5.4.0
Highlights
We are delighted to announce remarkable enhancements and updates in our latest release of Spark NLP for Healthcare. This release comes with a brand new LLM Loader to load and run any size of LLMs in gguf format, a few-shot assertion classifier, contextual assertion detection, and a demo to showcase accuracy differences between Healthcare NLP and GPT-4 for information extraction tasks as well as the first Menopause-specific medical models, 81 new and updated clinical pretrained models, and pipelines.
- Introducing a brand new
LLMLoaderannotator to load and run large language models in gguf format. We also announce 9 LLMs at various sizes and quantization (3x small size medical summarizer and QA model, 3x medium size general model and 3x small size zero shot entity extractor) - Introducing a brand new
FewshotAssertionClassifierannotator to train assertion detection models using a few samples with better accuracy - Introducing a rule-based
ContextualAssertionannotator to detect assertion status using patterns and rules without any training or annotation - Introducing
VectorDBPostProcessorannotator to filter and sort the document splits returned by vector databases in a RAG application - Introducing
ContextSplitAssemblerannotator to assemble the document post-processed splits as a context into an LLM stage in a RAG application - SNOMED entity resolver model for
Veterinarydomains - Voice of the Patients named entity recognition (NER) model
- New rule-based entity matcher models to customize De-IDentification pipelines
- New NER, assertion, relation extraction, and classification models to identify
AlcoholandSmokingrelated Medical Entities - New NER and assertion models to extract
Menopauserelated entities - Clinical document analysis with one-liner pretrained pipelines for specific clinical tasks and concepts
- Formal release of oncological assertion status detection and relation extraction models
- 11 new fine-tuned sentence embedding models finetuned with medical assertion datasets
- Significantly faster vector-db based entity resolution models than existing Sentence Entity Resolver models
- RxNorm code mapping benchmarks and cost comparisons: Healthcare NLP, GPT-4, and Amazon Comprehend Medical
- New blog posts on using NLP in opioid research and healthcare: harnessing NLP, knowledge graphs, and regex techniques for critical insights
- New notebooks for medication and resolutions concept
- Updated Udemy MOOC (our online courses) notebooks
- Various core improvements; bug fixes, enhanced overall robustness and reliability of Spark NLP for Healthcare
- Resolved broken links in healthcare demos
- Added a unique ID field for each entity into the result of the
pipeline_ouput_parsermodule - Fixed deidentification AGE obfuscation hanging issue
- Added DatasetInfo parameter into the
MedicalNERModelannotator
- Updated notebooks and demonstrations for making Spark NLP for Healthcare easier to navigate and understand
- New Clinical Medication Use Case notebook
- New Resolving Medical Terms to Terminology Codes Directly notebook
- New Contextual Assertion notebook
- New VectorDB and PostProcessor for RAG Generative AI notebook
- New Analyse Veterinary Documents with Healthcare NLP notebook
- Updated FewShot Assertion Classifier notebook
- New ALCOHOL SMOKING Demo
- New JSL vs GPT4 Demo to showcase accuracy differences between Healthcare NLP and GPT-4 for information extraction tasks
- The addition and update of numerous new clinical models and pipelines continue to reinforce our offering in the healthcare domain
These enhancements will elevate your experience with Spark NLP for Healthcare, enabling more efficient, accurate, and streamlined analysis of healthcare-related natural language data.
Introducing a Brand New LLMLoader Annotator to Load and Run Large Language Models in GGUF format
LLMLoader is designed to interact with a LLMs that are converted into gguf format. This module allows using John Snow Labs’ licensed LLMs at various sizes that are finetuned on medical context for certain tasks. It provides various methods for setting parameters, loading models, generating text, and retrieving metadata. The LLMLoader includes methods for setting various parameters such as input prefix, suffix, cache prompt, number of tokens to predict, sampling techniques, temperature, penalties, and more. Overall, the LLMLoader provides a flexible and extensible framework for interacting with language models in a Python and Scala environment using PySpark and Java.
| Model Name | Description |
|---|---|
| JSL_MedS_q16_v1 | Summarization and Q&A |
| JSL_MedS_q8_v1 | Summarization and Q&A |
| JSL_MedS_q4_v1 | Summarization and Q&A |
| JSL_MedM_q16_v1 | Summarization, Q&A, RAG, and Chat |
| JSL_MedM_q8_v1 | Summarization, Q&A, RAG, and Chat |
| JSL_MedM_q4_v1 | Summarization, Q&A, RAG, and Chat |
| JSL_MedSNer_ZS_q16_v1 | Extract and link medical named entities |
| JSL_MedSNer_ZS_q8_v1 | Extract and link medical named entities |
| JSL_MedSNer_ZS_q4_v1 | Extract and link medical named entities |
We recommend using 8b quantized versions of the models as the qualitative performance difference between q16 and q8 versions is very negligible.
Example:
from sparknlp_jsl.llm import LLMLoader
llm_loader_pretrained = LLMLoader(spark).pretrained("jsl_meds_q16_v1", "en", "clinical/models")
llm_loader_pretrained.generate("What is the indication for the drug Methadone?")
Result:
Methadone is used to treat opioid addiction. It is a long-acting opioid agonist that is used to help individuals who are addicted to short-acting opioids such as heroin or other illicit opioids. It is also used to treat chronic pain in patients who have developed tolerance to other opioids.
Please check the LLMLoader Notebook for more information
Introducing a Brand New FewshotAssertionClassifier Annotator to Train Assertion Detection Models Using a Few Samples with Better Accuracy
The newly refactored FewShotAssertionClassifierModel and FewShotAssertionClassifierApproach simplify assertion annotation in clinical and biomedical texts. By leveraging sentence embeddings, these models deliver precise assertion annotations and integrate seamlessly with any SparkNLP sentence embedding model.
A key feature is the FewShotAssertionSentenceConverter, an annotator that formats documents/sentences and NER chunks for assertion classification, requiring an additional step in the pipeline.
This comprehensive approach significantly enhances the extraction, analysis, and processing of assertion-related data, making it an indispensable tool for healthcare text annotation.
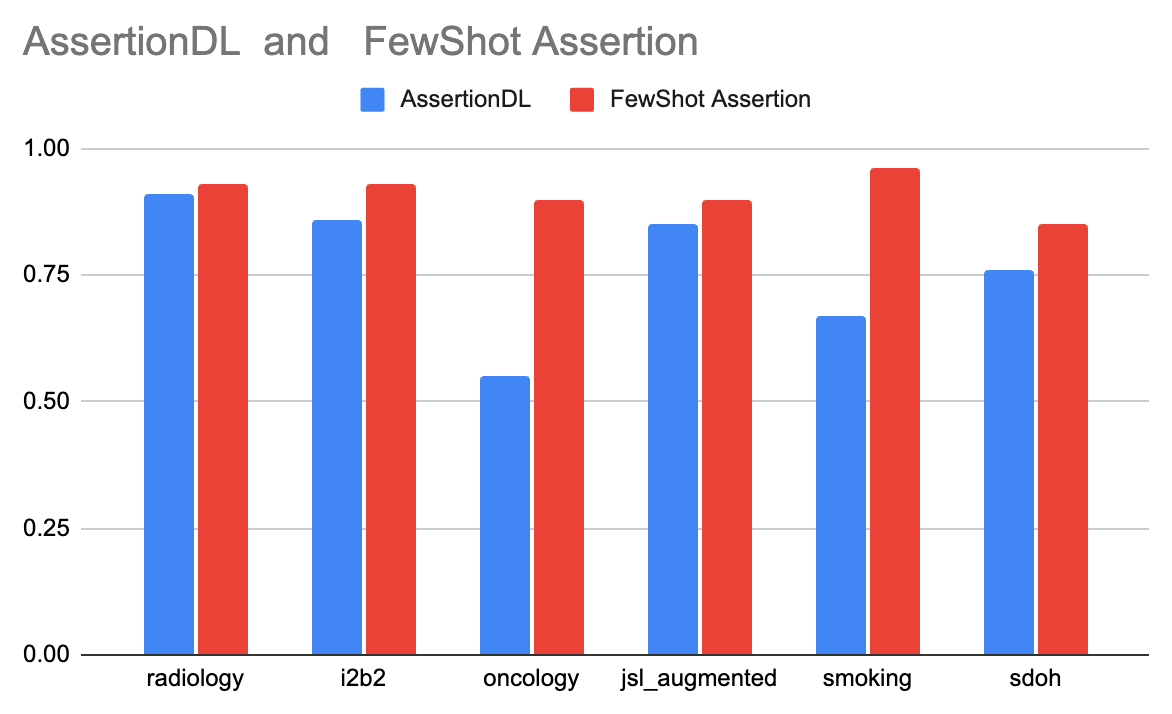
The following table demonstrates the enhanced results achieved using the FewShot Assertion model compared to the traditional AssertionDL model across various datasets. The FewShot Assertion model showcases significant improvements in accuracy scores, particularly in complex medical domains.
