6.3.0
Release date: 02-02-2026
Visual NLP 6.3.0 Release Notes 🕶️
We are glad to announce that Visual NLP 6.3.0, has been released! 📢📢📢
Main Changes 🔴
- Dicom Midi-B benchmarks.
- New features in: DicomToMetadata and DicomMetadataDeIdentifier.
- New Blogposts and notebooks.
- Bug Fixes and Maintenance
Dicom Midi-B benchmarks
In this release, we tackled the Midi-B dataset for Dicom De-identification. Midi-B is a popular dataset for the Dicom De-Identification Task that appeared in 2025. Today we are releasing benchmarks, and a notebook to reproduce results.
Benchmarks
The metrics in Midi-B dataset are organized as a set of accuracy numbers across a predefined set of actions. Two different subsets are provided, Validation and Test. We report results for both datasets and each of the actions defined in the dataset.
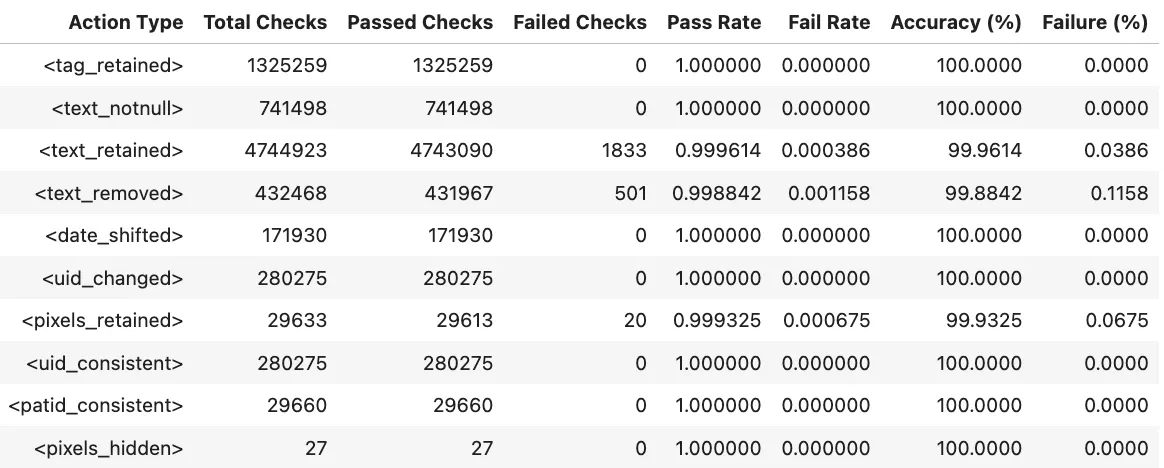
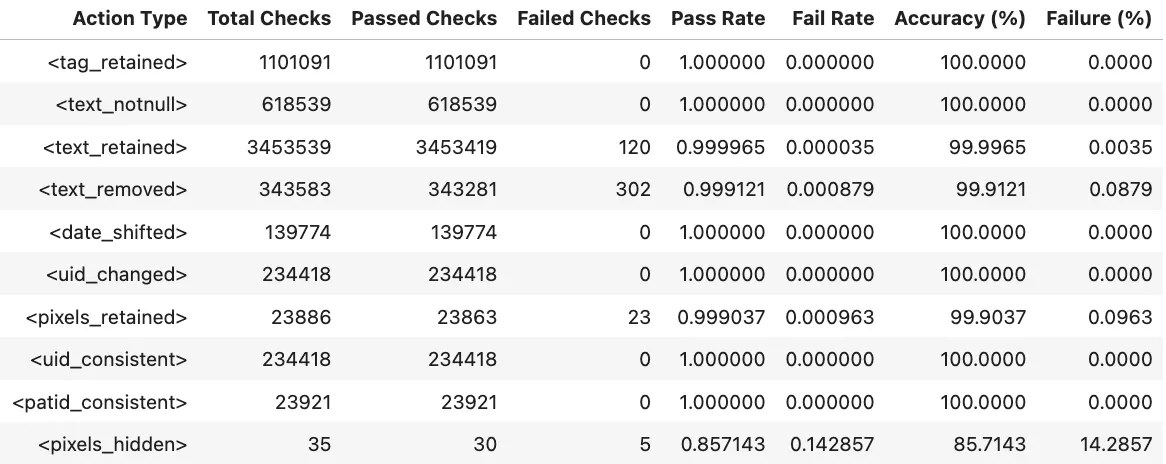
Notebooks
You can find all the details for how to run over the MIDI-B dataset in this notebook: SparkOcrMIDIBSolution.ipynb
New features in: DicomToMetadata and DicomMetadataDeIdentifier
DicomToMetadata
Exposing tags to enable external NLP to operate on them.
