John Snow Labs NLP Models on Databricks Marketplace
This section demonstrates the process of obtaining an AI model from John Snow Labs on Databricks Marketplace and deploying it for inference. Let’s assume a data scientist from an healthcare company is interested in building an intelligent application to help detect cancer genetics in patients records and intends to use an NLP model to analyze the available clinical notes at scale by using an API service.
Step 1: Navigate to the Databricks Marketplace
Access the Marketplace: Open the Databricks Marketplace homepage.
Search for Models: Use the search functionality to find specific AI models. For our purpose, input the search term e.g. “cancer” on the search box and filter results by product type on the first filter dropdown.
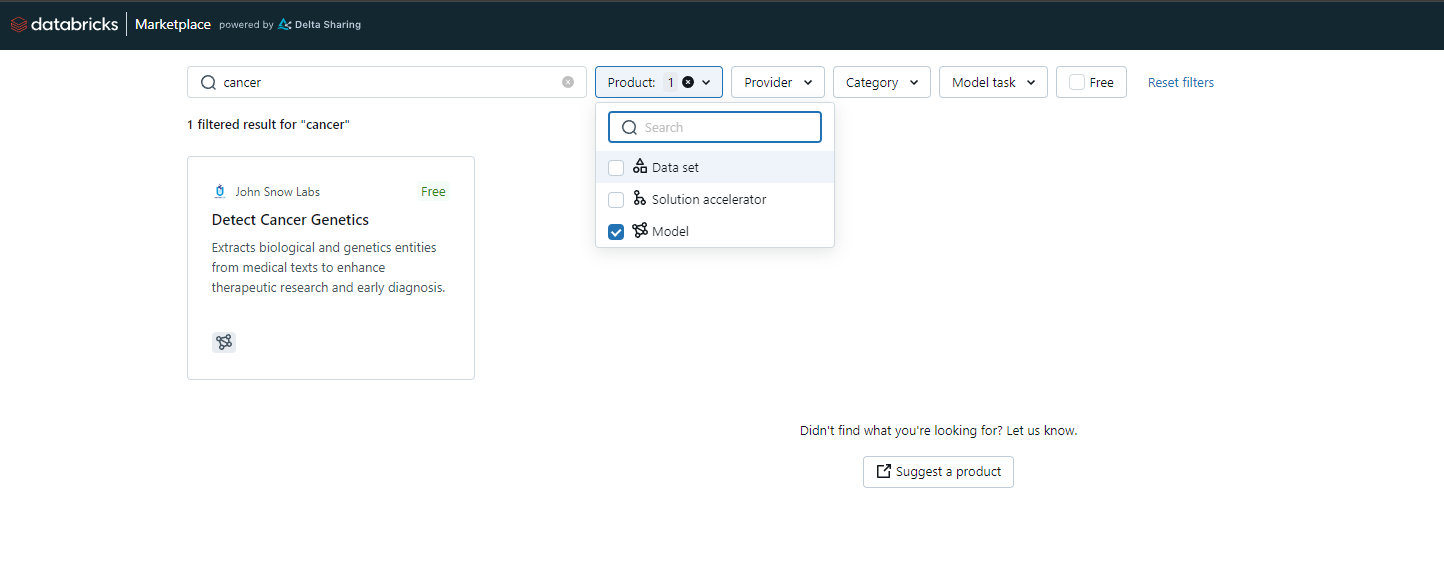
Step 2: Select the AI Model to Deploy
Identify the Listing: Locate the “Detect Cancer Genetics” listing on the Marketplace and click on the model card.This opens the model page on the Databricks Marketplace. An extended set of information on a model is provided in this page as well as usage intructions.
Understand the Model: This AI model is designed to identify and extract various biological entities such as genes, anatomical systems, cellular structures, or chemicals from clinical texts, research articles, and/or pathology reports, capturing intricate biological and oncological concepts, facilitating targeted therapeutic research, early diagnosis, and personalized treatment plans.
License: Note that this is a paid model and requires a license from John Snow Labs.
Step 3: Obtain Access to the Model
Instant Access: On the model page, click on ‘Get Access’ button to integrate the model’s metadata into the Unity Catalog.
Open the Listing: Once access is granted, click on ‘Open in Listing’.
Locate in Unity Catalog: The models should now be available in the Unity Catalog and ready for deployment to a model serving endpoint.