| Dataset Name | AssertionDL | FewShot Assertion |
|---|---|---|
| radiology | 0.91 | 0.93 |
| i2b2 | 0.86 | 0.93 |
| oncology | 0.55 | 0.90 |
| jsl_augmented | 0.85 | 0.90 |
| smoking | 0.67 | 0.96 |
| sdoh | 0.76 | 0.85 |
| FewShot Assertion Model Name | Predicted Classed |
|---|---|
| fewhot_assertion_jsl_e5_base_v2_jsl | Present, Absent, Possible, Planned, Past, Family, Hypothetical, SomeoneElse |
| fewhot_assertion_e5_base_v2 | absent, associated_with_someone_else, conditional, hypothetical, possible, present |
| fewhot_assertion_sdoh_e5_base_v2_sdoh | Absent, Past, Present, Someone_Else, Hypothetical, Possible |
| fewhot_assertion_smoking_e5_base_v2_smoking | Present, Absent, Past |
| fewhot_assertion_oncology_e5_base_v2_oncology | Absent, Past, Present, Family, Hypothetical, Possible |
| fewhot_assertion_radiology_e5_base_v2_radiology | Confirmed, Negative, Suspected |
Example:
few_shot_assertion_converter = FewShotAssertionSentenceConverter()\
.setInputCols(["sentence","token", "ner_jsl_chunk"])\
.setOutputCol("assertion_sentence")
e5_embeddings = E5Embeddings.pretrained("e5_base_v2_embeddings_medical_assertion_oncology", "en", "clinical/models")\
.setInputCols(["assertion_sentence"])\
.setOutputCol("assertion_embedding")
few_shot_assertion_classifier = FewShotAssertionClassifierModel()\
.pretrained("fewhot_assertion_oncology_e5_base_v2_oncology", "en", "clinical/models")\
.setInputCols(["assertion_embedding"])\
.setOutputCol("assertion")
sample_text= """The patient is suspected to have colorectal cancer. Her family history is positive for other cancers. The result of the biopsy was positive. A CT scan was ordered to rule out metastases."""
Result:
| chunks | begin | end | entities | assertion | confidence | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | colorectal cancer | 33 | 49 | Cancer_Dx | Possible | 0.581282 |
| 1 | cancers | 93 | 99 | Cancer_Dx | Family | 0.234656 |
| 2 | biopsy | 120 | 125 | Pathology_Test | Past | 0.957321 |
| 3 | positive | 131 | 138 | Pathology_Result | Present | 0.956439 |
| 4 | CT scan | 143 | 149 | Imaging_Test | Past | 0.95717 |
| 5 | metastases | 175 | 184 | Metastasis | Possible | 0.549866 |
Please check the FewShot Assertion Classifier Notebook for more information
Introducing a Rule-Based ContextualAssertion Annotator to Detect Assertion Status Using Patterns and Rules without any Training or Annotation
Introducing Contextual Assertion which identifies contextual cues within text data, such as negation, uncertainty, etc. It is used for clinical assertion detection, etc. It annotates text chunks with assertions based on configurable rules, prefix and suffix patterns, and exception patterns.
- Dataset: 253 Clinical Texts from in-house dataset
| Assertion Label | Contextual Assertion | AssertionDL |
|---|---|---|
| Absent | 0.88 | 0.78 |
| Past | 0.77 | 0.65 |
- Dataset: Used in-house jsl_augmented dataset
| Assertion Label | Contextual Assertion | AssertionDL |
|---|---|---|
| Absent | 0.82 | 0.90 |
| Family | 0.63 | 0.73 |
| Hypothetical | 0.51 | 0.69 |
| Past | 0.73 | 0.77 |
| Planned | 0.57 | 0.62 |
| Possible | 0.49 | 0.74 |
| SomeoneElse | 0.61 | 0.81 |
Contextual Assertion, a powerful component within Spark NLP, extends beyond mere negation detection. Its ability to identify and classify a diverse range of contextual cues, including uncertainty, temporality, and sentiment, empowers healthcare professionals to extract deeper meaning from complex medical records.
| Model Name | Description |
|---|---|
contextual_assertion_someone_else |
Identifies contextual cues within text data to detect someone else assertions |
contextual_assertion_absent |
Identifies contextual cues within text data to detect absent assertions |
contextual_assertion_past |
Identifies contextual cues within text data to detect past assertions |
Example:
contextual_assertion = ContextualAssertion() \
.setInputCols(["sentence", "token", "ner_chunk"]) \
.setOutputCol("assertion") \
.setPrefixKeywords(["no", "not"]) \
.setSuffixKeywords(["unlikely", "negative", "no"]) \
.setPrefixRegexPatterns(["\\b(no|without|denies|never|none|free of|not include)\\b"]) \
.setSuffixRegexPatterns(["\\b(free of|negative for|absence of|not|rule out)\\b"]) \
.setExceptionKeywords(["without"]) \
.setExceptionRegexPatterns(["\\b(not clearly)\\b"]) \
.addPrefixKeywords(["negative for", "negative"]) \
.addSuffixKeywords(["absent", "neither"]) \
.setCaseSensitive(False) \
.setPrefixAndSuffixMatch(False) \
.setAssertion("absent") \
.setScopeWindow([2, 2])\
.setIncludeChunkToScope(True)\
example_text = """Patient resting in bed. Patient given azithromycin without any difficulty. Patient has audible wheezing, states chest tightness.
No evidence of hypertension. Patient denies nausea at this time. zofran declined. Patient is also having intermittent sweating associated with pneumonia.
"""
Result:
| ner_chunk | begin | end | ner_label | Assertion |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| any difficulty | 59 | 72 | PROBLEM | absent |
| hypertension | 149 | 160 | PROBLEM | absent |
| nausea | 178 | 183 | PROBLEM | absent |
| zofran | 199 | 204 | TREATMENT | absent |
Please check the Contextual Assertion Notebook for more information
Introducing VectorDBPostProcessor Annotator to Filter and Sort the Document Splits Returned by VectorDB in a RAG Application
The VectorDBPostProcessor is a powerful tool designed to filter and sort output from the VectorDBModel (our own VectorDB implementations will be released soon). This processor refines VECTOR_SIMILARITY_RANKINGS input annotations and outputs enhanced VECTOR_SIMILARITY_RANKINGS annotations based on specified criteria.
Key Parameters:
filterBy(str): Select and prioritize filter options (metadata, diversity_by_threshold). Options can be given as a comma-separated string, determining the filtering order. Default: metadatasortBy(str): Select sorting option (ascending, descending, lost_in_the_middle, diversity). Default: ascendingcaseSensitive(bool): Determines if string operators’ criteria are case-sensitive. Default: FalsediversityThreshold(float): Sets the threshold for the diversity_by_threshold filter. Default: 0.01- maxTopKAfterFiltering (int): Limits the number of annotations returned after filtering. Default: 20
allowZeroContentAfterFiltering(bool): Determines whether zero annotations are allowed after filtering. Default: False
This processor ensures precise and customizable annotation management, making it an essential component for advanced data processing workflows.
Example:
post_processor = VectorDBPostProcessor() \
.setInputCols("vector_db") \
.setOutputCol("post") \
.setSortBy("ascending")
.setMaxTopKAfterFiltering(5)
.setFilterBy("metadata") \
.setMetadataCriteria([
{"field": "pubdate", "fieldType": "date", "operator": "greater_than", "value": "2017 May 11", "dateFormats": ["yyyy MMM dd", "yyyy MMM d"], "converterFallback": "filter"},
{"field": "distance", "fieldType": "float", "operator": "less_than", "value": "0.5470"},
{"field": "title", "fieldType": "string", "operator": "contains", "matchMode": "any", "matchValues": ["diabetes", "immune system"]}
])
Please check the VectorDB and PostProcessor for RAG Generative AI Notebook for more information
Introducing ContextSplitAssembler Annotator to Assemble the Document Post-processed Splits as a Context into an LLM Stage in a RAG Application
The ContextSplitAssembler is a versatile tool designed to work seamlessly with vector databases (our own VectorDB implementations will be released soon) and VectorDBPostProcessor. It combines and organizes annotation results with customizable delimiters and optional splitting.
