The Medical Terminology Server offers users the ability to look up standard medical codes from text phrases. It uses both string matching and embeddings to efficiently search for concepts across multiple vocabularies, with filters that can constrain results to meet your specific needs.
The Medical Terminology Server combines up-to-date editions of a wide range of terminologies with extensive supplementary datasets of synonyms, common misspellings, and colloquialisms to provide code mappings for input text, whether it is from the clinical record, patient statements, or other sources of written information about health.
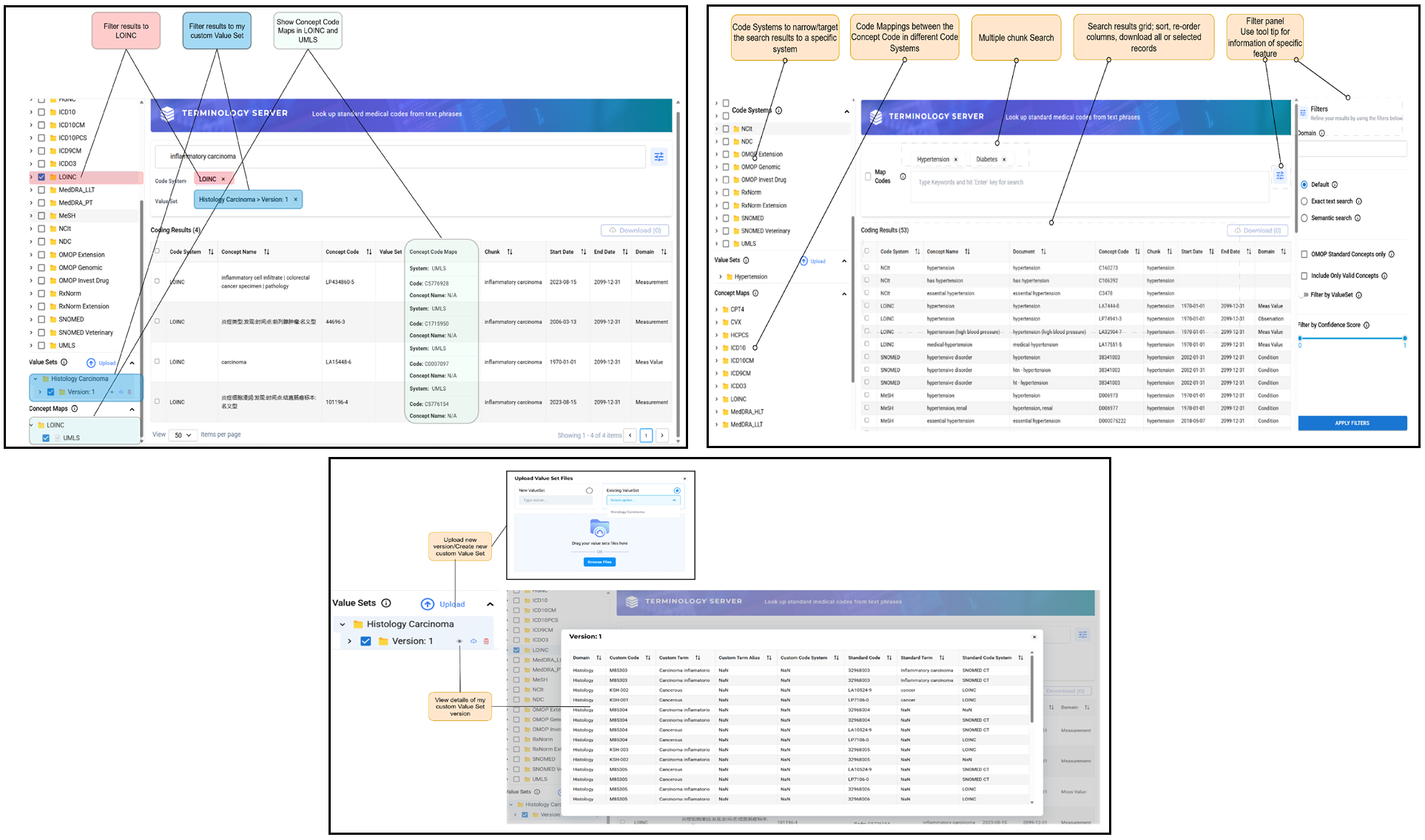
In addition to being to select from many standard vocabularies, the Medical Terminology Server is also aware of OMOP CDM conventions. It can also be constrained to only return codes that are OMOP Standard concepts and is able to check any concept for current validity. Batch transaction support makes efficient use of network calls.
Highlights
- Tailored for healthcare, the Medical Terminology Server allows uses data created by using state of the art John Snow Labs models that understands the nuances of clinical language and medical terminologies, ensuring that the information it generates is accurate and highly relevant.
- The Medical Terminology Server comes pre-loaded with all widely used medical terminologies; it offers a robust API and user interface that enable advanced concept search, mapping, and normalization.
- The Medical Terminology Server addresses challenges often faced by traditional terminology servers in healthcare: identifying concepts without exact matches by correcting spelling errors and using synonyms; finding the most relevant concept based on clinical context for accurate coding of diagnoses, drugs, treatments, or adverse events; identifying semantically close concepts for terms that may vary in expression, such as ICD-10 descriptions or prescriptions.
Example use cases & target audience
🎯 Target audience : Clinical Coders & Medical Billing Specialists
🧑🔬Use Case 1: Accurate Code Assignment from Clinical Notes
Scenario: Coders can input free-text from clinical documentation (e.g., “high blood pressure”, “sugar disease”) into Terminology Server to retrieve the most relevant codes from systems like ICD-10 or SNOMED CT. The server interprets synonyms, common misspellings, and colloquialisms using advanced search techniques.
Benefits:
- Reduces manual lookup time and reliance on clinical intuition.
- Minimizes errors by handling spelling variations and informal terms.
- Ensures coding accuracy for billing, documentation, and compliance.
🧑🔬 Use Case 2: Cross-Mapping Diagnoses Across Code Systems
Scenario: Coders working across international or multi-payer environments often need to convert codes between SNOMED CT, ICD-10, or OMOP Standard concepts. Terminology Server simplifies this with direct mapping support and concept relationships.
Benefits:
- Ensures consistency and traceability across code systems.
- Reduces duplicate effort in translating codes manually.
- Supports diverse documentation and billing requirements in global settings.
🎯 Target audience : Researchers & Pharmacovigilance Professionals
🧑🔬 Use Case 1: Concept Expansion for Adverse Event Detection
Scenario: Researchers analyzing narrative data (e.g., clinical notes, social media, or patient feedback) can input vague or colloquial descriptions of symptoms (e.g., “woozy,” “fainting”) and retrieve corresponding standardized adverse event codes.
Benefits:
- Enhances detection of underreported or informally described events.
- Improves sensitivity and completeness in pharmacovigilance analyses.
Expands search coverage across structured and unstructured sources.
🧑🔬 Use Case 2: Search & Linkage Across Clinical Contexts
Scenario: A study aims to identify all variations of “hypertension” across SNOMED, ICD-10, and patient language. Terminology Server uses semantic search and mappings to connect equivalent and closely related concepts.
Benefits:
- Facilitates comprehensive and flexible cohort discovery.
- Supports broader clinical research by capturing related expressions.
- Enhances study accuracy and reproducibility across vocabularies.