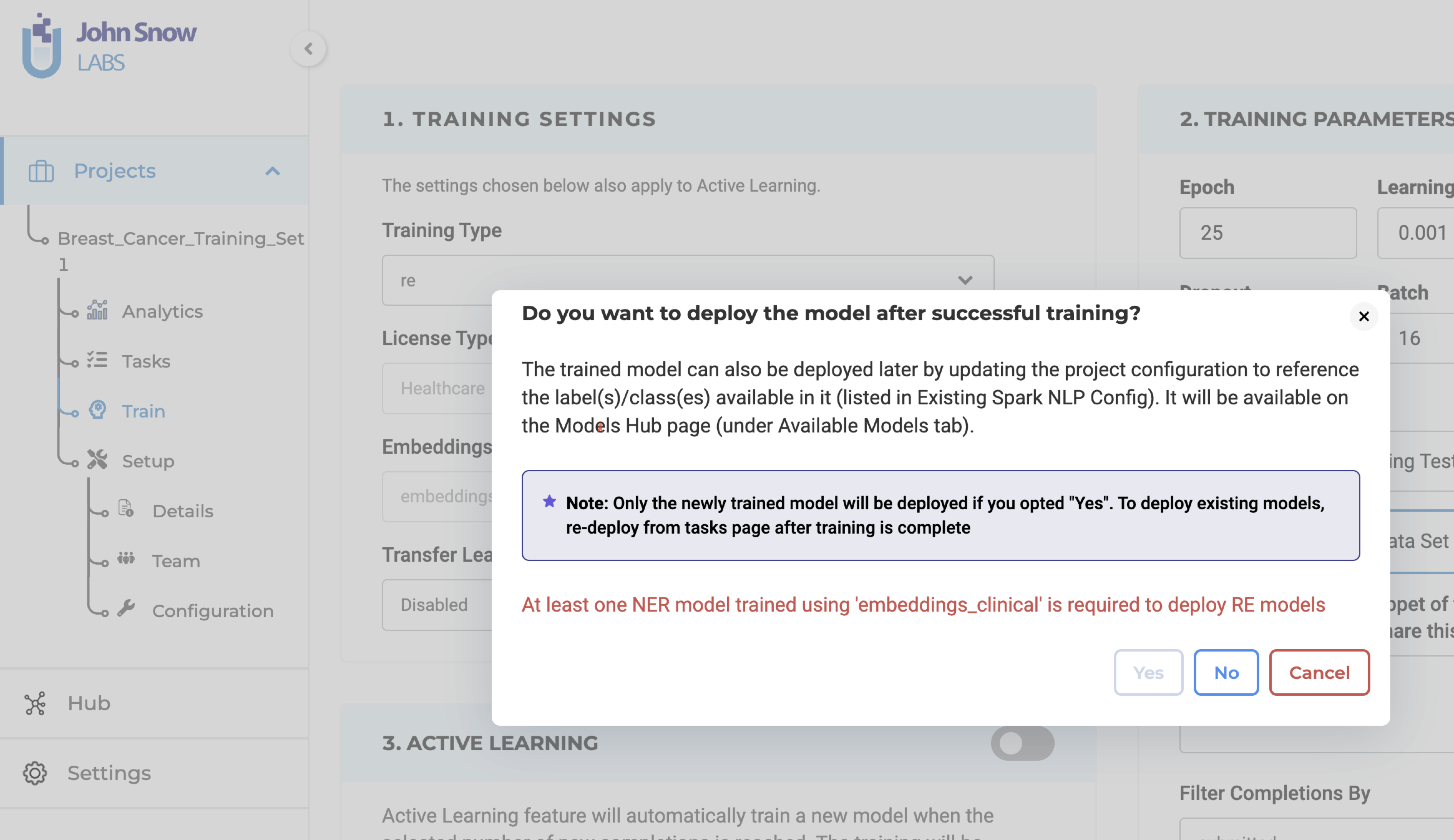
Deployment Choices: When triggering the training, users can opt for immediate model deployment post-training. This implies the automatic update of the project configuration with the new model’s name.
Prerequisite for RE Model Training:
To achieve successful training of an RE model, it is essential to have at least one Named Entity Recognition (NER) model trained using the “embeddings_clinical” type specified in the project configuration. This guarantees the best performance and compatibility of features. Users have the option to pre-train a NER model or utilize an existing pre-trained model available within the project. This approach ensures optimal results and maximizes efficiency during RE model training.
Upon verifying the adequacy of the project configuration and training parameters, the system will commence the training process for the RE model. Once the training is finished, the resulting trained RE model will be accessible on the “Models” page for further utilization. Furthermore, you have the option to retrieve comprehensive training logs by clicking on the download icon associated with the Trained RE model. These logs offer valuable information concerning the training parameters and evaluation metrics, allowing for deeper insights into the training process.
Pre-annotation with Trained Relations Extraction (RE) Models
If you opt for immediate deployment, the trained RE model automatically serves as a pre-annotation server for the tasks within your project once the training is complete. This significantly reduces the need for manual annotation, saving valuable time and effort. Additionally, you can utilize the trained RE models in other projects by accessing the “Re-Use Resources” section within the desired project’s configuration. It is important to include the model and ensure that the target project has at least one “embeddings_clinical” NER model trained for compatibility. By saving the configuration, you can deploy both the RE and NER models as a pre-annotation server. Alternatively, you can create a new server directly from the task list page using the “Pre-Annotate” button for immediate deployment.
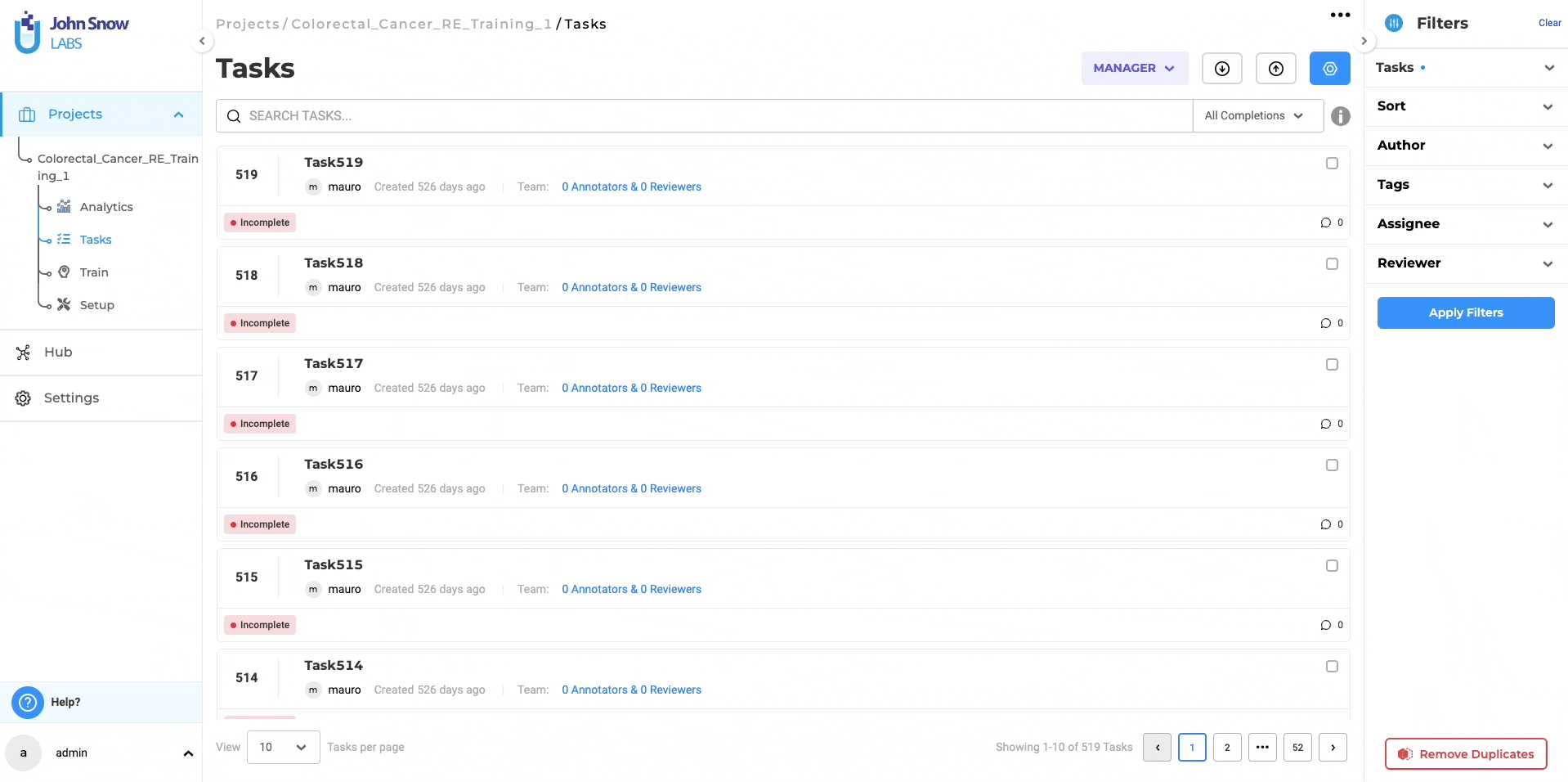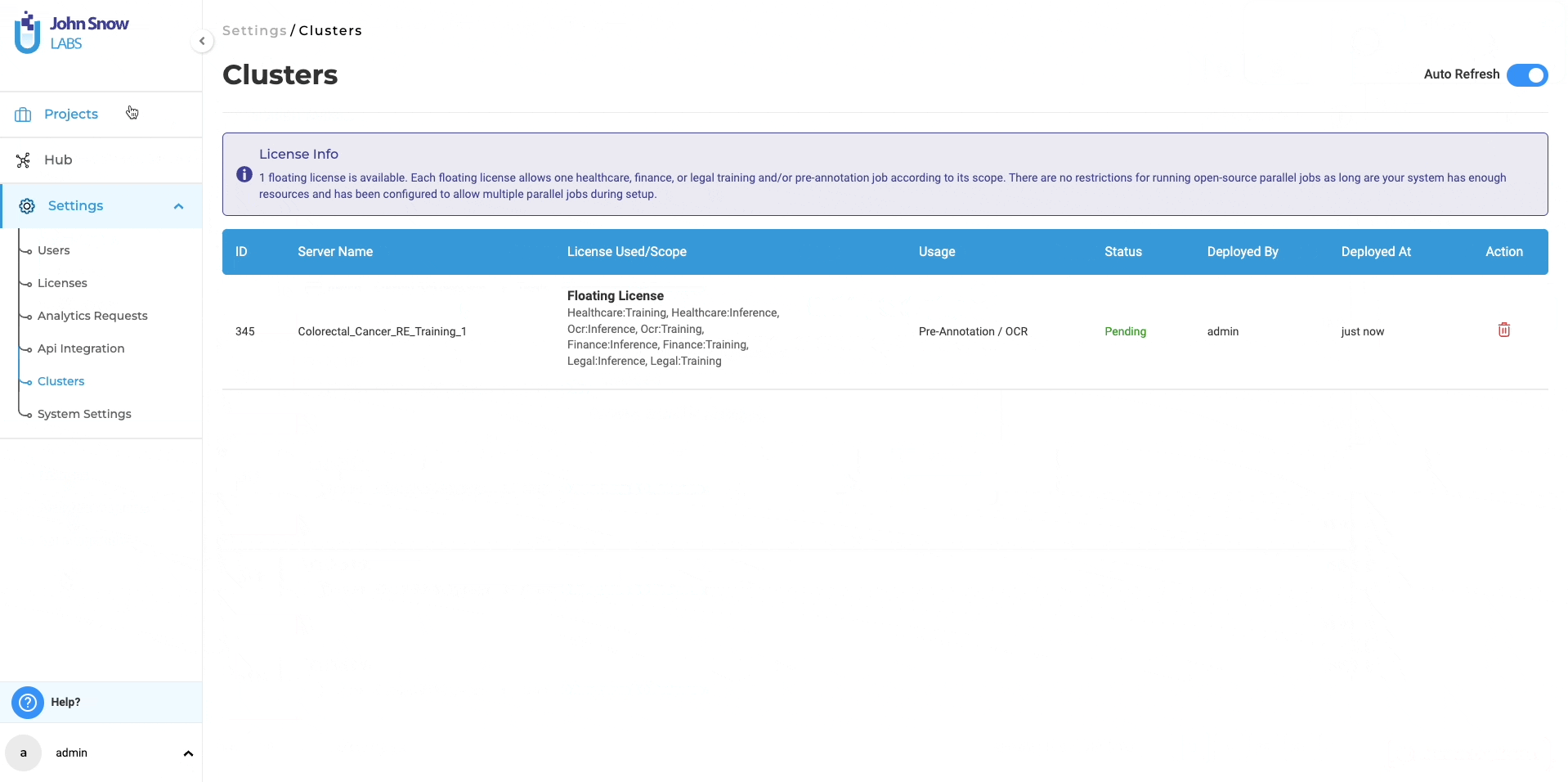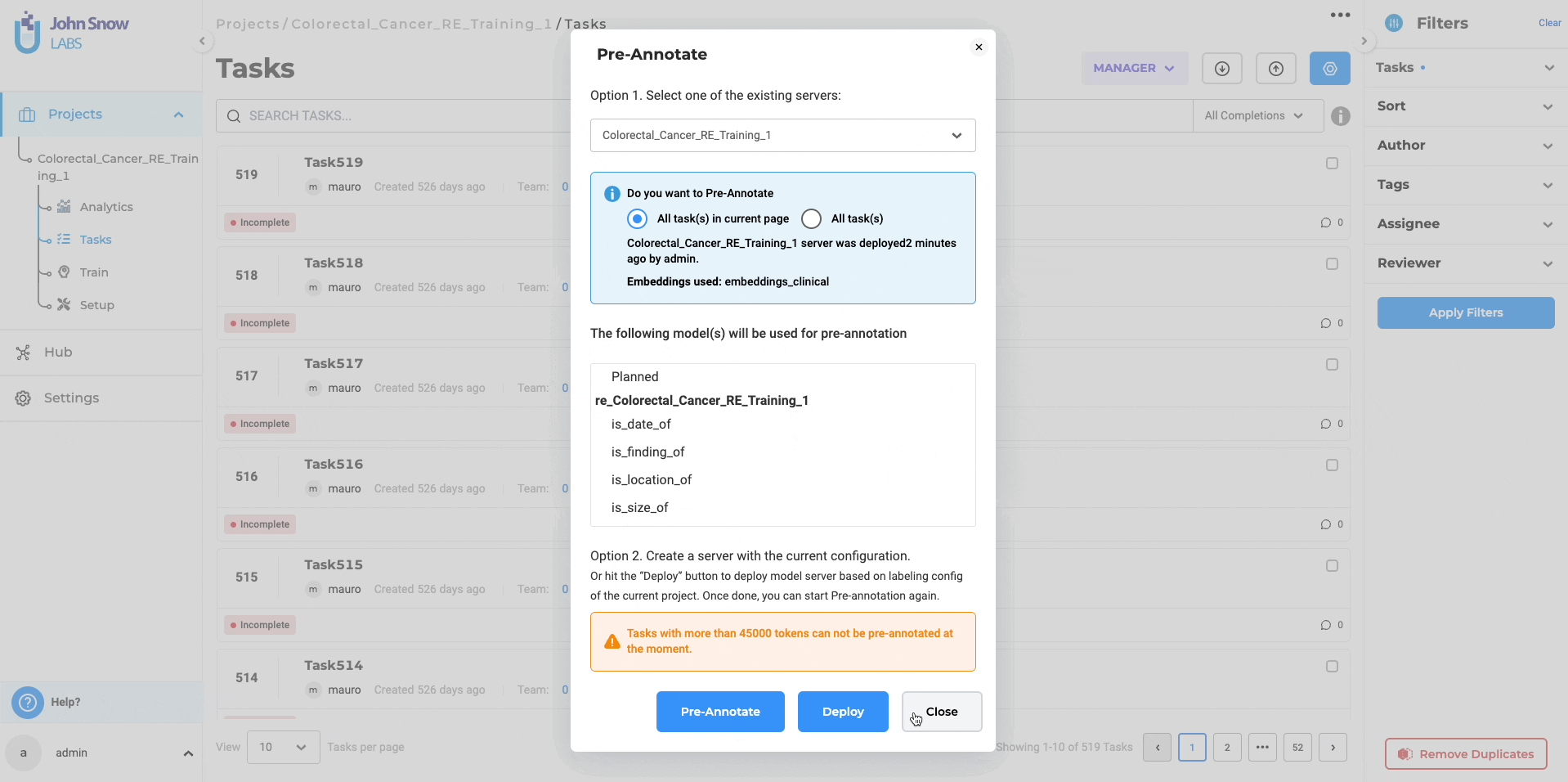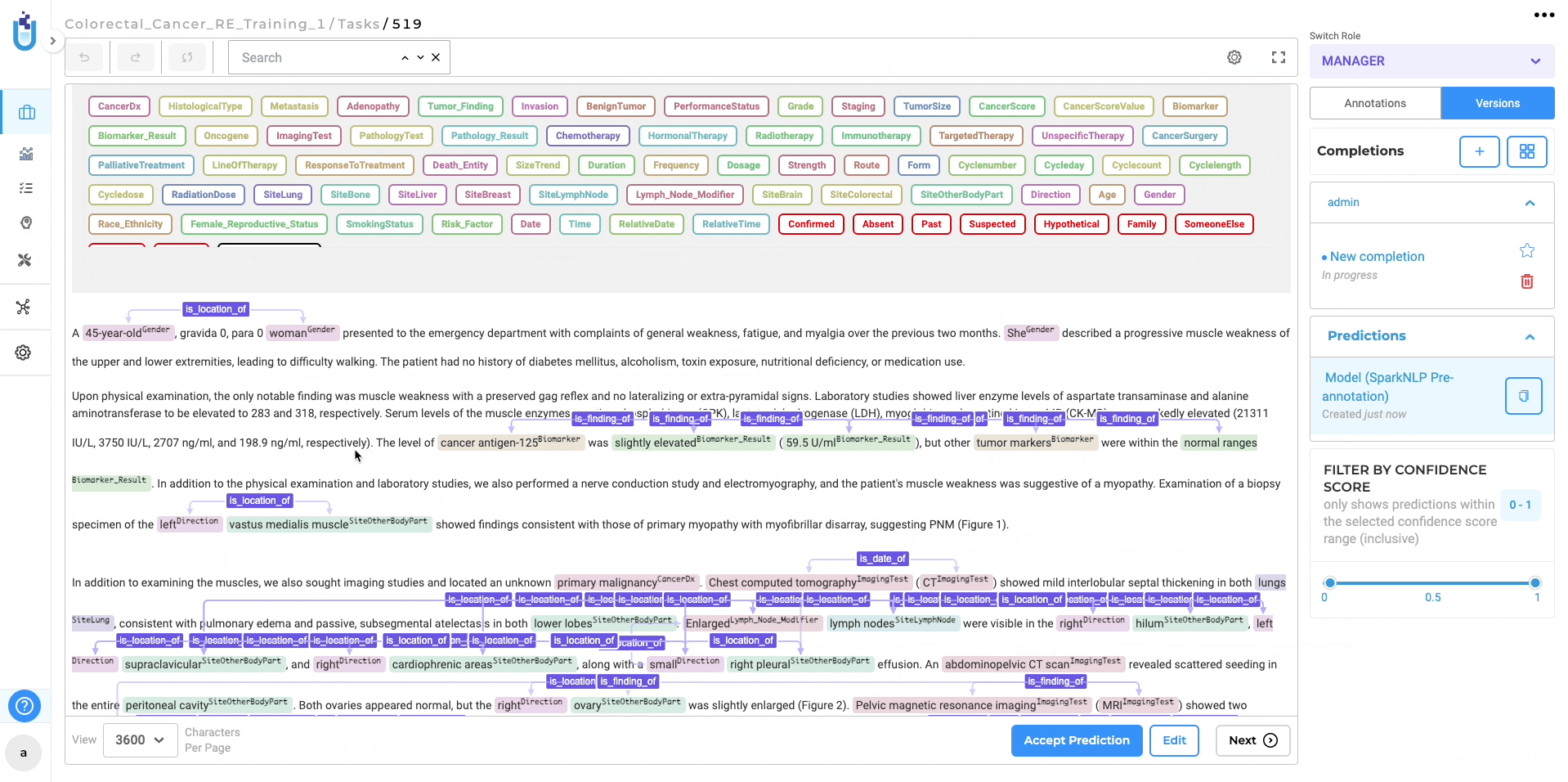
RE Model Management and Sharing:
The “Models” page under the Hub of resources, serves as a centralized hub where you can conveniently access all pre-trained and trained models, including RE models. You have the option to download the trained RE models for offline use and even upload them back to the NLP Lab using the Upload Model Feature. Furthermore, from the “Models” page, you can directly publish the trained RE models to the Models Hub, enabling broader sharing within the community. This facilitates collaboration and knowledge exchange among a wider audience.
Known issues and Resolutions:
- Issue with Immediate Deployment: If immediate deployment is chosen when training an RE model, only the NER model (or a Blank Pre-annotation server in certain cases) is deployed after the training is completed. Resolution: Delete the pre-annotation server from the Cluster Page and deploy the pre-annotation for the project again. By following this resolution process, the pre-annotation server will be correctly deployed, ensuring the desired functioning of the system.
- Benchmarking Data Anomaly: For RE models, the Models page may display training Epoch Data instead of Benchmarking Values. Resolution: Evaluation metrics can be reviewed in the downloadable training logs.
Note: The above issues will be fixed in the upcoming version.
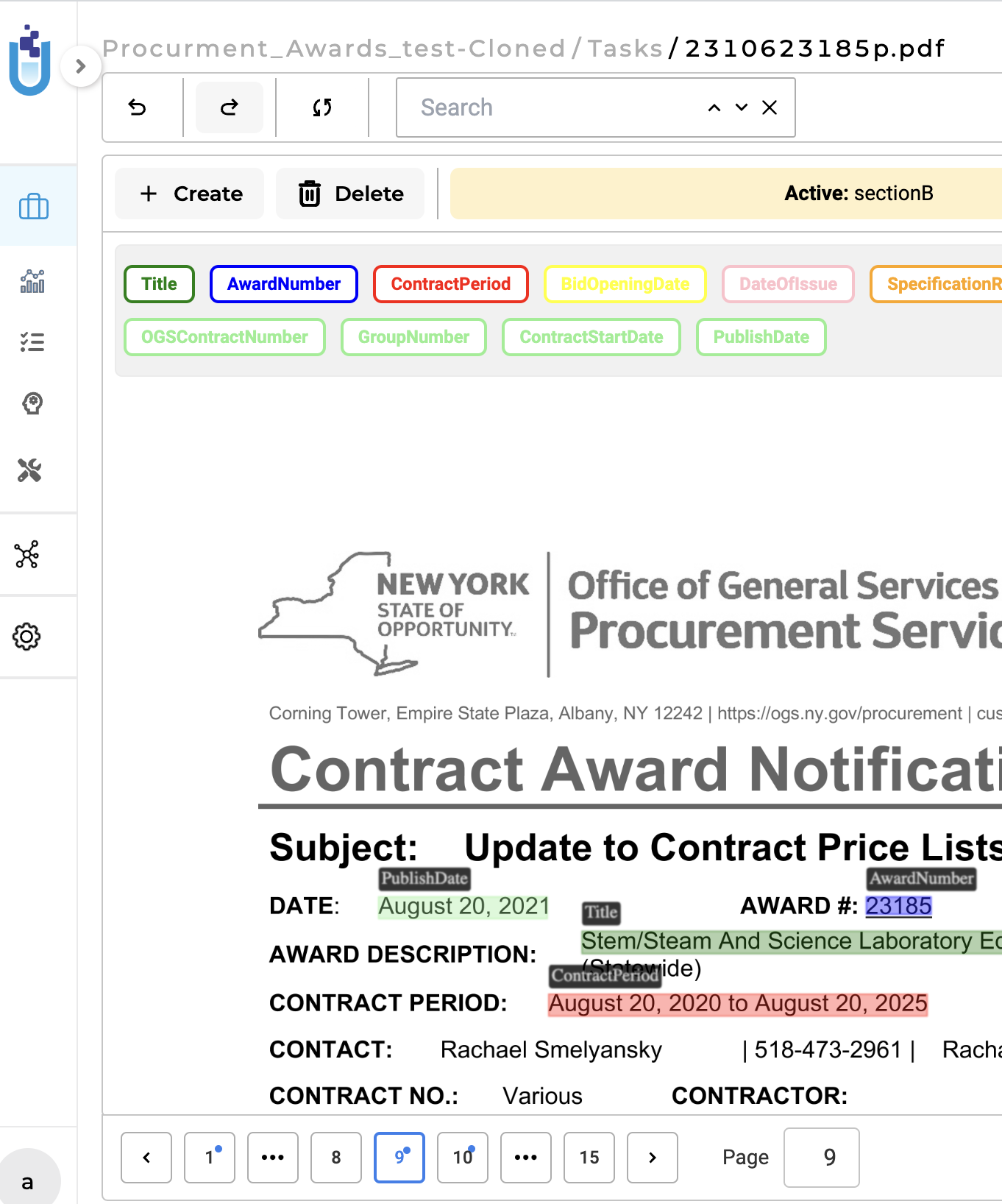
Support For OCR Pipelines
In NLP Lab 5.7, an exciting addition is the support for Visual OCR Pipelines, bringing notable advancements to OCR documents within the platform. These dedicated pipelines provide enhanced functionality, resulting in improved accuracy, consistency, and precise text extraction specifically tailored for NER projects. This update brings greater reliability and efficiency when working with OCR documents in NLP Lab, further empowering users in their natural language processing endeavors.
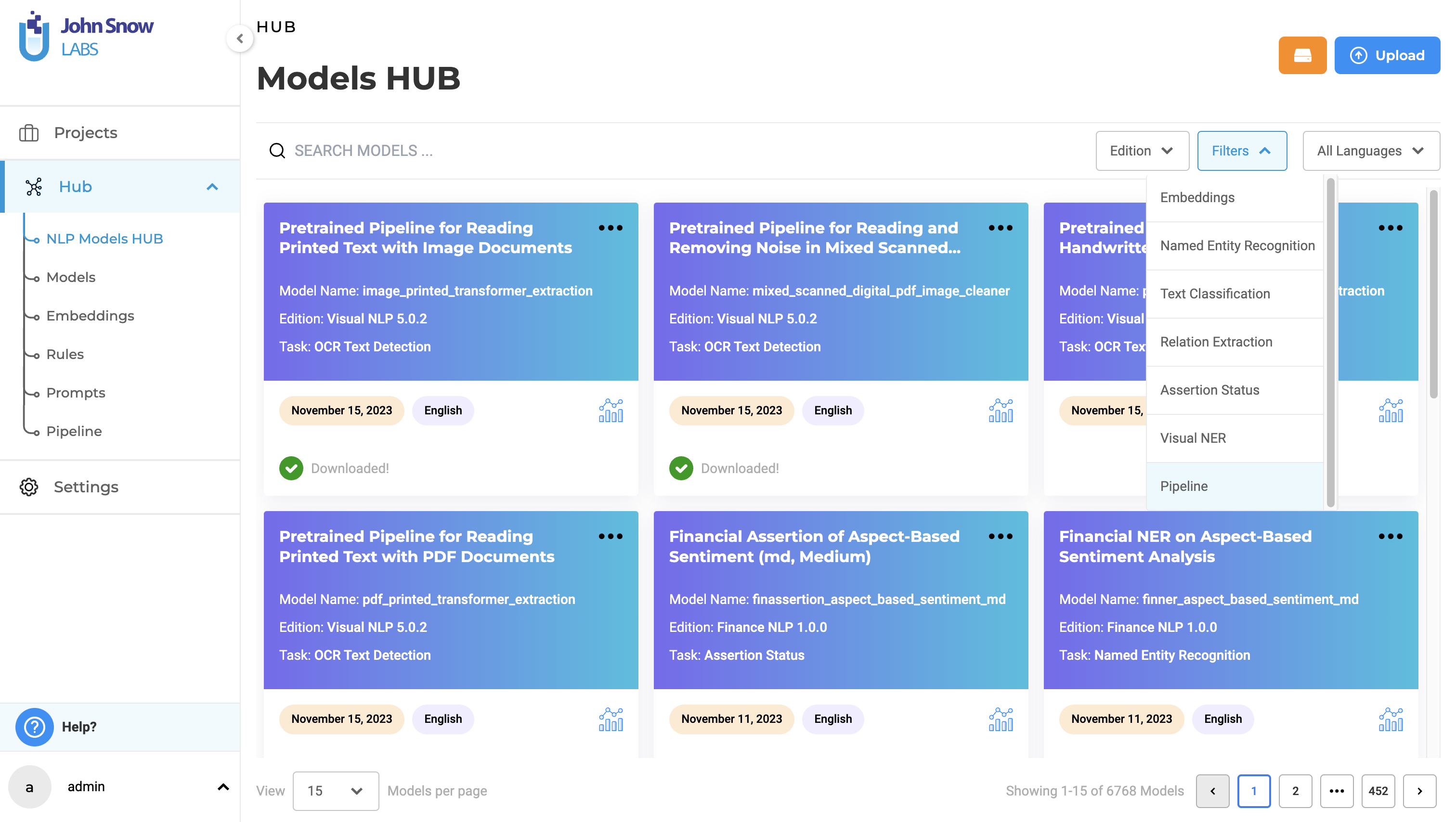
Centralized Access through Models Hub Page
All supported pipelines are now discoverable and accessible on the NLP Models Hub page.
- Unified Pipeline Access: The NLP Models Hub page serves as the main entry point for users to explore and download a variety of pre-annotation resources, including Visual OCR Pipelines.
- Enhanced Search and Filter Tools: Users can effortlessly locate specific pipelines tailored to their project needs using the advanced search and filter options.
- Streamlined Pipeline Acquisition: Pipelines can be easily downloaded from the NLP Models Hub page, by clicking on the three dots menu and selecting the download option.