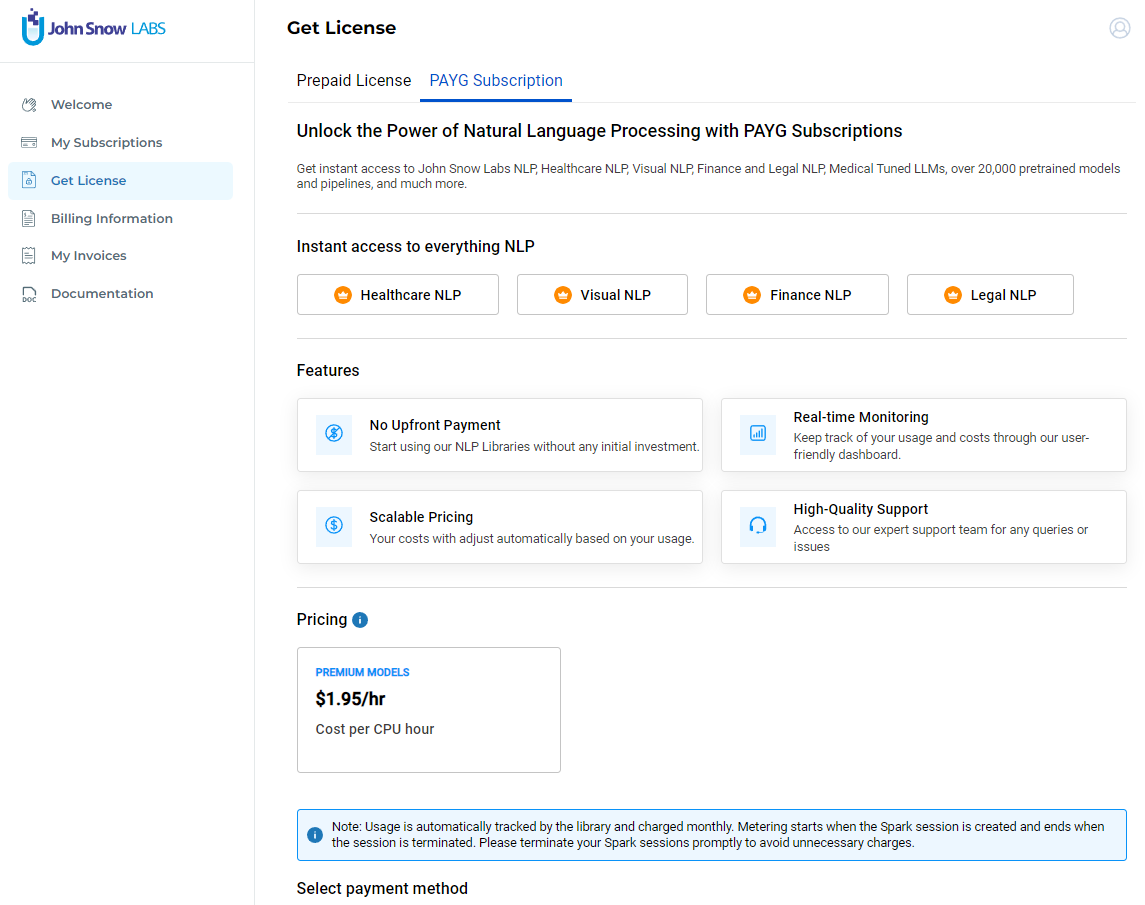
Step 4: Obtain PAYG License for John Snow Labs Models
Login to your account: Access my.JohnSnowLabs.com and log in to your account. If you don’t have an account, create one.
Get a PAYG License: Go to the Get License page. Switch to the PAYG Subscription tab and provide your credit card details. Carefully review the End User License Agreement and the Terms and Conditions documents. If you agree, click on the Create Subscription button.
Copy License Key: Once the process is complete, you will find your PAY-As-You-Go license listed on the My Subscriptions page. Visit the My Subscriptions page and copy the PAYG license key by clicking on the corresponding copy icon in the License Key column.
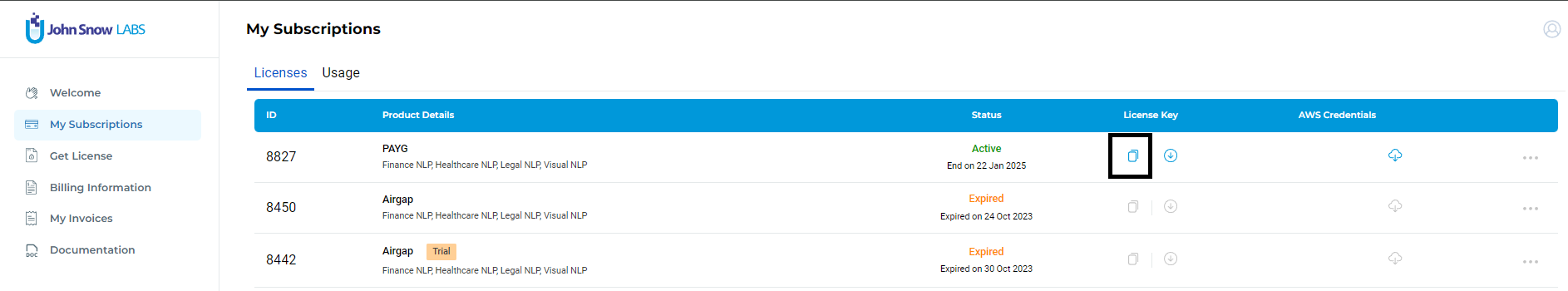
Go to your Databricks notebook and paste the license key into the JSL-License widget in the top of the notebook (see Step 5).