Key Parameters:
joinString(str): Specifies the delimiter string inserted between annotations when combining them into a single result. Ensures proper separation and organization. Default: “ “explodeSplits(bool): Determines whether to split the annotations into separate entries. Default: False
This assembler enhances the management and presentation of annotations, making it an essential tool for advanced data processing workflows.
Example:
context_split_assembler = ( ContextSplitAssembler()
.setInputCols("vector_db")
.setOutputCol("document")
.setJoinString("\n")
.setExplodeSplits(False))
Please check the VectorDB and PostProcessor for RAG Generative AI Notebook for more information
SNOMED Entity Resolver Model for Veterinary Domains
This advanced model facilitates the mapping of veterinary-related entities and concepts to SNOMED codes using sbiobert_base_cased_mli Sentence BERT embeddings. It is trained with an enhanced dataset derived from the sbiobertresolve_snomed_veterinary_wip model. The model ensures precise and reliable resolution of veterinary terms to standardized SNOMED codes, aiding in consistent and comprehensive veterinary data documentation and analysis.
Example:
snomed_resolver = SentenceEntityResolverModel.pretrained("sbiobertresolve_snomed_veterinary", "en", "clinical/models") \
.setInputCols(["sentence_embeddings"]) \
.setOutputCol("snomed_code")\
.setDistanceFunction("EUCLIDEAN")
text = "The veterinary team is closely monitoring the patient for signs of lymphoblastic lymphoma, a malignant neoplasm of lymphoid origin. They are also treating the patient's osteoarthritis, a degenerative joint disease. Additionally, the team is vigilantly observing the facility for potential outbreaks of mink distemper."
Result:
| ner_chunk | entity | snomed_code | description |
|---|---|---|---|
| lymphoblastic lymphoma | PROBLEM | 312281000009102 | lymphoblastic lymphoma |
| a malignant neoplasm of lymphoid origin | PROBLEM | 443495005 | neoplasm of lymphoid system structure |
| the patient’s osteoarthritis | PROBLEM | 201826000 | erosive osteoarthrosis |
| a degenerative joint disease | PROBLEM | 201819000 | degenerative joint disease involving multiple joints |
| mink distemper | PROBLEM | 348361000009108 | mink distemper |
Please check the model card for more information
Voice of the Patients Named Entity Recognition (NER) Model
The Voice of the Patients NER Model is designed to extract healthcare-related terms from patient-generated documents. This model processes the natural language used by patients to identify and categorize medical terms, facilitating better understanding and documentation of patient-reported information.
Example:
ner_model = MedicalNerModel.pretrained("ner_vop_v2", "en", "clinical/models")\
.setInputCols(["sentence", "token", "embeddings"])\
.setOutputCol("ner")
text = "Hello,I'm 20 year old girl. I'm diagnosed with hyperthyroid 1 month ago. I was feeling weak, light headed,poor digestion, panic attacks, depression, left chest pain, increased heart rate, rapidly weight loss, from 4 months. Because of this, I stayed in the hospital and just discharged from hospital. I had many other blood tests, brain mri, ultrasound scan, endoscopy because of some dumb doctors bcs they were not able to diagnose actual problem."
Result:
| chunk | begin | end | ner_label |
|---|---|---|---|
| 20 year old | 15 | 25 | Age |
| girl | 27 | 30 | Gender |
| hyperthyroid | 52 | 63 | Disease |
| 1 month ago | 65 | 75 | DateTime |
| weak | 92 | 95 | Symptom |
| light | 98 | 102 | Symptom |
| panic attacks | 127 | 139 | PsychologicalCondition |
| depression | 142 | 151 | PsychologicalCondition |
| left | 154 | 157 | Laterality |
| chest | 159 | 163 | BodyPart |
| pain | 165 | 168 | Symptom |
| increased | 171 | 179 | TestResult |
| heart rate | 181 | 190 | VitalTest |
| rapidly | 193 | 199 | Modifier |
| weight loss | 201 | 211 | Symptom |
| 4 months | 220 | 227 | Duration |
| hospital | 263 | 270 | ClinicalDept |
| discharged | 281 | 290 | AdmissionDischarge |
| hospital | 297 | 304 | ClinicalDept |
| blood tests | 324 | 334 | Test |
| brain | 337 | 341 | BodyPart |
| mri | 343 | 345 | Test |
| ultrasound scan | 348 | 362 | Test |
| endoscopy | 365 | 373 | Procedure |
Please check the model card for more information
New Rule-Based Entity Matcher Models to Customise De-IDentification Pipelines
We introduce a suite of text and regex matchers, specifically designed to enhance the deidentification and clinical document understanding process with rule-based methods.
| Model Name | Description |
|---|---|
cancer_diagnosis_matcher |
This model extracts cancer diagnoses in clinical notes using a rule-based TextMatcherInternal annotator. |
country_matcher |
This model extracts countries in clinical notes using a rule-based TextMatcherInternal annotator. |
email_matcher |
This model extracts emails in clinical notes using a rule-based RegexMatcherInternal annotator. |
phone_matcher |
This model extracts phone entities in clinical notes using a rule-based RegexMatcherInternal annotator. |
state_matcher |
This model extracts states in clinical notes using a rule-based RegexMatcherInternal annotator. |
zip_matcher |
This model extracts zip codes in clinical notes using a rule-based RegexMatcherInternal annotator. |
city_matcher |
This model extracts city names in clinical notes using a rule-based TextMatcherInternal annotator. |
Example:
text_matcher = TextMatcherInternalModel.pretrained("cancer_diagnosis_matcher", "en", "clinical/models") \
.setInputCols(["sentence", "token"])\
.setOutputCol("cancer_dx")\
.setMergeOverlapping(True)
example_text = """A 65-year-old woman had a history of debulking surgery, bilateral oophorectomy with omentectomy, total anterior hysterectomy with radical pelvic lymph nodes dissection due to ovarian carcinoma (mucinous-type carcinoma, stage Ic) 1 year ago. The patient's medical compliance was poor and failed to complete her chemotherapy (cyclophosphamide 750 mg/m2, carboplatin 300 mg/m2). Recently, she noted a palpable right breast mass, 15 cm in size which nearly occupied the whole right breast in 2 months. Core needle biopsy revealed metaplastic carcinoma. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy with the regimens of Taxotere (75 mg/m2), Epirubicin (75 mg/m2), and Cyclophosphamide (500 mg/m2) was given for 6 cycles with poor response, followed by a modified radical mastectomy (MRM) with dissection of axillary lymph nodes and skin grafting. Postoperatively, radiotherapy was done with 5000 cGy in 25 fractions. The histopathologic examination revealed a metaplastic carcinoma with squamous differentiation associated with adenomyoepithelioma. Immunohistochemistry study showed that the tumor cells are positive for epithelial markers-cytokeratin (AE1/AE3) stain, and myoepithelial markers, including cytokeratin 5/6 (CK 5/6), p63, and S100 stains. Expressions of hormone receptors, including ER, PR, and Her-2/Neu, were all negative."""
Result:
| chunk | begin | end | label |
|---|---|---|---|
| ovarian carcinoma | 176 | 192 | Cancer_dx |
| mucinous-type carcinoma | 195 | 217 | Cancer_dx |
| metaplastic carcinoma | 528 | 548 | Cancer_dx |
| metaplastic carcinoma | 937 | 957 | Cancer_dx |
| adenomyoepithelioma | 1005 | 1023 | Cancer_dx |
New NER, Assertion, Relation Extraction, and Classification Models to Identify Alcohol and Smoking Related Medical Entities
A suite of models designed for the identification and analysis of alcohol and smoking related entities in text data. These models include Named Entity Recognition (NER), assertion status, relation extraction, and classification, providing a comprehensive toolkit for analyzing substance use information.
- NER Model
| Model Name | Predicted Entities | Description |
|---|---|---|
| ner_alcohol_smoking | Drinking_Status, Alcohol_Type, Smoking_Status, Smoking_Type, Substance_Duration, Substance_Frequency, Substance_Quantity, Cardiovascular_Issues, Respiratory_Issues, GUT_Issues, Neurologic_Issues, Psychiatric_Issues, Other_Health_Issues, Drinking_Environment, Cessation_Treatment, Withdrawal_Treatment |
Detects alcohol and smoking related entities within text data |
This ner_alcohol_smoking model is designed to detect and label alcohol and smoking-related entities within text data. Alcohol refers to beverages containing ethanol, a psychoactive substance that is widely consumed for its pleasurable effects. Smoking typically involves inhaling smoke from burning tobacco, a highly addictive substance. The model has been trained using advanced deep learning techniques on a diverse range of text sources and can accurately recognize and classify a wide range of entities related to alcohol and smoking. The model’s accuracy and precision have been carefully validated against expert-labeled data to ensure reliable and consistent results.