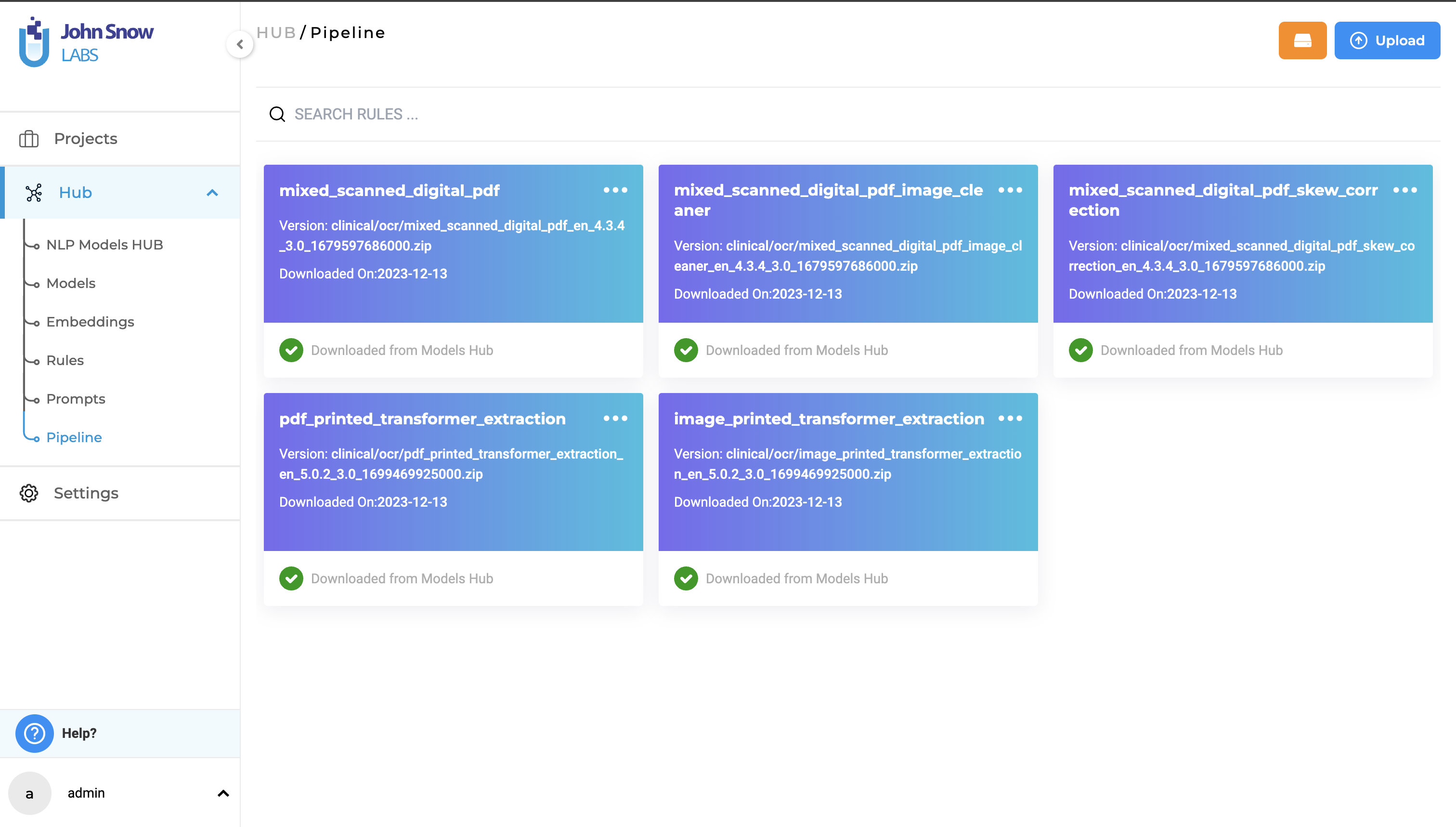
Pipeline Page under the Hub Section
In NLP Lab, downloaded pipelines are conveniently listed on the dedicated Pipeline Page, which can be found under the Hub of Resources menu. This centralized space allows users to effectively manage and view their collection of pipelines. By accessing the Pipeline Page, users gain an organized overview of their downloaded pipelines, enabling them to easily keep track of available models and quickly reference the list of pipelines they have at their disposal. This streamlined approach enhances productivity and facilitates efficient management of pipelines within the NLP Lab environment.
Supported Pipelines and Usage Instruction
NLP Lab version 5.7 introduces a set of seven Visual OCR Pipelines, each tailored for specific purposes, providing users with versatile options to address diverse document processing needs:
- mixed_scanned_digital_pdf
- mixed_scanned_digital_pdf_image_cleaner
- mixed_scanned_digital_pdf_skew_correction
- image_printed_transformer_extraction
- pdf_printed_transformer_extraction
- image_handwritten_transformer_extraction
- pdf_handwritten_transformer_extraction
These pipelines offer a comprehensive set of tools, each optimized for specific scenarios, providing flexibility and precision in processing various document types in OCR projects within NLP Lab.
User Guide
To enable OCR functionality and perform OCR tasks, follow these steps:
- Go to the Task Import Page.
- Activate the “OCR Document” Checkbox and deploy an OCR server.
- Select OCR Pipeline.
- Once the OCR server is ready, choose the desired OCR pipeline from the dropdown menu.This allows you to configure the processing settings for your OCR task.
- Import your OCR fileswith support for both individual files and multiple files in a zipped format.
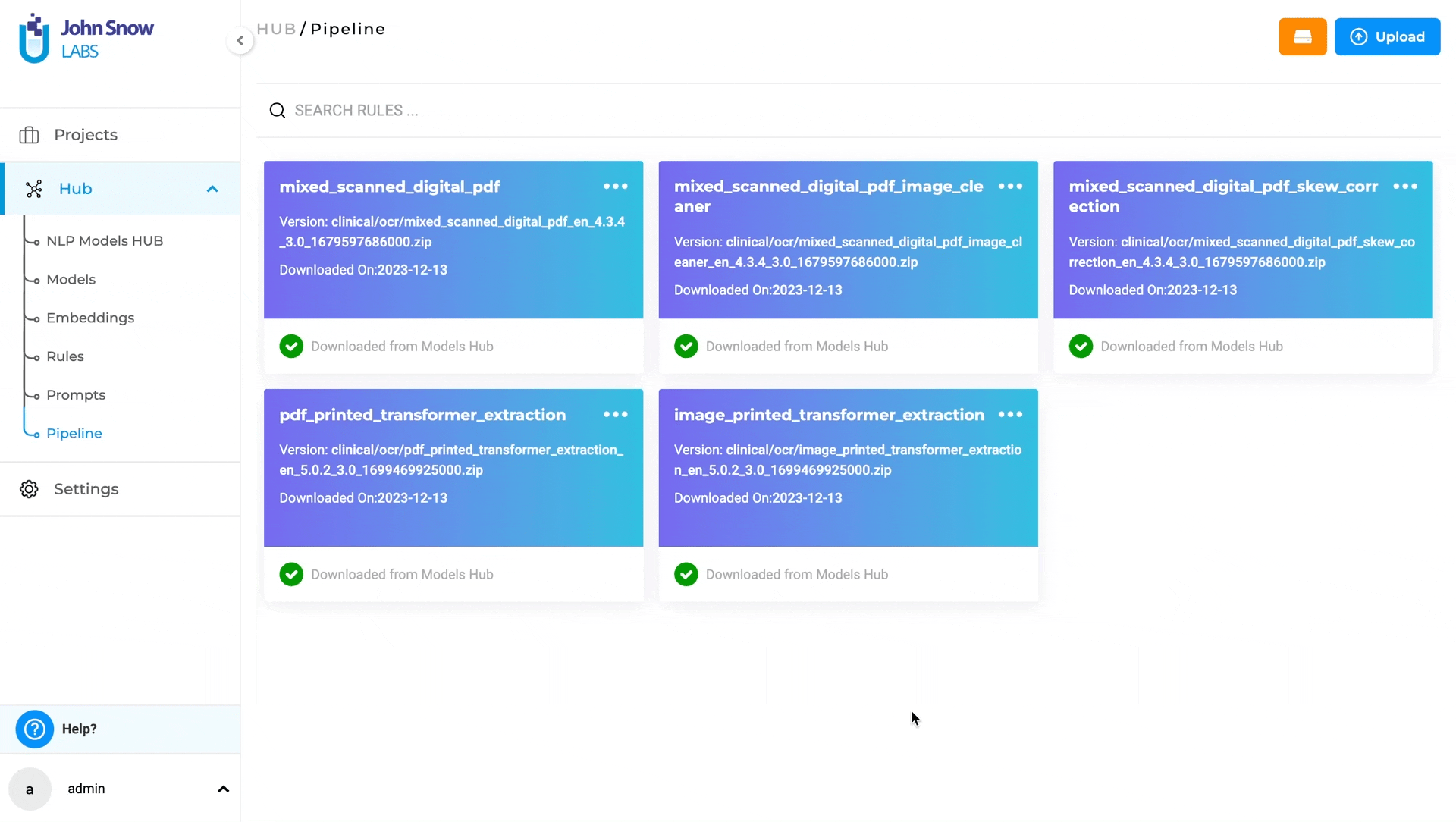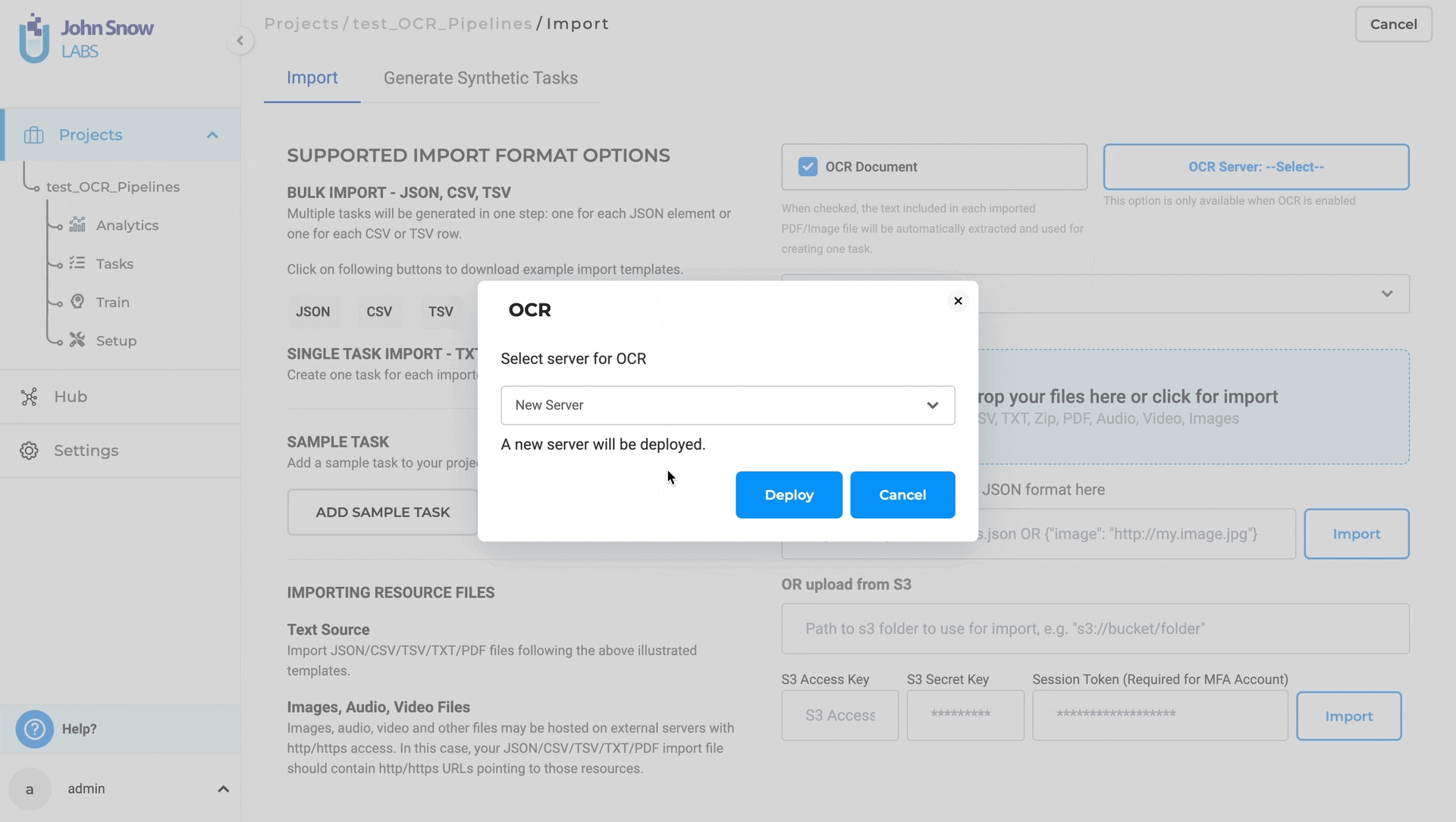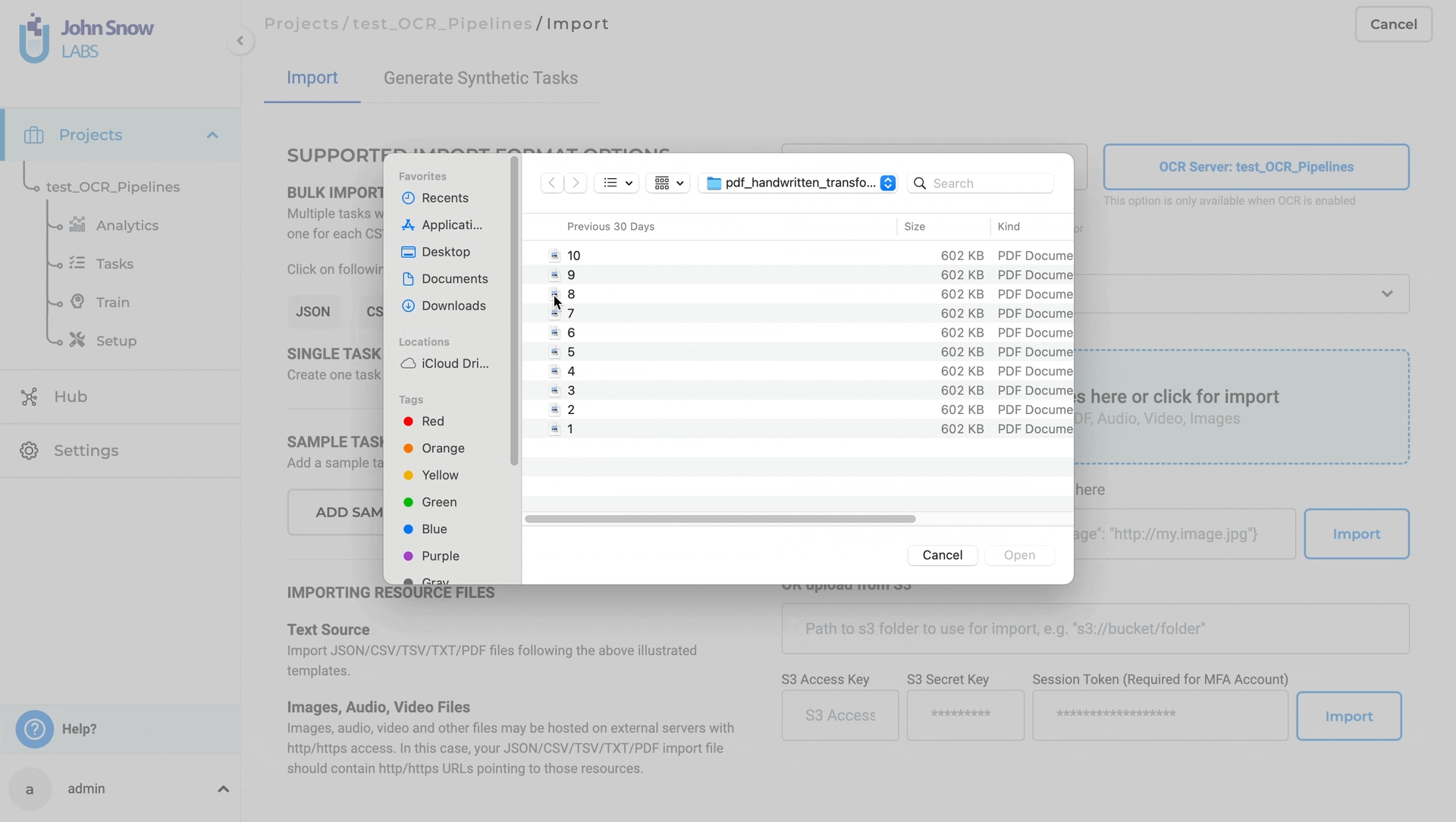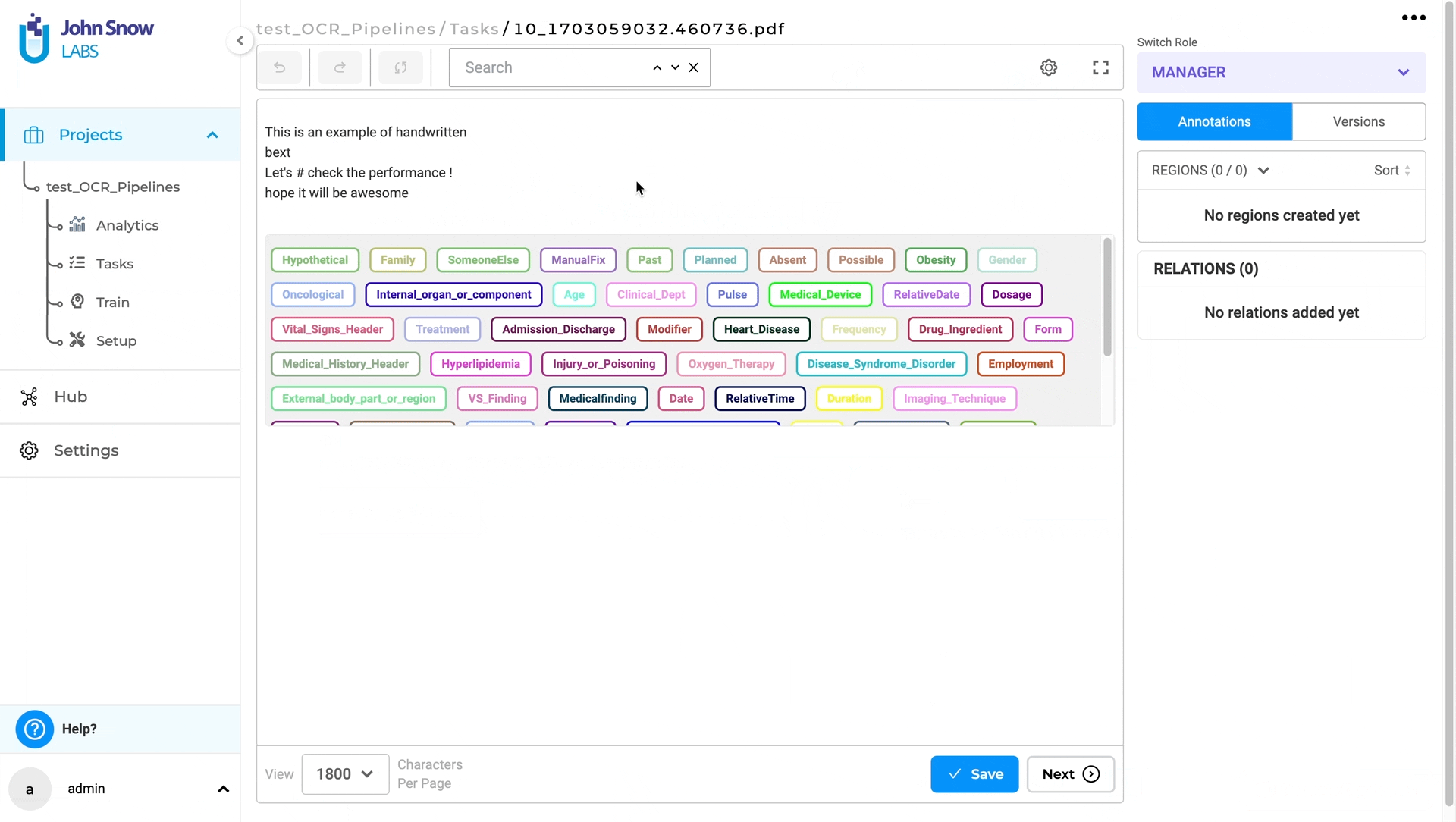
Note: Pipelines are automatically downloaded when selected from the import page, even if they haven’t been previously downloaded from the Models Hub. These steps streamline the process of enabling OCR, deploying a server, selecting a pipeline, and importing OCR files, facilitating efficient OCR document handling within the given context.