Step 5: Use the Embedded Notebook to Deploy the Model
Import the Notebook: Import the provided embedded notebook from the listing.
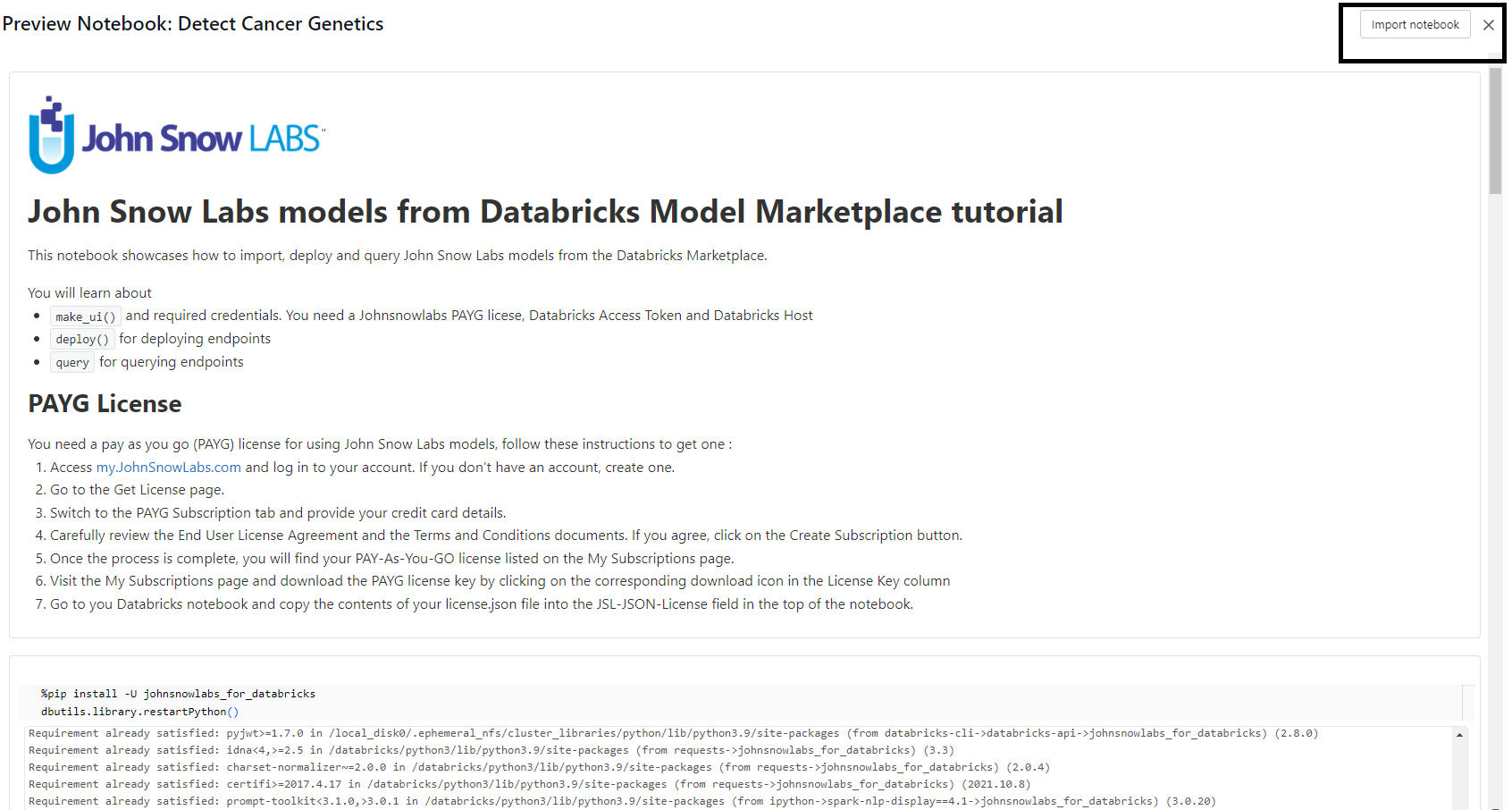
Configure the Notebook: Fill in the widgets with workspace-specific values and the PAYG license that you can copy from my.JohnSnowLabs.com (see Step 4).