Example:
ner_model = MedicalNerModel.pretrained("ner_alcohol_smoking", "en", "clinical/models")\
.setInputCols(["sentence", "token","embeddings"])\
.setOutputCol("ner")
sample_texts = ["""The outpatient clinic addressed a complaint from the patient regarding severe anxiety and withdrawal symptoms.
He disclosed a history of alcohol addiction, with weekly episodes of intense binge drinking over the past decade.
However, due to recent challenges in his personal and professional life, he decided to quit drinking cold turkey a week ago.
Since then, he has been experiencing escalating symptoms including tremors, sweating, nausea, and severe anxiety.
The patient denies recent use drugs or smoking, focusing her struggles solely on alcohol.
He was placed on CIWA protocol w/ lorazepam for management. Scheduled for cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT)."""]
Result:
| chunk | begin | end | ner_label |
|---|---|---|---|
| anxiety | 78 | 84 | Psychoneurologic_Issue |
| alcohol addiction | 138 | 154 | Drinking_Status |
| weekly | 162 | 167 | Substance_Frequency |
| binge | 189 | 193 | Substance_Quantity |
| drinking | 195 | 202 | Drinking_Status |
| over the past decade | 204 | 223 | Substance_Duration |
| drinking | 319 | 326 | Drinking_Status |
| tremors | 420 | 426 | Psychoneurologic_Issue |
| sweating | 429 | 436 | Other_Health_Issues |
| nausea | 439 | 444 | GUT_Issues |
| anxiety | 458 | 464 | Psychoneurologic_Issue |
| smoking | 507 | 513 | Smoking_Status |
| alcohol | 549 | 555 | Drinking_Status |
| CIWA | 575 | 578 | Withdrawal_Treatment |
| lorazepam | 592 | 600 | Withdrawal_Treatment |
| cognitive-behavioral therapy | 632 | 659 | Cessation_Treatment |
| CBT | 662 | 664 | Cessation_Treatment |
- Assertion Models
| Model Name | Assertion Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| assertion_alcohol_smoking_wip | Absent, Hypothetical_Possible, Past_History, Present_Planned |
This model detects the assertion status of entities related to alcohol-smoking. |
| assertion_alcohol_smoking_general_symptoms_wip | Overdose_Symptom, Withdrawal_Symptom |
This model detects the assertion status of general symptoms entity related to alcohol-smoking. |
Example:
assertion = AssertionDLModel.pretrained("assertion_alcohol_smoking_wip", "en", "clinical/models")\
.setInputCols(["sentence", "ner_chunk", "embeddings"]) \
.setOutputCol("assertion")
sample_texts = ["""Per the patient, the last drink was on ___, prior to admission. The patient admits to having experienced tremors, palpitations, and diaphoresis during the past alcohol withdrawals, but he denies ever having experienced seizures. Mr. ___ did not report experiencing any symptoms of withdrawal throughout his hospital stay, and an examination revealed no evidence of withdrawal.""",
"""SUBSTANCE ABUSE: The patient admitted to occasional binge drinking, but admitted to normally consuming one pint of liquor a day in the week before her admission. Before she attempted suicide, she was heavily intoxicated and had a high blood alcohol level (BAL). Attending the AA meetings and expressing a desire to keep going to AA to support sobriety were two ways the patient showed motivation to stop drinking. The patient was put on the CIWA protocol upon admission, but no PRN Valium was needed for alcohol withdrawal."""]
Result:
| chunk | begin | end | ner_label | assertion | confidence |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| drink | 26 | 30 | Drinking_Status | Past_History | 0.8507 |
| tremors | 105 | 111 | Psychoneurologic_Issue | Past_History | 0.9315 |
| palpitations | 114 | 125 | Cardiovascular_Issues | Past_History | 0.9251 |
| diaphoresis | 132 | 142 | Other_Health_Issues | Past_History | 0.9181 |
| alcohol | 160 | 166 | Drinking_Status | Past_History | 0.9109 |
| seizures | 219 | 226 | Psychoneurologic_Issue | Absent | 0.5359 |
| binge | 52 | 56 | Substance_Quantity | Present_Planned | 0.5528 |
| drinking | 58 | 65 | Drinking_Status | Present_Planned | 0.5704 |
| one pint | 103 | 110 | Substance_Quantity | Present_Planned | 0.6838 |
| liquor | 115 | 120 | Alcohol_Type | Present_Planned | 0.6879 |
| a day | 122 | 126 | Substance_Frequency | Present_Planned | 0.8029 |
| suicide | 183 | 189 | Psychoneurologic_Issue | Past_History | 0.731 |
| intoxicated | 208 | 218 | Psychoneurologic_Issue | Past_History | 0.7832 |
| alcohol | 241 | 247 | Drinking_Status | Past_History | 0.507 |
| AA | 276 | 277 | Cessation_Treatment | Present_Planned | 0.4559 |
| AA | 329 | 330 | Cessation_Treatment | Present_Planned | 0.5112 |
| drinking | 404 | 411 | Drinking_Status | Present_Planned | 0.5385 |
| CIWA | 441 | 444 | Withdrawal_Treatment | Present_Planned | 0.5693 |
| Valium | 482 | 487 | Withdrawal_Treatment | Absent | 0.553 |
| alcohol | 504 | 510 | Drinking_Status | Present_Planned | 0.5135 |
- Relation Extraction Model
| Model Name | Predicted Entities | Description |
|---|---|---|
| re_alcohol_smoking_clinical_wip | is_caused_by, is_used_for |
It recognizes relations between treatment cessation and withdrawal with drinking and smoking status, as well as relations between various health issues (Neurologic, Psychiatric, Cardiovascular, Respiratory, GUT, and Other Health Issues) and drinking and smoking status. |
Example:
clinical_re_Model = RelationExtractionModel()\
.pretrained("re_alcohol_smoking_clinical_wip", "en", "clinical/models")\
.setInputCols(["embeddings", "pos_tags", "ner_chunk", "dependencies"])\
.setOutputCol("relations")\
.setMaxSyntacticDistance(4)\
.setRelationPairs(["Cessation_Treatment-Drinking_Status",
"Cessation_Treatment-Smoking_Status",
"Respiratory_Issues-Drinking_Status",
"Respiratory_Issues-Smoking_Status"])
text = ["""Pulmonary Function Tests: Demonstrates airflow limitation consistent with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
(COPD). Diagnosis: Acute exacerbation of COPD secondary to smoking.
Diagnosis: Alcoholic fatty liver disease and smoking-related respiratory symptoms.Management: The patient received alcohol cessation counseling and support services to address her alcohol use disorder. She was also provided with smoking cessation pharmacotherapy and behavioral interventions to help her quit smoking."""]
Result:
| sentence | entity1_begin | entity1_end | chunk1 | entity1 | entity2_begin | entity2_end | chunk2 | entity2 | relation | confidence | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 2 | 154 | 157 | COPD | Respiratory_Issues | 172 | 178 | smoking | Smoking_Status | is_caused_by | 0.999902 |
| 2 | 4 | 297 | 303 | alcohol | Drinking_Status | 305 | 324 | cessation counseling | Cessation_Treatment | is_used_for | 0.999512 |
| 3 | 4 | 297 | 303 | alcohol | Drinking_Status | 330 | 345 | support services | Cessation_Treatment | is_used_for | 0.933377 |
| 4 | 5 | 411 | 417 | smoking | Smoking_Status | 419 | 443 | cessation pharmacotherapy | Cessation_Treatment | is_used_for | 0.996433 |
| 5 | 5 | 411 | 417 | smoking | Smoking_Status | 449 | 472 | behavioral interventions | Cessation_Treatment | is_used_for | 0.9565 |
- Classification Models
| Model Name | Assertion Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| genericclassifier_alcohol_mpnet_wip | Current_Drinker, Others |
The primary goal of the model is to categorize texts into two main label categories: ‘Current_Drinker’ and ‘Others.’ (past or non-smoker) |
| genericclassifier_smoking_mpnet_wip | Current_Smoker, Others |
The primary goal of the model is to categorize texts into two main label categories: ‘Current_Smoker’ and ‘Others.’ (past or non-smoker) |
Example:
generic_classifier = GenericClassifierModel.pretrained('genericclassifier_alcohol_mpnet_wip', 'en', 'clinical/models')\
.setInputCols("features")\
.setOutputCol("prediction")
text_list = [
"The patient, with a history of COPD and alcohol dependence, was initially admitted due to a COPD exacerbation and community-acquired pneumonia. The situation was further complicated by alcohol withdrawal. He was later transferred to another facility for treatment of left hand cellulitis, which raised concerns for necrotizing fasciitis.",
"Until recently, the patient had maintained stability on his antidepressant regimen. However, he experienced a notable worsening of depressive symptoms last week, leading him to engage in heavy binge drinking as an ineffective way to suppress his emotional distress and feelings of despair.",
"Ms. Jane Doe, a 60-year-old retired teacher, presented to the emergency department complaining of severe abdominal pain and vomiting. She has a history of gallstones but has been asymptomatic for years. Currently, she does not smoke or drink alcohol, focusing on a healthy lifestyle.",
"Mr. John Smith, a 45-year-old accountant, came to the clinic reporting intense chest pain and shortness of breath. He has a history of hypertension but has managed it well with medication. He currently does not smoke or drink alcohol, maintaining a healthy lifestyle."]