- Added support for strategy file-driven configuration via the setStrategyFile parameter: a strategy file is a configuration file that helps in defining actions like the ones described in the charts above.
- Enabled the extraction of raw metadata tag value for all tags marked with cleanTag in the strategy file. As a result, a String column will be created in the output dataframe. The name of the output column for this raw tag text is configurable via setTagCol. The purpose of this column is to expose the content of the tags that are in natural language so the redaction can be carried out using NLP methods.
- Enabled extraction of tag mappings for all tags marked with the cleanTag action, as described in the item above, configurable through setTagMappingCol. This output column allows to map the tags values present in the tag column back to the original tag identifiers.
- Introduced setExtractTagForNer to optionally skip String tag extraction.
DicomMetadataDeidentifier
DicomMetadataDeidentifier is the component in charge of redacting metadata tags in Dicom files. It can apply a wide variety of actions, some of which are pre-defined, and some of which are user-defined. In this release, new actions were added:
- Added a new action shiftTimeByRandom (VR: TM) to randomly shift time values.
- Added two new actions shiftDateByFixedNbOfDays and shiftDateByRandomNbOfDays (VR: DA, DT) to shift date and datetime values.
- Added a new action shiftUnixTimeStampRandom (VR: SL, FD) to randomly shift Unix timestamp values.
- Added a new action ensureTagExists (VR: ALL) to ensure a tag exists with a default value. Some other changes,
- Improved date and datetime handling to support all valid DICOM date formats.
- Improved hashUID and patientHashID implementations in accordance with DICOM guidelines.
- Added the ability to remove residual PHI post de-identification, ensuring sensitive metadata is fully cleared from the DICOM file.
New Blogposts and notebooks
Bug Fixes
- Improved support for accessing Python resources across different Python versions.
- Compatibility with Google Colab.
Compatibility:
Spark-NLP 6.3.2, and Spark-NLP for Healthcare 6.3.0, LV 1.11.0.
Previous versions
- 6.3.0
- 6.0.0
- 5.5.0
- 5.4.2
- 5.4.1
- 5.4.0
- 5.3.2
- 5.3.1
- 5.3.0
- 5.2.0
- 5.1.2
- 5.1.0
- 5.0.2
- 5.0.1
- 5.0.0
- 4.4.4
- 4.4.3
- 4.4.2
- 4.4.1
- 4.4.0
- 4.3.3
- 4.3.0
- 4.2.4
- 4.2.1
- 4.2.0
- 4.1.0
- 4.0.2
- 4.0.0
- 3.14.0
- 3.13.0
- 3.12.0
- 3.11.0
- 3.10.0
- 3.9.1
- 3.9.0
- 3.8.0
- 3.7.0
- 3.6.0
- 3.5.0
- 3.4.0
- 3.3.0
- 3.2.0
- 3.1.0
- 3.0.0
- 1.11.0
- 1.10.0
- 1.9.0
- 1.8.0
- 1.7.0
- 1.6.0
- 1.5.0
- 1.4.0
- 1.3.0
- 1.2.0
- 1.1.2
- 1.1.1
- 1.1.0
- 1.0.0