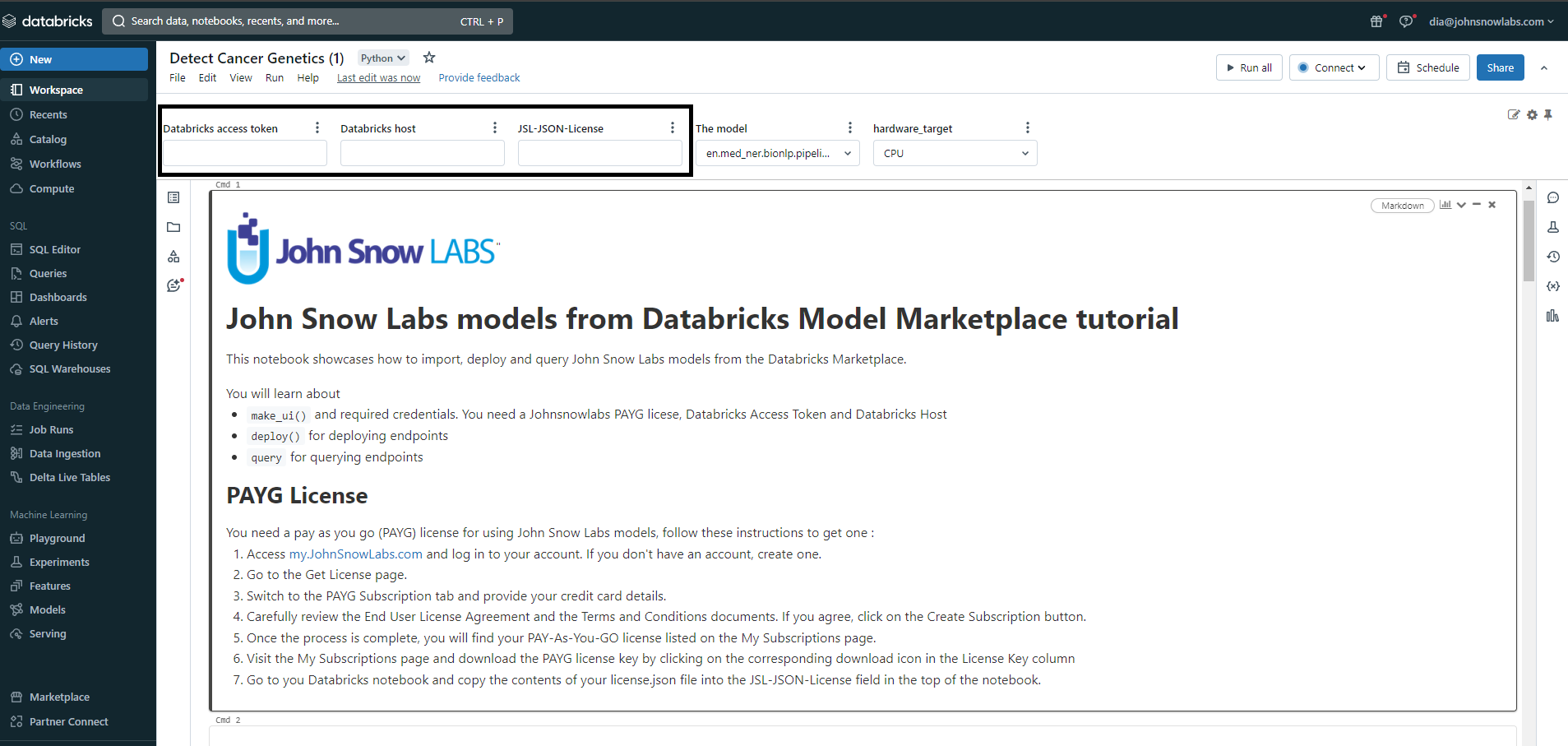
Run the Notebook: Execute the notebook to initiate the process.
Step 6: Model Endpoint Creation and Querying
Endpoint Creation: The notebook will create a serving endpoint, visible in the Databricks serving UI.
Sample Text Query: Use a sample text to query against the newly created endpoint.
Observing Results: The results will showcase the identified and classified biological entities.
Manual Endpoint Creation
You can Query&Deploy John Snow Labs models with 1 line of code as Databricks Model Serve Endpoints.
Data is passed to the predict() function and predictions are shaped accordingly.
You must create endpoints from a Databricks cluster created by nlp.install.
See Cluster Creation Notebook and Databricks Endpoint Tutorial Notebook
# You need `mlflow_by_johnsnowlabs` installed until next mlflow is released
! pip install mlflow_by_johnsnowlabs
from johnsnowlabs import nlp
nlp.deploy_endpoint('bert')
nlp.query_endpoint('bert_ENDPOINT','My String to embed')
nlp.deploy_endpoint will register a ML-FLow model into your registry and deploy an Endpoint with a JSL license.
It has the following parameters:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
model |
Model to be deployed as endpoint which is converted into NluPipelines, supported classes are: String Reference to NLU Pipeline name like ‘bert’, NLUPipeline, List[Annotator], Pipeline, LightPipeline, PretrainedPipeline, PipelineModel. In case of a NLU reference, the endpoint name is auto-generated aus <nlu_ref>_ENDPOINT i.e. bert_ENDPOINT. ‘.’ is replaced with ‘_’ in the nlu reference for the endpoint name |
endpoint_name |
Name for the deployed endpoint. Optional if using NLU model reference but mandatory for custom pipelines. |
re_create_endpoint |
if False, endpoint creation is skipped if one already exists. If True, it will delete existing endpoint if it exists |
re_create_model |
if False, model creation is skipped if one already exists. If True, model will be re-logged again, bumping the current version by 2 |
workload_size |
one of Small, Medium, Large. |
gpu |
True/False to load GPU-optimized jars or CPU-optimized jars in the container. Must use a gpu based workload_type if gpu=true |
new_run |
if True, mlflow will start a new run before logging the model |
block_until_deployed |
if True, this function will block until the endpoint is created |
workload_type |
CPU by default, use GPU_SMALL to spawn a GPU based endpoint instead. Check Databricks docs for alternative values |
db_host |
the databricks host URL. If not specified, the DATABRICKS_HOST environment variable is used |
db_token |
the databricks Access Token. If not specified, the DATABRICKS_TOKEN environment variable is used |
nlp.query_endpoint translates your query to JSON, sends it to the endpoint and returns the result as pandas DataFrame.