Result:
| text | result |
|---|---|
| The patient, with a history of COPD and alcohol dependence, was initially admitted due to a COPD … | Current_Drinker |
| Until recently, the patient had maintained stability on his antidepressant regimen. However, he e… | Current_Drinker |
| Ms. Jane Doe, a 60-year-old retired teacher, presented to the emergency department complaining of… | Others |
| Mr. John Smith, a 45-year-old accountant, came to the clinic reporting intense chest pain and sho… | Others |
New NER and Assertion Models to Extract Menopause Related Entities
A set of sophisticated models aimed at extracting and analyzing menopause-related entities in text data. These models include a Named Entity Recognition (NER) model and assertion models, which identify and determine the status of various menopause-related terms, aiding in comprehensive menopause data analysis.
- NER Model
| Model Name | Predicted Entities | Description |
|---|---|---|
| ner_menopause_core | Perimenopause, Menopause, Gynecological_Symptom, Gynecological_Disease, Other_Symptom, Irregular_Menstruation, G_P, Hypertension, Osteoporosis, Oncological, Fracture, Hormone_Replacement_Therapy, Osteporosis_Therapy, Antidepressants, Procedure, Hormone_Testing, Vaginal_Swab, Age, Test_Result |
Detects menopause related entities within text data |
This ner_menopause_core model is designed to detect and label core entities related to menopause and associated conditions within text data. Menopause-related terms and conditions are crucial factors that influence individuals’ health outcomes, especially among women undergoing the menopausal transition. The model has been trained using advanced machine-learning techniques on a diverse range of text sources. It can accurately recognize and classify a wide range of menopause-related entities. The model’s accuracy and precision have been carefully validated against expert-labeled data to ensure reliable and consistent results.
Example:
ner_model = MedicalNerModel.pretrained("ner_menopause_core", "en", "clinical/models"))\
.setInputCols(["sentence", "token","embeddings"])\
.setOutputCol("ner")
sample_texts = ["""The patient is a 52-year-old female, G3P2, who presents with complaints of irregular menstruation and symptoms suggestive of perimenopause. She reports experiencing hot flashes, night sweats, and vaginal dryness. Her medical history includes polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), fatigue, mood swings, hypertension diagnosed 5 years ago and currently managed with medication, and osteoporosis diagnosed 2 years ago with ongoing treatment.
Current medications include estradiol for hormone replacement therapy, alendronate for osteoporosis therapy, and fluoxetine for depressive symptoms related to menopause. Recent tests and procedures include a bone density scan to monitor osteoporosis, blood tests for estradiol and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) levels, and a vaginal swab collected for routine infection screening. Test results showed elevated FSH levels indicating menopause."""]
Result:
| chunk | begin | end | ner_label |
|---|---|---|---|
| irregular menstruation | 76 | 97 | Irregular_Menstruation |
| perimenopause | 126 | 138 | Perimenopause |
| hot flashes | 166 | 176 | Other_Symptom |
| night sweats | 179 | 190 | Other_Symptom |
| vaginal dryness | 197 | 211 | Gynecological_Symptom |
| polycystic ovary syndrome | 243 | 267 | Gynecological_Disease |
| PCOS | 270 | 273 | Gynecological_Disease |
| fatigue | 277 | 283 | Other_Symptom |
| hypertension | 299 | 310 | Hypertension |
| osteoporosis | 377 | 388 | Osteoporosis |
| estradiol | 466 | 474 | Hormone_Replacement_Therapy |
| hormone replacement therapy | 480 | 506 | Hormone_Replacement_Therapy |
| alendronate | 509 | 519 | Osteporosis_Therapy |
| osteoporosis | 525 | 536 | Osteoporosis |
| fluoxetine | 551 | 560 | Antidepressants |
| menopause | 597 | 605 | Menopause |
| osteoporosis | 675 | 686 | Osteoporosis |
| estradiol | 705 | 713 | Hormone_Testing |
| follicle-stimulating hormone | 719 | 746 | Hormone_Testing |
| FSH | 749 | 751 | Hormone_Testing |
| vaginal swab | 768 | 779 | Vaginal_Swab |
| elevated | 844 | 851 | Test_Result |
| FSH | 853 | 855 | Hormone_Testing |
| menopause | 875 | 883 | Menopause |
- Assertion Models
| Model Name | Assertion Status | Description |
|---|---|---|
| assertion_menopause_wip | Present, Absent, Possible, Past, Hypothetical, Planned, Family, Menarche_Age, Menopause_Age |
This model detects the assertion status of menopause-related entities. |
Example:
assertion = AssertionDLModel.pretrained("assertion_menopause_wip", "en", "clinical/models")\
.setInputCols(["sentence", "ner_chunk", "embeddings"]) \
.setOutputCol("assertion")
sample_texts = ["""A 50-year-old woman, G2P1, presents with symptoms of perimenopause including night sweats, irregular menstruation, and fatigue.She has previously been diagnosed with hypertension. She is taking hormone replacement therapy with estradiol and norethindrone acetate. Recent tests included a bone density scan, which confirmed osteoporosis and showed elevated FSH levels. She also underwent a vaginal swab test for routine screening. Her mother has a history of breast cancer. Her menarche age was 11."""]
Result:
| chunk | begin | end | ner_label | assertion | confidence |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G2P1 | 21 | 24 | G_P | Present | 0.9999 |
| perimenopause | 53 | 65 | Perimenopause | Present | 0.9999 |
| night sweats | 77 | 88 | Other_Symptom | Present | 0.9997 |
| irregular menstruation | 91 | 112 | Irregular_Menstruation | Present | 0.9997 |
| fatigue | 119 | 125 | Other_Symptom | Present | 0.9954 |
| hypertension | 166 | 177 | Hypertension | Past | 0.9916 |
| hormone replacement therapy | 194 | 220 | Hormone_Replacement_Therapy | Present | 0.9988 |
| estradiol | 227 | 235 | Hormone_Replacement_Therapy | Present | 0.9696 |
| norethindrone acetate | 241 | 261 | Hormone_Replacement_Therapy | Present | 0.9984 |
| osteoporosis | 323 | 334 | Osteoporosis | Present | 1.0 |
| elevated | 347 | 354 | Test_Result | Present | 1.0 |
| FSH | 356 | 358 | Hormone_Testing | Present | 0.9999 |
| vaginal swab | 389 | 400 | Vaginal_Swab | Present | 1.0 |
| breast cancer | 458 | 470 | Oncological | Family | 0.9843 |
| 11 | 494 | 495 | Age | Menarche_Age | 0.9891 |
Clinical Document Analysis with One-Liner Pretrained Pipelines for Specific Clinical Tasks and Concepts
We introduce a suite of advanced, hybrid pretrained pipelines, specifically designed to streamline the clinical document analysis process. These pipelines are built upon multiple state-of-the-art (SOTA) pretrained models, delivering a comprehensive solution for quickly extracting vital information.
| Model Name | Description |
|---|---|
ner_deid_context_nameAugmented_pipeline |
In this pipeline, there are ner_deid_generic_augmented, ner_deid_subentity_augmented, ner_deid_name_multilingual_clinical NER models and several ContextualParser, RegexMatcher, and TextMatcher models were used |
ner_profiling_vop |
This pipeline can be used to simultaneously evaluate various pre-trained named entity recognition (NER) models, enabling comprehensive analysis of text data pertaining to patient perspectives and experiences, also known as the “Voice of Patients”. |
ner_profiling_sdoh |
This pipeline can be used to simultaneously evaluate various pre-trained named entity recognition (NER) models, enabling comprehensive analysis of text data pertaining to the social determinants of health (SDOH). When you run this pipeline over your text, you will end up with the predictions coming out of each pretrained clinical NER model trained with the embeddings_clinical, which are specifically designed for clinical and biomedical text. |
Example:
from sparknlp.pretrained import PretrainedPipeline
pipeline_sdoh = PretrainedPipeline("ner_profiling_sdoh", "en", "clinical/models")
text = """
The patient reported experiencing symptoms of anxiety and depression, which have been affecting his quality of life.