Current Limitation and Future Optimizations
Currently, task importing via dedicated OCR pipelines may take longer than using the default OCR import option. This aspect is earmarked for optimization in the subsequent releases.
The objective of these enhancements is to improve the user experience in NLP Lab by making it more accessible and powerful. While implementing these improvements, the familiar user interface and core functionalities are retained to ensure a seamless transition for users.
Interactive Help
In version 5.7, a new feature called Interactive Help has been added to NLP Lab. This feature aims to provide users with an intuitive and accessible way to seek help and find relevant information from within the application.
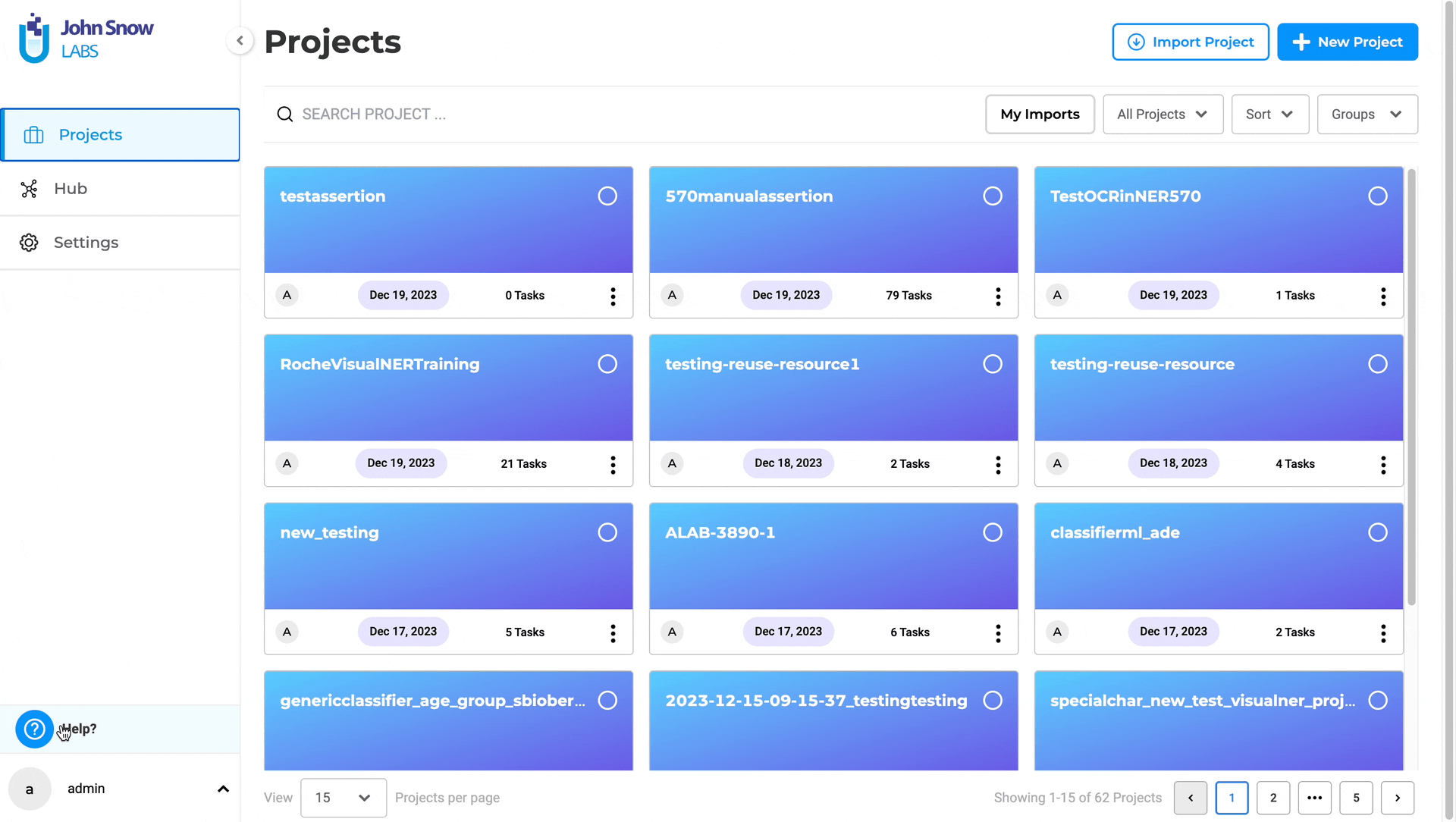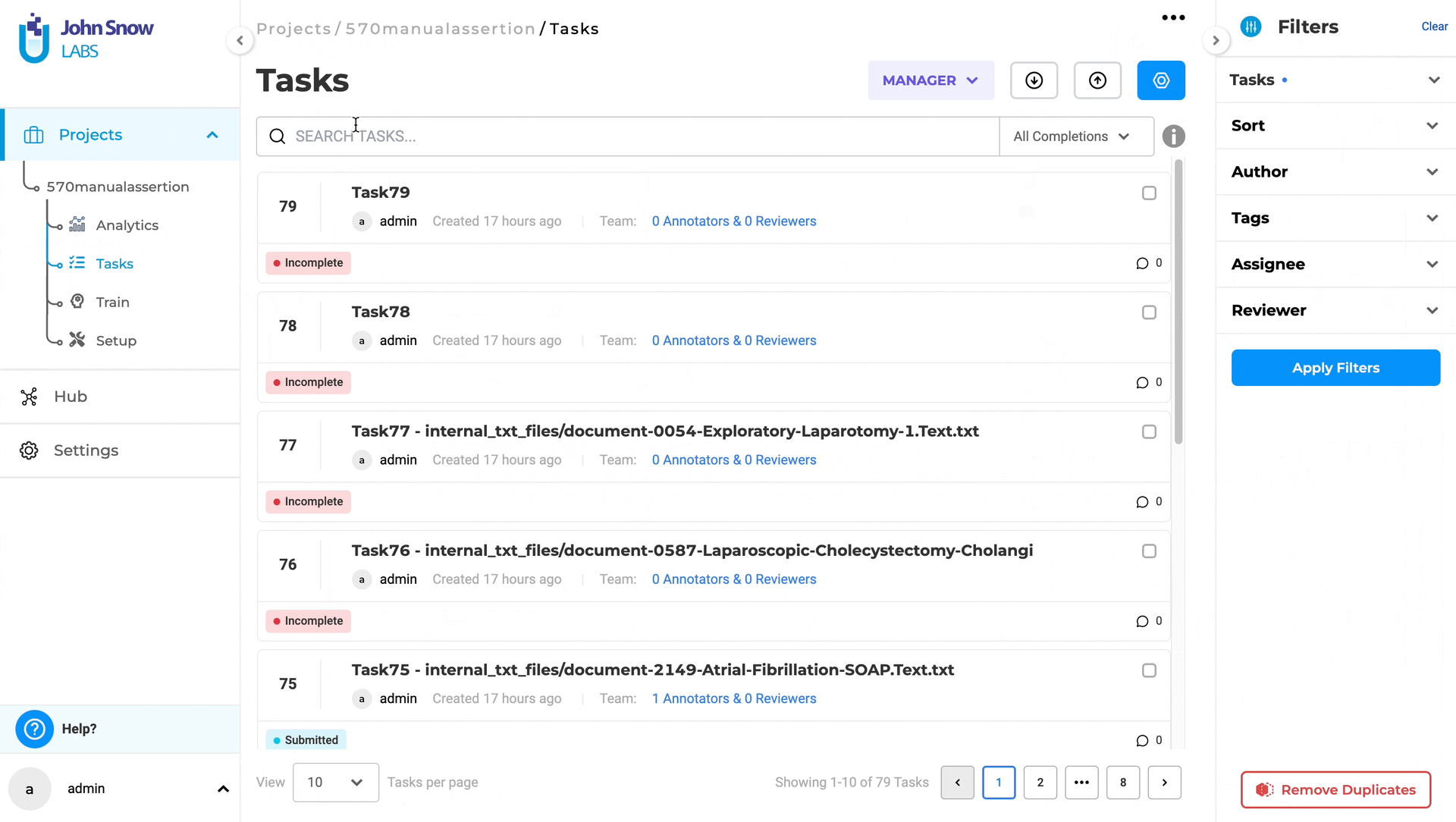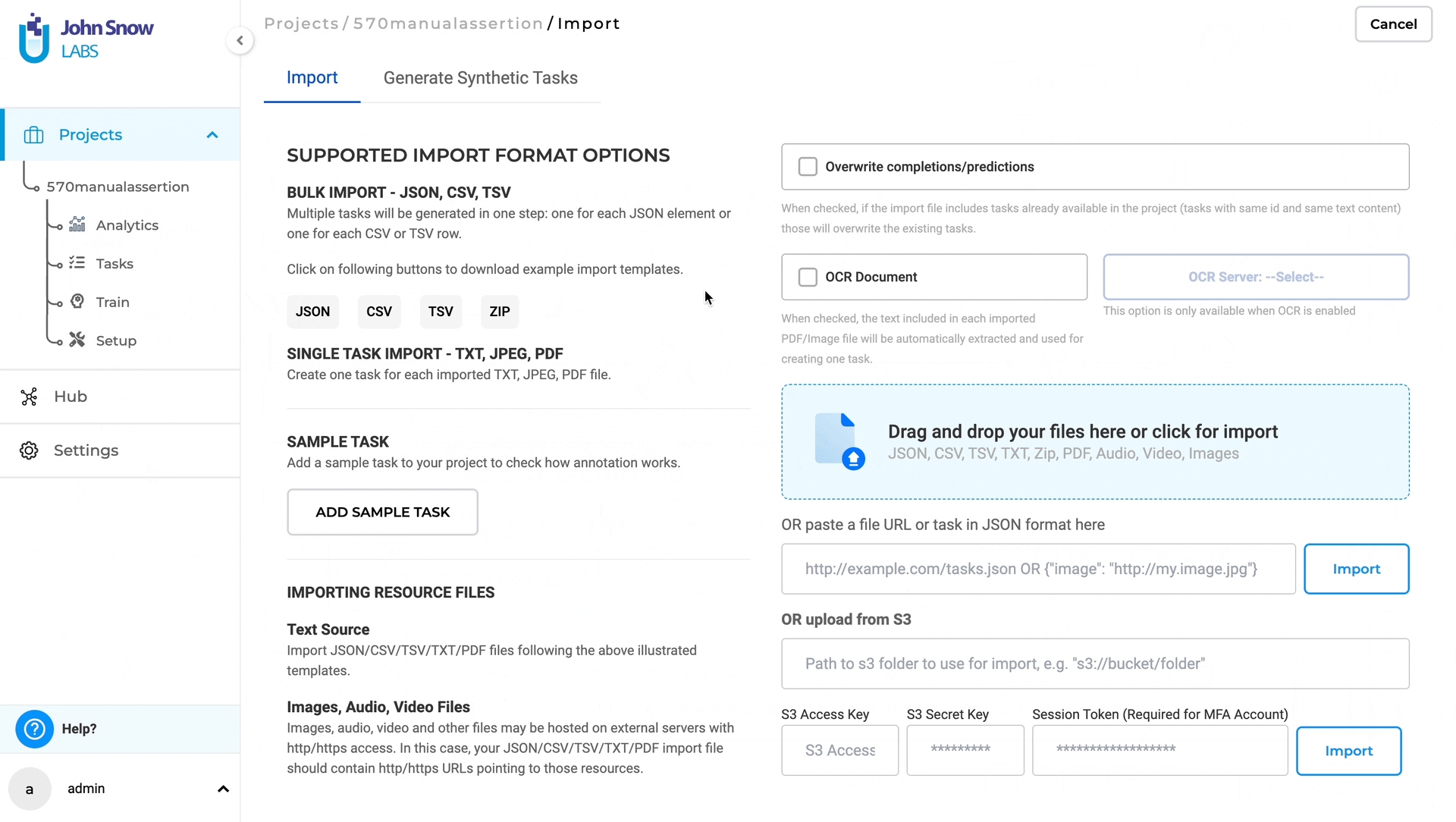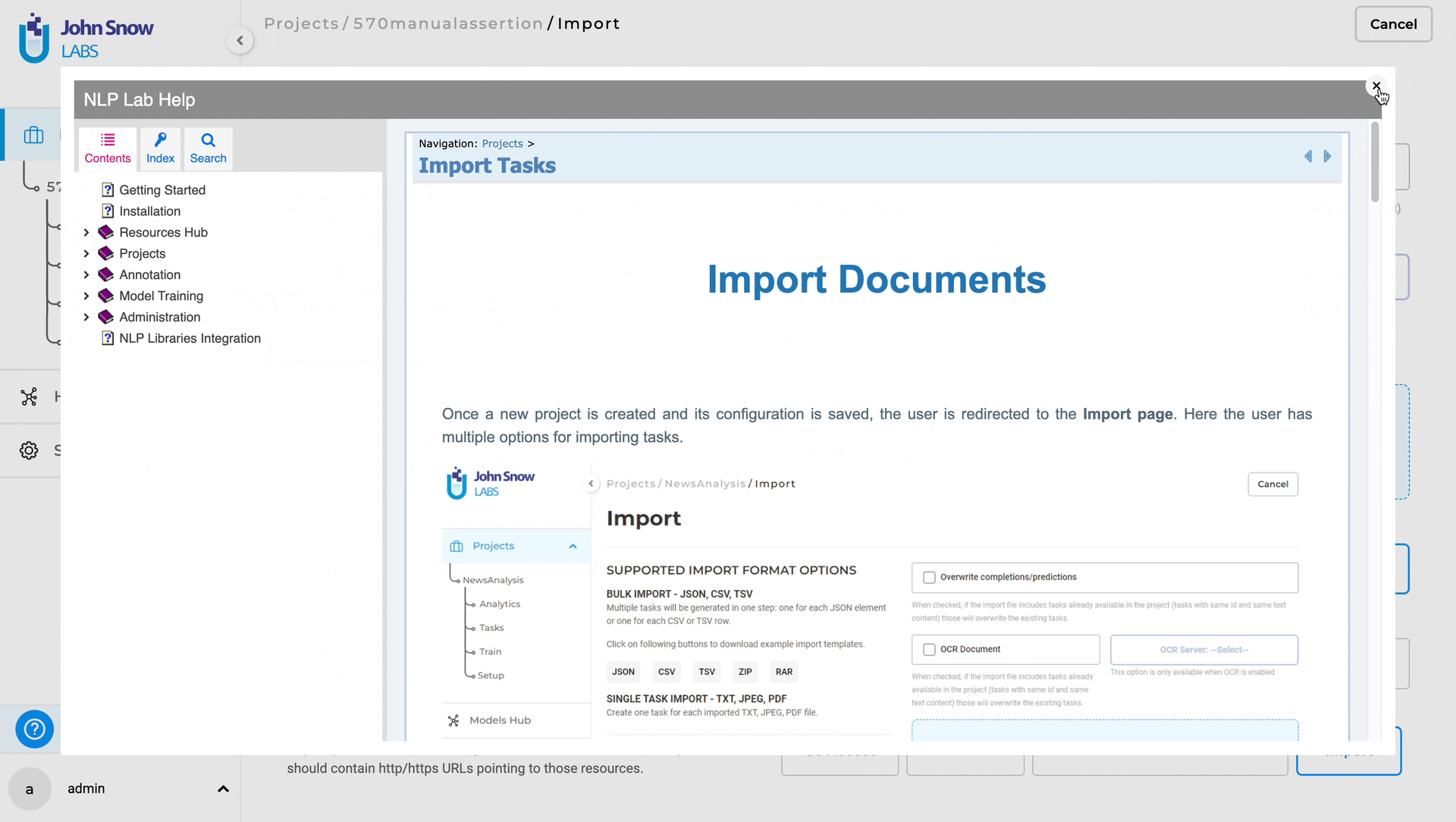
Dedicated Help Button
A dedicated “Help” button has been incorporated into the user interface, located in the bottom left corner of the application. Help documentation button is not restricted to specific pages and can be accessed from any page within NLP Lab application, allowing instant access to relevant resources and specific topics.