It has the following parameters which are forwarded to the model.predict() call inside of the endpoint:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
endpoint_name |
Name of the endpoint to query |
query |
str or list of strings or raw json string. If raw json, is_json_query must be True |
is_json_query |
if True, query is treated as raw json string |
output_level |
One of token, chunk, sentence, relation, document to shape outputs |
positions |
Set True/False to include or exclude character index position of predictions |
metadata |
Set True/False to include additional metadata |
drop_irrelevant_cols |
Set True/False to drop irrelevant columns |
get_embeddings |
Set True/False to include embedding or not |
keep_stranger_features |
Set True/False to return columns not named “text”, ‘image” or “file_type” from your input data |
multithread |
Set True/False to use multi-Threading for inference. Auto-inferred if not set |
db_host |
the databricks host URL. If not specified, the DATABRICKS_HOST environment variable is used |
db_token |
the databricks Access Token. If not specified, the DATABRICKS_TOKEN environment variable is used |
nlp.query_endpoint and nlp.deploy_endpoint check the following mandatory env vars to resolve wheels for endpoints
| Env Var Name | Description |
|---|---|
HEALTHCARE_SECRET |
Automatically set on your cluster if you run nlp.install() |
VISUAL_SECRET |
Automatically set if you run. nlp.install(..., visual=True). You can only spawn visual endpoint from a cluster created by nlp.install(..., visual=True) |
JOHNSNOWLABS_LICENSE_JSON |
JSON content of your john snow labs licensed to use for endpoints. Should be airgap license |
Submit a Task with nlp.run_in_databricks
Easily run Python code in a Databricks cluster, using the John Snow Labs library.
The fastest way to test this out, is to create a cluster with nlp.install() and then use nlp.run_in_databricks to start a task.
You can parameterize your jobs, according to the Databricks docs via the
# Execute a Raw Python string as script on Databricks
from johnsnowlabs import *
script = """
import nlu
print(nlu.load('sentiment').predict('That was easy!'))"""
cluster_id = nlp.install(json_license_path=my_license, databricks_host=my_host,databricks_token=my_token)
nlp.run_in_databricks(script,
databricks_cluster_id=cluster_id,
databricks_host=my_host,
databricks_token=my_token,
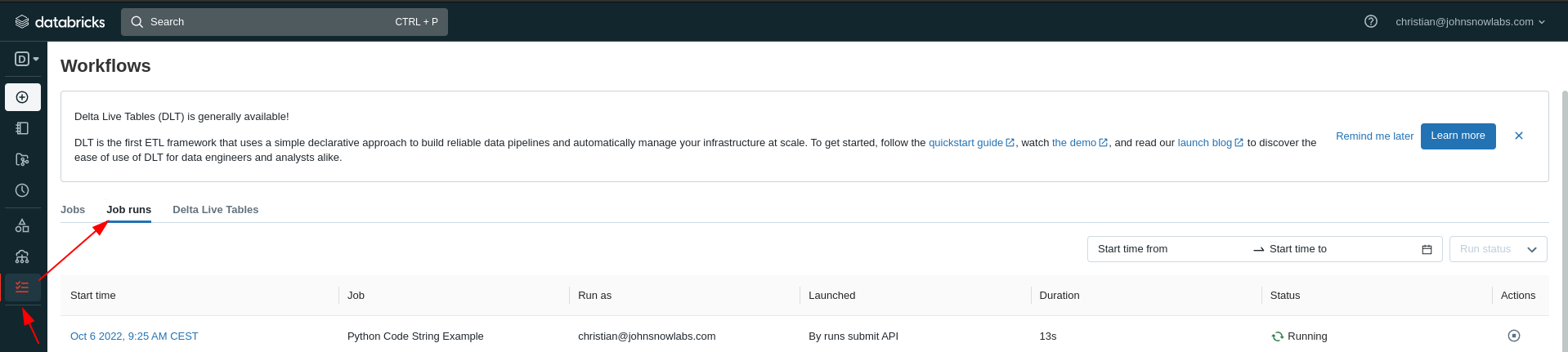
run_name='Python Code String Example')
This will start a Job Run which you can view in the Workflows tab
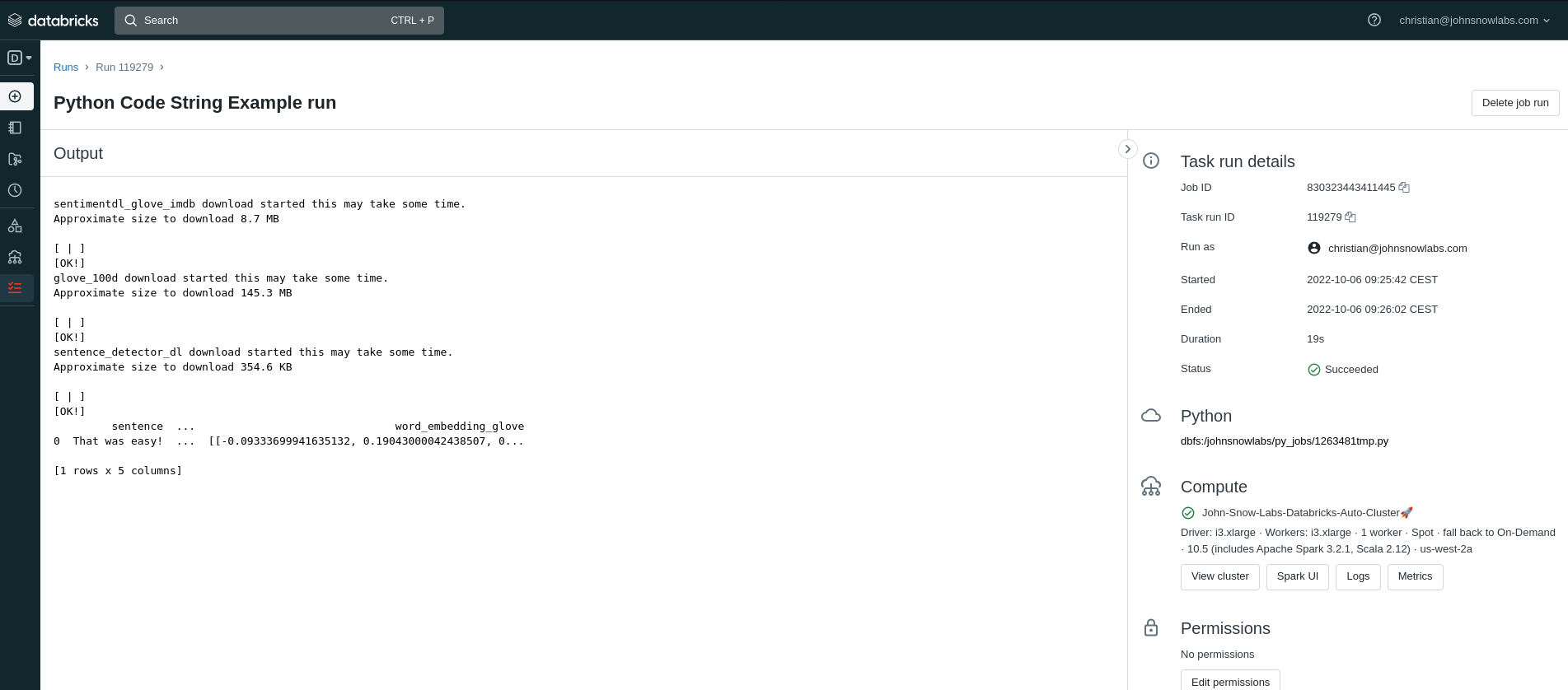
And after a while you can see the results
Run a local Python Notebook in Databricks
Provide the path to a notebook on your localhost, it will be copied to HDFS and executed by the Databricks cluster.