He reported a history of childhood trauma related to violence and abuse in his household, which has contributed to his smoking, alcohol use and current mental health struggles.
He denied any recent substance use or sexual activity and reported being monogamous in his relationship with his wife.
The patient is an immigrant and speaks English as a second language.
He reported difficulty accessing healthcare due to lack of medical insurance.
He has a herniated disc, hypertension, coronary artery disease (CAD) and diabetes mellitus.
The patient has a manic disorder, is presently psychotic and shows impulsive behavior. He has been disabled since 2001.
"""
Results:
******************** ner_sdoh_substance_usage_wip Model Results ********************
('smoking', 'Smoking') ('alcohol use', 'Alcohol') ('substance use', 'Substance_Use')
******************** ner_sdoh_health_behaviours_problems_wip Model Results ********************
('anxiety', 'Mental_Health') ('depression', 'Mental_Health') ('quality of life', 'Quality_Of_Life') ('mental health struggles', 'Mental_Health') ('sexual activity', 'Sexual_Activity') ('monogamous', 'Sexual_Activity') ('herniated disc', 'Other_Disease') ('hypertension', 'Hypertension') ('coronary artery disease', 'Other_Disease') ('CAD', 'Other_Disease') ('diabetes mellitus', 'Other_Disease') ('manic disorder', 'Mental_Health') ('psychotic', 'Mental_Health') ('impulsive behavior', 'Mental_Health') ('disabled', 'Disability')
******************** ner_jsl_greedy Model Results ********************
('anxiety', 'Psychological_Condition') ('depression', 'Psychological_Condition') ('smoking', 'Smoking') ('alcohol', 'Alcohol') ('substance', 'Substance') ('sexual activity', 'Symptom') ('difficulty accessing healthcare', 'Symptom') ('herniated disc', 'Disease_Syndrome_Disorder') ('hypertension', 'Hypertension') ('coronary artery disease', 'Heart_Disease') ('CAD', 'Heart_Disease') ('diabetes mellitus', 'Diabetes') ('manic disorder', 'Psychological_Condition') ('psychotic', 'Psychological_Condition') ('impulsive behavior', 'Symptom')
******************** ner_jsl_enriched Model Results ********************
('anxiety', 'Psychological_Condition') ('depression', 'Psychological_Condition') ('smoking', 'Smoking') ('alcohol', 'Alcohol') ('substance', 'Substance') ('difficulty accessing healthcare', 'Symptom') ('lack of medical insurance', 'Symptom') ('herniated disc', 'Disease_Syndrome_Disorder') ('hypertension', 'Hypertension') ('coronary artery disease', 'Heart_Disease') ('CAD', 'Heart_Disease') ('diabetes mellitus', 'Diabetes') ('manic disorder', 'Psychological_Condition') ('psychotic', 'Symptom') ('impulsive behavior', 'Symptom') ('disabled', 'Symptom')
Please check the Task Based Clinical Pretrained Pipelines Notebook for more information
Formal Release of Oncological Assertion Status Detection and Relation Extraction Models
We are releasing the formal version of the “work-in-progress (WIP)” assertion status detection and relation extraction models in the Oncology domain.
Here is the reference table:
| WIP Version | Formal Version | Task |
|---|---|---|
| assertion_oncology_demographic_binary_wip | assertion_oncology_demographic_binary | Assertion Status Detection |
| assertion_oncology_family_history_wip | assertion_oncology_family_history | Assertion Status Detection |
| assertion_oncology_problem_wip | assertion_oncology_problem | Assertion Status Detection |
| assertion_oncology_response_to_treatment_wip | assertion_oncology_response_to_treatment | Assertion Status Detection |
| assertion_oncology_smoking_status_wip | assertion_oncology_smoking_status | Assertion Status Detection |
| assertion_oncology_test_binary_wip | assertion_oncology_test_binary | Assertion Status Detection |
| assertion_oncology_treatment_binary_wip | assertion_oncology_treatment_binary | Assertion Status Detection |
| assertion_oncology_wip | assertion_oncology | Assertion Status Detection |
| re_oncology_biomarker_result_wip | re_oncology_biomarker_result | Relation Extraction |
| re_oncology_granular_wip | re_oncology_granular | Relation Extraction |
| re_oncology_location_wip | re_oncology_location | Relation Extraction |
| re_oncology_size_wip | re_oncology_size | Relation Extraction |
| re_oncology_temporal_wip | re_oncology_temporal | Relation Extraction |
| re_oncology_test_result_wip | re_oncology_test_result | Relation Extraction |
| re_oncology_wip | re_oncology | Relation Extraction (DL) |
| redl_oncology_biobert_wip | redl_oncology_biobert | Relation Extraction (DL) |
| redl_oncology_biomarker_result_biobert_wip | redl_oncology_biomarker_result_biobert | Relation Extraction (DL) |
| redl_oncology_granular_biobert_wip | redl_oncology_granular_biobert | Relation Extraction (DL) |
| redl_oncology_location_biobert_wip | redl_oncology_location_biobert | Relation Extraction (DL) |
| redl_oncology_size_biobert_wip | redl_oncology_size_biobert | Relation Extraction (DL) |
| redl_oncology_temporal_biobert_wip | redl_oncology_temporal_biobert | Relation Extraction (DL) |
| redl_oncology_test_result_biobert_wip | redl_oncology_test_result_biobert | Relation Extraction (DL) |
11 New Fine-Tuned Sentence Embedding Models finetuned with medical assertion datasets
Discover our new fine-tuned transformer-based sentence embedding models, meticulously trained on a curated list of clinical and biomedical datasets. These models are specifically optimized for Few-Shot Assertion tasks but are versatile enough to be utilized for other applications, such as Classification and Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG). Our collection offers precise and reliable embeddings tailored for various medical domains, significantly enhancing the extraction, analysis, and processing of assertion-related data in healthcare texts.
| Model Name | Description |
|---|---|
mpnet_embeddings_medical_assertion |
Fine-tuned on the in-house dataset using the MPNet architecture. |
mpnet_embeddings_medical_assertion_jsl |
Fine-tuned on the in-house dataset using the MPNet architecture. |
mpnet_embeddings_medical_assertion_oncology |
Fine-tuned on the oncology dataset using the MPNet architecture. |
mpnet_embeddings_medical_assertion_sdoh |
Fine-tuned on the social determinants of health dataset using the MPNet architecture. |
e5_base_v2_embeddings_medical_assertion_base |
Fine-tuned on the in-house dataset using the E5 architecture. |
e5_base_v2_embeddings_medical_assertion_jsl |
Fine-tuned on the in-house dataset using the E5 architecture. |
e5_base_v2_embeddings_medical_assertion |
Fine-tuned on the the in-house dataset using the E5 architecture. |
e5_base_v2_embeddings_medical_assertion_sdoh |
Fine-tuned on the social determinants of health dataset using the E5 architecture. |
e5_base_v2_embeddings_medical_assertion_smoking |
Fine-tuned on the smoking dataset using the E5 architecture. |
e5_base_v2_embeddings_medical_assertion_oncology |
Fine-tuned on the oncology dataset using the E5 architecture. |
e5_base_v2_embeddings_medical_assertion_radiology |
Fine-tuned on the radiology dataset using the E5 architecture. |
Example:
mpnet_embedding = MPNetEmbeddings.pretrained("mpnet_embeddings_medical_assertion_sdoh", "en", "clinical/models")\
.setInputCols(["document"])\
.setOutputCol("mpnet_embeddings")
text = [
["I feel a bit drowsy after taking an insulin."],
["Peter Parker is a nice lad and lives in New York"]
]
Result:
| embeddings |
|---|
| [{sentence_embeddings, 0, 43, I feel a bit drowsy after taking an insulin., {sentence -> 0}, [-0.09830807, 0.0137982415, -0.051585164, -0.0023749713, -0.017916167, 0.017543513, 0.025593378, 0.05106… |
| [{sentence_embeddings, 0, 47, Peter Parker is a nice lad and lives in New York, {sentence -> 0}, [-0.10453681, 0.010062916, -0.024983741, 0.009945293, -0.01242009, 0.018787898, 0.039723188, 0.04624… |
Significantly Faster Vector-DB Based Entity Resolution Models Than Existing Sentence Entity Resolver Models
We have developed vector database-based entity resolution models that are 10x faster on GPU and 2x as fast on CPU compared to the existing Sentence Entity Resolver models.