When users navigate to different pages under the Project section, the system dynamically maps the context and seamlessly directs users to the relevant help file associated with that specific page, ensuring tailored assistance.
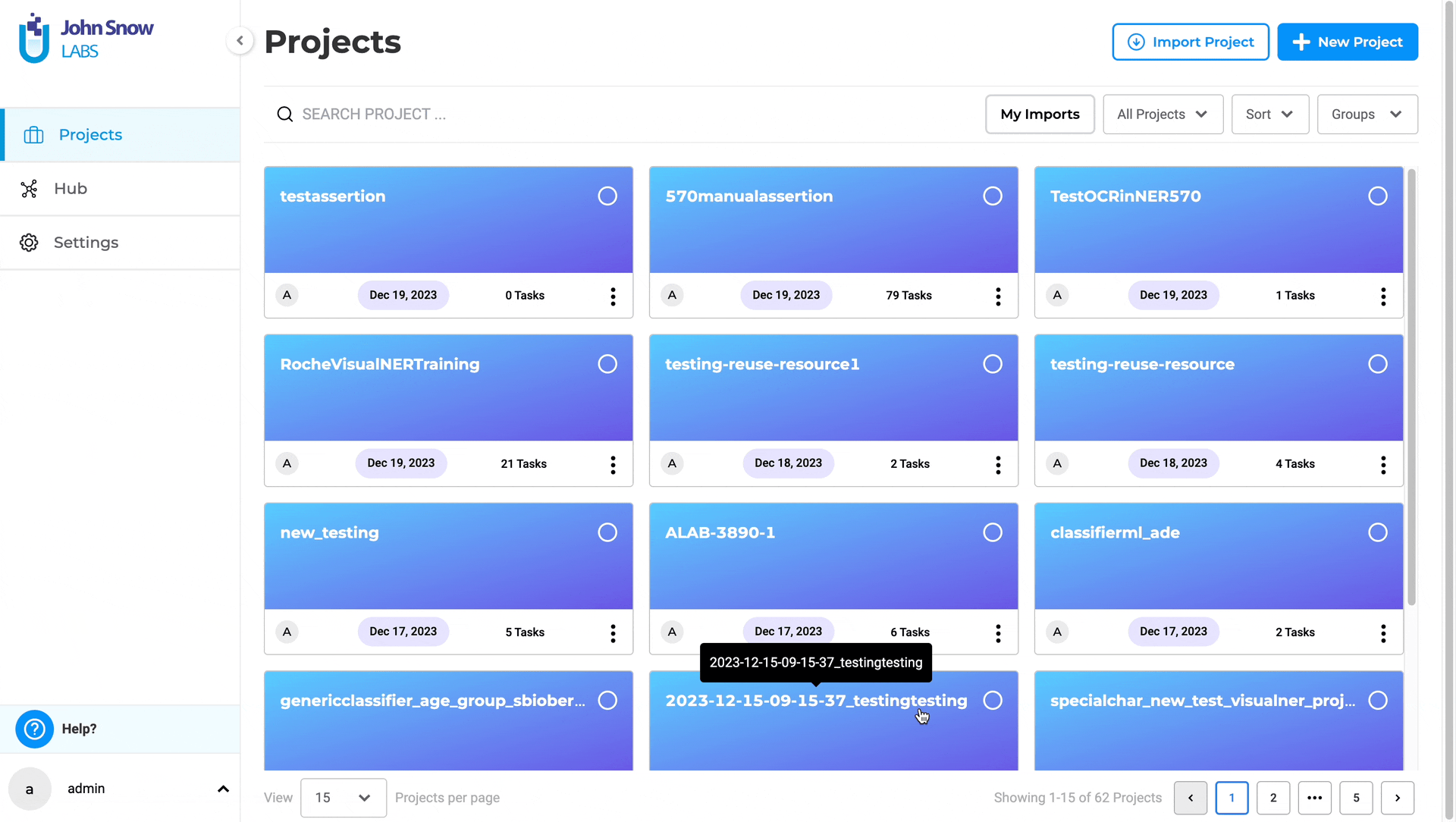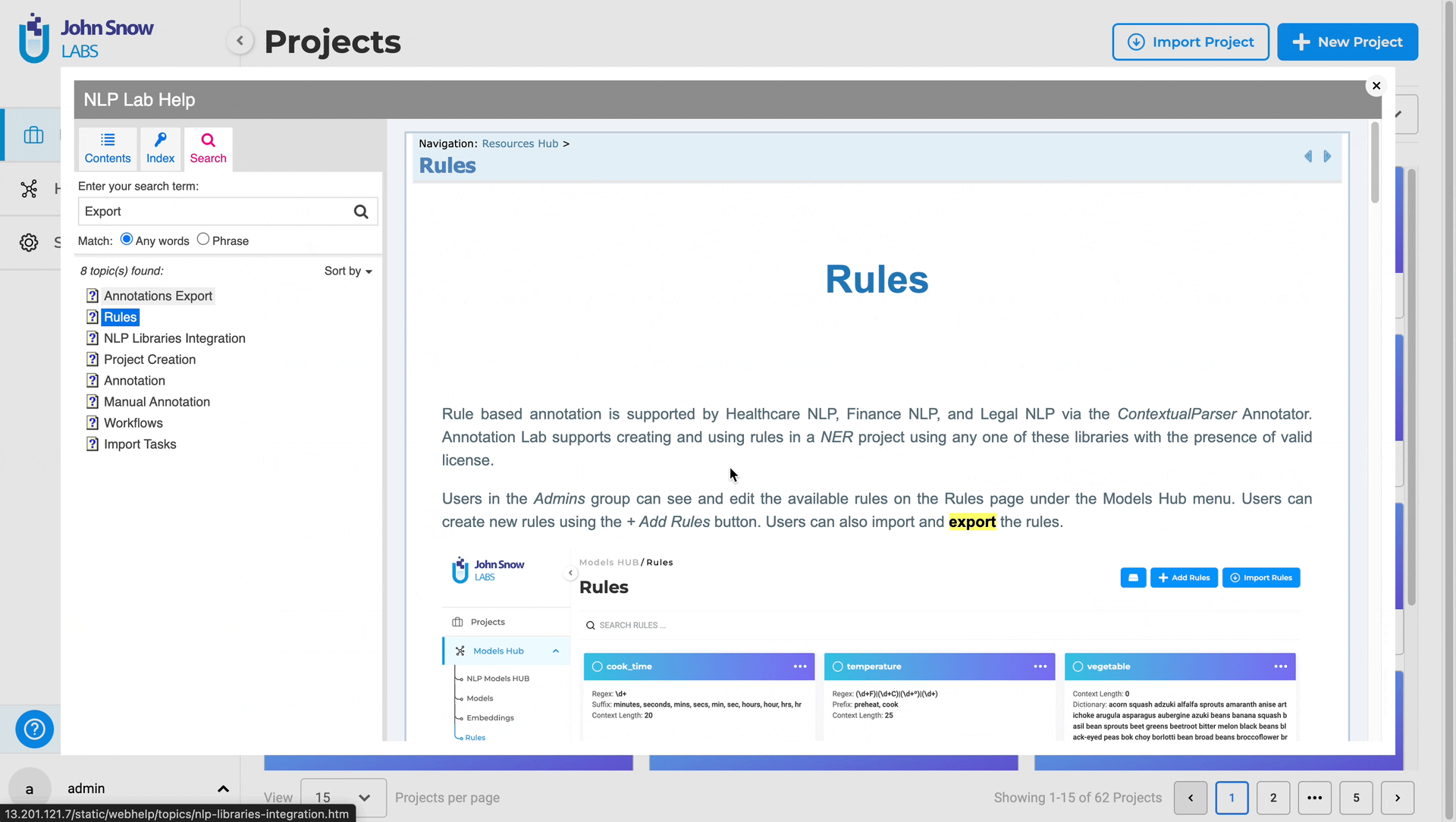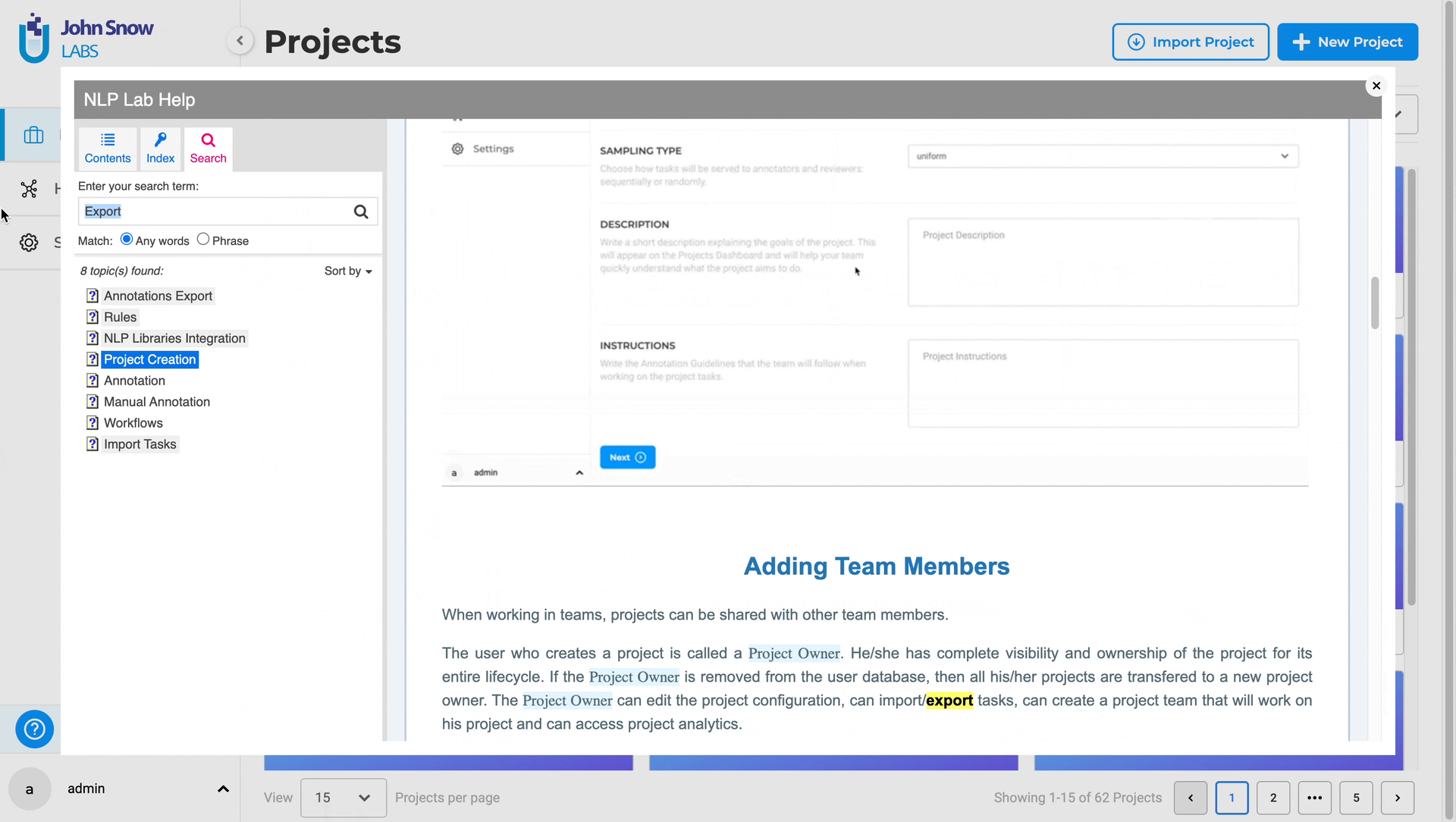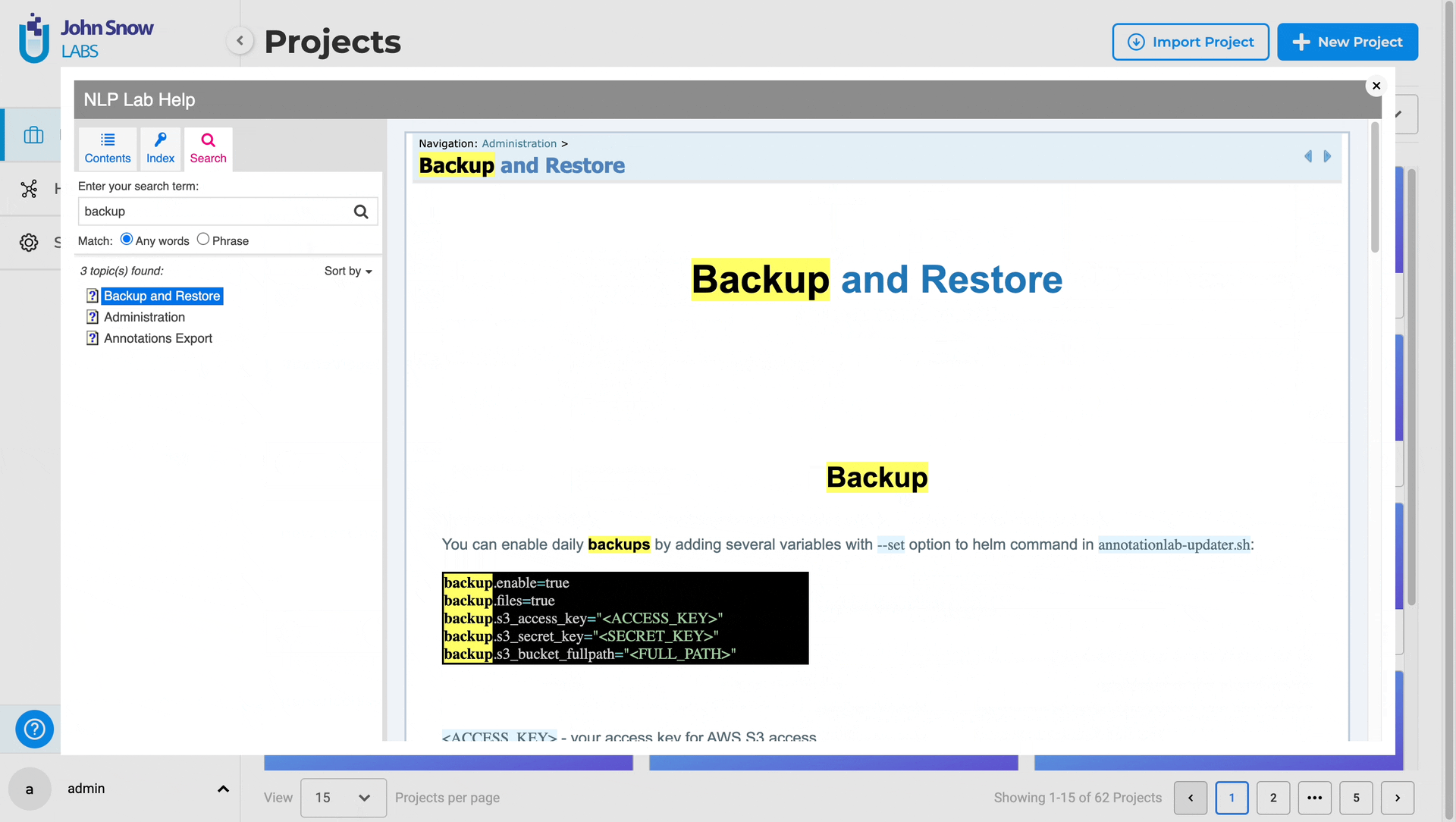
Search Feature
Clicking the “Help” button triggers a popup view displaying application help and documentation, providing users with a quick and unobtrusive way to access relevant information without disrupting their workflow. Users can utilize the search feature within the popup view to find information on specific topics or functionalities, enhancing navigation and promoting a better understanding of the application’s features.