You need to provide a destination path to your Workspace, where the notebook will be copied to and you have write access to.
A common pattern that should work is/Users/<your_databricks_email@somewhere.com>/test.ipynb
local_nb_path = "path/to/my/notebook.ipynb"
remote_dst_path = "/Users/christian@johnsnowlabs.com/test.ipynb"
# notebook.ipynb will run on databricks, url will be printed
nlp.run_in_databricks(
local_nb_path,
databricks_host=host,
databricks_token=token,
run_name="Notebook Test",
dst_path=remote_dst_path,
)
This could be your input notebook
A URL where you can monitor the run will be printed, which will look like this
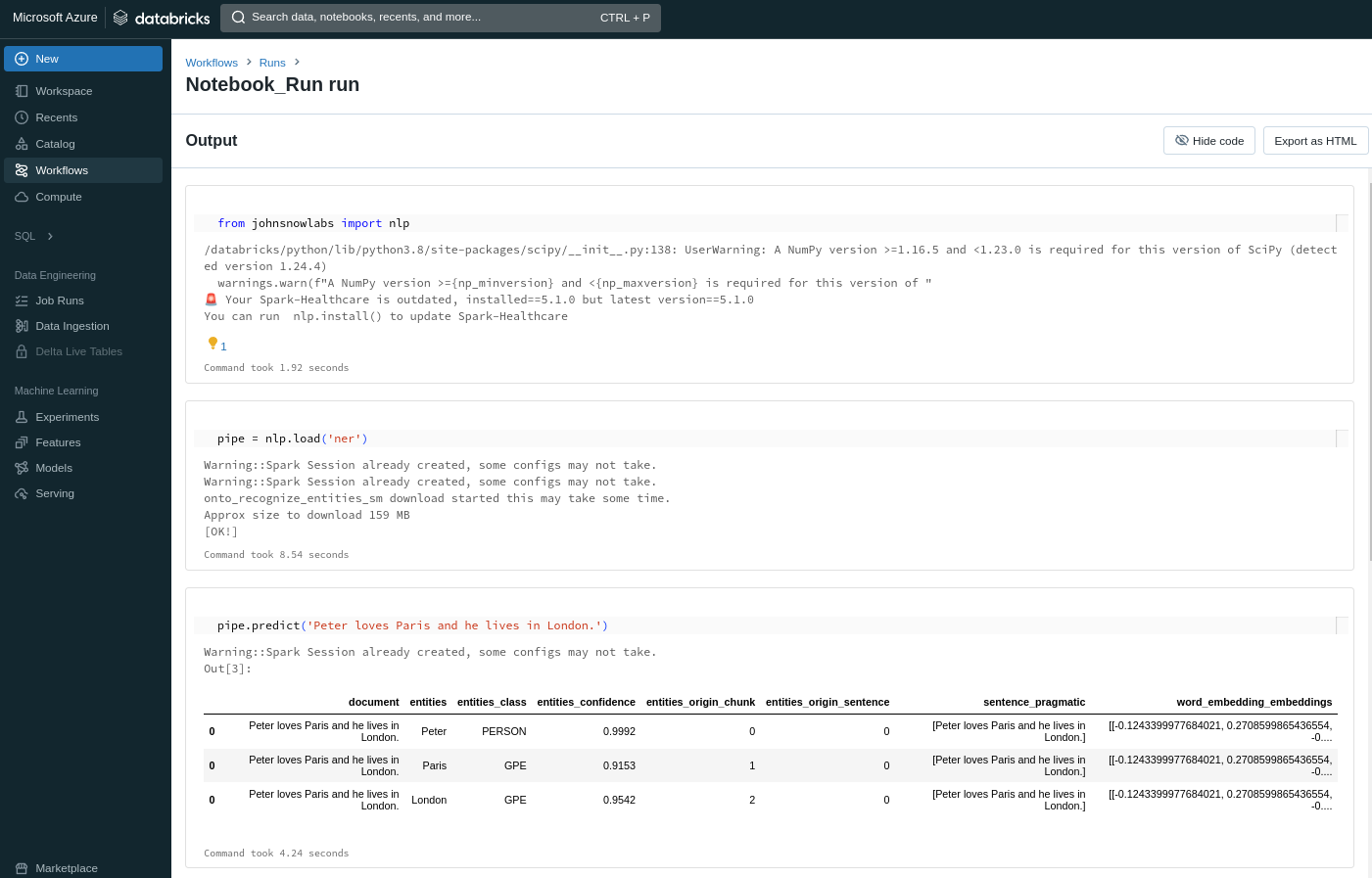
Run a Python Function in Databricks
Define a function, which will be written to a local file, copied to HDFS and executed by the Databricks cluster.
def my_function():
import nlu
medical_text = """A 28-year-old female with a history of gestational
diabetes presented with a one-week history of polyuria ,
polydipsia , poor appetite , and vomiting ."""
df = nlu.load('en.med_ner.diseases').predict(medical_text)
for c in df.columns: print(df[c])
# my_function will run on databricks
nlp.run_in_databricks(my_function,
databricks_cluster_id=cluster_id,
databricks_host=my_host,
databricks_token=my_token,
run_name='Function test')
This example will print all columns of the resulting dataframe which contains medical NER predictions.
