Description
The LiLT model, as introduced in the paper titled “LiLT: A Simple yet Effective Language-Independent Layout Transformer for Structured Document Understanding” authored by Jiapeng Wang, Lianwen Jin, and Kai Ding, offers a versatile solution for structured document comprehension across various languages. It accomplishes this by seamlessly integrating any pre-trained RoBERTa text encoder with a lightweight Layout Transformer, thereby enabling LayoutLM-like document understanding capabilities for a wide range of languages.
To prepare the LiLT model for its tasks, it underwent pretraining on the RVL-CDIP dataset for document image classification. This dataset comprises scanned document images categorized into 16 classes, including letter, form, email, resume, memo, and more. With a dataset size of 320,000 training images, 40,000 validation images, and 40,000 test images, RVL-CDIP presents challenges such as low quality, noise, and typically low resolution at around 100 dpi.
In the LiLT paper’s abstract, the authors emphasize the importance of structured document understanding in the context of intelligent document processing. They highlight a common limitation in existing models, which are often tailored to specific languages, primarily English, based on their pretraining data. To overcome this limitation, LiLT is introduced as a straightforward yet effective Language-independent Layout Transformer. This model can be pretrained on structured documents from a single language and then fine-tuned on other languages using readily available monolingual or multilingual pre-trained text models. The paper reports experimental results across eight languages, demonstrating that LiLT achieves competitive or even superior performance on various widely-used downstream benchmarks. This capability allows for language-independent benefits from document layout structure pretraining.
Predicted Entities
label.
Live Demo Open in Colab Download
How to use
binary_to_image = BinaryToImage()\
.setOutputCol("image") \
.setImageType(ImageType.TYPE_3BYTE_BGR)
img_to_hocr = ImageToHocr()\
.setInputCol("image")\
.setOutputCol("hocr")\
.setIgnoreResolution(False)\
.setOcrParams(["preserve_interword_spaces=0"])
doc_class = VisualDocumentClassifierLilt() \
.pretrained("lilt_rvl_cdip_296K", "en", "clinical/ocr") \
.setInputCol("hocr") \
.setOutputCol("label")
pipeline = PipelineModel(stages=[
binary_to_image,
img_to_hocr,
doc_class
])
test_image_path = pkg_resources.resource_filename('sparkocr', 'resources/ocr/visualdoc/00556614_00556648.tif')
bin_df = spark.read.format("binaryFile").load(test_image_path)
results = pipeline.transform(bin_df).cache()
val binary_to_image = new BinaryToImage()
.setOutputCol("image")
.setImageType(ImageType.TYPE_3BYTE_BGR)
val img_to_hocr = new ImageToHocr()
.setInputCol("image")
.setOutputCol("hocr")
.setIgnoreResolution(False)
.setOcrParams(Array("preserve_interword_spaces=0"))
val doc_class = VisualDocumentClassifierLilt()
.pretrained("lilt_rvl_cdip_296K", "en", "clinical/ocr")
.setInputCol("hocr")
.setOutputCol("label")
val pipeline = new PipelineModel().setStages(Array(
binary_to_image,
img_to_hocr,
doc_class))
val test_image_path = pkg_resources.resource_filename("sparkocr", "resources/ocr/visualdoc/00556614_00556648.tif")
val bin_df = spark.read.format("binaryFile").load(test_image_path)
val results = pipeline.transform(bin_df).cache()
Example
Input:
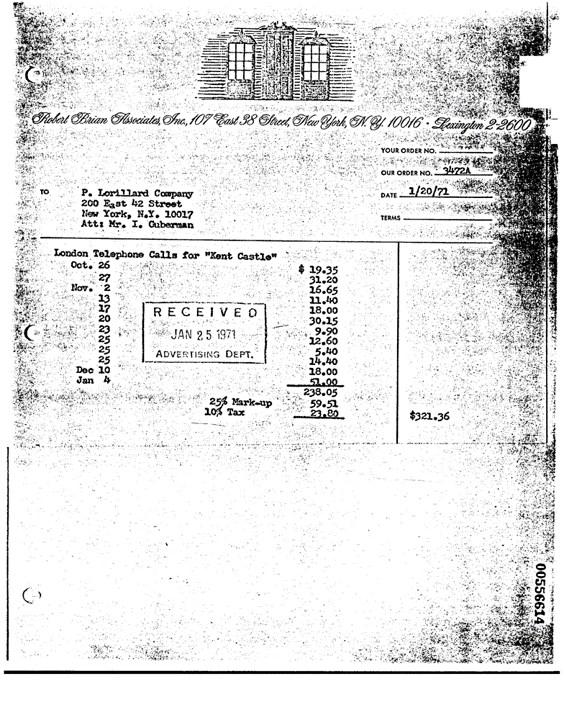
Output text
+-------+
|label |
+-------+
|invoice|
+-------+
Model Information
| Model Name: | lilt_rvl_cdip_296K |
| Type: | ocr |
| Compatibility: | Visual NLP 4.0.0+ |
| License: | Licensed |
| Edition: | Official |
| Language: | en |
References
IIT-CDIP, RVL-CDIP