NOTE: These models are not available on the Models Hub page yet and cannot be used like the other Spark NLP for Healthcare models. They will be integrated into the marketplace and made available there soon.
RxNorm Code Mapping Benchmarks and Cost Comparisons: John Snow Labs, GPT-4, and Amazon Comprehend Medical
We have prepared an accuracy benchmark and the cost analysis between Healthcare NLP, GPT-4, and Amazon Comprehend Medical for mapping medications to their RxNorm terms. Here are the notes:
- For the ground truth dataset, we used 79 in-house clinical notes annotated by the medical experts of John Snow Labs.
- John Snow Labs: We used
sbiobertresolve_rxnorm_augmentedandbiolordresolve_rxnorm_augmentedmodels for this benchmark. These models can return up to 25 closest results sorted by their distances. - GPT-4: Both GPT-4 (Turbo) and GPT-4o models are used. According to the official announcement, the performance of GPT-4 and GPT-4o is almost identical, and we used both versions for the accuracy calculation. Additionally, the GPT-4 returns only one result, which means you will see the same results in both evaluation approaches.
- Amazon Comprehend Medical: The RxNorm tool of this service is used, and it returns up to 5 closest matches sorted by their distances.
- We adopted two approaches for evaluating these tools, given that the model outputs may not precisely match the annotations:
- Top-3: Compare the annotations to see if they appear in the first three results.
- Top-5: Compare the annotations to see if they appear in the first five results.
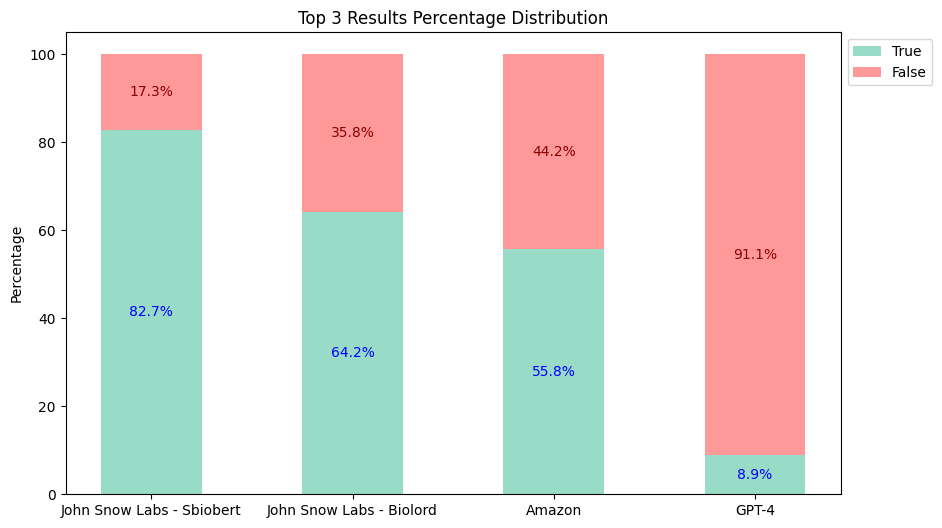
Here are the accuracy results:
Top-3 Results:
Top-5 Results:
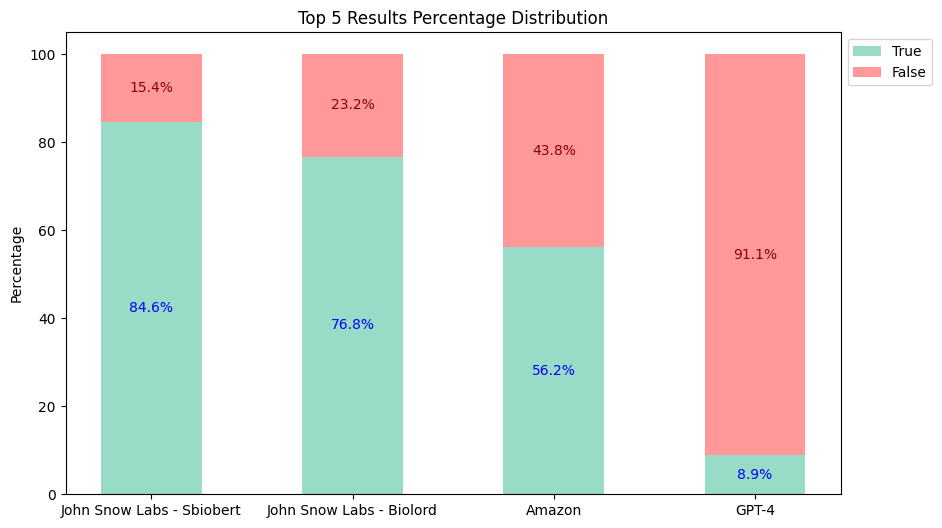
Conclusion:
Based on the evaluation results:
- The
sbiobertresolve_rxnorm_augmentedmodel of John Snow Labs consistently provides the most accurate results in each top_k comparison. - The
biolordresolve_rxnorm_augmentedmodel of John Snow Labs outperforms Amazon Comprehend Medical and GPT-4 in mapping terms to their RxNorm codes. - The GPT-4 could only return one result, reflected similarly in both charts, and has proven to be the least accurate.
If you want to process 1M documents and extract RxNorm codes for medication entities (excluding the NER stage), the total cost:
- With John Snow Labs is about $4,500, including the infrastructure costs.
- $24,250 with Amazon Comprehend Medical
- $44,000 with the GPT-4 and $22,000 with the GPT-4o model.
Therefore, John Snow Labs is almost 5 times cheaper than its closest alternative, not to mention the accuracy differences (Top 3: John Snow Labs 82.7% vs Amazon 55.8% vs GPT-4 8.9%).
| Top-3 Accuracy | Top-5 Accuracy | Cost | |
|---|---|---|---|
| John Snow Labs | 82.7% | 84.6% | $4,500 |
| Amazon Comprehend Medical | 55.8% | 56.2% | $24,250 |
| GPT-4 (Turbo) | 8.9% | 8.9% | $44,000 |
| GPT-4o | 8.9% | 8.9% | $22,000 |
If you want to see more details, please check Benchmarks Page and State-of-the-art RxNorm Code Mapping with NLP: Comparative Analysis between the tools by John Snow Labs, Amazon, and GPT-4 blog post.
New Blogposts on Using NLP in Opioid Research and Healthcare: Harnessing NLP, Knowledge Graphs, and Regex Techniques for Critical Insights
Explore the latest developments in healthcare NLP and Knowledge Graphs through our new blog posts, where we take a deep dive into the innovative technologies and methodologies transforming the medical field. These posts offer insights into how the latest tools are being used to analyze large amounts of unstructured data, identify critical medical assets, and extract meaningful patterns and correlations. Learn how these advances are not only improving our understanding of complex health issues but also contributing to more effective prevention, diagnosis, and treatment strategies.
- Harnessing the Power of NLP and Knowledge Graphs for Opioid Research discusses how Natural Language Processing (NLP) and Knowledge Graphs (KG) are transforming opioid research. By using NLP to process large volumes of unstructured medical data and employing Knowledge Graphs to map intricate relationships, researchers can achieve greater insights into the opioid crisis.
- Extracting Critical Insights on Opioid Use Disorder with Healthcare NLP Models discusses how John Snow Labs’ Healthcare NLP models are transforming the extraction of crucial insights on opioid use disorder. These advanced NLP techniques efficiently identify and categorize medical terminology related to opioid addiction, improving clinical understanding and treatment strategies.
- Extract Medical Named Entities with Regex in Healthcare NLP at Scale explains that the RegexMatcherInternal class employs regular expressions to detect and associate specific text patterns with predefined entities like dates, SSNs, and email addresses. This method facilitates targeted entity extraction by matching text patterns to these predefined entities.