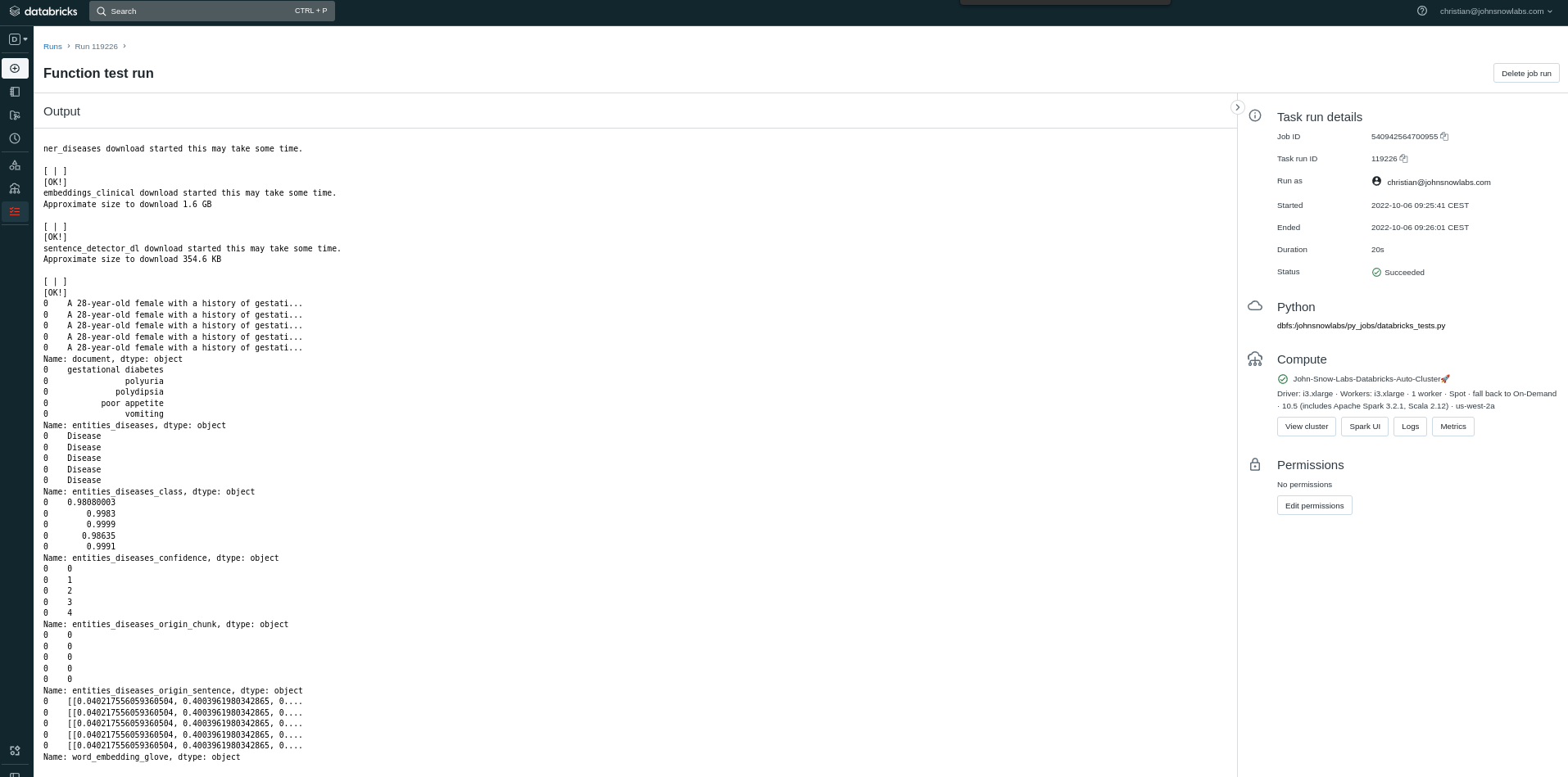
Run a Raw Python Code String in Databricks
Provide a string which must be valid Python Syntax.
It will be written to string, copied to HDFS and executed by the Databricks Cluster.
script = """
import nlu
print(nlu.load('sentiment').predict('That was easy!'))"""
nlp.run_in_databricks(script,
databricks_cluster_id=cluster_id,
databricks_host=my_host,
databricks_token=my_token,
run_name='Python Code String Example')
Run a Python Script in Databricks
Provide the path to a script on your machine. It will be copied to the Databricks HDFS and executed as task.
nlp.run_in_databricks('path/to/my/script.py',
databricks_cluster_id=cluster_id,
databricks_host=my_host,
databricks_token=my_token,
run_name='Script test ')
Run a Python Module in Databricks
Provide a module accessible to the john snow labs library. It’s content’s will be written to a local file, copied to HDFS and executed by the databricks cluster.
import johnsnowlabs.auto_install.health_checks.nlp_test as nlp_test
nlp.run_in_databricks(nlp_test,
databricks_cluster_id=cluster_id,
databricks_host=my_host,
databricks_token=my_token,
run_name='nlp_test')
Parameterizing your Databricks Jobs
You can parameterize run_in_databricks with parameters formatted according to the job task API
Parameterizing a Notebook run in Databricks
In your notebook you can use dbutils.widgets.text("my_parameter", "my_default_value") and other ipywidets to parameterize your notebook.
You just pass a dictionary to run_in_databricks where key=parameter_name and value=parameter_value.
See this example parameterized DB-Notebook for a full example which you can use as nb_path parameter.
nb_path = "parameterized_nb_example.ipynb"
dst_path = "/Users/christian@johnsnowlabs.com/test.ipynb"
nlp.run_in_databricks(
nb_path,
databricks_cluster_id=cluster_id,
databricks_host=host,
databricks_token=token,
run_name="Parameterized Notebook",
dst_path=dst_path,
parameters={"input_text": "I love peanut butter", "model_name": "sentiment"},
)
Parameterizing a Python Script run in Databricks
Simply pass a list of parameters to the run_in_databricks function. They will be passed to the script as sys.argv arguments.
script = """
import sys
print(f"First argument: {sys.argv[1]}, Second argument: {sys.argv[2]}")
"""
arg1 = "My first arg"
arg2 = "My second arg"
nlp.run_in_databricks(
script,
databricks_cluster_id=cluster_id,
databricks_host=host,
databricks_token=token,
run_name="Parameterized Script",
parameters=[arg1, arg2],
)