Improvements
Rejects annotations in CSV/TSV import
Starting from version 5.7, annotations are exclusively supported in JSON format. Consequently, annotations in CSV/TSV format will be disregarded. Only the text contained within the CSV file will be imported into the project. Additionally, as part of this enhancement, the title of a task is now limited to 70 characters. Extra characters exceeding this limit will be truncated from the task name.
Redesign Team definition UI
In previous versions, the placement of the “Add Team Members” feature was not optimal and confused some users. To optimize effective team management within the project, the addition of team members was moved to the left, with the definitions of the added team members now presented on the right side. This adjustment allows clear view off added team members without the need to scroll.
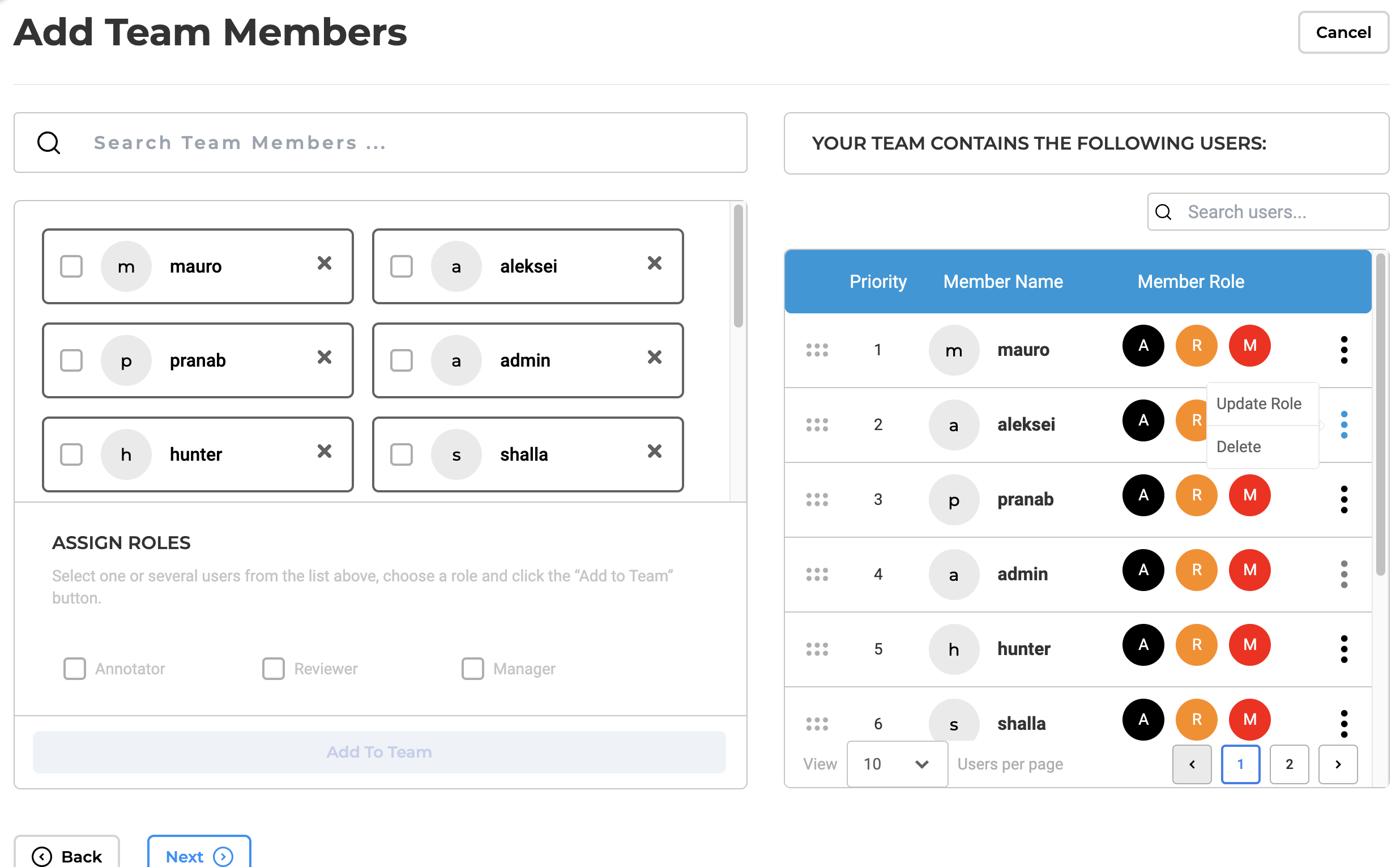
In addition, search and pagination functionalities are now incorporated into the list of added team members, enhancing the user’s ability to quickly locate specific accounts. Moreover, role management does not require searching for accounts. Editing a role for an existing account can simply be done by selecting a new role for the specific account via a pop-up view. These enhancements collectively contribute to a more user-friendly experience and a simplified team management process.
Multi-page Visual NER task indicates relevant and irrelevant pages
Users can now effortlessly locate relevant pages of a multipage document task , simplifying the process of finding relevant information. This improvement facilitates annotators to swiftly navigate to the next relevant page for the visual Named Entity Recognition (NER) task, eliminating the need to manually visit each page.
Note: when using a section based configuration project, if a section rule matches and therefore a section is identified as a positive match for a specific page of a multi-page document or if a user manually assigns a specific page as a relevant section, that page will be designated/identified by the application as a relevant page and visually marked as such. All other pages are considered irrelevant.
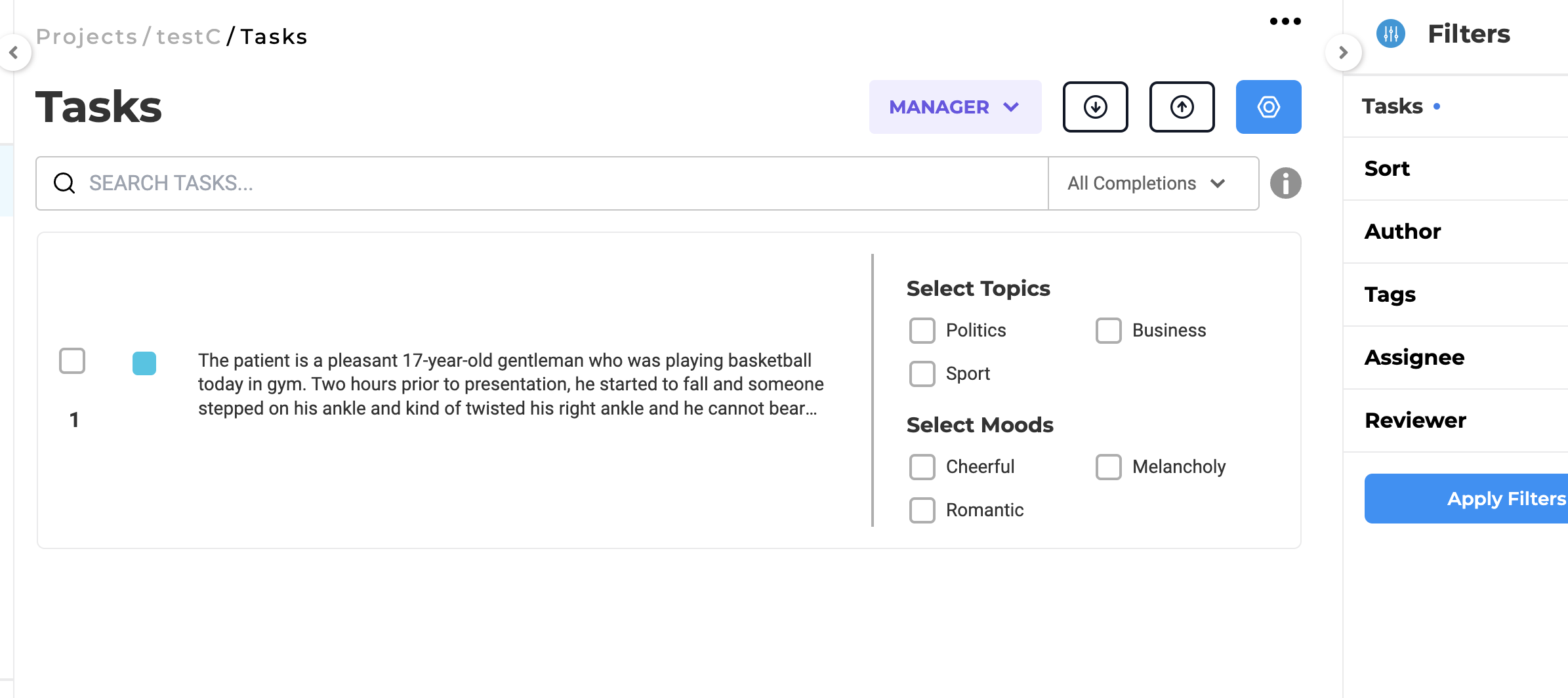
Wrap tasks and align choices in compact view
In the past, when the Compact View option was activated, the visual alignment of the text in the tasks list on the left side and the options/choices for classification on the right side lacked a consistent pattern. To address this, the current view now displays a table with two columns. This design ensures that the labels on the right side of the task list are vertically aligned. Users can adjust the border between the columns by dragging it left or right. Additionally, both the text on the left side and the choices on the right side are wrapped for improved readability.
Bug Fixes:
-
Installation fails in Red Hat OpenShift
In the earlier installation of the NLP Lab on Red Hat OpenShift, some features did not work as expected. Issues were encountered with the training and deployment of models, and the project import and export functionalities were not operational. With the introduction of version 5.7, all these issues have been successfully resolved. As a result, NLP Lab can now be utilized on Red Hat OpenShift without encountering any issues.
-
External Classification Prompt: Mandatory choices field
In previous versions, when creating an external prompt of type Classification, providing choices using the designated field was not mandatory.This allowed the creation and saving of a classification prompt without providing any choices. However, when such a prompt was used in a project, a validation error was raised. With the new version, it is not possible to create a classification prompt without providing choices, thus avoiding validation errors during project configuration step.
-
For any secret key that is added in UI of NLP lab, after saving there should not be “eye” icon to view the secret
Previously, any secret key that was saved in NLP Lab could be viewed from the UI. With the current version the secret key is not exposed in the UI anymore; the access keys are masked and only a hint of it is shown in UI.
-
Text Color for selected classifier classes unreadable (black on grey)
Corrected the readability of text for selected classifier classes; previously, it was displayed in black on grey, and it has now been replaced with the primary color along with a border for improved visibility.