- Extracting Medical Named Entities with Healthcare NLP’s EntityRulerInternal explains that EntityRulerInternal in Spark NLP extracts medical entities from text using regex patterns or exact matches defined in JSON or CSV files. This post explains how to set it up and use it in a Healthcare NLP pipeline, with practical examples.
- Using Contextual Assertion for Clinical Text Analysis: A Comprehensive Guide dive into leveraging Healthcare NLP, a robust NLP library, for clinical text analysis, emphasizing the role of Contextual Assertion. Contextual Assertion markedly enhances the accuracy of detecting negation, possibility, and temporality in medical records. It surpasses deep learning-based assertion status detection in accurately categorizing health conditions. Benchmark comparisons reveal an average F1 score improvement of 10-15%, highlighting the superior precision and reliability of Contextual Assertion in healthcare data analysis.
- State-of-the-art RxNorm Code Mapping with NLP: Comparative Analysis between the tools by John Snow Labs, Amazon, and GPT-4 compares RxNorm code mapping accuracy and a price analysis between John Snow Labs, GPT-4, and Amazon.
New Notebooks for Medication and Resolutions Concept
To better understand the Medication and Resolutions Concept, the following notebooks have been developed:
- New Clinical Medication Use Case notebook: This notebook is designed to extract and analyze medication information from a clinical dataset. Its purpose is to identify commonly used medications, gather details on dosage, frequency, strength, and route, determine current and past usage, understand pharmacological actions, identify treatment purposes, retrieve relevant codes (RxNorm, NDC, UMLS, SNOMED), and find associated adverse events.
- New Resolving Medical Terms to Terminology Codes Directly notebook: In this notebook, you will find how to optimize the process to get SentenceEntityResolverModel model outputs.
- New Analyse Veterinary Documents with Healthcare NLP notebook: In this notebook, we use Spark NLP for Healthcare to process veterinary documents. We focus on Named Entity Recognition (NER) to identify entities, Assertion Status to confirm their condition, Relation Extraction to understand their relationships, and Entity Resolution to standardize terms. This helps us efficiently extract and analyze critical information from unstructured veterinary texts.
Updated Udemy MOOC (Our Online Courses) Notebooks
Recently updated Udemy MOOC (Massive Online Course) notebooks that focus on using Spark NLP annotators for healthcare applications. These notebooks provide practical examples and exercises for learning how to implement and utilize various Spark NLP tools and techniques specifically designed for processing and analyzing healthcare-related text data. The update might include new features, improvements, or additional content to enhance the learning experience for students and professionals in the healthcare field.
Please check the Spark_NLP_Udemy_MOOC folder for the all Healthcare MOOC Notebooks
Various Core Improvements; Bug Fixes, Enhanced Overall Robustness, and Reliability of Spark NLP for Healthcare
- Resolved broken links in healthcare demos
- Added a unique ID field for each entity into the result of the
pipeline_ouput_parsermodule - Fixed deidentification AGE obfuscation hanging issue
- Added DatasetInfo parameter into the
MedicalNERModelannotator
Updated Notebooks And Demonstrations For making Spark NLP For Healthcare Easier To Navigate And Understand
- New Clinical Medication Use Case notebook
- New Resolving Medical Terms to Terminology Codes Directly notebook
- New Contextual Assertion notebook
- New VectorDB and PostProcessor for RAG Generative AI notebook
- New Analyse Veterinary Documents with Healthcare NLP notebook
- LLMLoader notebook
- Updated FewShot Assertion Classifier notebook
- New ALCOHOL SMOKING Demo
- New JSL vs GPT4 Demo
We Have Added And Updated A Substantial Number Of New Clinical Models And Pipelines, Further Solidifying Our Offering In The Healthcare Domain.
pdf_deid_subentity_context_augmented_pipelinener_deid_context_nameAugmented_pipelinener_profiling_vopner_vop_v2ner_alcohol_smokingsbiobertresolve_snomed_veterinarycancer_diagnosis_matchercountry_matcheremail_matcherphone_matcherstate_matcherzip_matchercontextual_assertion_someone_elsecontextual_assertion_absentcontextual_assertion_pastner_alcohol_smokingassertion_alcohol_smoking_wipassertion_alcohol_smoking_general_symptoms_wipre_alcohol_smoking_clinical_wipgenericclassifier_alcohol_mpnet_wipgenericclassifier_smoking_mpnet_wipner_menopause_coreassertion_menopause_wipfewhot_assertion_jsl_e5_base_v2_jslfewhot_assertion_e5_base_v2fewhot_assertion_sdoh_e5_base_v2_sdohfewhot_assertion_smoking_e5_base_v2_smokingfewhot_assertion_oncology_e5_base_v2_oncologyfewhot_assertion_radiology_e5_base_v2_radiologympnet_embeddings_medical_assertionmpnet_embeddings_medical_assertion_jslmpnet_embeddings_medical_assertion_oncologympnet_embeddings_medical_assertion_sdohe5_base_v2_embeddings_medical_assertion_basee5_base_v2_embeddings_medical_assertion_jsle5_base_v2_embeddings_medical_assertione5_base_v2_embeddings_medical_assertion_sdohe5_base_v2_embeddings_medical_assertion_smokinge5_base_v2_embeddings_medical_assertion_oncologye5_base_v2_embeddings_medical_assertion_radiologyner_profiling_vopner_profiling_sdohner_profiling_oncologyexplain_clinical_doc_granularexplain_clinical_doc_radiologyexplain_clinical_doc_medicationmedication_resolver_pipelinemedication_resolver_transform_pipelinerxnorm_resolver_pipelinerxnorm_mapperbiolordresolve_rxnorm_augmentedsbiobertresolve_rxnorm_augmentedsbiobertresolve_umls_clinical_drugssbiobertresolve_umls_disease_syndromesbiobertresolve_umls_drug_substancesbiobertresolve_umls_findingssbiobertresolve_umls_general_conceptssbiobertresolve_umls_major_conceptsclinical_deidentificationclinical_deidentification_multi_mode_outputclassifierml_adeassertion_dl_radiologyner_oncology_wipner_sdoh_access_to_healthcare_wipner_sdoh_community_condition_wipner_sdoh_demographics_wipner_sdoh_health_behaviours_problems_wipner_sdoh_income_social_status_wipner_sdoh_slim_wipner_sdoh_social_environment_wipner_sdoh_substance_usage_wipner_sdoh_wipJSL_MedS_q16_v1JSL_MedS_q8_v1JSL_MedS_q4_v1JSL_MedM_q16_v1JSL_MedM_q8_v1JSL_MedM_q4_v1JSL_MedSNer_ZS_q16_v1JSL_MedSNer_ZS_q8_v1JSL_MedSNer_ZS_q4_v1
For all Spark NLP for Healthcare models, please check: Models Hub Page
Versions
- 6.3.0
- 6.2.2
- 6.2.1
- 6.2.0
- 6.1.1
- 6.1.0
- 6.0.4
- 6.0.3
- 6.0.2
- 6.0.1
- 6.0.0
- 5.5.3
- 5.5.2
- 5.5.1
- 5.5.0
- 5.4.1
- 5.4.0
- 5.3.3
- 5.3.2
- 5.3.1
- 5.3.0
- 5.2.1
- 5.2.0
- 5.1.4
- 5.1.3
- 5.1.2
- 5.1.1
- 5.1.0
- 5.0.2
- 5.0.1
- 5.0.0
- 4.4.4
- 4.4.3
- 4.4.2
- 4.4.1
- 4.4.0
- 4.3.2
- 4.3.1
- 4.3.0
- 4.2.8
- 4.2.4
- 4.2.3
- 4.2.2
- 4.2.1
- 4.2.0
- 4.1.0
- 4.0.2
- 4.0.0
- 3.5.3
- 3.5.2
- 3.5.1
- 3.5.0
- 3.4.2
- 3.4.1
- 3.4.0
- 3.3.4
- 3.3.2
- 3.3.1
- 3.3.0
- 3.2.3
- 3.2.2
- 3.2.1
- 3.2.0
- 3.1.3
- 3.1.2
- 3.1.1
- 3.1.0
- 3.0.3
- 3.0.2
- 3.0.1
- 3.0.0
- 2.7.6
- 2.7.5
- 2.7.4
- 2.7.3
- 2.7.2
- 2.7.1
- 2.7.0
- 2.6.2
- 2.6.0
- 2.5.5
- 2.5.3
- 2.5.2
- 2.5.0
- 2.4.6
- 2.4.5
- 2.4.2
- 2.4.1
- 2.4.0