-
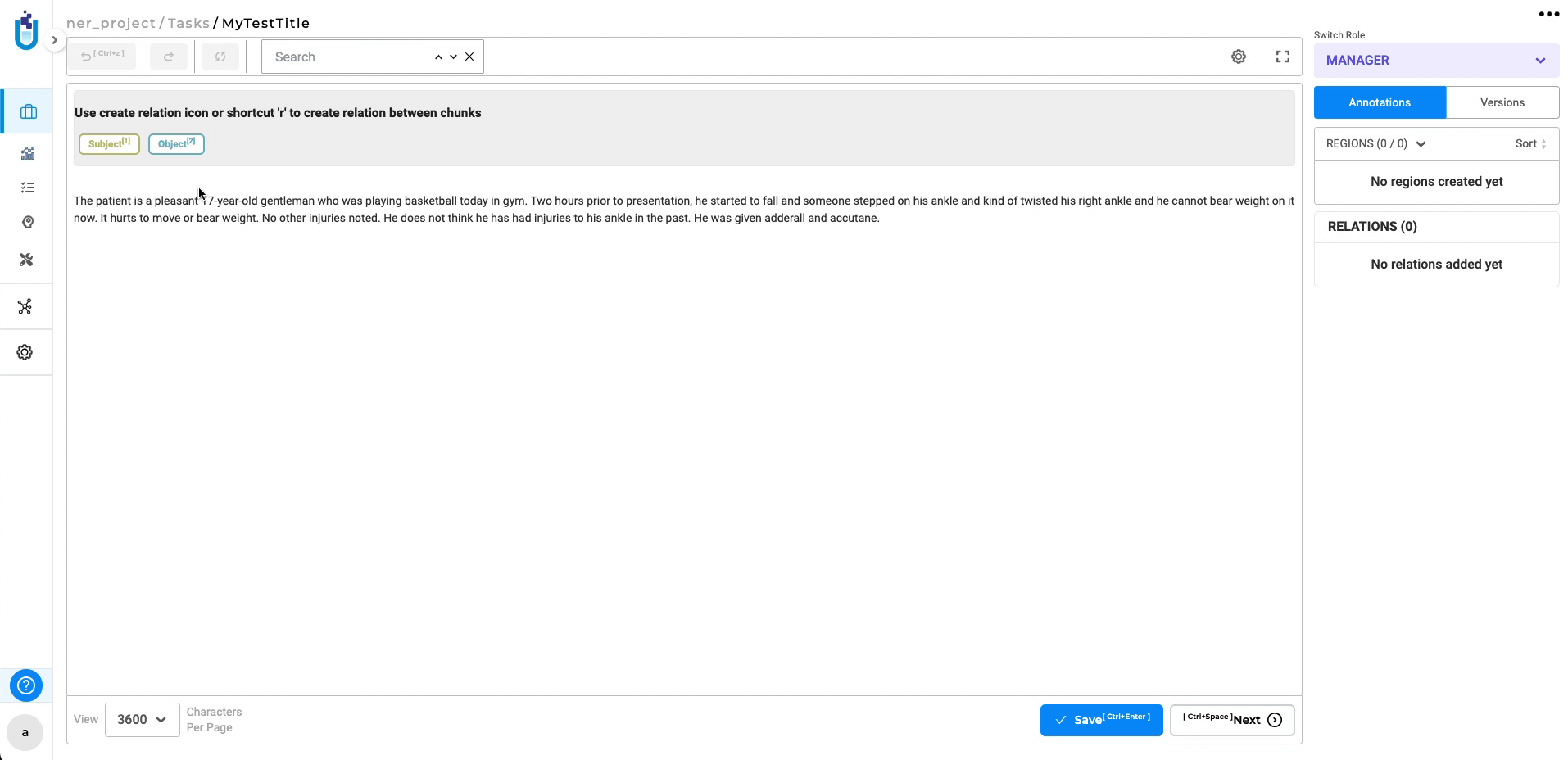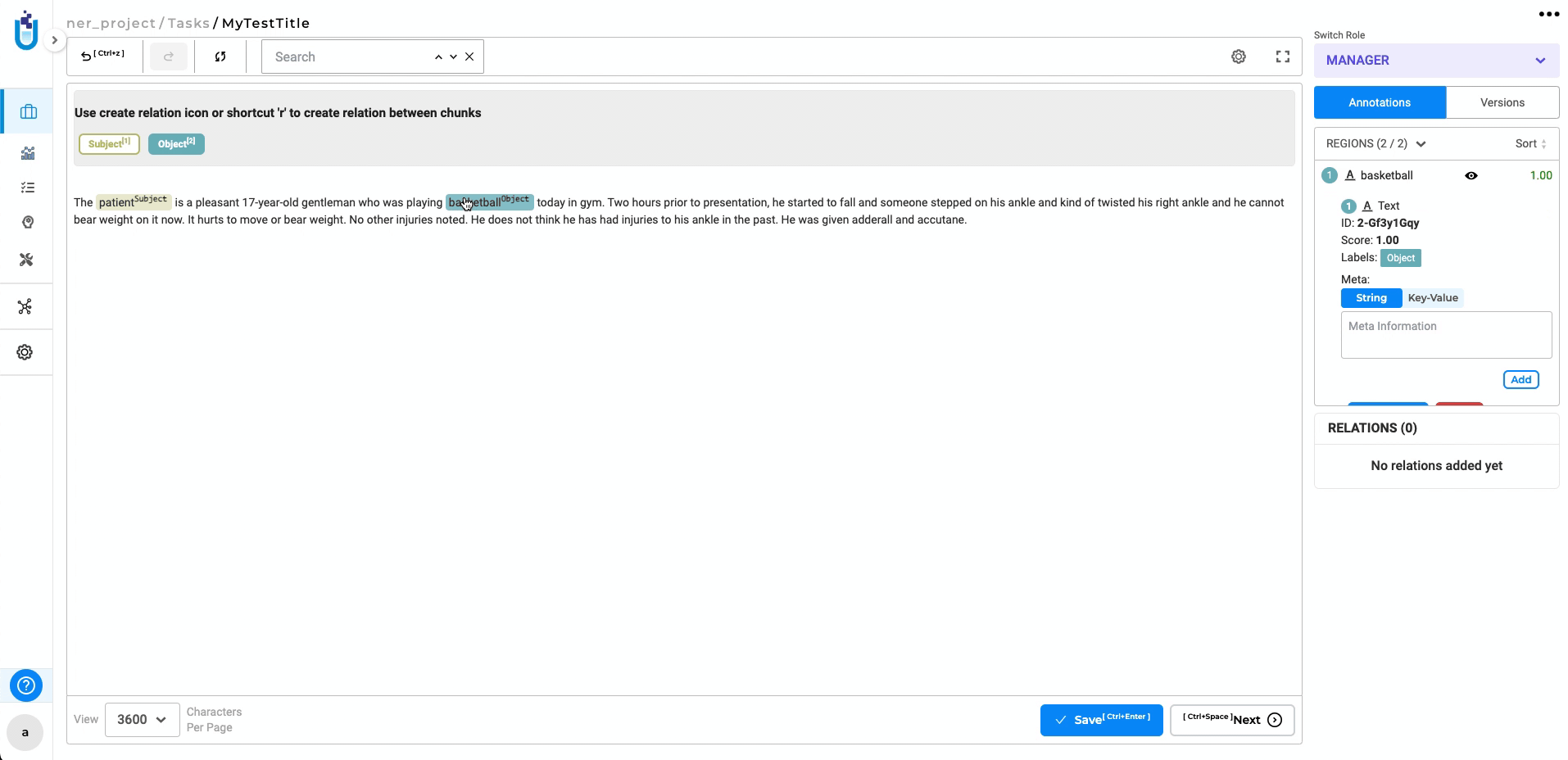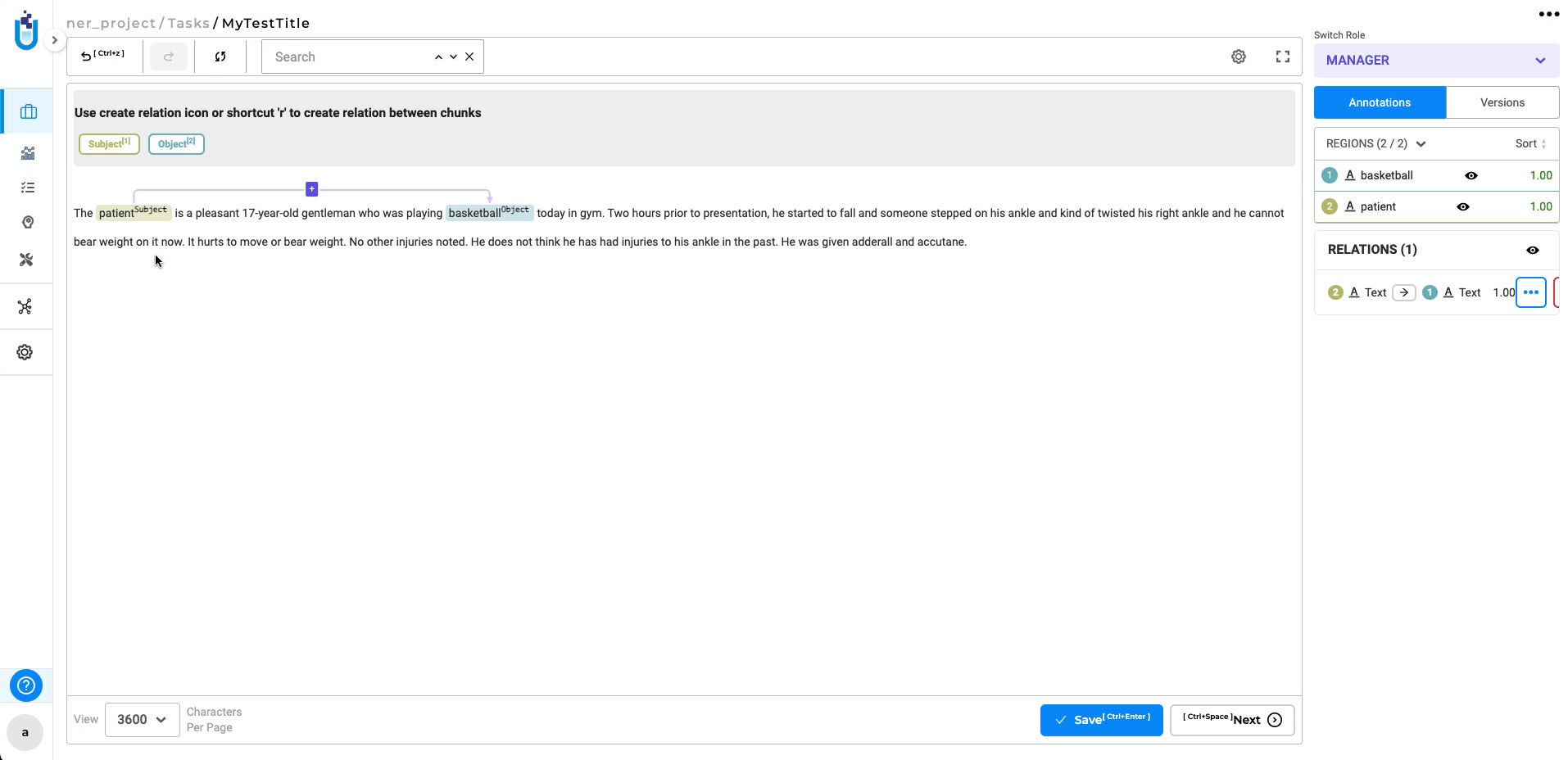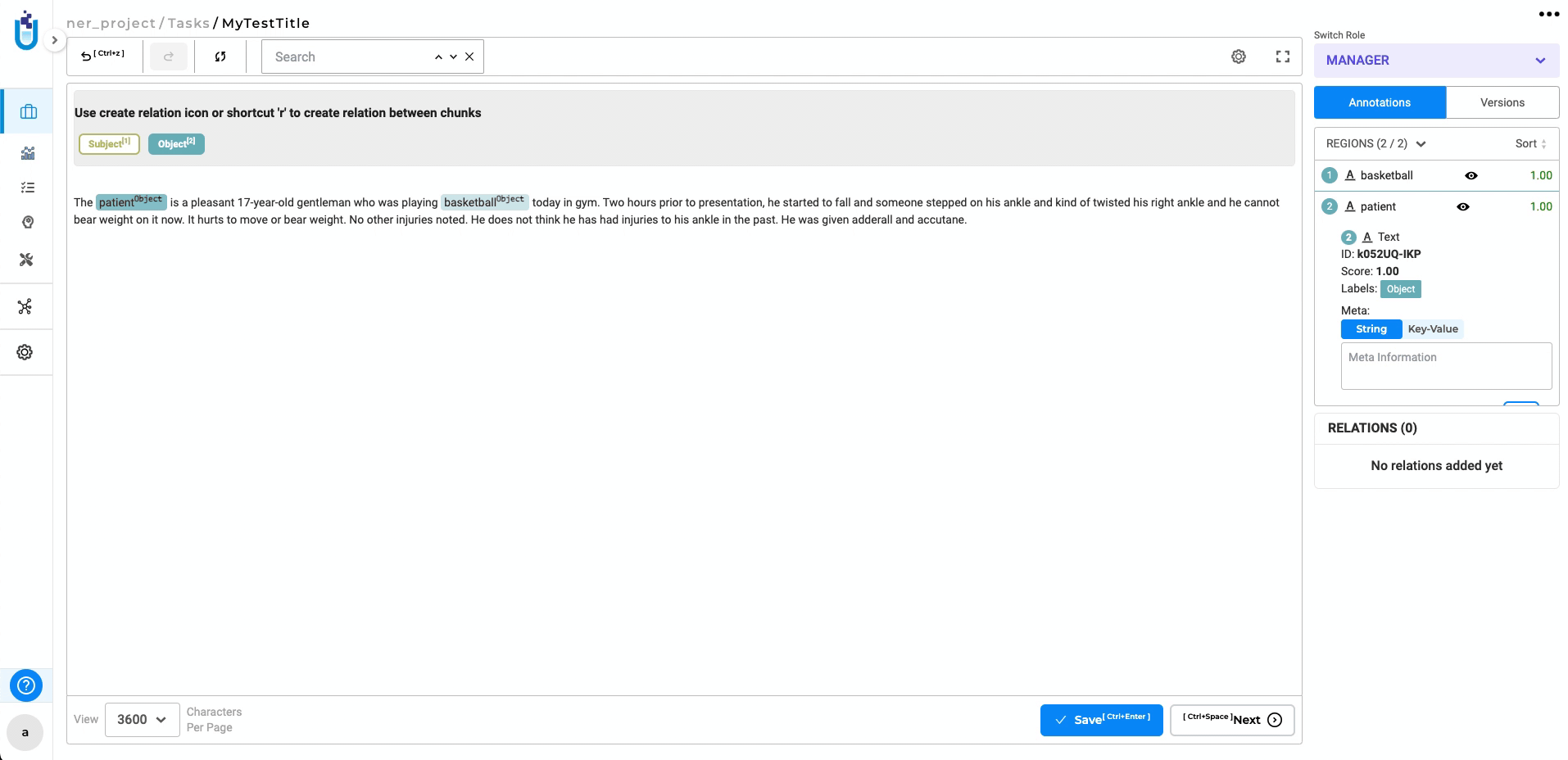
Relations constraint is not applied correctly when the labels of the token are changed after creating relations
Previously, changing labels with associated relations could lead to outdated relationships. Now, when labels are updated, associated relations are automatically removed, ensuring accurate and consistent data.
-
Extra special character added after training Visual NER project with special character.
Following the completion of Visual NER training, where the model is trained and deployed, labels containing the ‘%’ character exhibited an additional ‘%’character in their names. This issue was exclusively noted within the project configuration. The latest vesrion, fixes this issue and the extra character is no longer appended to the label names.
-
Editing a copied completion in draft mode incorrectly updates the edit count
When editing a copied completion in draft mode, the system mistakenly updates the edit count as it treats the action as a new edit. The issue is fixed, Edit count is consistent for copied completions.
-
Analytics: Empty Charts are shown when loading the Analytics Page for the first time
When the analytics page is visited for the first time after project creation, empty charts are shown confusing users. A loading animation has been added to visualy indicate that charts are being generated.
-
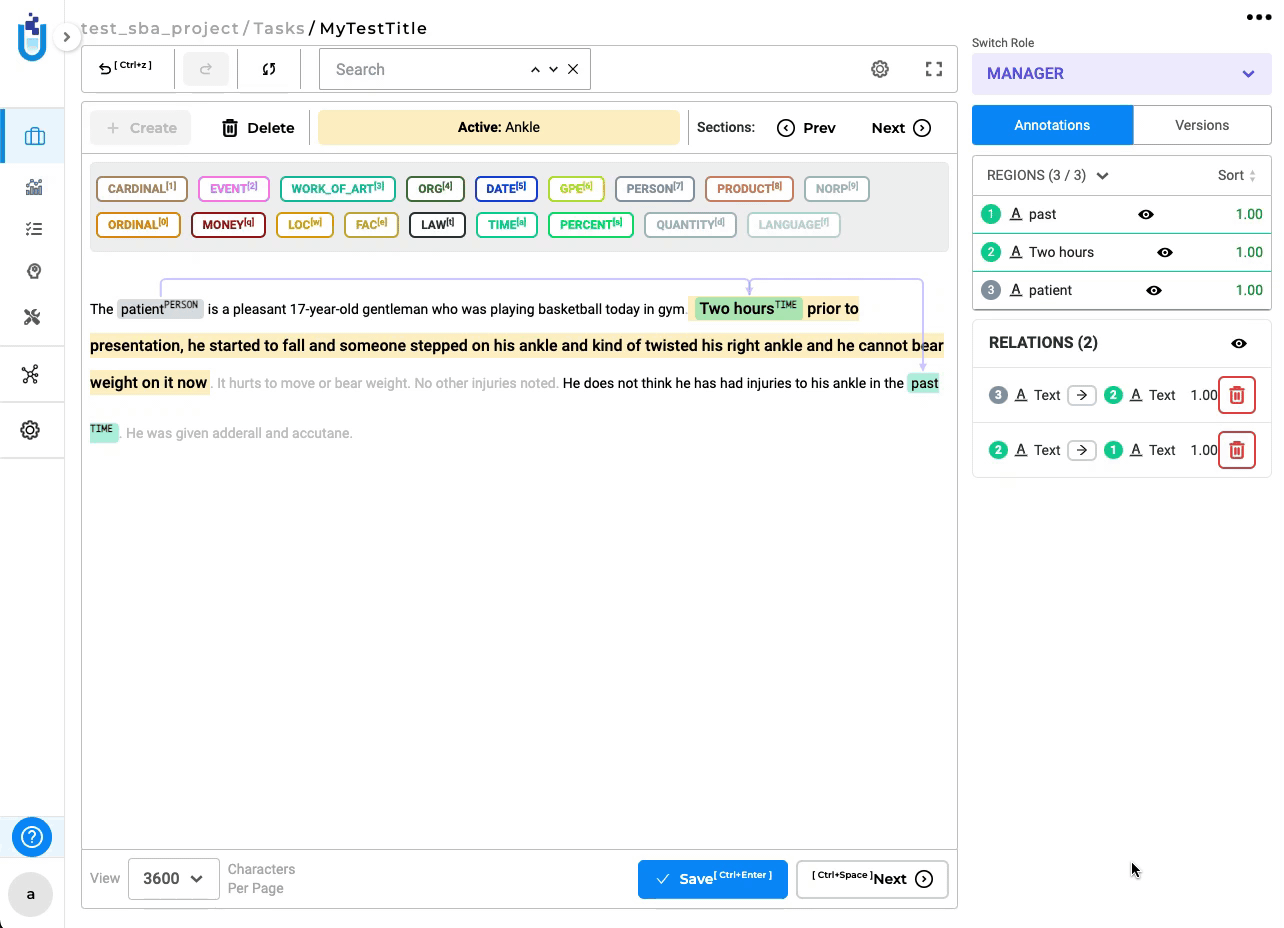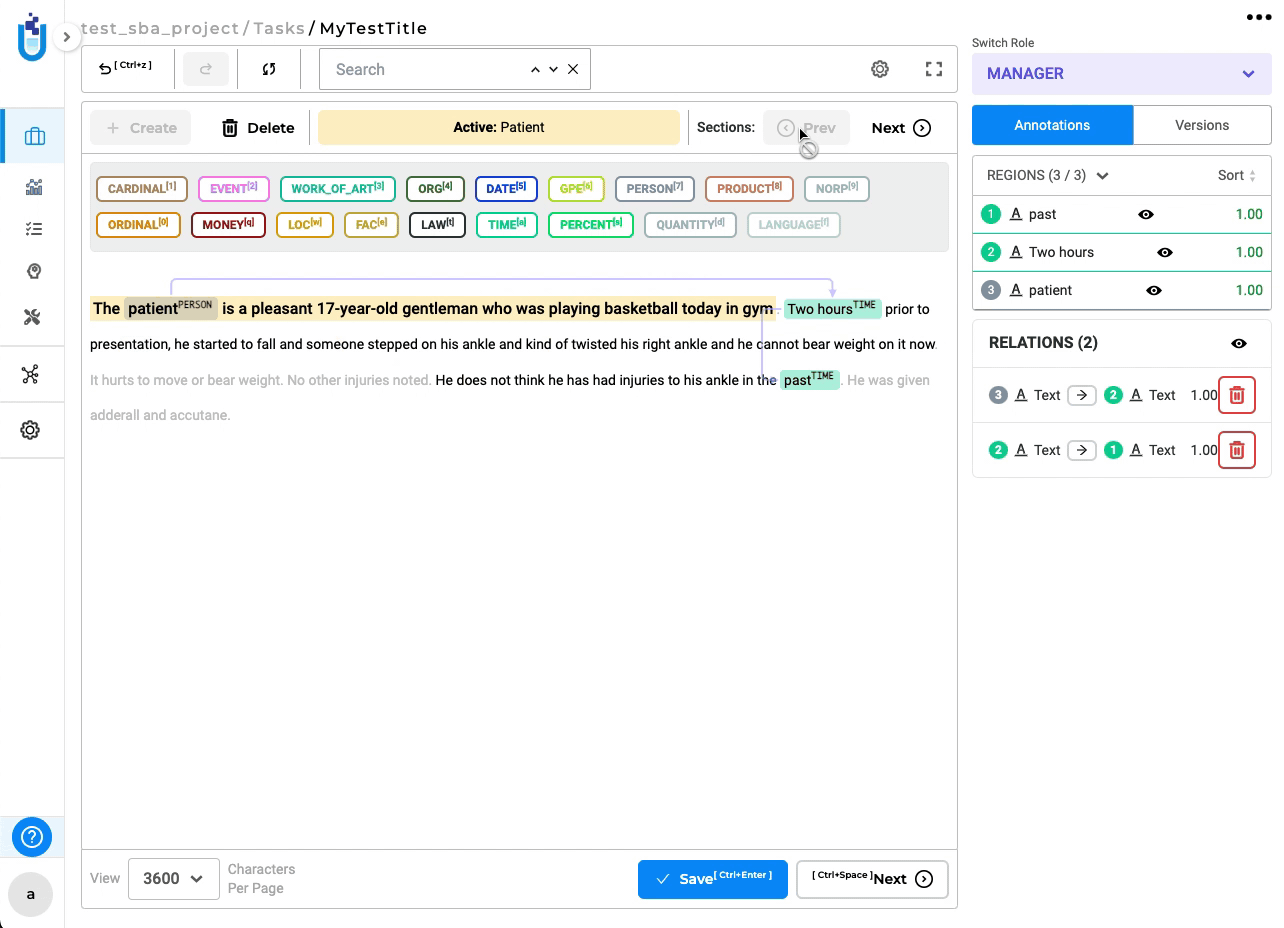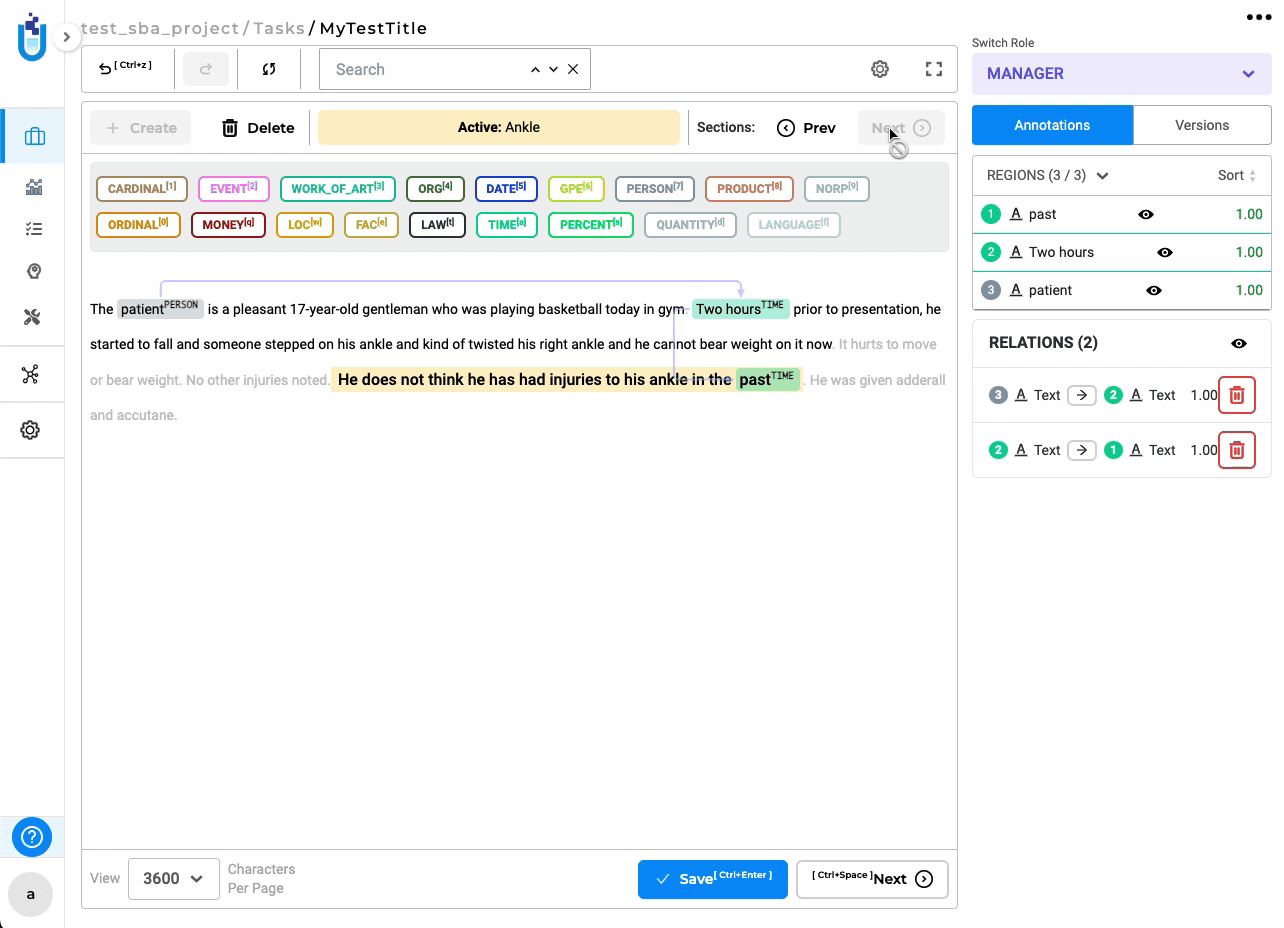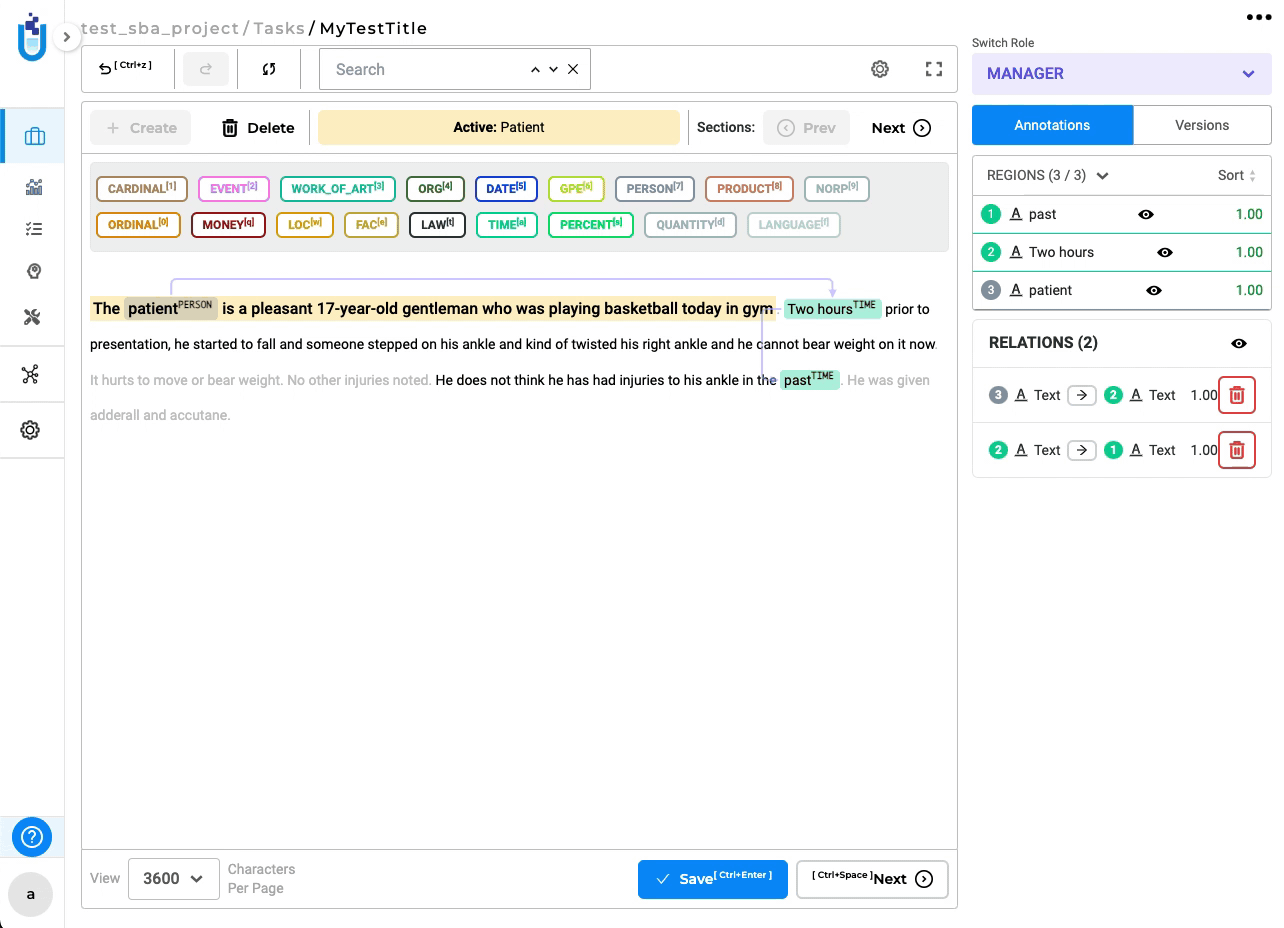
Relation lines are not aligned properly to the annotated entity for SBA enabled RE project
In this version, relation lines dynamically update while navigating sections, ensuring that the start and end of relations stay consistently aligned with their respective labels.
-
The button to switch to submitted/last updated completion from the current draft is not working
Previously, the button to switch between submitted and last updated completion for the draft was not working. The issue has been fixed. allowing users to switch between submitted and last updated completion.
-
Draft is not saved when text is selected before the label
In the earlier version, selecting text before labeling prevented the draft from being saved. The issue has been resolved, enabling automatic draft saving even when text is selected before labeling.
-
Publish Model: Spark NLP version field currently doesn’t display the version for licensed model
Previously, the Spark NLP version displayed on the publish model form was incorrect for licensed models. The issue has been resolved - the correct version is now displayed .
-
Hotkey Shortcuts aren’t disabled from task settings options
After disabling hotkeys from the settings, they remain disabled even if the page is refreshed, ensuring a consistent user experience.
-
“Task Title Edit” Settings is not shown until Compact View is enabled in the Task List Page
Addressed an issue where the task burger menu, including the checkbox for task title editing, was inaccessible until the compact view was activated.
-
Task Page: Counts of comments is always showing 0 despite having comments
Resolved an issue where the comments count wasn’t accurately displayed on the tasks list page. This issue has been addressed, and the comment count reflects the correct number.
Versions
- 7.8.2
- 7.8.1
- 7.8
- 7.7
- 7.6.0
- 7.5.1
- 7.5.0
- 7.4.0
- 7.3.1
- 7.3.0
- 7.2.2
- 7.2.2
- 7.2.0
- 7.1.0
- 7.0.1
- 7.0.0
- 6.11.3
- 6.11.2
- 6.11.1
- 6.11.0
- 6.10.1
- 6.10.0
- 6.9.1
- 6.9.0
- 6.8.1
- 6.8.0
- 6.7.2
- 6.7.0
- 6.6.0
- 6.5.1
- 6.5.0
- 6.4.1
- 6.4.0
- 6.3.2
- 6.3.0
- 6.2.1
- 6.2.0
- 6.1.2
- 6.1.1
- 6.1.0
- 6.0.2
- 6.0.0
- 5.9.3
- 5.9.2
- 5.9.1
- 5.9.0
- 5.8.1
- 5.8.0
- 5.7.1
- 5.7.0
- 5.6.2
- 5.6.1
- 5.6.0
- 5.5.3
- 5.5.2
- 5.5.1
- 5.5.0
- 5.4.1
- 5.3.2
- 5.2.3
- 5.2.2
- 5.1.1
- 5.1.0